
Siebel Developer’s
Reference
Siebel Innovation Pack 2013
Version 8.1/8.2
September 2013

Copyright © 2005, 2013 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions
on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in
your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast,
modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any
means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for
interoperability, is prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-
free. If you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing
it on behalf of the U.S. Government, the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs, including any operating system, integrated software,
any programs installed on the hardware, and/or documentation, delivered to U.S. Government end users
are “commercial computer software” pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and
agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and
adaptation of the programs, including any operating system, integrated software, any programs installed
on the hardware, and/or documentation, shall be subject to license terms and license restrictions
applicable to the programs. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management
applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including
applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous
applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and
other measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any
damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be
trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks
are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD,
Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced
Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information on content,
products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and
expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services.
Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due
to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services.
Documentation Accessibility
For information about Oracle's commitment to accessibility, visit the Oracle Accessibility Program website
at http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
Access to Oracle Support
Oracle customers have access to electronic support through My Oracle Support. For information,
visit http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=info or visit
http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=trs if you are hearing impaired.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 3
Contents
Siebel Developer’s Reference 1
Chapter 1: What’s New in This Release
Chapter 2: Overview for Using This Book
How This Book Describes Objects 19
Getting Help From Oracle 20
Chapter 3: Applet Classes
Overview of Applet Classes 21
CSSSWEFrame Class 21
CSSSWEFrameBase Class 22
CSSSWEFrameList Classes 23
CSSSWEFrameListBase Class 23
CSSSWEFrameListFile Class 23
CSSSWEFrameListDocGen Class 23
CSSSWEFrameListWeb Class 24
CSSSWEFrameSalutation Class 24
CSSSWEFrameContactOrgChart Class 24
CSSSWEFrameListFINApplication Class 25
CSSSWEFrameUserRegistration Class 25
Chapter 4: Business Component Classes
Overview of Business Component Classes 28
Generalized and Specialized Business Component Classes 28
Guidelines for Using Methods in Business Component Classes 29
Calling a Method 30
CSSBusComp Class 30
CSSBCBase Class 30
User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCBase Class 31
Methods That the CSSBCBase Class Can Reference 31
CSSBCAccountSIS Class 35

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Contents
■
4
Dependencies and Limitations for the CSSBCAccountSIS Class 35
Business Component User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCAccountSIS Class
35
CSSBCActivity Class 36
Dependencies and Limitations for the CSSBCActivity Class 36
Business Component User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCActivity Class 39
Methods That the CSSBCActivity Class Can Reference 40
CSSBCActivityPlan Class 42
CSSBCContactSIS Class 43
User Properties and Methods That You Can Use with the CSSBCContactSIS Class 43
CSSBCFile Class 44
Dependencies and Limitations for the CSSBCFile Class 44
Methods That the CSSBCFileClass Can Reference 45
CSSBCFINOppty Class 48
User Properties and Methods That You Can Use with the CSSBCFINOppty Class 48
CSSBCFINSActivity Class 49
CSSBCForecast Class 49
Dependencies and Limitations for Forecast Classes 50
Business Component User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCForecast Class 50
Methods That the CSSBCForecastClass Can Reference 51
CSSBCForecastBase Class 53
Methods That the CSSBCForecastBase Class Can Reference 54
CSSBCForecastItem Class 54
CSSBCForecastItemDetail Class 54
Methods That the CSSBCForecastItemDetail Class Can Reference 55
CSSBCFundReq Class 55
CSSBCOppty Class 56
CSSBCOrderMgmtQuoteItem Class 56
CSSBCPharmaSpecializedAct Class 57
CSSBCPosition Class 57
Methods That the CSSBCPosition Class Can Reference 58
CSSBCProposal Class 58
Methods That the CSSBCProposal Class Can Reference 58
CSSBCServiceRequest Class 58
Dependencies and Limitations 59
CSSBCTaskTransient Class 59

Contents ■
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 5
CSSBCTaskTransientBase Class 60
CSSBCUser Class 60
Guidelines for Using the CSSBCUser Class 60
Chapter 5: User Properties
Overview of User Properties 63
How This Book Describes the User Property Format 64
Numbering Instances of a User Property 65
Alphabetic List of User Properties 66
Application User Properties 69
Calling Business Services from the Client 70
Disabling Predefined Queries in Views 70
Disabling the View Cache 70
Applet User Properties 71
Calling Methods from Applets 72
Disabling Data Loss Warnings in Standard Interactivity 74
Disabling Hierarchies in List Applets 74
Disabling Methods for FINS Applets in Query Mode 75
Disabling New Record Creation 75
Enabling Methods for Applets 75
Enabling High Interactivity for Applets 76
Enabling Record Manipulation in Field Service and Task Views 76
Hiding Applets That Contain No Data 77
Making an Applet Control Required 77
Specifying Gantt Chart Behavior 78
Specifying Template Values for Proposals 81
Specifying Drilldown Visibility 82
Specifying Field Names According to Parent Id 82
Specifying Political Influence in Organization Charts 82
Specifying Post Invoke Methods 83
Specifying Relationships in Organization Charts 83
Specifying the Application That Creates Proposals 83
Specifying the Calendar Visibility Filter 84
Specifying the Default Applet Focus 84
Specifying the Error Web Page for SmartScript 85
Specifying the Finish or Cancel Web Page for SmartScript 85
Specifying the Method That the Enter Key Calls 85
Specifying the Parent Business Component 86
Business Service User Properties 86
Specifying the BAPI Adapter Service 86

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Contents
■
6
Specifying the Batch Size for SAP IDOCs 87
Specifying the Time Out Interval for Receive Requests 87
Control User Properties 87
Forcing Controls to Be Active 87
Saving Unsaved Data 87
Specifying the Goto URL 88
Specifying the Goto View 88
Specifying the Goto Web Page 88
Field User Properties 89
Disabling Search on Text Fields or Unindexed Fields 89
Disabling Sort on Business Component Fields 90
Making a Field Required 90
Setting the Field Text Length 90
Specifying Encryption for Fields 91
Updating Assets 93
Cascading Asset Updates 94
Specifying the Field That Stores the Account Id of a Contact 95
Specifying the SQL for EXISTS Search Specifications 95
Using Literals Instead of Bind Variables 96
Integration Component User Properties 97
Specifying Association Business Components 97
Specifying MVG Business Components 97
Preventing Siebel EAI From Deleting Records 98
Preventing Siebel EAI From Inserting Records 98
Integration Component Field User Properties 98
Specifying the Field Name for an MVG 98
Preventing Siebel EAI From Updating Fields 98
Integration Object User Properties 98
Specifying the IDOC Message Type for SAP 99
List Column User Properties 99
Disabling Sort on List Columns 99
Forcing Fields That a List Column References to be Active 100
View User Properties 100
Specifying the Default Applet Focus 100
Chapter 6: Business Component User Properties
Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties 101
Viewing a Business Component User Property 108
Controlling Siebel CRM Data 108

