
10-inch Contractor Table Saw
Scie de table de 10 pouces (254 mm) pour entrepreneurs
Sierra de mesa de 10 pulgadas (254 mm) para contratista
Français (32)
Español (61)
www.DeltaMachinery.com
Instruction Manual
Manuel d’utilisation
Manual de instrucciones
To reduce risk of serious injury, thoroughly read and comply with all warnings and instructions in this manual and on product.
KEEP THIS MANUAL NEAR YOUR SAW FOR EASY REFERENCE AND TO INSTRUCT OTHERS
36-725 T2

2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS ..............................3
SAFETY LOGOS ..................................................................3
GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY RULES ...........................4
TABLE SAW SAFETY RULES ...............................................5
POWER CONNECTIONS .....................................................7
Power Source ................................................................ 7
Grounding Instructions ................................................... 7
Extension Cords ..............................................................8
UNPACKING .......................................................................9
Components and Parts List ..............................................9
Hardware Package ........................................................10
ASSEMBLY ........................................................................ 10
Stand ...........................................................................10
Fixed Wheels and Stationary Feet ................................... 11
Front and Rear Rails ...................................................... 11
Extension Wings ...........................................................12
Fence Guide and Power Control Box ...............................12
Throat Plate..................................................................13
Blade and Riving Knife ................................................... 13
Anti-kickback Pawls .......................................................13
Blade Guard .................................................................14
Rip Fence .....................................................................14
Miter Gauge ..................................................................14
On-Board Storage .........................................................14
Adjusting the 90° and 45° Positive Bevel Stops ...............15
Securing Saw to Floor ...................................................15
PREPARING TO CUT ........................................................15
Raising and Lowering the Blade .....................................16
Tilting the Blade ............................................................16
Selecting and Storing Saw Blades ................................... 17
Changing the Saw Blade ................................................17
Riving Knife Position ...................................................... 17
Height Settings ............................................................18
Checking Riving Knife Alignment ...................................18
Using the Miter Gauge ................................................... 19
Using Blade Guard Assembly .......................................... 19
Checking Fence Alignment .............................................19
The DELTA
®
#36-725 T2 10-inch Contractor Table Saw is
designed for portability and high quality performance. It includes:
basic machine, sturdy tubular steel stand, integral dust chute,
a T-Square
®
fence system, t-slot miter gage, 15-amp induction
motor, on/off switch, cast iron table, extension wings, see-through
blade guard with anti-kickback fingers, and 10-inch carbide blade.
OPERATION ........................................................................20
Starting and Stopping the Saw ..........................................20
Overload Protection ..........................................................21
Making Cuts.....................................................................21
Rip Cuts .........................................................................22
Bevel Rip Cuts ................................................................22
Cross-Cuts ...................................................................... 23
Bevel Cross-Cuts .............................................................23
Miter Cuts ......................................................................23
Compound Miter Cuts ...................................................... 24
Large Panel Cuts ............................................................. 24
Non-Through Cuts ............................................................ 24
Non-through Cuts ...........................................................24
Using Cutting Aids ............................................................ 25
Push Sticks .....................................................................25
Push Blocks ....................................................................26
Auxiliary Rip Fence Facing................................................26
Auxiliary Miter Gage Facing .............................................. 26
Featherboards ................................................................27
CutoGauge ..................................................................27
Jigs ................................................................................ 27
ALIGNMENT ........................................................................28
Riving Knife Alignment With The Blade ..............................28
Adjusting The Miter Stops ................................................. 28
Aligning Fence Parallel To Miter Slot ..................................29
Aligning Fence Perpendicular to the Table ..........................29
MAINTENANCE ....................................................................30
TROUBLESHOOTING ...........................................................30
ACCESSORIES .....................................................................31
WARRANTY .........................................................................31
PARTS, SERVICES AND WARRANTY ASSISTANCE ............31
REPLACEMENT PARTS ........................................................31
FRENCH ...............................................................................32
SPANISH .............................................................................61
SPECIFICATIONS
NOTICE: The manual cover illustrates the current production model. All other illustrations contained in the manual are
representative only and may not be exact depictions of the actual labeling or accessories included. They are intended for
illustrative purposes only.
Max depth of cut at 90 degrees: 3-1/8”
Max depth of cut at 45 degrees: 2-1/4”
Max rip to right of blade: 30”
Max rip to left of blade: 15”
Max width of dado: 13/16”
MOTOR SPECIFICATIONS:
Amps 15
Voltage 120

3
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
CAREFULLY READ AND FOLLOW ALL WARNINGS AND INSTRUCTIONS ON YOUR PRODUCT AND IN THIS MANUAL.
SAVE THIS MANUAL. MAKE SURE ALL USERS ARE FAMILIAR WITH ITS WARNING AND INSTRUCTIONS WHEN USING THE TOOL.
Improper operation, maintenance or modication of tools or equipment could result in serious injury and/or property damage.
If you have any questions or concerns relative to the use of your tool or the contents of this manual, stop using the tool and contact Delta Power
Equipment Corporation Customer Care at 1-800-223-7278.
CAREFULLY READ AND FOLLOW ALL WARNINGS AND INSTRUCTIONS ON YOUR PRODUCT AND IN
THIS MANUAL. SAVE THIS MANUAL. MAKE SURE ALL USERS ARE FAMILIAR WITH ITS WARNINGS AND
INSTRUCTIONS WHEN USING THE TOOL. Improper operation, maintenance or modification of tools or equipment could result in
serious injury and/or property damage.
SAFETY SYMBOLS- DEFINITIONS
This manual contains information that is important for you to know and understand. This information relates to protecting YOUR SAFETY and
PREVENTING EQUIPMENT PROBLEMS. To help you recognize this information, we use the symbols below. Please read the manual and pay attention to
these sections.
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury.
Used without the safety alert symbol indicates potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result
in property damage.
PH:1 Phase 1
This is a 1 phase motor

4
GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY RULES
1. Work area safety
a. Keep work area clean and well lit. Cluttered or dark areas invite accidents.
b. Do not operate power tools in explosive atmospheres, such as in the presence of ammable liquids, gases
or dust. Power tools create sparks which may ignite the dust or fumes.
c. Keep children and bystanders away while operating a power tool. Distractions can cause you to lose control.
2. Electrical safety
a. Power tool plugs must match the outlet. Never modify the plug in any way. Do not use any adapter with
earthed (grounded) power tools. Unmodiedplugsandmatchingoutletswillreduceriskofelectricshock.
b. Avoid body contact with earthed or grounded surfaces, such as pipes, radiators, ranges and refrigerators.
There is an increased risk of electric shock if your body is earthed or grounded.
c. Do not expose power tools to rain or wet conditions. Water entering a power tool will increase the risk of electric
shock.
d. Do not abuse the cord. Never use the cord for carrying, pulling or unplugging the power tool. Keep cord
away from heat oil, sharp edges or moving parts. Damaged or entangled cords increase the risk of electric shock.
e. When operating a power tool outdoors, use an extension cord suitable for outdoor use. Use of a cord
suitable for outdoor use reduces the risk of electric shock.
f. If operating a power tool in a damp location is unavoidable, use a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI)
protected supply. Use of an GFCI reduces the risk of electric shock.
3. Personal safety
a. Stay alert, watch what you are doing and use common sense when operating a power tool. Do not use a
power tool while you are tired or under the inuence of drugs, alcohol or medication. A moment of inattention
while operating power tools may result in serious personal injury.
b. Use personal protective equipment. Always wear eye protection. Protective equipment such as dust mask, non-
skid safety shoes, hard hat, or hearing protection and dust protection used for appropriate conditions will reduce personal
injuries. Gloves are recommended when changing blades.
c. Prevent unintentional starting. Ensure the switch is in the o-position before connection to power source,
picking up, or carrying the tool.Carryingpowertoolswithyourngerontheswitchorenergising power tools that
have the switch on invites accidents.
d. Remove any adjusting key or wrench before turning the power tool on. A wrench or a key left attached to a
rotating part of the power tool may result in personal injury.
e. Do not overreach. Keep proper footing and balance at all times. This enables better control of the power tool in
unexpected situations
f. Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing or jewelery. Keep your hair, clothing and gloves away from
moving parts. Loose clothes, jewelery or long hair can be caught in moving parts.
g. If devices are provided for the connection of dust extraction and collection facilities, ensure these are
connected and properly used. Use of dust collection can reduce dust-related hazards.
h. Do not let familiarity gained from frequent use of tools allow you to become complacent and ignore tool
safety principles. A careless action can cause severe injury within a fraction of a second.
4. Power tool use and care
a. Do not force the power tool. Use the correct power tool for you application. The correct power tool will do the
job better and safer at the rate for which it was designed.
b. Do not use the power tool if the switch does not turn it on and o. Any power tool that cannot be controlled with
the switch is dangerous and must be repaired.
c. Disconnect the plug from the power source before making any adjustments, changing accessories, or
storing power tools. Such preventive safety measures reduce the risk of starting the power tool accidentally.
d. Store idle power tools out of the reach of children and do not allow persons unfamiliar with the power tool
or these instructions to operate the power tool. Power tools are dangerous in the hands of untrained users.
e. Maintain power tools and accessories. Check for misalignment or binding of moving parts, breakage of
parts and any other condition that may aect the power tool’s operation. If damaged, have the power tool
repaired before use. Many accidents are caused by poorly maintained power tools.
f. Keep cutting tools sharp and clean. Properly maintained cutting tools with sharp cutting edges are less likely to bind
and are easier to control.
g. Use the power tool, accessories and tools bits etc. in accordance with these instructions, taking into
account the working conditions and the work to be performed. Use of the power tool for operations dierent
from those intended could result in a hazardous situation.
h. Keep handles and grasping surfaces dry, clean and free from oil and grease. Slippery handles and grasping
surfaces do not allow for safe handling and control of the tool in unexpected situations.
5. Service
a. Have your power tool serviced by a qualied repair person using only identical replacement parts. This will
ensure that the safety of the power tool is maintained.
The term “power tool” in the warnings refers to your mains-operated (corded) power tool or BATTERY-operated (cordless) power tool.
Read all safety warnings, instructions, illustrations and specifications provided with this power tool. Failure to follow
all instructions listed below may result in electric shock, fire and/or serious injury.
Save all warnings and instructions for future reference.