Contents ■
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 7
Controlling Accounts 109
Controlling Activities 110
Controlling Revenues 111
Controlling Campaigns 113
Controlling Forecasts 113
Allowing Users to Update Closed Service Requests 116
Allowing Users to Update Assets 116
Adding Contacts to the Action Business Component 117
Creating Numbered Revisions of Quotes, Orders, or Agreements 117
Extending Quote Quantities 118
Automatically Assigning Responsibilities to Users 118
Making Sure the Current Employee Holds a Position 119
Setting the Close Out Flag Field 119
Specifying State Models 120
Specifying Assignment Objects 120
Protecting Seed Data 120
Controlling Search and Sort 121
Optimizing Sort Searches 121
Removing Duplicate Records From Queries 122
Overriding Sort Specifications on Business Components 123
Sorting According to the View Mode That the Business Component Uses 124
Disabling Automatic Trailing Wildcards in Queries 125
Adding Search Criteria to the Query Assistant 126
Saving Query Results in Target Lists 127
Specifying How to Sort Predefined Queries for Opportunities 127
Specifying Search Specifications for the Action Business Component 129
Specifying Search Specifications for Nonsales Rep Views 129
Controlling Visibility Filters 130
Controlling Global Account Visibility 130
Controlling My Visibility Filters 131
Controlling Manager Visibility Filters 132
Controlling Records 132
Making Records Read-Only According to a Field Value 133
Disabling Modifications to Saved Records 133
Allowing Administrators to Modify Records 133
Preventing Administrators from Deleting Records 134
Preventing Administrators from Updating Records 134
Calculating Values When Writing Records 135
Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records 135
Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records According to Maximum Values 135
Setting Business Components to Read-Only According to a Field Value 136

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Contents
■
8
Setting Business Components to Read-Only According to a Name 137
Using Literals Instead of Bind Variables When Merging Records 137
Controlling Fields 138
Making Fields Active 138
Making Fields Read-Only 139
Disallowing Empty Fields 139
Disabling Field Deletion 140
Setting Field Values According to Conditions 140
Updating Fields When Siebel CRM Updates Other Fields 141
Calling Methods When Siebel CRM Updates Fields 142
Setting the Field Created Date to the Saved Date 143
Updating the Planned Field if the Start Date Field Is Modified 143
Overriding the Type for Fields That Users Read from Right-To-Left 143
Setting Default Values for Fields That Use Drop-Down Lists 144
Modifying the Currency That a Field Uses 145
Specifying Field Name Prefixes for File Attachment Business Components 145
Controlling Primaries 146
Specifying Who Can Modify Primary Team Members 146
Setting the Primary Sales Rep as the Owner 147
Setting the Current User as the Primary Contact 147
Allowing Only the Primary to Modify Sales Methods for Opportunities 147
Restricting How Siebel CRM Displays Private Activities for Primaries 148
Specifying Business Services 148
Calling Business Service Methods from Business Components 148
Specifying Business Service Parameters 149
Specifying External Data Sources for Business Services 149
Specifying Business Services for Virtual Business Components 149
Controlling Parent and Child Relationships 149
Copying and Deleting Child and Grandchild Records 150
Updating the Parent Business Component if Siebel CRM Modifies Children 152
Specifying Recursive Links Between Parent and Child Business Components 153
Enabling Service Request Updates in Child Business Components 154
Controlling Email 154
Specifying Statuses for Outgoing Email 155
Specifying the Manager That Sends Email 156
Sending Email Packages to Recipients 156
Responding to Email or Web Offers 158
Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications 158
Controlling Siebel Automotive 159
Specifying Activities to Synchronize for Siebel Handheld 161

Contents ■
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 9
Specifying Position Join Fields for Siebel Life Sciences 162
Specifying Business Components for Product Selection and Pricing 163
Identifying Business Components That Siebel Financial Services Uses 165
Specifying Room Types for Siebel Hospitality 165
Specifying Arrival Dates, Room Blocks, and Function Spaces for Siebel Hospitality 165
Enabling Credit Check 166
Specifying the Workflow Process for Credit Check 166
Specifying Credit Card User Properties 167
Doing Other Work 167
Specifying the Application Name 168
Using Aspects to Control Read Only, Insert, and Other Behavior 168
Specifying the Default Bookmark View 170
Enabling the Dispatch Board 170
Making Sure an Attachment File Exists 170
Enabling the Revise Button According to Conditions 171
Specifying Joins to the S_PARTY Table 172
Specifying the DB2 Optimization Level for SQL Statements 172
Capturing User Drilldown Behavior 173
Chapter 7: Siebel Web Engine Tags
About SWE Tags 177
Applet Tags 178
Applet Tag 178
Applet Layout Tag 178
Control Tag 179
Form Applet Layout Tag 180
Master and Detail Applet Tags 180
Select Row Tag 182
Form and Web Page Tags 184
Form Tag 184
Web Page Item Tag 184
Frame Tags 185
Frame Tag 186
Frameset Tag 186
Navigation Control Tag 187
Program Logic Tags 189
Error Tag 189
JavaScript Tag 190
If Tag 191
Iterate Tag 192

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Contents
■
10
Iterate Rows Tag 192
Switch, Case, and Default Tags 192
Referential Tags 193
Include Tag 193
Map Siebel Object to SWE Tag 194
This Tag 195
This Id Tag 196
This Table Id Tag 196
Screen Tags 196
For Each Screen Tag 197
Screenbar Tag 197
Screen Link Tag 197
Screen Name Tag 198
Subview Tags 198
Subview Bar Tag 198
For Each Subview Tag 200
Threadbar Tags 200
About Threadbar Behavior 201
For Each Thread Tag 201
Step Separator Tag 201
Thread Link Tag 202
About Link Navigation 202
Example of Using the Threadbar Tags 202
Togglebar Tags 203
For Each Toggle Tag 203
Toggle Bar Tag 203
Toggle Link Tag 204
Toggle Name Tag 204
Examples of Using the Togglebar Tags 204
Toolbar Tags 205
Configuring an HTML or Java Toolbar 205
Toolbar Tag 206
Toolbar Item Tag 206
Tree Tags 207
Applet Tree List Tag 207
For Each Indent Tag 208
For Each Node Tag 208
Indent Image Tag 208
Node Tag 208

Contents ■
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 11
View Tags 209
Overview of Using View Tags 209
Current View Tag 211
For Each View Tag 212
View Tag 212
View Bar Tag 212
View Link Tag 214
View Name Tag 215
Predefined Query Tag 215
Tags That Support a Specific Feature 215
Language Conversion Tag 215
Training Tag 216
Wireless Tag 216
XSL Stylesheet Tag 216
Tags That Are for Oracle Internal Use Only 217
All Applets, All Controls, and List Control Tags 217
Calendar Tags 217
Gantt Chart Tags 218
Chapter 8: Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
Overview of Configuring Siebel Templates for Employee Applications 219
Guidelines for Configuring Applet Templates 219
About Mapping IDs to Placeholders 220
Elements in the Client of an Employee Application 220
Form Templates 221
Overview of Using Applet Form Templates 222
Form Template for Edit, New, or Query Mode 227
One Column Form Template 229
One Column Form, Light Template 229
One Column Form, Light Template for Base, Edit, or New Mode 230
Four Column Form Template for Base Mode 231
Four Column Form Template for Edit or New Mode 234
Four Column Form Template With No Record Navigation 236
Grid Layout Form Template 239
List Templates 240
List Template for Base or Edit List Mode 241
Inverted Axis List Template 243
Message List Template 245
Portal List Template 248
Portal List Template With Graphics 250

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Contents
■
12
Totals List Template for Base or Edit List Mode 253
Calendar Templates 255
Daily Calendar Template 255
Daily Calendar Template for Portals 257
Weekly Calendar Template 259
Monthly Calendar Template 260
Service Calendar Template 262
Chart Templates 263
Chart Template 263
Gantt Chart Template 265
Gantt Chart Activity Template 266
Gantt Chart Template for Portals 266
Container Templates 267
Container Template 268
CC Container Logic Template 269
Popup Templates 269
Popup Form Template 270
Popup Form, Grid Layout Template 271
Popup List Template 273
Popup Spell Checker Template 275
Popup Query Template 276
Search Templates 276
Search Center, Top Template 277
Search Center, Bottom Template 277
Advanced Search Template 278
Find Template 279
Save Search Template 280
Search Preference Template 281
Search Results Templates 283
Tree Templates 287
Applet Tree Template 287
Applet Tree, Marketing Template 289
View Tree Template 289
View Tree Two Template 291
View Templates 292
Overview of Using View Templates 293
View 1 Over 2 Over 1 Template 293
View 25 - 50 – 25 Template 295
View 25 – 75 Template 296
View 25 – 75 Framed Template 297

Contents ■
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 13
View 25 – 75 Framed Two Template 298
View 50 – 50 Template 299
View 66 – 33 Template 300
View Admin Template 302
View Admin Template With Grandchild Indented Applets 303
View Basic Template 304
View Catalog Admin Template 305
View Detail Template 306
View Detail Template With Grandchild Indented Applets 308
View Detail Two Template 309
View Detail Two Template With Grandchild Indented Applets 311
View Detail Three Template 312
View Detail Three Template With Grandchild Indented Applets 314
View Detail Three Multichild Template 315
View Detail Multichild Template 316
View Parent List With Tabs Template 317
Specialized Employee Templates 319
Columns Displayed Template 320
Dashboard Template 321
Email Response Template for Inbound Messages 322
Email Response Template for Outbound Messages 324
Salutation Applet Template 326
Salutation Applet Template With Graphics 326
Screen Links Template 327
Send Mail Template 329
Send Mail Template for Picking Recipients 330
Site Map Template 331
View Dashboard Template 331
View Segment Detail Template 332
Wizard, Error, and Smart Script Templates 333
Applet Wizard Template 333
Error Page Template 334
Smart Script Player Template 335
Smart Script Player Template With Tree Only 336
Chapter 9: Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
Overview of Configuring Siebel Templates for Customer Applications 337
Customer Form Templates 339
Basic Form Template 339
One Column Form Template 340
Two Column Form Template 342

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Contents
■
14
Four Column Form Template 344
Item Detail Form Template 347
Search, Top Form Template 349
Title, Form Template 349
Four Column, Merged, Form Template for Base, Edit, or New Mode 350
Customer List Templates 352
Brief, Bullet, List Template 353
Brief, Bullet, Border, List Template 355
Brief, Bullet, Shade, List Template 357
Brief, Image Bullet, List Template 358
Brief, Image Bullet Two, List Template 360
Brief, Image Bullet, Border, List Template 362
Categorized List Template With Tabs 363
Categorized List Template With No Tabs 364
Brief, Image Bullet, Shade, List Template 365
Categorized Bullet, List Template 366
Categorized Bullet, List Template With Tabs 368
Categorized Table of Contents, List Template 369
Detailed, Image Bullet, List Template 370
Detailed, Image Bullet, List Template With Record Navigation 372
Detailed, Image Bullet, List Template With Record Navigation Two 374
Go To View, List Template 376
Horizontal List Template 377
List Template With Tabs 379
Light List Template 381
Search Results, List Template 383
Subcategory List Template 385
Subcategory, One Per Row, List Template 385
Subcategory, Four Per Column, List Template 386
Subcategory, Six Per Column, List Template 387
Subcategory, Indented, List Template 388
Merged List Template for Base or Edit List Mode 389
Links List Template 390
Customer View Templates 391
Admin View Template 391
Basic View Template 393
Detail View Template 394
Detail View Two Template 395
Detail, Multiple Child, View Template 396
25 50 25, View Template 398
25 50 25, Home, View Template 399
50 50, View Template 401

Contents ■
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 15
66 33, View Template 402
100 66 33 100, View Template 403
Customer Container Templates 405
Container Template With Frames 405
Container Template Without Frames 406
Container Template for Employee and Customer Applications 407
Specialized Customer Templates 408
Find Template 408
License, Base, One Column Template 409
Parametric Search, Head Template 410
Parametric Search, Tail Template 411
Real-Time Shopping Cart Template 412
Advanced Search Template 413
Advanced Search Template With Tabs 413
Basic Search Template 414
Totals Template 415
Chapter 10: Cascading Style Sheets
Overview of Cascading Style Sheets 417
Elements of Cascading Style Sheets 417
Applet Elements 419
Banner Elements 422
Calendar Elements 422
Control Elements 423
Customer Application Elements 425
Dashboard Elements 425
Dialog Box Elements 426
Divider Elements 426
ePortal Elements 426
External News Elements 429
Fonts and Link Color Elements 430
Form Elements 430
Login Page Elements 431
Navigation Elements 432
Page Header Elements 435
Rich Text Component Elements 436
Search Center Elements 436
SmartScript Player Elements 436
Status Message Elements 437
Text Elements 437