5
Failure to follow these rules may result in serious personal injury.
• SEE GENERAL POWER TOOL SAFETY SECTION OF THIS MANUAL. Read entire instruction manual before operating saw.
Learningthesaw’sproperapplications,limitations,andspecicpotentialhazardswillgreatlyminimizethepossibilityofaccidents
and injury. Make sure all users are familiar with its warnings and instructions before using saw.
• SEE POWER CONNECTION SECTION OF THIS MANUAL for instructions and warnings regarding power cords and connections.
TERMINOLOGY
The following terms will be used throughout the manual and you should become familiar with them.
– Through-cut refers to any cut that completely cuts through the
workpiece.
– Non-through cut refers to any cut that does not completely cut through
the workpiece.
_ Push stick refers to a wooden or plastic stick, usually homemade, that is
used to push a small workpiece through the saw and keeps the operator’s
hands clear of the blade.
– Kickback occurs when the saw blade binds in the cut or between the
blade and the fence and thrusts the workpiece back toward the operator.
or lowering the workpiece down to the blade.
– Re-sawing – Flipping material to make a cut the saw is not capable of
making in one pass.
– Cove cutting – Also known as coving, cove cutting is an operation where
the work is fed at an angle across the blade.
– Freehand refers to cutting without the use of a miter gauge or rip fence
or any other means of guiding or holding the workpiece other than the
operator’s hand.
– Plunge cutting refers to blind cuts in the workpiece made by either
raising the blade through the workpiece the workpiece.
Accessories for use with your saw are available at extra cost from your
local dealer or authorized service center.
Failure to follow these rules may result in serious personal injury.
TABLE SAW SAFETY RULES
Table Saw Specic Safety Rules
WARNING READ ALL SAFETY WARNINGS DESIGNATED BY THE SYMBOL AND ALL INSTRUCTIONS.
1. GUARDING RELATED WARNINGS (FOR TABLE SAW, 62841-3-1)
a. Keep guards in place. Guards must be in working order and be properly mounted. A guard that is loose, damaged, or is
not functioning correctly must be repaired or replaced.
b. Always use saw blade guard, riving knife and anti-kickback device for every through-cutting operation. For through-
cutting operations where the saw blade cuts completely through the thickness of the workpiece, the guard and other safety devices
help reduce the risk of injury.
c. Immediately reattach the guarding system after completing an operation (such as rabbeting or resawing cuts) which
requires removal of the guard, riving knife and/or anti-kickback device. The guard, riving knife, and anti-kickback device
help to reduce the risk of injury.
d. Make sure the saw blade is not contacting the guard, riving knife or the workpiece before the switch is turned on.
Inadvertent contact of these items with the saw blade could cause a hazardous condition.
e. Adjust the riving knife as described in this instruction manual. Incorrect spacing, positioning and alignment can make the
rivingknifeineectiveinreducingthelikelihoodofkickback.
f. For the riving knife and anti-kickback device to work, they must be engaged in the workpiece. The riving knife and
anti-kickbackdeviceareineectivewhencuttingworkpiecesthataretooshorttobeengagedwiththerivingknifeandanti-kickback
device. Under these conditions a kickback cannot be prevented by the riving knife and antikickback device.
g. Use the appropriate saw blade for the riving knife. For the riving knife to function properly, the saw blade diameter must
match the appropriate riving knife and the body of the saw blade must be thinner than the thickness of the riving knife and the
cutting width of the saw blade must be wider than the thickness of the riving knife.
2. CUTTING PROCEDURES WARNINGS
a. DANGER: Never place your ngers or hands in the vicinity or in line with the saw blade. A moment of inattention or a slip
could direct your hand towards the saw blade and result in serious personal injury.
b. Feed the workpiece into the saw blade or cutter only against the direction of rotation. Feeding the workpiece in the same
direction that the saw blade is rotating above the table may result in the workpiece, and your hand, being pulled into the saw blade.
c. Never use the mitre gauge to feed the workpiece when ripping and do not use the rip fence as a length stop when
cross cutting with the mitre gauge. Guiding the workpiece with the rip fence and the mitre gauge at the same time increases the
likelihood of saw blade binding and kickback.
d. When ripping, always apply the workpiece feeding force between the fence and the saw blade. Use a push stick when
the distance between the fence and the saw blade is less than 150 mm, and use a push block when this distance is less than 50 mm.
"Work helping" devices will keep your hand at a safe distance from the saw blade.
e. Use only the push stick provided by the manufacturer or constructed in accordance with the instructions. This push
stickprovidessucientdistanceofthehandfromthesawblade.
f. Never use a damaged or cut push stick. A damaged push stick may break causing your hand to slip into the saw blade.
g. Do not perform any operation "freehand". Always use either the rip fence or the mitre gauge to position and guide the
workpiece. "Freehand" means using your hands to support or guide the workpiece, in lieu of a rip fence or mitre gauge. Freehand
sawing leads to misalignment, binding and kickback.
h. Never reach around or over a rotating saw blade. Reaching for a workpiece may lead to accidental contact with the moving
saw blade.
i. Provide auxiliary workpiece support to the rear and/or sides of the saw table for long and/or wide workpieces to
keep them level. A long and/or wide workpiece has a tendency to pivot on the table’s edge, causing loss of control, saw blade
binding and kickback.
j. Feed workpiece at an even pace. Do not bend or twist the workpiece. Ifjamming occurs, turn the tool o immediately,

6
TABLE SAW SAFETY RULES
unplug the tool then clear the jam. Jamming the saw blade by the workpiece can cause kickback or stall the motor.
k. Do not remove pieces of cut-o material while the saw is running. The material may become trapped between the fence or
insidethesawbladeguardandthesawbladepullingyourngersintothesawblade.Turnthesawoandwaituntilthesawbladestops
before removing material.
l. Use an auxiliary fence in contact with the table top when ripping workpieces less than 2 mm thick. A thin workpiece may
wedge under the rip fence and create a kickback.
m. Never Cut Metals, Cement Board or Masonry. Certain man-made materials have special instructions for cutting on table saws.
Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations at all times to avoid overheating the saw blade tips as well as melting the plastic. Avoid
overheating blade tips by pushing material through blade evenly. Forcing material too fast can cause heating and damage to blade or
workpiece. If cutting plastics is permitted, to avoid melting the plastic.
3. Kickback causes and related warnings
Kickback is a sudden reaction of the workpiece due to a pinched, jammed saw blade or misaligned line of cut in the workpiece with respect to
thesawbladeorwhenapartoftheworkpiecebindsbetweenthesawbladeandtheripfenceorotherxedobject.
a. Most frequently during kickback, the workpiece is lifted from the table by the rear portion of the saw blade and is propelled
towards the operator. Kickback is the result of saw misuse and/or incorrect operating procedures or conditions and can be avoided by taking
proper precautions as given below.
b. Never stand directly in line with the saw blade. Always position your body on the same side of the saw blade as the fence.
Kickback may propel the workpiece at high velocity towards anyone standing in front and in line with the saw blade.
c. Never reach over or in back of the saw blade to pull or to support the workpiece. Accidental contact with the saw blade may
occurorkickbackmaydragyourngersintothesawblade.
d. Never hold and press the workpiece that is being cut o against the rotating saw blade.Pressingtheworkpiecebeingcuto
against the saw blade will create a binding condition and kickback.
e. Align the fence to be parallel with the saw blade. A misaligned fence will pinch the workpiece against the saw blade and create
kickback.
f. Use a featherboard to guide the workpiece against the table and fence when making non-through cuts such as
rabbeting, or resawing cuts. A featherboard helps to control the workpiece in the event of a kickback.
g. Use extra caution when making a cut into blind areas of assembled workpieces. The protruding saw blade may cut objects
that can cause kickback.
h. Support large panels to minimise the risk of saw blade pinching and kickback. Large panels tend to sag under their own
weight. Support(s) must be placed under all portions of the panel overhanging the table top.
i. Use extra caution when cutting a workpiece that is twisted, knotted, warped or does not have a straight edge to guide
it with a mitre gauge or along the fence. A warped, knotted, or twisted workpiece is unstable and causes misalignment of the kerf
with the saw blade, binding and kickback.
j. Never cut more than one workpiece, stacked vertically or horizontally. The saw blade could pick up one or more pieces and
cause kickback.
k. When restarting the saw with the saw blade in the workpiece, centre the saw blade in the kerf so that the saw teeth are
not engaged in the material. If the saw blade binds, it may lift up the workpiece and cause kickback when the saw is restarted.
l. Keep saw blades clean, sharp, and with sucient set. Never use warped saw blades or saw blades with cracked or broken teeth.
Sharp and properly set saw blades minimize binding, stalling and kickback.
4. Table saw operating procedure warnings
a. Turn o the table saw and disconnect the power cord when removing the table insert, changing the saw blade or making
adjustments to the riving knife, ant kickback device or saw blade guard, and when the machine is left unattended.
Precautionary measures will avoid accidents.
b. Never leave the table saw running unattended. Turnit o and don’t leave the tool until it comes to a complete stop. An
unattended running saw is an uncontrolled hazard.
c. Locate the table saw in a well-lit and level area where you can maintain good footing and balance. It should be installed in
anareathatprovidesenoughroomtoeasilyhandlethesizeofyourworkpiece.Cramped,darkareas,andunevenslipperyoorsinvite
accidents.
d. Frequently clean and remove sawdust from under the saw table and/or the dust collection device. Accumulated sawdust is
combustible and may self-ignite.
e. The table saw must be secured. A table saw that is not properly secured may move or tip over.
f. Remove tools, wood scraps, etc. from the table before the table saw is turned on. Distraction or a potential jam can be
dangerous.
g. Always use saw blades with correct size and shape (diamond versus round) of arbor holes. Saw blades that do not match the
mountinghardwareofthesawwillruno-center,causinglossofcontrol.
h. Never use damaged or incorrect saw blade mounting means such as anges, saw blade washers, bolts or nuts. These
mounting means were specially designed for your saw, for safe operation and optimum performance.
i. Never stand on the table saw, do not use it as a stepping stool. Serious injury could occur if the tool is tipped or if the cutting
tool is accidentally contacted.
j. Make sure that the saw blade is installed to rotate in the proper direction. Do not use grinding wheels, wire brushes, or
abrasive wheels on a table saw. Improper saw blade installation or use of accessories not recommended may cause serious injury.
k. DO NOT REMOVE A WORKPIECEwithoutrstturningothesawandunpluggingitfromthepowersource.

7
POWER CONNECTIONS
POWER SOURCE
This saw is equipped with a 15-amp motor for use with a 120-volt,
60-HZ alternating current.
For voltage, the wiring in a shop is as important as the motor’s
rating. A line intended only for lights may not be able to properly
carry the current needed for a power tool motor; wire that is
heavy enough for a short distance may be too light for a greater
distance; and a line that can support one power tool may not be
able to support two or three. A separate electrical circuit should
be used for your machines. This circuit should not be less than
#12 wire and should be protected with a 20-amp time lag fuse. If
an extension cord is used, use only 3-wire extension cords which
have 3-prong grounding-type plugs and matching receptacle
which will accept the machine’s plug. Before connecting the
machine to the power line, make sure the switch is in the
“OFF” position and be sure that the electric current is of the
same characteristics as indicated on the machine. A substantial
voltage drop will cause a loss of power and overheat the motor.
It may also damage the machine. This power tool is provided
with Type Y attachment power supply cord. If the replacement
of the SUPPLY CORD is necessary, this has to be done by the
manufacturer or his agent in order to avoid a safety hazard.
DO NOT EXPOSE THE MACHINE TO RAIN OR OPERATE THE MACHINE IN DAMP LOCATIONS.
GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS
THIS MACHINE MUST BE GROUNDED WHILE IN USE TO PROTECT THE OPERATOR FROM
ELECTRIC SHOCK.
In the event of a malfunction or breakdown, grounding provides
a path of least resistance for electric current to reduce the risk
of electric shock. This machine is equipped with an electric cord
having a grounding conductor and a grounding plug. The plug
must be plugged into a matching receptacle that is properly
installed and grounded in accordance with all local codes and
ordinances.
Do not modify the plug as provided on your saw or as rewired by
yourelectrician.Ifitwillnottthe7 receptacle, have the proper
receptacleinstalledbyaqualiedelectrician.
Improper connection of the equipment-grounding conductor
can result in risk of electric shock. The conductor with insulation
having an outer surface that is green with or without yellow
stripes is the grounding conductor. If repair or replacement of the
electric cord or plug is necessary, do not connect the equipment-
grounding conductor to a live terminal. Checkwithaqualied
electrician or service personnel if the grounding instructions
are not completely understood, or if in doubt as to whether the
machine is properly grounded.
Use only 3-wire extension cords that have 3-prong grounding type
plugs and matching, properly grounded 3-conductor receptacles
that accept the machine’s plug, as shown in Figure A, or a
properly grounded receptacle with a grounding means adapter, as
shown in Figure B.
Repair or replace damaged or worn cord immediately.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
Refer to them often and use them to instruct others.
If tool is loaned to someone, also loan them these instructions.
PROPOSITION 65 WARNING:
Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities contains chemicals
known to the state of California to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. Some examples of these chemicals are:
• Lead from lead-based paints
• Crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry products
• Arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated lumber
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to these chemicals:
work in a well-ventilated area and work with approved safety equipment, such as dust masks that are specifically designed to filter out
microscopic particles.