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Contents
■
16
Chapter 11: Operators and Expressions
Operators 439
Operator Precedence 439
Comparison Operators 440
Logical Operators 441
Arithmetic Operators 441
LIKE and NOT LIKE Operators 441
NULL Operator 443
Using the EXISTS Operators with Multivalue Groups 445
Expressions 447
Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression 448
Using the Division Functions 458
Using the IIf Function 460
Using Julian Functions 460
Using the Timestamp Function 461
Using Functions in the Predefault and Postdefault Properties 462
Using Expressions In the Calculated Field and Field Validation Properties 466
Using the Invoke Service Method in a Calculated Field 468
Using Calculated Fields with Chart Coordinates 469
How Siebel CRM Handles Data Types During a Calculation 470
Guidelines for Configuring Calculated Fields 471
Index

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 17
1 What’s New in This Release
What’s New in Siebel Developer’s Reference, Version 8.1/8.2
Table 1 lists changes described in this version of the documentation to support Siebel CRM releases
8.1.1.11 and 8.2.2.4.
What’s New in Siebel Developer’s Reference, Version 8.1, Rev. C and
Version 8.2, Rev. A
Table 2 describes changes described in this version of the documentation to support this release of
the software.
Table 1. New Product Features in Siebel Developer’s Reference, Version 8.1/8.2
Topic Description
“Capturing User Drilldown
Behavior” on page 173
New topic. Describes how to use business component user
properties to capture the user drilldown behavior.
“Functions You Can Use in a
Calculated Expression” on
page 448
Revised topic. If you do not specify the format argument of the
ToChar function, then this function returns a string that it
formats according to the current locale.
Table 2. New Product Features in Siebel Developer’s Reference, Version 8.1, Rev. C and Version
8.2, Rev. A
Topic Description
“Specifying Gantt Chart Behavior”
on page 78
Modified topic. The X-Num Tool Tips applet user property
specifies the number of tooltips that the applet contains.
“Specifying Post Invoke Methods”
on page 83
New topic. The PostInvokeMethod n user property sets a value
in some predefined applets.
“Allowing Users to Update Closed
Service Requests” on page 116
Modified topic. The number suffix you specify depends on the
number of instances of Always Enable Field that exist.
Searching a Multilingual List of
Values
Topic removed. This topic was moved to Configuring Siebel
Business Applications.
Defining the Search Specification
Property or the Sort Specification
Property
Topic removed. This topic was moved to Configuring Siebel
Business Applications.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
What’s New in This Release
■
18

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 19
2 Overview for Using This Book
This book describes reference information that you can use to configure Oracle’s Siebel CRM. It uses
the following terms:
■ A user is a person who uses the client of a Siebel Business Application to access Siebel CRM data.
■ The client is the client of a Siebel Business Application. Siebel Call Center is an example of a
Siebel Business Application.
■ The server is the Siebel Server, unless noted otherwise.
■ An administrator is anyone who uses an administrative screen in the client to configure Siebel
CRM. The Administration - Server Configuration screen is an example of an administrative
screen.
This book describes reference information. For information about how to configure Siebel CRM, see
Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
Computer font indicates a value you enter or text that Siebel CRM displays. For example:
This is computer font
Italic text indicates a variable value. For example, the
n
and the
method_name
in the following format
description are variables:
Named Method
n
:
method_name
The following is an example of this code:
Named Method 2: WriteRecord
A predefined object is an object that comes defined with Siebel CRM. The objects that Siebel Tools
displays in the Object List Editor immediately after you install Siebel Tools and the SRF (Siebel
Repository File) but before you make any customization are predefined objects.
The term focus indicates the currently active object in the client. To indicate the object that is in
focus, Siebel CRM typically sets the border of this object to a solid blue line.
Depending on the software configuration you purchase, your Siebel Business Application might not
include all the features that this book describes.
How This Book Describes Objects
For brevity, this book describes how an object, such as a user property, does something. For
example, this book states the following:
The Copy Contact user property copies contacts.
In reality, the Copy Contact user property only includes information that some other Siebel CRM
component uses to copy contacts.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Overview for Using This Book
■
20
For brevity, to describe how Siebel CRM uses the value that a property contains, this book typically
only describes the property name. For example, assume Siebel CRM displays the value that the
Display Name property contains. This is a property of a tree node object. This book only states the
following:
Siebel CRM displays the Display Name property of the tree node.
In reality, Siebel CRM displays the value that the Display Name property contains.
How This Book Describes Relationships Between Objects
An object definition includes properties and a property includes a value. For example, the Business
Object property of the Account Address view contains a value of Account. To describe this
relationship, this book states the following:
The Account Address view references the Account business object.
Sometimes the relationship between objects occurs through multiple objects. For brevity, this book
does not always describe the entire chain of relationships that exists between objects through the
entire Siebel object hierarchy. For example, because the Account business object references the
Account business component, and the Account Address view references the Account business object,
this book states the following:
The Account Address view references the Account business component.
Getting Help From Oracle
If you require help from Oracle for using object types, you can create a service request (SR) on My
Oracle Support. Alternatively, you can phone Global Customer Support directly to create a service
request or get a status update on your current SR. Support phone numbers are listed on My Oracle
Support. You can also contact your Oracle sales representative for Oracle Advanced Customer
Services to request assistance from Oracle's Application Expert Services.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 21
3 Applet Classes
This chapter describes applet classes. It includes the following topics:
■ Overview of Applet Classes on page 21
■ CSSSWEFrame Class on page 21
■ CSSSWEFrameBase Class on page 22
■ CSSSWEFrameList Classes on page 23
■ CSSSWEFrameListBase Class on page 23
■ CSSSWEFrameListFile Class on page 23
■ CSSSWEFrameListDocGen Class on page 23
■ CSSSWEFrameListWeb Class on page 24
■ CSSSWEFrameSalutation Class on page 24
■ CSSSWEFrameContactOrgChart Class on page 24
■ CSSSWEFrameListFINApplication Class on page 25
■ CSSSWEFrameUserRegistration Class on page 25
Overview of Applet Classes
An applet class is an object type that Siebel CRM uses to create an instance of a frame object. For
important caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28.
Using SWE Classes Starting with Siebel CRM Version 7.x
Starting with Siebel CRM version 7.x, the Siebel Web Engine converts all classes that include a
CSSFrame prefix in the class name to a counterpart class that includes a CSSSWEFrame prefix. For
example, Siebel CRM converts a call that calls a method in the CSSFrameBase class to a call that
calls the corresponding method in the CSSSWEFrameBase class. It does this conversion at run time.
The descriptions in this chapter use the SWE name for the class. These descriptions also apply to the
corresponding class that does not use SWE. For example, the description for the CSSSWEFrame class
also applies to the CSSFrame class.
CSSSWEFrame Class
The CSSSWEFrame class represents an applet that resides in the Siebel UI Frameworks. You can use
this class to call a generalized applet method.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Applet Classes
■ CSSSWEFrameBase Class
22
The CSSSWEBase class is the parent of this class.
The “Specifying the Method That the Enter Key Calls” on page 85 applet user property can reference
the CSSSWEFrame class.
The CSSSWEFrame class requires the CSSSWEFrameMgr class and the business component objects
that use the CSSSWEFrameMgr class.
The CSSSWEFrame class can reference the following methods:
■ ExecuteQuery. Runs the query. You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item
described in “Calling a Method” on page 30 except from an external interface.
■ NewQuery. Modifies the mode to query mode and starts a new query.
■ Other methods. Any method that Siebel CRM gets from a CSSSWEBase method.
You can specify each method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSSWEFrame class.
CSSSWEFrameBase Class
The CSSSWEFrameBase class provides functionality through applet user properties and call methods,
such as Aspect user properties and the GotoView method.
The FrameListBase classes provide the same support as their FrameBase counterparts. The following
descriptions also apply to the CSSFrameListBase class and the CSSSWEFrameListBase class.
Siebel CRM uses the CSSSWEFrameBase class for basic frame support. It uses applet user properties
and methods that are common to many Siebel Business Applications.
The CSSSWEFrame class is the parent of this class.
The following topics describe applet user properties that can reference the CSSSWEFrameBase class:
■ Using Aspects to Control Read Only, Insert, and Other Behavior on page 168
■ Specifying the Method That the Enter Key Calls on page 85
The CSSSWEFrameBase class can reference the following methods:
■ GotoPage. Displays a Web page. The Page user property must specify the Web page. For more
information, see “Specifying the Goto Web Page” on page 88.
■ GotoUrl. Displays a URL. The Url user property must specify the URL. For more information, see
“Specifying the Goto URL” on page 88.
■ GotoView. Displays a view. The View user property must specify the view. For more information,
see “Specifying the Goto View” on page 88.
You can specify each method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSSWEFrameBase class. You can configure Siebel CRM to call each of these methods only
through a named method.