8
POWER CONNECTIONS
Keep the extension cord clear of the work area. Position the cord so it will not get caught on lumber, tools or other
obstructions
• Use proper extension cords. Make sure your extension cord is a 3-wire extension cord which has a 3-prong grounding type plug
and matching receptacle which will accept the machine’s plug, as described in this manual’s Grounding Instructions. When using
an extension cord, be sure to use one heavy enough to carry the current of the machine. An undersized cord will cause a drop in
line voltage, resulting in loss of power and overheating. The table below shows the maximum gauge to use depending on the cord
length. If in doubt, use the next heavier gauge. The smaller the gauge number, the heavier the cord. Only round, jacketed cords
listed by Underwriter’s Laboratories (UL) should be used.
Never use a damaged extension cord. Check extension cords before each use. If damaged, replace immediately.
Touching the damaged area could case electrical shock resulting in serious injury.
IN ALL CASES, MAKE CERTAIN THE RECEPTACLE IN QUESTION IS PROPERLY GROUNDED. IF YOU ARE
NOT SURE, HAVE A QUALIFIED ELECTRICIAN CHECK THE RECEPTACLE.
This is a grounded, cord-connected tool intended for use on a supply circuit having a nominal voltage of 120 volts. It is intended to
for use on a circuit that has an outlet as shown in FIG. A. It has a plug as shown in FIG A. If you have a 2 pole receptacle as shown
in FIG. B you may use a temporary adapter, as shown in FIG. B. if a properly grounded outlet is not available. The green ear lug
extending from the adapter must be connected to a permanent grounded outlet box. The temporary adapter should be used only until
aproperlygroundedoutletcanbeinstalledbyaqualiedelectrician.
FIG. A
CURRENT
CARRYING
PRONGS
GROUNDING BLADE
IS LONGEST OF THE 3 BLADES
GROUNDED
OUTLET BOX
FIG. B
ADAPTER
GROUNDED OUTLET BOX
GROUNDING
MEANS
FIG. C
Grounding Pin
MINIMUM GAUGE EXTENSION CORD
RECOMMENDED SIZES FOR USE WITH STATIONARY ELECTRIC MACHINES
Ampere
Rating
Volts
Total Length of
Cord in Feet
Gauge of
Extension Cord
0-6
0-6
0-6
0-6
120
120
120
120
up to 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
18 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
6-10
6-10
6-10
6-10
120
120
120
120
up to 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
18 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
10-12
10-12
10-12
10-12
120
120
120
120
up to 25
25-50
50-100
100-150
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
12-16 120 up to 25 14 AWG
12-16 120 25-50 12 AWG
12-16 120
GREATER THAN 50 FEET NOT RECOMMENDED
MINIMUM GAUGE EXTENSION CORD
RECOMMENDED SIZES FOR USE WITH STATIONARY ELECTRIC MACHINES
Ampere
Rating
Volts
Total Length of
Cord in Feet
Gauge of
Extension Cord
0-6
0-6
0-6
0-6
240
240
240
240
up to 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
18 AWG
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
6-10
6-10
6-10
6-10
240
240
240
240
up to 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
18 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
10-12
10-12
10-12
10-12
240
240
240
240
up to 50
50-100
100-200
200-300
16 AWG
16 AWG
14 AWG
12 AWG
12-16
12-16
240
240
up to 50
50-100
14 AWG
12 AWG

9
UNPACKING
3
2
11
1
4
5
6
17
19
15
18
16
7
14
9
8
13
10
20
12
• The machine is heavy, two people are required to unpack and
lift.
• Use a safety strap to avoid tip over when lifting machine.
• Prior to tool assembly and use, read this manual thoroughly to
familiarize yourself with proper assembly, maintenance and safety
procedures.
Check shipping carton and machine for damage before unpacking.
Carefully remove components in top foam layer. Remove the top
layer of foam then remove all components in the bottom layer of
foam.Layoutallpartsonapieceofcardboardorotherclean,at
surface. Two or more people are needed to lift the saw out of the
carton. Always check for and remove protective shipping materials
around motors and moving parts. Do not discard shipping carton
and packing materials until you have carefully inspected the
COMPONENT
PARTS LIST
DESCRIPTION (QTY)
1. Table Saw with attached
Carbide Blade, and
Closed-End Wrench (1)
2. Extension Wing (2)
3. Rear Rails (right & left) (2)
4. Switch Box (attached to
saw) (1)
5. Tubular Stand (2)
6. Fixed Wheels (2)
7. Adjustable Feet (2)
8. Pivoting Pedal and Caster
(attached to saw) (1)
9. Handwheel Handles (2)
(attached to saw)
10. Lock Knobs (2)
11. Miter Gauge (1)
12. Rip Fence Handle (1)
13. Fence Guides (right & left)
(2)
14. Front Fence Rails (right &
left) (2)
15. Rip Fence (1)
16. Throat Plate (1)
17. Blade Guard and Anti-
Kickback Pawls
contents,assembledthemachineandaresatisedthatit
operates correctly.
Compare package contents to Component Parts List and Hardware
Package List prior to assembly to make sure all items are present.
Carefully inspect parts to make sure no damage occurred during
shipping. If any parts are missing, damaged or pre-assembled, do
not assemble. Instead, call DELTA
®
Customer Care at 1-800-223-
7278 for assistance.
After assembly remove any protective materials and coatings from
all of the parts and the table saw. The protective coatings can be
removed by spraying WD-40
®
onthemandwipingthemowitha
soft cloth. This may need to be redone several times before all of
the protective coatings are removed completely.
After cleaning, apply a good quality paste wax to any unpainted
castironsurfaces.Makesuretobuoutthewaxbeforeassembly.
18. Rail Spreader Bar
19. Blade (1)
20. Push Stick (1)
10
ASSEMBLY
UNPACKING
C
HARDWARE PACKAGE
DESCRIPTION (QTY) Item
Parts List
1. M8 x 70mm carriage bolt (1) 153
2. M8 nylock nut (3) 155
3. M6 x 72mm carriage bolt (4) 144
4. M6 nut (4) 145
5. M8 spring washer (1) 154
6. M8 x 53mm Axle Pin (2) 151
7. M6 x 10mm self-tapping bolt (16) 146
8. 3/16’’ hex wrench - T shape (1) *
9. 3/16’’ hex wrench - L shape (1) *
10. 6mm Allen hex wrench - L shape (1) *
*= Item is not shown on the parts list.
• Do not lift saw without help. Hold it close to your body while
lifting. Keep knees bent and lift with your legs, not your back.
• Fully assemble saw with leg assembly prior to use. Leg
assembly is an integral and necessary part of the support
structure for this saw.
• Do not modify saw, or create accessories not recommended
for use with this saw.
• Make sure power switch is in “OFF” position before connecting
to power supply.
• Do not connect to power supply until assembly is complete.
STAND
Avoid contact with blade teeth. Keep blade
stored or lowered when possible.
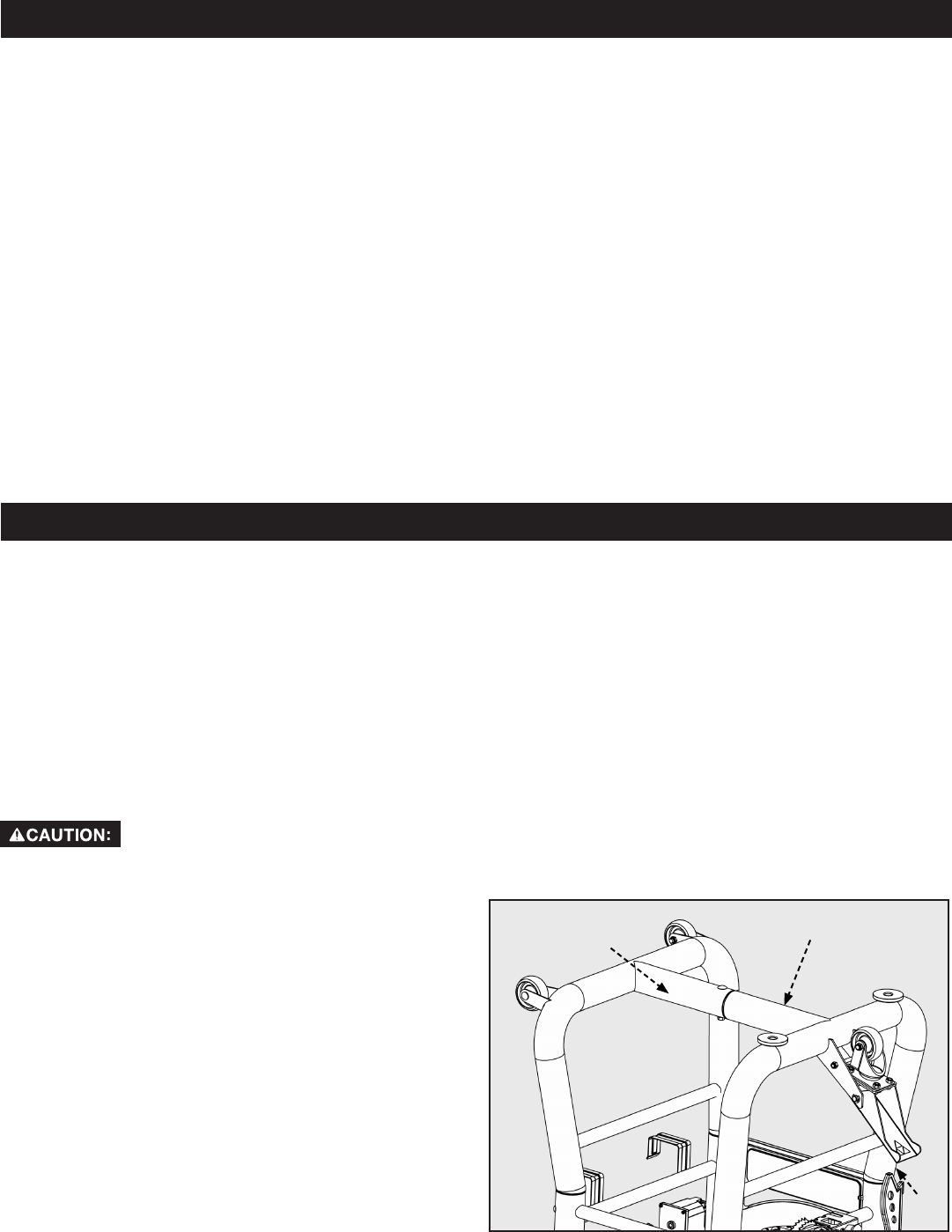
1. Connect the two tube legs by inserting the end of the left
leg (A) into the end of the right leg (B) as shown in Figure
1. Secure with a M8 x 70mm carriage bolt,lock washer and
nylock nut and tighten.
2. Insert the four open ends of the tube legs into the leg
collars (C) as shown. Secure each leg with a M6 x 72mm
bolt and nut.
NOTE:Placescrewthroughsmallholerst.Snugdown
but do not tighten this screw. Place rest of the screws
through the slots and start threading into holes on mount
tab on stand. Once all screws are started, tighten all four
sucientlytoholdplatermly.Theseareself-tapping
screwsandmaybehardtothreadatrst.Followthis
procedure for all four panels or 16 screws.
TOOLS REQUIRED FOR ASSEMBLY (NOT
INCLUDED):
• Slotted screwdriver
• Phillips head screwdriver
• 8mm wrench
• 10mm wrench
• 12mm wrench
• 13mm wrench
• 1/2-inch wrench
• 9/16-inch wrench
• 6mm Allen hex wrench
• 5/32-inch Allen wrench
• 3/16-inch Allen wrench
B
FIGURE 1
A
Item #
Parts List
11. 1/4”-20 x 1/2” hex butt hd screw w/ ¼” spring
washer (5) 1/4”-20 x 1/2” hex hd cap screw w/ ¼”
spring washer (2) 35
12. Front rail union plate(1) 32
13. M5 x16mm shoulder bolt (2) 34
14. M5 nylock nut (2) 33
15. 5/16-18 x 7/8 hex screw w/spring washer (10) 58
16. M5 x 6mm Phillips head screw (1) 26
17. M8 x16 shoulder bolt (4) 20
18. M8 nylock nut (4) 21
19. 5/16-18x11/8inchatheadscrew(12) 19
20. 5/16-18hexangenut(12) 22
21. 5/16 lock washer (12) 23
22. Wire clip: UC-1.5 white (1) 25
23. Rail alignment gauge (1) *

11
B
A
FRONT AND REAR RAILS
1. Attach the front rail halves (1&2) to the table front using
four 5/16-18 x 1 1/8-inch flat head screws, 5/16 lock
washers,and5/16-18hexangenuts,asshowninFigure
4A and 4B. The front rails have holes on both surfaces
of the rail for attachment to both the table and the fence
guide.
2. Use supplied rail alignment gauge to ensure the rails are
the proper distance from the top of the table.
3. Attach the rail union plate (C) using two M5 x 16 shoulder
bolts and M5 nylock nuts in the two holes where the rail
sections meet.
4. Attach the rear rail halves (3&4) to the table with four
5/16”-18 hex screws with lock washers. Use the slot in the
supplied gauge to ensure the rail is the proper distance
from the top of the table. See Figures 5 and 6.
REAR LEFT RAIL
FIGURE 6
REAR RIGHT RAIL
FRONT RIGHT
RAIL (Long)
1
3
2
4
FIGURE 4A
FIGURE 4B
FIGURE 2
FIGURE 3
FIGURE 5
ASSEMBLY
FIXED WHEELS AND STATIONARY
FEET
1. Attach the two xed wheels (A) to the left leg using the
carriage shoulder bolt as in Figure 2.
2. Screw the adjustable feet (C) into the threaded inserts in
the right leg.
3. Lay a scrap piece of 2x4 on the back of the saw, as shown
in Figure 3, to prevent damage to the dust chute when
righting the saw.
4. Stand the saw right side up.
5. The two adjustable feet (C) can be raised and lowered by
rotating them. The feet may be adjusted to level the saw
and locked in place with the locking set screws using a
6mm Allen hex wrench. See Figure 2.
C
FRONT LEFT RAIL FRONT LEFT RAIL
(SHORT) (SHORT)
The machine is heavy, two people are
required to stand the machine up.
C

12
ASSEMBLY
EXTENSION WINGS
1. Attach the extension wings (5) to the Front and Rear rails
usingfour5/16-18x11/8-inchatheadscrews,5/16lock
washers,and5/16-18hexangenuts.
2. Attach the extension wings (5) to the table using three
5/16”-18 hex screws with spring washers for each wing.
The wings attach from underneath.
3. Use a ruler to make sure the wings are ush with the
tabletop.
4. Repeat this process for both left and right extension wings.
5. Attach the spreader bar (6) to the outboard end of the
front and rear rails using four M8 x 16 shoulder bolts and
M8 nylock nuts. See Figure 8.
LEFT EXTENSION LEFT EXTENSION
WINGWING
5
5
FIGURE 7A
FIGURE 7B
FIGURE 8
6
FENCE GUIDE AND POWER
CONTROL BOX
LEFT FENCE LEFT FENCE
GUIDE (SHORT) GUIDE (SHORT)
RULERRULER
BACK BACK
1. Attach the right fence guide using three 1/4-20 x 1/2-
inch hex button head screws and 1/4-inch spring washers
through the holes on the bottom side of the front rail. See
Figure 9A.
2. Attach the left fence guide to the front rail using four 1/4-
20 x 1/2-inch hex button head screws and ¼-inch spring
washers through the holes on the bottom side of the front
rail.
3. Align the two holes in the switch box bracket with the holes
underneath the front rail, shown in Figure 10, located on
the left side of the saw. Secure the power control box to
the front rail using two 1/4-20 x 1/2-inch hex head cap
screws and ¼-inch spring washers. Use a ruler to check
that both left and right fence guides are parallel. See
Figure 9C.
4. Fix the hanging power cord at rear side of front rail by wire
clip and M5 x 6mm round head cross screw. See Figure 10.
8
FIGURE 9A
FIGURE 9B
FIGURE 9C
RIGHT FENCE
GUIDE (LONG)
FIGURE 10
7
RIGHT EXTENSION RIGHT EXTENSION
WINGWING

13
ASSEMBLY
To reduce the risk of serious personal injury,
the riving knife must be installed and properly
positioned for every possible through and non-
through cut.
1. Your saw is shipped with the blade and riving knife installed and
properly aligned. The riving knife comes installed in the low, non-
through cutting position. Prior to operating your saw, check to make
sure the alignment of the blade to the miter slot and the riving knife
tothebladewasnotaectedbyshipping.Tocheckalignmentofthe
blade and riving knife, see page 28 in the Alignment section of this
manual.
2. The riving knife comes installed in the low, non-through cutting
position. To attach the anti-kickback pawls and blade guard
assemblies, the riving knife must be in the raised position as shown in Figure 9. To raise and lower the riving knife, see Riving Knife Height
Settings on page 18.
FIGURE 11A
FIGURE 11B
THROAT PLATE
1. To install throat plate, lower blade below tabletop, then carefully
feedthethroatplate,slottedendrst,fromthefrontofthetable
to the rear, keeping the blade centered within the slot on the
throat plate. See Figure 11A. The plate should rest within the
cavity in the tabletop.
2. Ensurethatthethroatplateisushwiththetopofthetable.
3. Ifthethroatisnotushwiththetabletop,Adjusttheheightofthe
throat plate using the four set screws.
NOTE:Ifthroatplateisnotushwiththetabletopthekickbackpawcan
interfere with the blade adjustment.
4. To remove throat plate, lower blade below tabletop, then carefully
slide the throat plate from out from the rear of the table to the
front, keeping the blade centered within the slot on the throat
plate. Figure 11B.
BLADE AND RIVING KNIFE
NOTE: No portion of table insert shall be above or more than 0,7 mm
below the plane of the table top surface at the infeed side and no portion
of the table insert is below or more than 0,7 mm above the plane of the
table top at the out-feed side.
NOTE: When installing riving knife, anti-kickback pawls and blade
guard, blade must be at 90° setting and raised to the maximum
height. See Raising and Lowering Blade, page 16.
SAW BLADE GUARD, ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS
AND RIVING KNIFE ASSEMBLY
Your table saw is equipped with a blade guard, anti-kickback pawls and
riving knife assembly that covers the blade and reduces the possibility of
accidentalbladecontact.Therivingknifeisaatplatethattsintothe
cutmadebythesawbladeandeectivelyghtskickbackbylessening
the tendency of the blade to bind in the cut. Two anti-kickback pawls
are located on the sides of the riving knife that allow the wood to pass
through the blade in the cutting direction but reduce the possibility of the
material being thrown backwards toward the operator. The blade guard
and anti-kickback pawls can only be used when making through cuts that
sever the wood. When making rabbets and other non-through cuts, the
blade guard and anti-kickback pawls must be removed and riving knife
lowered to the non-through cut position marked on the riving knife.
Use all components of the guarding system (blade guard assembly,
riving knife and anti-kickback pawls) for every operation for which they
can be used including all through-cutting. If you elect not to use any of
these components for a particular application, exercise additional caution
regarding control of the workpiece, the use of push sticks, the position
of your hands relative to the blade, the use of safety glasses, the means
to avoid kickback and all other warnings contained in this manual and
on the saw itself. Replace the guarding systems as soon as you return to
through-cutting operations. Keep the guard assembly in working order.
KICKBACKS
Kickbacks can cause serious injury. A kickback occurs when a part of
the workpiece binds between the saw blade and the rip fence, or other
xedobject,andrisesfromthetableandisthrowntowardtheoperator.
Kickbacks can be avoided by attention to the following conditions.
HOW TO REDUCE THE RISK OF KICKBACKS AND PROTECT
YOURSELF FROM POSSIBLE INJURY:
• Be certain that the rip fence is parallel to the saw blade.
• DO NOT rip by applying the feed force to the section of the workpiece
that will become the cut-o (free) piece. Feed force when ripping
should always be applied between the saw blade and the fence; use a
push stick for narrow work, 6 inches (152 mm) wide or less.
• Keep saw blade guard, riving knife and anti-kickback assembly in place
and operating properly. The riving knife must be in alignment with the
saw blade and the anti-kickback assembly must stop a kickback once
it has started. Check their action before ripping by pushing the wood
under the anti-kickback assembly. The teeth must prevent the wood
from being pulled toward the front of the saw. If any part of assembly
is not operational, return to the nearest authorized service center for
repair.
• Plastic and composite materials (like hardboard) may be cut on your
saw. However, since these are usually quite hard and slippery, the
anti-kickback pawls may not stop a kickback. Therefore, be especially
attentive to following proper set up and cutting procedures for ripping
to avoid overheating the saw blade tips as well as melting the plastic.
• Use saw blade guard, anti-kickback pawls, and riving knife assembly
for every possible operation, including all through-cut sawing.
• Push the workpiece past the saw blade prior to releasing control.
• NEVER rip a workpiece that is twisted or warped, or does not have a
straight edge to guide along the fence.
• NEVER saw a large workpiece that cannot be controlled.
• NEVER use the fence as a guide or length stop when crosscutting.
• NEVERsawaworkpiecewithlooseknots,aws,nailsorotherforeign
objects.
• NEVER rip a workpiece shorter than 10 inches (254 mm).
• NEVER use a dull blade. A dull blade should be replaced or
re-sharpened.

14
ASSEMBLY
BLADE GUARD
To reduce the risk of serious personal
injury, the blade guard must be in place
when making a through cut.
1. While holding the blade guard assembly (A) in a vertical
position, hook the locating pin (B) at the back end of the
blade guard assembly into the slot at the back edge of the
riving knife.
2. Rotate the blade guard assembly toward the front of
the saw until the metal portion (C) of the blade guard
assembly is parallel to the table as shown in Figure 13.
3. While holding down on the front of the metal portion of
the guard (C) press the blade guard lock lever (D) down
until it snaps into the locked position. Check to make sure
the guard is locked onto the riving knife by pulling on the
guard. If the guard is not locked, the blade guard lock
leverwillipuptotheunlockedposition.
If the metal portion of the blade guard
assembly (C) is not parallel to the table,
the riving knife is not in the raised position. Remove blade
guard assembly and anti-kickback pawls and raise riving
knife, then reinstall the anti-kickback pawls and the blade
guard assembly.
RIP FENCE
Attach the handle to the fence cam
The rip fence slides onto the rear fence rail so that the hook is under
the rear rail and rides on the front guide tube. The fence locks in place
by applying pressure in a downward motion on the rip fence handle. Rip
fence alignment should be checked prior to using your saw. To check
alignment of the rip fence, see alignment instructions on page 29.
MITER GAUGE
Insert miter gauge into each miter slot to make sure it slides freely. See
Adjusting the Miter Stops section on page 28 for adjustment of miter
gauge accuracy.
ON-BOARD STORAGE
The Delta #36-725 T2 contractor table saw comes with on-board storage
for the provided miter gauge, arbor wrench, riving knife push stick
and fence. There is also on-board storage for spare saw blades (sold
separately). The miter gauge, spare blade and arbor wrench storage areas
are located on the right side panel of the machine and come pre-installed.
On-board storage for the fence and the push stick is located on the left
side of the saw.
To remove the blade guard assembly:
1. Lift the blade guard assembly lock lever (D) to the
unlocked position.
2. Rotate the guard back and slide the pin (B) from the riving
knife slot.
FIGURE 13
D
C
Note: Check the blade gaurd for clearances and free movement.
FIGURE 12
ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS AND BLADE GUARD
ANTI-KICKBACK PAWLS
To reduce the risk of serious personal
injury, anti-kickback pawls must be in
place when making a through cut.
1. Refer to Figure 12 and locate the anti-kickback pawls
mounting slot (A) in the middle of the top edge of the
riving knife.
2. Slide slot in the middle of the anti-kickback pawls assembly
along the top of the riving knife until the stem (B) locates
the center slot on the riving knife.
3. Depress the stem on the anti-kickback pawls assembly (B)
to allow the assembly to drop into the slot. Push down on
the anti-kickback pawls assembly until it snaps into place
and locks. Release stem. NOTE: Pull up on the anti-
kickback pawls to make sure it is locked in place.
To remove the anti-kickback pawls, depress the stem (B) and pull
theanti-kickbackassemblyotherivingknife.