Applet Classes ■ CSSSWEFrameList Classes
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 23
CSSSWEFrameList Classes
The CSSSWEFrameList class:
■ Represents a list applet in the Siebel UI Frameworks. You can use it to call a method that is
specific to an applet.
■ Requires a list object.
■ Can reference any method that Siebel CRM gets from the methods described in “CSSSWEFrame
Class” on page 21.
The CSSSWEFrame class is the parent of the CSSSWEFrameList class.
CSSSWEFrameListBase Class
Siebel CRM uses the CSSSWEFrameListBase class for basic frame support in a list applet. The
FrameListBase classes provides the same support as their FrameBase counterparts. For more
information about these classes, see “CSSSWEFrameBase Class” on page 22.
CSSSWEFrameListFile Class
Siebel CRM uses the CSSSWEFrameListFile class for file attachment frames in Siebel UI Frameworks.
You can use it to call file attachment methods.
The CSSSWEFrameList class is the parent of the CSSSWEFrameListFile class.
The business component that provides data to the file attachment frame must reference the
CSSBCFile class.
CSSSWEFrameListDocGen Class
The CSSSWEFrameListDocGen class supports proposal and presentation features. It does the
following work:
■ Sets the document context. For example, opportunity proposal, account proposal, and so on.
■ Sets the context. For example, Microsoft Word or Microsoft PowerPoint.
■ To create proposals, it submits requests to the Document Server server component.
The following classes are specialized subclasses of the CSSSWEFrameListDocGen class:
■ CSSFrameListProposal and CSSSWEFrameListProposal. Sets the type of document as a
proposal. Supports proposal applets that create Microsoft Word documents.
■ CSSFrameListPresentation and CSSSWEFrameListPresentation. Sets the type of
document as a presentation. Supports presentation applets that create Microsoft PowerPoint
documents.
These subclasses get all other functionality from the CSSSWEFrameListDocGen class. For important
caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Applet Classes
■ CSSSWEFrameListWeb Class
24
The CSSSWEFrameList class is the parent of this class.
The following topics describe applet user properties that can reference the CSSSWEFrameListDocGen
class:
■ Specifying the Application That Creates Proposals on page 83
■ Specifying the Parent Business Component on page 86
■ Specifying the Default Applet Focus on page 100
■ Removing Duplicate Records From Queries on page 122
CSSSWEFrameListWeb Class
The CSSSWEFrameListWeb class is a specialized frame class that Siebel CRM uses for ERM (Employee
Relationship Management), ePortal, and eBriefing applications. The Compensation Planning and
Group New modules in ERM use this class. It supports hiding an applet with no data, field visibility
control, and other support for ERM applications.
You can use this class only in a Siebel application that uses ERM. If you must use a modified version
of the CSSSWEFrameListWeb class, then you must create a new class that references the
CSSSWEFrameListWeb class. You must not make modifications directly to the CSSSWEFrameListWeb
class.
The CSSSWEFrameList class is the parent of the CSSSWEFrameListWeb class.
The applet user property described in “Hiding Applets That Contain No Data” on page 77 can reference
the CSSSWEFrameListWeb class.
For important caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28.
CSSSWEFrameSalutation Class
The CSSSWEFrameSalutation class supports the salutation frame. You can use it to display a
salutation, typically in the home page. It contains a control named Explorer that it uses to display
data. The frame removes the field values from the Result Text column and displays them together
when it displays the Explorer control.
The CSSSWEFrame class is the parent of the CSSSWEFrameSalutation class.
The CSSSWEFrameSalutation class can reference any method that Siebel CRM gets from the methods
described in “CSSSWEFrame Class” on page 21.
CSSSWEFrameContactOrgChart Class
CSSSWEFrameContactOrgChart supports the Contact Organization Chart frame and applet.
The CSSSWEFrame class is the parent of the CSSSWEFrameContactOrgChart class.