15
ASSEMBLY
FIGURE 14
PREPARING TO CUT
ADJUSTING 90° AND 45° POSITIVE BEVEL STOPS
There are positive stops at each end of the bevel range. To ensure
accurate cuts, the positive stops must be positioned at exactly at
90° and 45°. The bevel stops are properly adjusted as shipped.
However, for maximum accuracy, you should check the position
of the stops upon assembly and from time to time to assure that
the settings remain satisfactory. To check the position of the stops
and adjust if necessary, refer to Figure 14 and do the following.
1. Release the blade tilt lock knob located on the right side of
the saw by rotating counter clockwise.
2. Rotate the blade tilt handwheel counter clockwise and tilt
the blade to the 0° position until the stop is reached.
3. Using a carpenter’s square, check the angle of the blade
face to the table, as shown in Figure 20b, page 18. If the
blade is at 90° to the table, proceed to Step 6.
4. If the blade is not perpendicular to the table, turn
handwheel to slightly tilt the blade away from the stop
position then adjust the 90° stop by rotating the socket
set screw located in the table top immediately in front of
the left side of throat plate (A). Re-check angle using the
carpenter’s square and continue to adjust until the blade is
at 90 degrees when returned to the stop position.
SECURING SAW TO FLOOR
This saw is designed for portability. Do not
attempt to use the saw to cut a large or
cumbersomeworkpiecewithoutrsttakingappropriatestepsto
protect against tipping the saw. Examples of appropriate steps
include the use of support tables and/or securing the saw legs
totheoorbyreplacingthesawfeetwithconnectingboltsorby
attachingthelegstoaoormountedbracketwithu-straps.
Failure to comply with the following
warnings may result in serious personal
injury.
• ALWAYS make sure your workpiece is not in contact
with the blade before operating the switch to start the saw.
Blade contact could result in kickback or thrown workpiece.
• To reduce the risk of accidental starting, ALWAYS make
suretheswitchisintheopositionbeforepluggingsaw
into power source.
• DO NOT use blades rated less than the speed of this
tool. Failure to heed this warning could result in serious
personal injury.
•Turnunitoanddisconnectitfrompowersourcebefore
installing and removing accessories, before adjusting and
when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause
injury.
• Prior to operating the saw, make sure you are familiar
with its features and controls, and have made all
necessary adjustments as described below.
5. Rotate the blade tilt wheel counterclockwise until it rests on
the 45° stop. Then repeat Steps 4 and 5, adjusting the 45°
stop by rotating the socket set screw located in front of the
right side of the throat plate. (B)
A
B

16
A
PREPARING TO CUT
RAISING AND LOWERING THE
BLADE
For most applications, it is recommended that you raise the blade
1/8-inch (3.2mm) to 1/4-inch (6.4mm) above the top surface of
the workpiece.
Raise or lower the blade with the hand wheel (A) located
on the front of the saw ,maximum 45° (See Figure 15).
1. Before raising or lowering the blade, be sure to loosen the
lock knob (B) by turning it counterclockwise.
2. To raise the saw blade, turn the hand wheel clockwise.
To lower the saw blade, turn the hand wheel counter-
clockwise.
3. Tighten lock knob to keep blade at the desired height.
Only a small amount of force is required to lock the blade
raising mechanism securely. Any added force merely puts
unnecessary strain on the locking device.
4. When done operating the saw, and when performing
maintenance, adjustments or repairs, lower blade below
surface of table.
TILTING THE BLADE
The blade can be tilted up to 45° to the left using the blade tilt
wheel (A) located on the right side panel of the saw. The angle of
tilt is measured by the bevel gauge on the front of the saw. To tilt
the saw blade:
1. Loosen the lock knob (B) counterclockwise and turn the
hand wheel clockwise. A pointer on the front of the saw
indicates the angle of tilt in ½-degree increments.
2. To lock the saw blade at your desired angle, tighten the
lock knob by rotating it clockwise.
FIGURE 15
FIGURE 16
A
B
B

17
PREPARING TO CUT
CHANGING THE SAW BLADE
• Use only 10-inch (254 mm) diameter blades with 5/8-inch
(16mm) arbor holes, rated at 3,600 rpm or higher, 0.102-
inch (2.6mm) minimum kerf width and 0.073-inch (1.8mm)
maximum body thickness. Use only a saw blade diameter in
accordance with the markings on the saw.
• To reduce the risk of injury, turn unit o and disconnect it
from power source before installing and removing blades and
accessories, before adjusting and when making repairs. An
accidental start-up can cause injury.
1. Remove the throat plate and raise the saw blade to its
maximum height.
2. Push and hold arbor lock button (A) shown in Figure 17.
3. Use included arbor wrench to remove the blade by turning
counter clockwise and retaining nut and flange (B).
Remove old blade.
4. Place the new blade on the arbor with the teeth pointing
FIGURE 17
A
B
SELECTING AND STORING SAW BLADES
Riving knives must be matched to saw blade dimensions in
ordertofunctioneectively.
The saw blade furnished with your new saw is a 10-inch
(254 mm) combination blade, used for cross cutting
(across the grain) and ripping (with the grain) through the
workpiece. The arbor hole of the blade is 5/8-inch (16 mm)
diameter. This blade will produce a good quality cut for
most applications.
Therearemanytypesofbladesavailabletodospecicand
special jobs such as cross cut only, rip only, dado cuts thin
plywood, paneling, etc.
RIVING KNIFE POSITION
NOTE: Safety devices, blade guard assembly and anti-kickback
assembly have been removed in Figure 15 in order to show the
locationofspecicfeatures.Whenoperatingthesaw,these
safety devices should be in place and working properly.
Therivingknifeisaatplatethattsintothecutmadebythe
sawbladeandeectivelyghtskickbackbylesseningthetension
of the blade to bind in the cut. It must be installed and properly
positioned for every through cut and for every non-through cut
unless the riving knife would interfere with the workpiece.
The riving knife thickness (A) must be greater than the blade
body or plate thickness (B) and less than the kerf or cutting width
(C) as shown in Figure 18. The riving knife provided with this saw
is 2.2mm thick and may be used only with a 10-inch (254mm)
blade with 0.102-inch (2.6mm) minimum kerf width and 0.073-
inch (1.8mm) maximum body thickness. Do not attempt to use
this riving knife with blades that are not within these dimensions.
FIGURE 18
down as the blade rotates toward the front of the saw
table.
5. Replaceandtightenthebladeretainingnutandange.
6. Replace throat plate.
Use only saw blades designed for maximum safe operating
speeds of 3,600 RPM or greater. Only use 10 in. blades
designed for wood cutting.
Saw blades should always be kept sharp. It is
recommended that you locate a reputable sharpening
service to sharpen your blades when needed.
Never stack blades on top of one another to store. Place
material such as cardboard between them to keep the
blades from coming in contact with one another, or place
them in storage drawer.
Abrasive wheels or blades (including diamond) should not
be used on this saw.
This tool can only be used with woodworking saw blades.

18
PREPARING TO CUT
FIGURE 19
TO CHECK ALIGNMENT:
1. Horizontal Alignment: Lay a straight edge on the table
against blade face (A) and make sure it extends out along
the riving knife (B), as shown in Figure 20a. The riving
knife should just touch the straight edge. Be sure the
straight edge goes between the teeth and rests on the
blade face and the riving knife for proper alignment.
A
FIGURE 20A
B
RIVING KNIFE HEIGHT SETTINGS
The height of the riving knife should be adjusted based on the
type of cut being made. For all through cuts (when the wood is
completely severed), it should be in the raised position, with anti-
kickbackngersandguardinstalled.Fornon-throughcuts(when
the blade does not penetrate the top of the workpiece), the riving
knifeshouldbeintheloweredpositionandanti-kickbackngers
and guard removed.
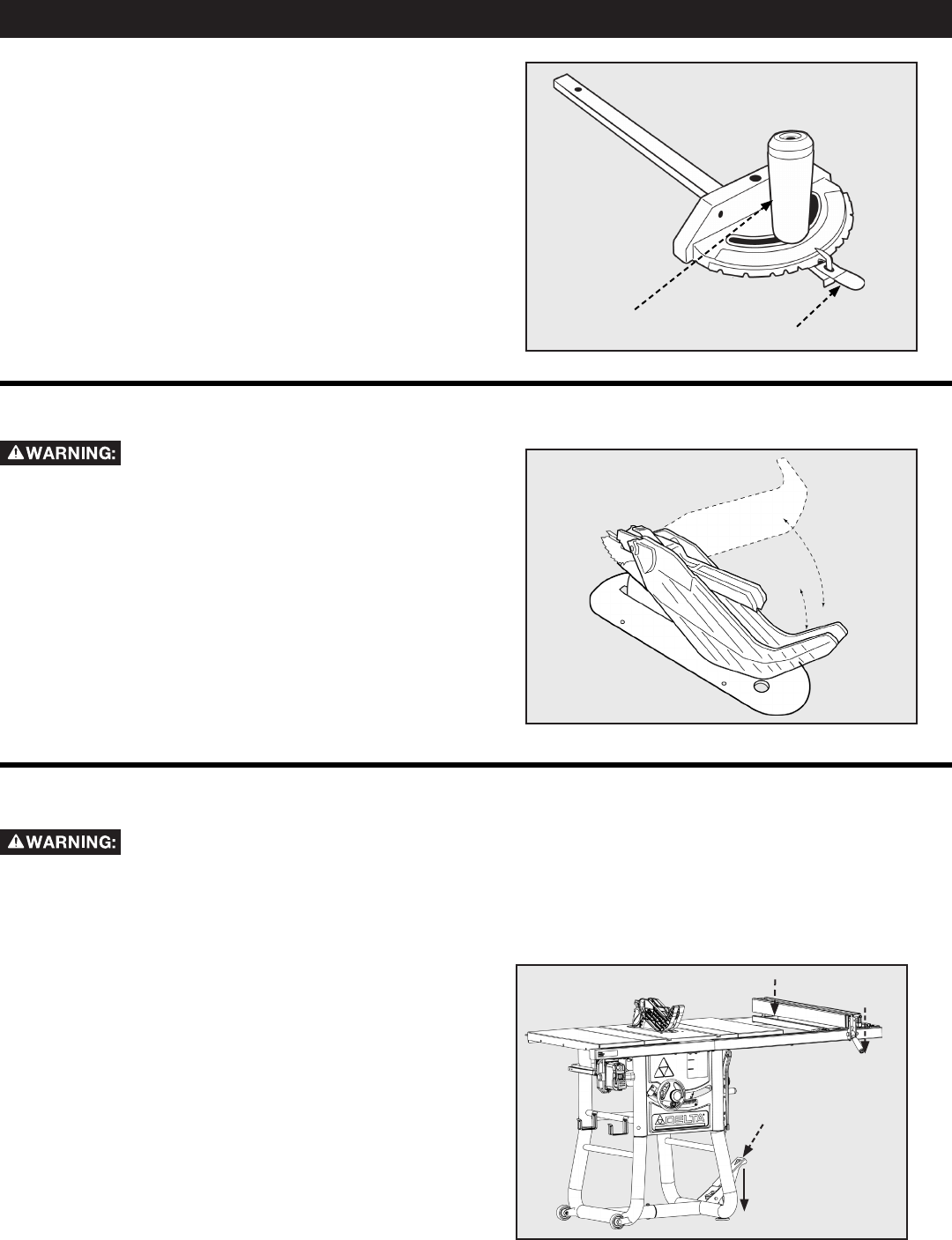
TO RAISE OR LOWER THE RIVING KNIFE:
1. Remove the throat plate and raise blade to the full height
above the table.
2. Locate the Locking Cam Lever near the base of the riving
knife.
3. Rotate the Cam Lever by turning clockwise to unlock and
release the riving knife from its locked position.
4. Using your hand positioned near the top of the knife, lean
the knife outward away fro the two locking pins beside
its middle slot. This now frees the knife to slide into the
upward/ cut through position.
5. Lift the knife upward along the sliding slot until you feel the
new locking pins position.
6. Release the knife and it should snap into its new position;
wiggle if necessary.
7. Return the locking cam lever to the locked position. If you
have done this properly the riving knife will be aligned with
the blade. If it is not retrace your steps until it does.
NOTE: When adjusting the riving knife up or down, be
sure to pull in a radial motion, as shown.
DO NOT operate saw unless riving knife is
securely clamped in the raised position for
through-cutting or the lowered position for non through-cutting.
1. Vertical Alignment: Place a carpenter’s square on the
table and against the blade face and make sure it extends
upalongtherivingknife(B) as showningure20b.The
riving knife and blade should touch the carpenter’s square
with no gaps. Be sure the straight edge goes between the
teeth and rests on the blade face and the riving knife for
proper alignment.
If the riving knife and blade are out of horizontal or vertical
alignment, refer to riving knife alignment instructions on page 28
of this manual.
CHECKING RIVING KNIFE
ALIGNMENT
Before connecting the table saw to
the power source and operating the
saw, always inspect the blade guard assembly and
riving knife for proper alignment and clearance with
saw blade. Check the riving knife alignment after
each blade change.
FIGURE 20B
Lower
Position
Detents
Upper Position
Detents on Pins
Pull Away
to Release
Riving Knife
A
Locked
Adjust
19
A
PREPARING TO CUT
USING THE MITER GAUGE
The miter gauge is equipped with adjustable index stops at 90°,
75°, 60°, 45° and 30°. To set the miter for an angled cut, see
Figure 21 and:
1. Loosen the handle (A).
2. Depress the thumb lever (B).
3. Move the body of the miter gauge to the desired angle
maximum 30° on either side.
4. Release the thumb lever and retighten the handle.
The miter gauge is equipped with a washer on the end of the bar
whichtsintothet-slotinthetable.Thisallowsthemitergauge
tobepulledothefrontedgeofthetablewithoutfalling.This
allows for an increased workpiece capacity in front of the blade.
B
FIGURE 21
USING BLADE GUARD ASSEMBLY
The anti-kickback pawls and blade guard
must be used for all through-cuts. Keep
both guard shields down and arms, hands and ngers
away from the blade, blade guard and anti-kickback
pawls when power is on to prevent serious injury. See
assembly instructions on page 13 for proper installation
and removal of anti-kickback pawls and blade guard.
Ifthereisaneedtobrieyraisethebladeguard(forexample,
to make a measurement) the guard can be parked in a raised
position.
1. Refer to Figure 22 and, lifting the guard from the front,
raise the guard shield until it snaps into a locked position
above the table. One or both guard shields can be raised.
2. When done making the measurement, return guard to
operating position.
FIGURE 22
Example
Pivot Pedal
CHECKING FENCE ALIGNMENT TO MOVE SAW
Do not attempt to use a rip fence that is
not properly aligned.
Every time you use the rip fence, check its alignment to make
sure the fence is parallel to the miter slot. To check the alignment
of your rip fence, place the fence adjacent to miter slot and lock
the fence in place. If the fence is not aligned to the miter slot
from the front to the back, see instructions for aligning rip fence
on page 29 of this manual. If you are not able to successfully
align the rip fence, replace the rip fence or contact
1-800-223-7278 for further instructions.
NOTE: Makesurethesawisoandthebladeiscompletelystill
before attempting to move the saw.
To move saw step down on pivot pedal (8), place hands on each
fence rail, and move saw to desired location. Lift the pivot pedal
up after the saw is moved to desired location.

20
OPERATION
STARTING AND STOPPING THE
SAW
The POWER switch (Figure 23) is located underneath the front left
extension wing.
1. To turn the saw “ON”, push the green “On” button.
2. To turn the saw “OFF”, push the red paddle switch in.
Whennotinuse,thesawshouldbeturnedoandthepower
switch locked out to prevent unauthorized use. To lock out power
switch, use a standard long shackle lock, with a shackle that is at
least 2 3/4 - inches (70mm) long and with shackle posts no larger
than 9/32-inch (7mm) thick.
B
A
FIGURE 23
Failure to comply with the following the warnings may result in serious personal injury.
READ ENTIRE MANUAL. In addition to reading these operating instructions, it is important to read and understand
the entire manual before operating this saw. Follow all applicable instructions regarding assembly, preparation,
and adjustment prior to making any cuts and comply with all safety rules and warnings in this section and elsewhere
throughout this manual.
1. Each time you use the saw, run through the following
checklist:
• Are the power source and power connections adequate
for the saw?
• Are the saw and work area free of clutter and
by-standers?
• Is the blade tight and properly aligned?
• Does the riving knife thickness match the blade?
• Are the blade and riving knife properly aligned?
• Is the operator qualied to make the cut and familiar
with all of the relevant safety rules, warnings and
instructions included in this manual?
• Is the operator and everyone in proximity to the saw
wearing appropriate eye, hearing and respiratory
equipment?
• Are the bevel angle and height adjustment knobs locked
in the proper position?
• Is the blade set at the proper height?
• If ripping, is the rip fence parallel to the blade and
securely locked in position?
• If crosscutting, is the miter gauge knob tight?
• If making through cuts with a standard blade, are the
blade guard riving knife and anti-kickback pawls properly
attached and properly functioning with both guards
contacting the table surface?
• Is there proper clearance and support for the workpiece
as it leaves the blade?
• Are any cutting aids needed? If so, are they in place, or
within reach for proper use?
2. The use of attachments and accessories not recommended
by Delta Power Equipment Corporation may result in injury.
3. Replace or sharpen the anti-kickback ngers when the
points become dull.
4. Make sure saw is stable and cutting can be accomplished
without tipping the saw. Do not attempt to cut large
workpieces without securing saw to a stable surface. To
properly secure the saw, see instructions in section entitled
Securing Saw to the Floor on page 15 of this manual.
5. Never use the fence and miter gauge together without
usingacutoblockaspreviouslydescribed.
6. The proper throat plate must be in place at all times.
7. If your saw makes an unfamiliar noise or if it vibrates
excessively, cease operating immediately until the source
has been located and the problem corrected.
8. Never perform freehand cutting, plunge cutting, re-sawing
or cove cutting.
AVOID KICKBACK
A kickback can occur when the workpiece pinches the blade, or
bindsbetweenthesawbladeandtheripfenceorotherxed
object. This can cause the workpiece to rise from the table and/or
be thrown back toward the operator. See instructions for reducing
the risk of kickback on page 7 of this manual.
IF KICKBACK OCCURS, turn the saw “OFF” and verify proper
alignment of the blade, riving knife and miter gauge or rip fence,
and the proper functioning of the riving knife, anti-kickback
assembly and blade guard assembly before resuming work.

21
OPERATION
OVERLOAD PROTECTION
Your saw is supplied with overload protection. If the motor shuts
oorfailstostartdueooverloading(cuttingstocktoofast,
using a dull blade, using the saw beyond its capacity, etc.) or low
voltage,letthemotorcoolthreetoveminutes.Thendepress
the red reset button (B), on the motor under the saw, shown in
Figure 23, and restart the saw.
NOTICE: If the motor continually shuts o due to over-
loading, contact a qualied electrician.
MAKING CUTS
Failure to comply with the following the
warnings may result in serious personal injury.
• Never touch the free end of the workpiece or a free piece
thatiscuto,whilethepowerisonand/orthesawbladeis
rotating. Blade contact or binding may occur, resulting in a
thrown workpiece
• When sawing a long workpiece or a panel, use a work
support, such as a sawhorse, rollers or outfeed table at the
same height as the table surface of the saw.
• Never try to pull the workpiece back with the blade turning. If
youneedtopulltheworkpiecebackorliftitothetable,turn
theswitcho,allowthebladetostop,raisetheanti-kickback
teeth on each side of the riving knife if necessary, and slide
the workpiece out.
• Always make sure the blade guard (A) and anti-kickback pawls
(B) are in place and working properly when making these cuts
to avoid possible injury.
• Do not use blades rated less than the speed of this tool.
Failure to heed this warning could result in personal injury.
• To avoid kickback, make sure one side of the workpiece is
securely against the rip fence during any rip cut, and hold the
workpiecermlyagainstthemitergaugeduringanymitercut.
• Do not attempt compound miter cuts, with blade beveled and
miter fence angled, until you are thoroughly familiar with the
basic cuts and understand how to avoid kickback.
• Avoid bevel rip cuts with majority of material on left side of
blade.
Cross Cut Mitered Crosscut Rip Cut
Beveled Cross Cut Beveled Rip Cut Compound Miter Cut
• Before connecting the table saw to the power source or
operating the saw, always inspect the blade guard assembly
and riving knife for proper alignment and clearance with saw
blade. Check alignment after each change of beveling angle.
• A rip fence should ALWAYS be used for ripping operations
to prevent loss of control and personal injury. Always lock
the fence to the rail. NEVER perform a ripping operation
freehand.
• When making bevel cuts, place the fence on the right side of
the blade so that the blade is tilted away from the fence and
hands. Keep hands clear of the blade and use a push stick to
feed the workpiece unless the workpiece is large enough to
allow you to hold it more than 6inches (152 mm) from the
blade.
• Before leaving the saw unattended, lock out power switch, or
take other appropriate measures to prevent unauthorized use
of the saw.