Applet Classes ■ CSSSWEFrameListFINApplication Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 25
The following topics describe applet user properties that can reference the
CSSSWEFrameContactOrgChart class:
■ Specifying Relationships in Organization Charts on page 83
■ Specifying Gantt Chart Behavior on page 78
■ Specifying Political Influence in Organization Charts on page 82
CSSSWEFrameListFINApplication Class
The CSSSWEFrameListFINApplication class provides specialized support in applets that Siebel CRM
uses for personal or business transactions, such as applying for credit or opening an account.
You can use this class only with an applet that references the Opportunity business component. This
class sets the Application Flag field to TRUE.
The CSSSWEFrameListBase class is the parent of this class.
The applet user property described in “Disabling Methods for FINS Applets in Query Mode” on page 75
can reference the CSSSWEFrameListFINApplication class.
For important caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28.
CSSSWEFrameUserRegistration Class
The CSSSWEFrameUserRegistration class supports required fields in applets in the User Registration
module. In some situations, it might be necessary to get information from a user that a business
component record does not require. You can use this class to enforce this kind of requirement.
The CSSSWEFrame class is the parent of the CSSSWEFrameUserRegistration class.
The applet user property described in “Disallowing Users to Pick Dates in the Forecast Date Dialog Box”
on page 116 can reference the CSSSWEFrameUserRegistration class.
You can use the CSSSWEFrameUserRegistration class only with the User Registration module. This
class assumes that the business component that provides data in this situation references the
CSSBCUser class. For example, the User Registration business component.
If your configuration uses the Show Required user property, then the corresponding business
component must reference the CSSBCUser class. The control that this user property specifies must
reside in the applet. If it does not, then the user cannot enter a value for the required control.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Applet Classes
■ CSSSWEFrameUserRegistration Class
26

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 27
4 Business Component Classes
This chapter describes business component classes. It includes the following topics:
■ Overview of Business Component Classes on page 28
■ CSSBusComp Class on page 30
■ CSSBCBase Class on page 30
■ CSSBCAccountSIS Class on page 35
■ CSSBCActivity Class on page 36
■ CSSBCActivityPlan Class on page 42
■ CSSBCContactSIS Class on page 43
■ CSSBCFile Class on page 44
■ CSSBCFINOppty Class on page 48
■ CSSBCFINSActivity Class on page 49
■ CSSBCForecast Class on page 49
■ CSSBCForecastBase Class on page 53
■ CSSBCForecastItem Class on page 54
■ CSSBCForecastItemDetail Class on page 54
■ CSSBCFundReq Class on page 55
■ CSSBCOppty Class on page 56
■ CSSBCOrderMgmtQuoteItem Class on page 56
■ CSSBCPharmaSpecializedAct Class on page 57
■ CSSBCPosition Class on page 57
■ CSSBCProposal Class on page 58
■ CSSBCServiceRequest Class on page 58
■ CSSBCTaskTransient Class on page 59
■ CSSBCTaskTransientBase Class on page 60
■ CSSBCUser Class on page 60

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ Overview of Business Component Classes
28
Overview of Business Component
Classes
This topic describes an overview of business component classes. It includes the following topics:
■ Generalized and Specialized Business Component Classes on page 28
■ Guidelines for Using Methods in Business Component Classes on page 29
■ Calling a Method on page 30
Generalized and Specialized Business Component
Classes
This topic describes generalized and specialized business component classes.
Generalized Business Component Classes
The following classes are generalized business component classes:
■ CSSBusComp Class on page 30
■ CSSBCBase Class on page 30
Using Specialized Classes
A specialized business component class is a type of class that Siebel CRM creates from a generalized
business component class.
A specialized applet class is a type of class that Siebel CRM creates from a generalized applet class.
It is recommended that you use a specialized class only if necessary. It is recommended that you do
not use a specialized business component class with a typical business component or applet. These
specialized classes often use functionality that references other objects, such as fields, other
business components, applets, or other classes. You must not configure Siebel CRM in such a way
that it modifies the values that these objects contain.
CAUTION: Using a specialized business component class or applet class improperly might cause an
unpredictable problem that can be difficult to fix. For example, Siebel CRM might add or delete a
child record, or modify an associate record. A run-time error might occur. It is recommended that
you configure the class property with extreme care and thoroughly test any modification you make.
Oracle only supports methods that Siebel Object Interfaces Reference describes for use in scripting.
Modifying method logic before or after Siebel CRM calls this method can cause unpredictable
behavior.
The following classes are specialized business component classes:
■ CSSBCAccountSIS Class on page 35
■ CSSBCActivity Class on page 36

Business Component Classes ■ Overview of Business Component Classes
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 29
■ CSSBCActivityPlan Class on page 42
■ CSSBCContactSIS Class on page 43
■ CSSBCFile Class on page 44
■ CSSBCFINOppty Class on page 48
■ CSSBCFINSActivity Class on page 49
■ CSSBCForecast Class on page 49
■ CSSBCForecastBase Class on page 53
■ CSSBCForecastItem Class on page 54
■ CSSBCForecastItemDetail Class on page 54
■ CSSBCOppty Class on page 56
■ CSSBCOrderMgmtQuoteItem Class on page 56
■ CSSBCPharmaSpecializedAct Class on page 57
■ CSSBCPosition Class on page 57
■ CSSBCProposal Class on page 58
■ CSSBCServiceRequest Class on page 58
■ CSSBCTaskTransient Class on page 59
■ CSSBCTaskTransientBase Class on page 60
■ CSSBCUser Class on page 60
Guidelines for Using Methods in Business Component
Classes
If you configure a method that Siebel CRM can access in a business component class, then it is
recommended that you use the following guidelines:
■ You can use a method in a script only if the Siebel Object Interfaces Reference describes the
method.
■ If Siebel Object Interfaces Reference does not specifically state that Siebel CRM can call a
method directly, then you must not assume that you can use only the method name and
arguments to call a method.
■ You typically configure Siebel CRM to use the InvokeMethod method to call a method.
■ The format for the InvokeMethod method varies depending on the scripting language that you
use. This book does not describe these specific formats.
■ Siebel Developer’s Reference lists method input arguments in the order that Siebel CRM must
use them in the call, independent of the scripting language that you use.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBusComp Class
30
■ If a custom button or command references a method, then you typically use InvokeMethod to
call this method. This is true if you use a predefined script or custom script. For more information
about the InvokeMethod method, see Siebel Object Interfaces Reference and Configuring Siebel
Business Applications.
■ Intercepting a method or modifying method behavior before or after Siebel CRM calls it can result
in unpredictable behavior.
■ Unless noted otherwise, method arguments use string values.
Calling a Method
You can configure Siebel CRM to use the InvokeMethod method to call most of the methods that this
book describes. In many situations you can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from one of the
following items:
■ Server script
■ Browser script
■ Custom button
■ Custom command
■ External interface
CSSBusComp Class
The CSSBusComp class is a base class. Siebel CRM gets other business component classes from this
CSSBusComp class. It provides functionality through business component user properties and an
object interface that you can use to meet typical configuration requirements.
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference business
component classes that Siebel CRM creates from the CSSBusComp class:
■ Overriding Sort Specifications on Business Components on page 123
■ Specifying the DB2 Optimization Level for SQL Statements on page 172
CSSBCBase Class
This topic describes the CSSBCBase class. It includes the following topics:
■ User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCBase Class on page 31
■ Methods That the CSSBCBase Class Can Reference on page 31
The CSSBCBase class is a base class. Siebel CRM creates other business component classes from this
CSSBCBase class. It provides functionality through business component user properties and invoke
methods, such as the On Field Update Invoke user property or the Sequence method.
The "CSSBusComp Class" on page 30 class is the parent of this class.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCBase Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 31
User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCBase
Class
The following topics describe user properties that can reference business component classes that
Siebel CRM creates from the CSSBCBase class:
■ Using Aspects to Control Read Only, Insert, and Other Behavior on page 168
■ Specifying the DB2 Optimization Level for SQL Statements on page 172
■ Using Deep Copy to Copy Records in Child Business Components on page 150
■ Using Deep Delete to Delete Records in Child Business Components on page 151
■ Extending Quote Quantities on page 118
■ Calling Methods from Applets on page 72
■ Calling Methods When Siebel CRM Updates Fields on page 142
■ Updating Fields When Siebel CRM Updates Other Fields on page 141
■ Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records on page 135
■ Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records According to Maximum Values on page 135
■ Specifying State Models on page 120
The following topics describe field user properties that can reference business component classes
that Siebel CRM creates from the CSSBCBase class:
■ Aspect Default Value: Aspect (Using Aspects to Control Read Only, Insert, and Other Behavior on
page 168)
■ Enabling Encryption on a Field on page 92
■ Specifying the Field That Contains the Encryption Key on page 92
■ Setting an Encrypted Field to Read Only if Encryption Fails on page 92
■ Specifying the RC2 or AES Encryption Service on page 92
■ Masking Credit Card, Account, and Other Secure Data on page 93
■ Making a Field Required on page 90
Methods That the CSSBCBase Class Can Reference
This topic describes the methods that the CSSBCBase class can reference. It includes the following
topics:
■ Evaluate Boolean Expression Method on page 32
■ Evaluate Expression Method on page 32
■ Is Active Method on page 32
■ Refresh Business Component Method on page 32

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCBase Class
32
■ Refresh Record Method on page 33
■ Revise Method on page 33
■ Sequence Method on page 34
■ Set Aspect Method on page 34
You can specify each method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSBCBase class.
Evaluate Boolean Expression Method
The EvalBoolExpr method evaluates a conditional Siebel expression against the current row. It
returns one of the following values in the result parameter:
■ Y. The expression is true.
■ N. The expression is not true.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call the EvalBoolExpr method from each item described in "Calling
a Method" on page 30 except from a custom button or command.
Table 3 describes the method argument that you can use with the EvalBoolExpr method.
Evaluate Expression Method
The EvalExpr method evaluates a Siebel expression against the current row and returns the value in
the result parameter. You can configure Siebel CRM to call the EvalExpr method from each item
described in "Calling a Method" on page 30 except from a custom button or command.
Is Active Method
The IsActive method reads the Active field value to determine if the row is active. It returns Y or N.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call the IsActive method from each item described in "Calling a
Method" on page 30 except from a custom command.
Refresh Business Component Method
The RefreshBusComp method runs the current query for the business component and places the
focus back on the record that Siebel CRM previously highlighted. It refreshes the data but highlights
the same record and places the cursor in the same position it occupied in the list applet before Siebel
CRM called the RefreshBusComp method. For more information about the IsActive method, see the
topic about InvokeMethod methods for business components in Siebel Object Interfaces Reference.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call the IsActive method from each item described in "Calling a
Method" on page 30 except from a custom command.
Table 3. Arguments That You Can Use with the EvalBoolExpr Method
Argument Description
expr_string Specifies the conditional expression that Siebel CRM evaluates.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCBase Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 33
Refresh Record Method
The RefreshRecord method refreshes the currently highlighted record. It updates the business
component fields in the client and positions the cursor in the context record. For more information
about this method, see the topic about InvokeMethod methods for business components object in
Siebel Object Interfaces Reference.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call the RefreshRecord method from each item described in "Calling
a Method" on page 30 except from a custom command.
Revise Method
The Revise method creates a new revision of the current record. Siebel CRM uses it to revise quotes,
orders, and agreement records. This method is similar to BusComp_CopyRecord except the Revise
method does the following work:
■ If the Active Field user property is defined, then it sets the current record to inactive.
■ If the Locked Field and Locked By Field user properties are defined, then it locks the current
record.
■ Increments the revision number of the new record. The Revision Field user property specifies the
field that contains the revision number.
■ Copies values that exist in fields of the current record to the new record. The Revision Copy Field
user property specifies the field that contains the new values.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call the Revise method from each item described in "Calling a
Method" on page 30 except from a custom command.
For information about the BusComp_CopyRecord event, see Siebel Object Interfaces Reference.
For more information, see the following topics:
■ Viewing a Business Component User Property on page 108
■ Creating Numbered Revisions of Quotes, Orders, or Agreements on page 117
■ Creating Numbered Revisions of Quotes, Orders, or Agreements on page 117
Viewing an Example That Uses the Revise Method
This topic describes how to view an example that uses the revise method.
To view an example that uses the Revise method
1
In the client, navigate to the Agreements screen, and then the Agreements List view.
2 Examine the My Agreements list that Siebel CRM displays.
This list references the Agreement List Applet No Parent applet. The Revise command in the drop-
down menu references the Revise method. If you choose a record, and then click Revise, then
Siebel CRM does the following:
■ Creates a new record that duplicates the chosen record.
■ Increments the Revision field by 1.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCBase Class
34
Sequence Method
The Sequence method recreates the sequence numbers for the records in the current business
component. It does this only if sequencing is enabled for this business component. Siebel CRM sets
the starting value depending on which of the following situations is true:
■ A field in a business component includes a sequenced field. For example, the FS
Agreement Item business component includes the Line Number field. The Sequence Field user
property specifies this Line Number field as the sequence field. The following business component
is the corresponding business component:
FS Agreement Item.Line Number (Sequence)
The Predefault Value property of the sequence field defines the starting value for the sequence.
This value is typically not 1.
■ A predefault value is not set for the sequence. Siebel CRM defaults the starting value for
the sequence to 1.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call the Sequence method from each item described in "Calling a
Method" on page 30.
For more information about creating a sequence field, see Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
For more information, see the following topics:
■ Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records on page 135
■ Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records According to Maximum Values on page 135
Set Aspect Method
The SetAspect method sets and overrides the default aspect of the current business component. The
applet code or script method calls the SetAspect method to override the business component aspect
with the applet aspect. You can configure Siebel CRM to call the SetAspect method only from a server
script or a browser script.
Table 4 describes the arguments that you can use with the SetAspect method. For more information,
see "Using Aspects to Control Read Only, Insert, and Other Behavior" on page 168.
Table 4. Arguments That You Can Use with the SetAspect Method
Argument Description
aspect Specifies the name of the aspect that Siebel CRM sets as the aspect.
reset_bool Optional. You can use one of the following values:
■ Y. Reset the business component aspect to the default aspect.
■ N or no value. Set the aspect to the value that the aspect argument specifies.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCAccountSIS Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 35
CSSBCAccountSIS Class
This topic describes the CSSBCAccountSIS class. It includes the following topics:
■ Dependencies and Limitations for the CSSBCAccountSIS Class on page 35
■ Business Component User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCAccountSIS Class on page 35
The CSSBCAccountSIS class supports accounts. It does the following:
■ Resides in the hierarchy of classes that constitute the account module in Siebel Industry
Applications.
■ Manages the account hierarchy through the account life cycle.
■ Manages the hierarchical relationships that exist between accounts if Siebel CRM modifies an
element in the hierarchy. For example, if Siebel CRM deletes a parent account or sets this parent
account as the child of another parent, then the CSSBCAccountSIS class maintains the correct
relationships between accounts. For example, it makes sure that it relates a child account to the
correct parent and grandparent.
■ Contains functionality that Siebel Life Sciences uses to schedule account calls according to the
most desirable call times that Siebel CRM sets for this account.
For more information about the methods that the CSSBCAccountSIS class can reference, see
"Methods That the CSSBCBase Class Can Reference" on page 31.
The "CSSBCBase Class" on page 30 is the parent of this class.
Dependencies and Limitations for the CSSBCAccountSIS
Class
The CSSBCAccountSIS class is a specialized class. It is recommended that you do not use it with a
typical business component. The Auto Schedule feature uses the names of controls in the Auto
Schedule pop-up applet that Siebel CRM predefines in the class. For more information, see "Using
Specialized Classes" on page 28.
You can use the CSSBCAccountSIS class only with an Account business component. The class
methods perform tasks that are specific to account data. They require a specific set of fields that
they use to evaluate the hierarchy.
Business Component User Properties That Can
Reference the CSSBCAccountSIS Class
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference the
CSSBCAccountSIS class. Siebel CRM requires each of these business component user properties:
■ Maintaining the Master Account in Account Hierarchies on page 110
■ Specifying the Master Account Field on page 110