22
OPERATION
BEVEL RIPPING
Bevel ripping is the same as ripping except the bevel angle (A) is
set to an angle other than 0°. When making a bevel rip cut, place
the fence on the right side of the blade so that the blade is tilted
away from the fence and hands.
45º
RIP CUTS
• Rip cutting: Rip cutting is performed predominantly in a
parallel direction with the grain of the wood.
• Make sure blade is parallel to miter gauge slot prior to cutting.
Instructions for adjustment on page 25.
1. Remove miter gauge.
2. Make sure bevel angle is set to 0°.
3. Set blade to correct height for workpiece.
4. Install rip fence and lock it down parallel with and at
desired distance from blade.
5. Keepngersatleast6inchesfromthebladeatalltimes.
When the hand cannot be safely put between the blade
and the rip fence, select a larger workpiece, or use a push
stick and other cutting aids, as needed, to control the
workpiece.
6. Make sure the workpiece is clear of the blade (at least 1
inch or 25mm away) before starting the saw
7. Turn saw on.
8. Holdtheworkpieceatonthetableandagainstthefence
(A). The workpiece must have a straight edge against the
fence and must not be warped, twisted or bowed. See
proper hand position in Figure 24.
9. Let blade build up to full speed before moving workpiece
into the blade.
10. Both hands can be used while starting the cut as long as
hands remain 6 inches from the blade.
11. Keep the workpiece against the table and fence and slowly
feed the workpiece rearward all the way through the saw
blade. Do not overload the motor by forcing the workpiece
into the blade.
A
FIGURE 24
FIGURE 25
12. Use the push stick and any other cutting aids, as needed,
to hold the workpiece against the table and fence, and
push the workpiece past the blade. A push stick is included
with this saw, and instructions are included to make
additional push sticks and other cutting aids.
13. Do not push or hold onto the free or cut-o side of the
workpiece.
14. Continue pushing the workpiece until it is clear of the
blade. Do not overload the motor by forcing the workpiece
into the blade.
15. Whencutiscomplete,turnsawo.Waitforbladetocome
to a complete stop before removing workpiece from table.
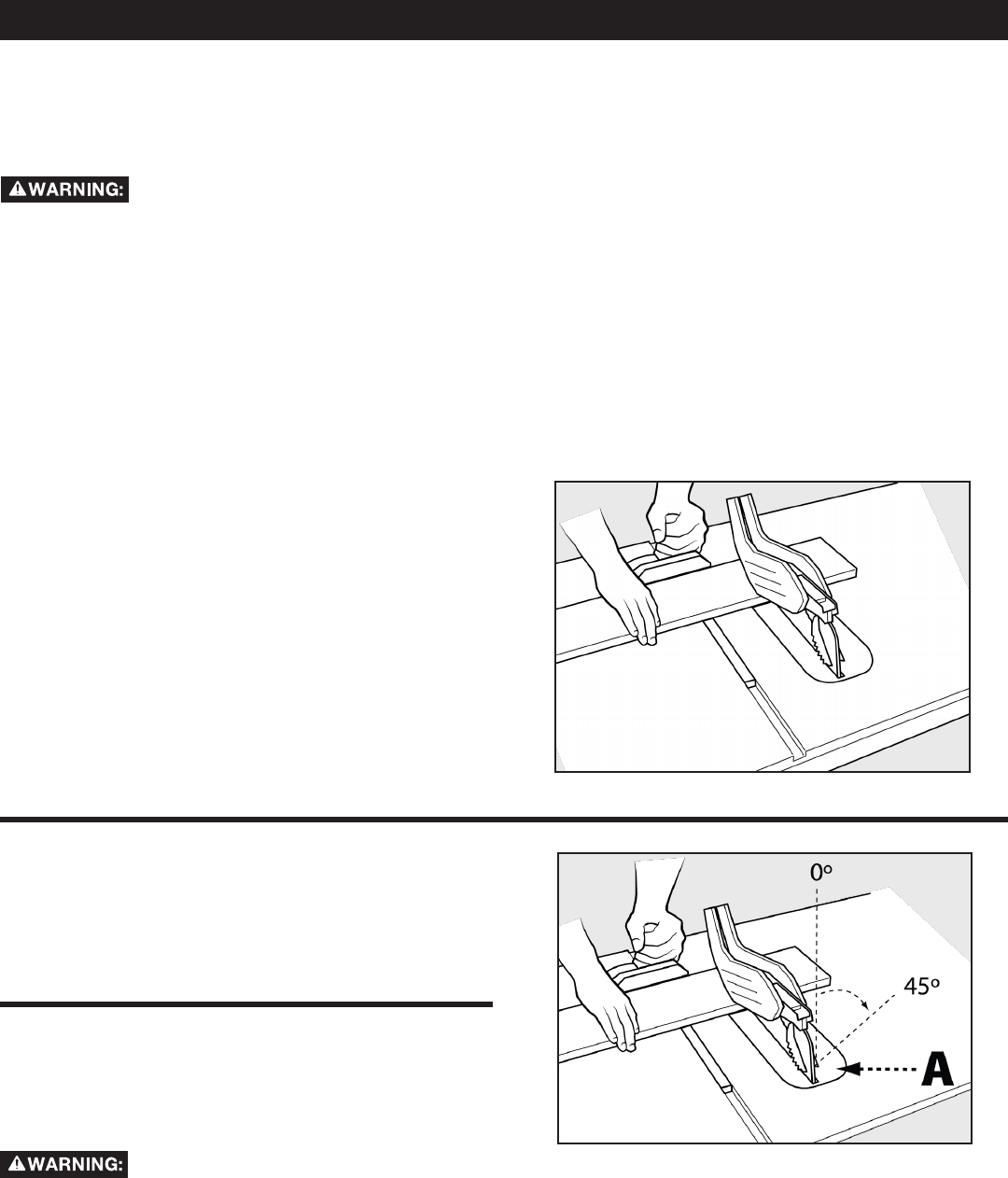
23
OPERATION
BEVEL CROSSCUTTING
Bevel crosscutting is the same as crosscutting except the bevel
angle (A) is set to an angle other than 90°. When making a bevel
crosscut, place the miter gauge in the right miter slot so that the
blade is tilted away from the gauge and hands. See Figure 31.
MITER CUTS
FIGURE 27
CROSSCUTTING
• NEVER use the fence as a guide or length stop when
crosscutting.
• The cut-o piece must never be conned in any through-
sawing (cutting completely through the workpiece) operation
to prevent pinching blade which may result in a thrown
workpiece and possibly injury.
• Whenusingablockasacut-ogauge,theblockmustbeat
least 3/4-inch (19mm) thick. It is very important that the rear
end of the block be secured in a position where the workpiece
is clear of the block before it enters the blade to prevent
binding of the workpiece.
You can use the miter gauge in either table slot on nonbevel cuts.
To increase surface area of miter gauge face, add an auxiliary
face (See Cutting Aids section on page 27 of this manual).
To make a crosscut, refer to Figure 30 and follow this process:
1. Remove rip fence.
2. Make sure bevel angle is set to 0°.
3. Set blade to correct height for workpiece.
4. Place miter gauge in either miter slot.
5. Set miter gauge to 0° and tighten miter gauge lock knob.
6. Hands must remain at least 6 inches from blade
throughout entire cut. If workpiece is too small to keep
hands at least 6 inches away from the blade, select
FIGURE 26
Miter cuts are cross cuts with the miter gauge set at an angle
other than 90°. For instructions about setting miter gauge angles,
see Preparing to Cut. To adjust the preset index miter stops, see
Adjusting the Miter Stops on page 28 of this manual.
• Miter angles less than 45˚ may force the blade guard
assembly into the saw blade causing damage to the blade
guard assembly and personal injury. Before starting the motor,
test the operation by feeding the workpiece into the blade
guard assembly. If the blade guard assembly contacts the
blade, place the workpiece under the blade guard assembly
but not touching the blade - before starting the motor.
a larger workpiece, or attach an auxiliary face to the
miter gauge and attach workpiece to auxiliary face, For
instructions about making auxiliary faces, see Cutting Aids
section on page 28 of this manual.
7. Make sure the workpiece is clear of the blade - at least 1
inch or 25mm away - before starting the saw.
8. Turn saw on.
9. Let blade build up to full speed before moving workpiece
into the blade.
10. Hand closest to blade should be placed on miter gauge lock
knob and hand farthest from blade should hold workpiece
rmly against the miter gage face. Do not push or hold
ontothefreeorcut-osideoftheworkpiece.
11. Slowly feed the workpiece rearward all the way through
the saw blade. Do not overload the motor by forcing the
workpiece into the blade.
12. Whencutiscomplete,turnsawo.Waitforbladetocome
to a complete stop before removing cut o piece from
table.
• Certain workpiece shapes, such as molding may not lift the
blade guard assembly properly. With the power off, feed
the workpiece slowly into the blade guard area and until the
workpiece touches the blade. If the blade guard assembly
contacts the blade, place the workpiece under the blade guard
assembly - but not touching the blade - before starting the
motor.
• Cross cutting: Cross cutting is performed predominantly in a
perpendicular direction with the grain of the wood.
• Make sure blade is parallel to miter gauge slot prior to cutting.
Instructions for adjustment on page 25.

24
OPERATION
90º
COMPOUND MITER CUTS
This is a combination of bevel crosscutting and mitering. Refer to
Figure 28 and follow the instructions for both bevel crosscutting
and mitering. Remember to use the right miter slot for all bevel
cuts.
LARGE PANEL CUTS
Place workpiece supports at the same height as the saw table
behind saw to support the cut workpiece, and alongside (s) of
saw, as needed. Depending on shape of panel, use rip fence or
miter gauge to control workpiece. If a workpiece is too large to
use either a rip fence or a miter gauge, it is too large for this saw.
FIGURE 28
NON-THROUGH CUTS
The use of a non-through cut is essential to cutting grooves
and rabbets. Non-through cuts can be made using a standard
blade having a diameter of 10 inches or less. Non-through cuts
are the only type of cuts that should be made without the blade
guard assembly installed. Make sure the blade guard assembly is
reinstalled upon completion of this type of cut.
• When making non-through cuts, follow all applicable warnings
and instructions listed below in addition to those listed above
for the relevant through cut.
• When making a non-through cut, blade is covered by
workpiece during most of cut. Be alert to exposed blade at
startandnishofeverycut.
• Never feed wood with hands when making any non-through
cuts such as rabbets. Always use miter gauge, push blocks or
push sticks, and featherboards where appropriate.
MAKING A NON-THROUGH CUT
• Once all non-through cuts are completed, unplug saw and
reinstall riving knife in raised position. Install anti-kickback
pawls and blade guard.
1. Unplug saw.
2. Unlock release lever.
3. Adjust bevel angle to 0°.
4. Lock release lever.
5. Remove blade guard and anti-kickback pawls.
6. Place riving knife in “lowered” position. See RIVING KNIFE
POSITION Section on page 18
7. Set blade to correct depth for workpiece. See instructions
below for use of other specialized blades.
• Read the appropriate section which describes the type of cut
in addition to this section on non-through. For example, if your
non-through cut is a straight cross cut, read and understand
the section on straight cross cuts before proceeding.
• Once all non-through cuts are completed, unplug saw and
reinstall riving knife or return it to raised position. Install anti-
kickback pawls and blade guard.
• Carefully follow the instructions accompanying any specialized
blades such as molding cutters for proper installation, set up
and operation.
8. Depending on shape and size of wood, use either rip fence
or miter gauge.
9. Plug saw into power source and turn saw on.
10. Let blade build up to full speed before moving workpiece
into blade.
11. Always use push blocks, push sticks, and/or featherboards
when making non-through cuts to reduce the risk of
serious injury.
12. Whencutismade,turnsawo.Waitforbladetocometo
a complete stop before removing workpiece.
13. When cut is complete re-adjust riving knife to position as
detailed on page 18.

25
OPERATION
FIGURE 29A
FIGURE 29B
CUTTING AIDS AND ACCESSORIES
PUSH STICK
In order to operate your table saw safely, you must use a push stick whenever the size or shape of the workpiece would otherwise
cause your hands to be within 6-inches (152mm) of the saw blade or other cutter. A push stick is included with this saw.
No special wood is needed to make additional push-sticks as long as it is sturdy and long enough with no knots, checks or cracks.
Alengthofapproximately16inches(400mm)isrecommendedwithanotchthattsagainsttheedgeoftheworkpiecetoprevent
slipping.It’sagoodideatohaveseveralpushsticksofthesameminimumlength,16inches(400mm),withdierentsizenotchesfor
dierentworkpiecethicknesses.
The shape can vary to suit your own needs as long as it performs its intended function of keeping your hands away from the blade.
Angling the notch so the push stick can be held at a 20- to 30-degree angle from the saw’s table will help you to hold down the
workplace while also moving the saw.
To construct a push stick, refer to the layout shown in Figure 30.
FIGURE 30
HEELING (PARALLELING) BLADE
TO MITER GAUGE GROOVE
• Blade (A) must be parallel to miter gauge groove so
that wood does not bind, resulting in kickback. Failure
to do so could result in serious personal injury.
• To reduce risk of injury from kickback, align rip fence
to blade (A) following any blade adjustments.
DO NOT loosen any screws for this adjustment until alignment
has been checked with a square to be sure adjustments are
necessary. Once screws are loosened, items must be reset.
Note: Unplug saw. Remove blade guard and anti-kickback pawls.
Raise the blade (A) by turning height adjusting wheel.
1. Mark beside one of blade teeth at front of blade (A). Place
a combination square even with front of saw table and side
of saw blade (A) as shown.
2. Turn blade (A) so that marked tooth is at back. Move
combination square to the rear and again measure the
distance. If the distances are the same, blade (A) is
square.
1
1
2
2
A
A

26
CUTTING AIDS AND ACCESSORIES
Wooden
dowel
Sandpaper
or old
mouse pad
material
AUXILIARY RIP FENCE FACING
Use an auxiliary rip fence facing when needed for special cuts,
such as ripping material that is thin enough to slide under the
rip fence provided with your saw, or when a taller rip fence is
necessary to complete your cut. To add an auxiliary wood facing
to one or both sides of the rip fence, select a piece of wood
with smooth surfaces, Attach the wood to the rip fence with two
clamps. (See Figure 31) For most work, 3/4-inch (19mm) or
1-inch (25mm) stock is suitable.
FIGURE 31
AUXILIARY MITER GAUGE FACING
An auxiliary miter gauge facing is used to increase the surface
area of the miter gauge face.
The use of miter gauge with auxiliary facing is the same as
original miter gauge (without auxiliary facing). See Page 19 for
the use of miter gauge.
Ifdesired,youcantthemitergaugewithanauxiliarywood
facing that should be at least 1-inch (25mm) higher than the
maximum depth of cut, and at least as wide as the miter gauge.
This auxiliary wood facing can be fastened to the front of the
miter gauge by using two wood screws through the holes (A)
provided in the miter gauge body and into the wood facing. See
Figure 32. Make sure the screws are long enough to secure the
facing, but do not extend all the way through the wood.
FIGURE 32
PUSH BLOCK
Push blocks are blocks used to securely hold down the workpiece
against the table. They include some gripping surface or handle to
hold the block. Any screws running through the underside of the
block to fasten the handle should be recessed in order to avoid
contact with the workpiece.
1. Select a piece of wood about 4-inches wide, 6-inches
longand1-to2-inchesthick(acutofroma2
by 4 makes a good blank for a push block).
2. Drill a hole in the block and glue in a dowel to use
as a handle (you can angle the hole to provide
a more comfortable grip on the handle).
3. Glue a piece of rough or soft material such as sandpaper
or rubber to the bottom of the block to grip the
workpiece (old mouse pads work well). See Figure 33.
FIGURE 33
Grooving and rabbeting
Clamping a featherboard in front of the blade can increase
safety during non-through cuts, like grooving and rabbeting,
and through cuts. Use a featherboard to guide the workpiece
against the table and fence when making non-through
cuts such as rabbeting. A featherboard helps to control the
kickback.

27
CUTTING AIDS AND ACCESSORIES
CUT OFF GAUGE
When crosscutting a number of pieces to the same length, you
can clamp a block of wood (A) (See Figure 35) to the fence and
useitasacut-ogauge.Theblock(A)mustbeatleast3/4-inch
(19mm)thicktopreventthecutopiecefrombindingbetween
thebladeandthefence.Oncethecut-olengthisdetermined,
lock the fence and use the miter gauge to fee d the workpiece
into the blade.
Always position the cut-o gauge in front
of the saw blade.
FIGURE 35
FEATHERBOARD
Featherboards are used to keep the work in contact with
the fence and table (Figure 34), and help prevent kickback.
Featherboards are especially useful when ripping small workpieces
and for completing non-through cuts. The end is angled with a
series of narrow slots to give a friction hold on the workpiece, It is
locked in place on the table or fence with a c-clamp. Clamping a
featherboard in front of the blade can increase safety during non-
through cuts, like grooving and rabbeting, and through cuts.
1. Select a solid piece of lumber approximately 3/4-inch thick,
2 1/2-inches wide and 12-inches long.
2. Mark the center width on one end of stock. Miter width to
70° (see miter cut section for information on miter cuts).
3. Setripfencetoallowapproximatelya1/4-inch“nger”to
be cut in the stock.
4. Feed stock only to mark previously made at 6 inches.
5. Turn saw o and allow blade to completely stop rotating
before removing stock.
6. Reset rip fence and cut spaced rips into workpiece to
allow approximately 1/4-inch ngers and 1/8-inch spaces
betweenngers.
To avoid binding bet ween the
workpiece and the blade, make sure a
horizontal feather board presses only on the uncut
portion of the workpiece in front of the blade.
Dimensions for making a typical featherboard are shown in Figure
34. Make our featherboard from a straight piece of wood that is
free of knots and cracks. Clamp featherboards to the fence and/or
table so that the featherboard will hold the workpiece against the
fence or table.
FIGURE 34 FIGURE 34A
JIGS
Jigs may be created with a variety of special set-ups to control
particular workpiece shapes for particular cuts. Guidance on
how to make specialized jigs can be found in woodworking and
carpentry websites and publications.
Do not attempt to create or use a jig
unless you are thoroughly familiar with
table saw safety. Do not use any jig that could result in
pinching a kerf or jamming the workpiece between the
jig and the blade. Incorrect setups may cause kickback
which could result in serious injury.
3/4 in.3/4 in.
12 in.12 in.
70˚70˚
2 1/2 in.2 1/2 in.
1/4 in.1/4 in.
1/8 in.1/8 in.
PUSH BLOCK PUSH BLOCK
FEATHER BOARD FEATHER BOARD
PUSH STICK PUSH STICK

28
ALIGNMENT
RIVING KNIFE ALIGNMENT
WITH THE BLADE
This procedure requires a 4mm T-handle hex wrench and straight
edge ruler. (Fig.36 b)
WARNING: Completely disconnect saw from power source
before making any adjustments.
1. Carefully remove throat plate,
2. Loosen the two hex-head screws (A) shown in Figure 36.
3. Using a straight edge ruler, align riving knife with blade
body shown in Figure 36 a.
4. Tighten the two hex-head screws (A) shown in Figure 1.
5. To adjust parallel alignment use the two set screws (B)
shown in Figure 36. Clockwise: adjust riving knife to the
right. Counter-clockwise: adjust riving knife to the left. If
needed, use the set screws (D) to align the riving knife
with blade face and the square.
6. Fully tighten the two socket head cap screws.
7. Replace throat plate, blade guard and anti-kickback
assemblies before use.
If any dragging or binding of the
workpiece is encountered as it reaches
the riving knife, turn unit o and disconnect machine
from power source and readjust the riving knife/blade
alignment or replace the blade. Never attempt to back
partially-cut workpiece out of blade while blade is
moving.
FIGURE 36
FIGURE 36 a FIGURE 36 b
ADJUSTING THE MITER STOPS
To adjust the index stops for angles other than 90°, 75°, 60°, 45°
and 30°:
1. Loosen the miter gauge handle.
2. Loosen the 2 screws for the miter stop segment for the
desired new angle. (A) is shown in Figure 37.
3. Move the stop to proper position.
4. Re-tighten the 2 segment screws and handle.
FIGURE 37
A
B
A

29
ALIGNMENT
ALIGNING FENCE PARALLEL TO
MITER SLOT
ALIGNING FENCE
PERPENDICULAR TO THE TABLE
Dust Collection
Auxiliary Fence
1. Move fence adjacent to right miter gauge and secure to the
guide tube by lowering the fence clamping lever.
2. Ifthefenceface(A)gure42,isnotparalleltothemiter
slot (B), raise the clamping lever and lift the fence and
place it on the saw table.
3. Adjust the one or both of the set screws (C) 1/4 turn or
less.
4. Replace fence on guide tube and repeat steps 1 through
3. If fence is closer to parallel, turn the set screw in the
same direction but a little less. If the fence is further out of
parallel, turn the set screw in the opposite direction.
5. Repeat steps 1 through 3.
1. Move fence over the cast iron table and secure to the guide
tube by lowering the fence clamping lever.
2. Use a square to check that the fence face is perpendicular
to the table.
3. If the fence face is not perpendicular to the table, release
the clamping lever and slightly adjust one of the slotted set
screws(A)gure43untilthefencefaceisperpendicularto
the table.
4. Secure the fence to the guide tube to insure the fence
remains perpendicular. If not, repeat steps 1 through 4.
1. Connect a shop vacuum or dust collection hose to dust port
on back of saw for best dust collection.
For thin materials use the fence on the left of the blade. Fold
down the thin fence to allow use of blade guard. Subtract 2
inches from the scale for accurate measurement.
FIGURE 38
FIGURE 39
FIGURE 40
FIGURE 41
C
B
A
A

30
ACCESSORIES
TROUBLESHOOTING
MAINTENANCE
Toreducetheriskofinjury,turnunitoanddisconnectitfrompowersourcebeforecleaningorservicing,beforeinstallingand
removing accessories, before adjusting and when making repairs. An accidental start-up can cause injury.
LUBRICATION & RUST PROTECTION
Applyhardwoodooringpastewaxtothemachinetable
occasionally or use a commercially available protective product
designed for this purpose. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions
for use and safety.
To clean cast iron tables of rust, you will need the following
materials: a medium sized scouring pad, a can of spray lubricant
and a can of degreaser. Apply the spray lubricant and polish the
table surface with the scouring pad. Degrease the table, then
apply the protective product as described above.
MAINTENANCE REMINDERS
Wearcertiedsafetyequipmentforeye,hearingand
respiratory protection while using compressed air.
Specic areas which require regular maintenance include:
RIVING KNIFE CLAMP PLATE: Keep this area free of dust and
debris buildup. Blow out area regularly with compressed air.
NOTE: If the riving knife clamp can’t move freely, have
the saw serviced by authorized DELTA
®
Power Equipment
Corporation service center personnel.
WORM GEARS: Keep the worm gears free of dust and debris
buildup. Blow out area regularly with compressed air. Use a
lithium-based multipurpose grease as needed on these gears.
CLEAN SAWDUST BUILDUP OUT OF CABINET
PERIODICALLY: NOTE: Debris can also be removed from the
saw from below the throat plate, inside the dust port.
For assistance with your machine, visit our website at www.DeltaMachinery.com for a list of service centers or call Delta Power
Equipment Customer Care at 1-800-223-7278.
FAILURE TO START
If your machine fails to start, check to make sure the prongs on the cord plug are making good contact in the receptacle, and check
reset button on power switch housing. Also, check for blown fuses or open circuit breakers in your power line.
A complete line of accessories is available from your DELTA
®
Supplier, DELTA
®
Factory Service Centers, and DELTA
®
Authorized Service
Centers. Please visit our Web Site www.DeltaMachinery.com for an online catalog or for the name or your nearest supplier.
Since accessories other than those oered by DELTA
®
have not been tested with this product, use of
such accessories could be hazardous. For safest operation, only DELTA
®
recommended accessories
should be used with this product.
KEEP MACHINE CLEAN
Periodically blow out all air passages with dry compressed air. All
plastic parts should be cleaned with a soft damp cloth. NEVER
use solvents to clean plastic parts. They could possibly dissolve or
otherwise damage the material.
Wearcertiedsafetyequipmentforeye,hearingandrespiratory
protection while using compressed air.
For best performance use a shop vacuum or blower to keep saw
blade area, the dust collection system, the guarding system and
rails free of saw dust and other debris.
ADJUSTING BELT TENSION
1. Lower the blade height to its lowest position.
2. Loosen the torx screw (A) that is used to mount the
motor housing. This should be loosened enough to feel
the motor weight providing tension to the belt.
3. Tighten the torx screw (A) to secure the motor in place.
FIGURE 42
A
NOTE: If table saw with belt tension adjusted function, only
the technician can do the adjustment.

31
PARTS, SERVICE OR WARRANTY ASSISTANCE
All Delta
®
Machines and accessories are manufactured to high quality standards and are serviced by a network of an Authorized
Service Centers. To obtain additional information regarding your product or to obtain parts, service, warranty assistance, or the
location of the nearest service center, please call 1-800-223-7278.
Five Year Limited Warranty
1. WHAT IS COVERED. Delta Power Equipment Corporation (“Company”) will, at its option, repair or replace this product, if purchased
at retail in the United States or Canada and the product, with normal use, has proven to be defective in workmanship or material, subject to
the conditions stated in this Limited Warranty. This Limited Warranty covers only materials and labor. All transportation costs are Customer’s
responsibility.
2. WARRANTY PERIOD. Allwarrantyclaimsmustbesubmittedwithinveyearsfromthedateofretailpurchase.Forallservicepartsand
factory refurbished products, the warranty period is 180 days.
3. HOW TO OBTAIN SERVICE. To obtain warranty service, you must return the defective product, at your expense, to a service center
authorized by Company to perform warranty service (a “Company Authorized Service Center”) within the applicable warranty period, together
with acceptable proof of purchase, such as your original receipt bearing the date of purchase, or product registration number. Company reserves
the right to restrict warranty claim service to the country where the purchase was made and/or to charge for the cost to export service parts or
providewarrantyserviceinadierentcountry.Forthispurpose,on-linepurchasesaredeemedmadeintheUnitedStates.Forthelocationof
your nearest Company Authorized Service Center, call Company’s Customer Care Center at (800) 223-7278.
4. EXCLUSIONS.
●Companydoesnotoeranywarrantyonproductspurchasedinusedordamagedcondition.
●CompanydoesnotwarrantanyproductspurchasedoutsidetheUnitedStatesorCanada
● Companywillnotberesponsibleforanydamage that has resulted from normal wear, misuse, abuse or anyrepairoralterationmade by
anyone other than a Company Authorized Service Center or a designated representative of Company’s Customer Care Center.
All IMPLIED WARRANTIES areexpresslylimitedtothewarrantyperiodidentiedabove.
Company will not be liable for INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL damages.
This limited warranty is Company’s sole warranty and sets forth the customer’s exclusive remedy with respect to defective products; all other
warranties,expressorimplied,whetherofmerchantability,tnessforpurpose,orotherwise,areexpresslydisclaimedbyCompany,exceptas
expressly stated in this warranty statement.
Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, or the limitation of implied warranties, so the above
limitationsorexclusionsmaynotapplytoyou.Thiswarrantygivesyouspeciclegalrightsandyoumayhaveotherrightswhichvaryincertain
states or provinces. For further details of warranty coverage and warranty repair information, call (800) 223-7278. To register your products
on-line, we encourage you to visit our website and register for a FREE DELTA
®
Member Account at http://www.deltamachinery.com/register.
LATIN AMERICA: This warranty does not apply to products sold in Latin America. For products sold in Latin America, call the local
company or see website for warranty information.
REPLACEMENT PARTS
SERVICE AND REPAIRS
FREE WARNING LABEL REPLACEMENT
Use only identical replacement parts. For a parts list or to order parts, visit our website at www.DeltaMachinery.com/service. You can
also order parts from your nearest Authorized Warranty Service Center or by calling Technical Service Manager at 1-800-223-7278 to
receive personalized support from one of our highly-trained representatives.
All quality tools will eventually require servicing and/or replacement of parts. For information about Delta Power Equipment
Corporation, its factory-owned branches, or to locate an Authorized Warranty Service Center, visit our website at
www.DeltaMachinery.com/service or call Customer Care at 1-800-223-7278. All repairs made by our service centers are fully
guaranteed against defective material and workmanship. We cannot guarantee repairs made or attempted by others. By calling this
numberyoucanalsondanswerstomostfrequentlyaskedquestions24hours/day.
You can also write to us for information at Delta Power Equipment Corporation, 2651 New Cut Road, Spartanburg, SC 29303
Attention: Technical Service Manager. Be sure to indicate all of the information shown on the nameplate of your saw (model number,
type, serial number, date code, etc.).
If your warning labels become illegible or are missing, call 1-800-223-7278 for a free replacement.