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCActivity Class
36
■ Specifying the Field That Stores Parent Account IDs on page 110
■ Validating Parent Account IDs on page 109
CSSBCActivity Class
This topic describes the CSSBCActivity class. It includes the following topics:
■ Dependencies and Limitations for the CSSBCActivity Class on page 36
■ Business Component User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCActivity Class on page 39
■ Methods That the CSSBCActivity Class Can Reference on page 40
The CSSBCActivity class supports actions and business components that handle activities. It also
supplies data for Siebel Calendar, Siebel Scheduler, and Siebel Email Response. You can use business
component user properties to enable behaviors for CSSBCActivity.
The "CSSBCBase Class" on page 30 class is the parent of this class.
Dependencies and Limitations for the CSSBCActivity
Class
This topic describes dependencies and limitations for the CSSBCActivity class.
Fields That the CSSBCActivity Class Requires
Activities and the calendar require the following fields:
■ Display. Indicates where Siebel CRM displays this activity. It can include one of the following
values:
■ Calendar and Activity. Display in Calendar and Activity.
■ To Do and Activities. Display in To Do and Activity.
■ Activities Only. Display in Activity only.
■ Type. Indicates that this record is an activity.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCActivity Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 37
Table 5 describes the fields that the CSSBCActivity class requires.
Table 5. Fields That the CSSBCActivity Class Requires
Field Name Description
The following date fields are required:
■ Done
■ Due
■ Due Date
■ Exchange Date
■ No Sooner Than Date
■ Planned
■ Planned Completion
■ Repeating Expires
■ Started
For more information, see "Date Fields That the
CSSBCActivity Class Requires" on page 38.
Display This field indicates where Siebel CRM displays
the activity.
The following email fields are required:
■ Email Format
■ Email Body
These fields are required for email reply.
Orig Appt Id This field contains the Original Appointment Id.
Owned By This field is a multivalue group field that
controls visibility.
The following primary fields are required:
■ Primary Owned By
■ Primary Owner Id
These fields control visibility.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCActivity Class
38
Date Fields That the CSSBCActivity Class Requires
Activities and calendar items depend on date fields. An action class uses a predefined validation that
you cannot configure. It does this to make sure that the date that the Planned Completion field
contains occurs after the dates that the Planned fields contain. The Validation or Validation Message
properties of these fields does not specify this validation.
You can write a script that configures a custom message and more restrictive validation on these
fields. To capture updates to these fields and to return a custom message, you can use the
BusComp_PreSetFieldValue event for the message. Any other validation that you write in the
BusComp_PreSetFieldValue event for these fields must be different from or more restrictive than the
validation that the classes specify. You cannot use a script to override or make the validation less
restrictive. Siebel CRM runs the validation that the classes specify after the
BusComp_PreSetFieldValue event finishes running. For more information about these date fields, see
the topic about how Siebel CRM validates start and end dates in Configuring Siebel Business
Applications.
The following repeating fields are required:
■ Repeating Type
■ Repeating
These fields specify a repeating activity for the
calendar.
The following fields are required:
■ Alarm
■ Appt Alarm Time Min
■ Contact First Name
■ Contact Id
■ Description
■ Done Flag
■ Duration Hours
■ Duration Minutes
■ Percent Complete
■ Personal Postal Code
■ Previous Activity Id
■ Primary Attachment Id
■ Service Region
■ Status
Not applicable.
Table 5. Fields That the CSSBCActivity Class Requires
Field Name Description

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCActivity Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 39
How an Applet Class Determines Whether or Not the CSSBCActivity
Class Is Required
If the Class property of an applet contains one of the following values, then the CSSBCActivity class
is required:
■ CSSFrameAlarmList
■ CSSFrameAlarmSeeOtherList
■ CSSFrameCalGrid
■ CSSFrameCalRerouteBase
■ CSSFrameCECalAddModify
■ CSSFrameCEGridDay
■ CSSFrameCEGridMonth
■ CSSFrameCEGridWeek
■ CSSFrameCEMultPart
■ CSSFrameGanttActivity
■ CSSFrameGanttActivityBusyFree
■ CSSFrameListCommSrc
■ CSSFramePopupCalAppt
■ CSSFrameSRActivity
■ CSSSWECalToDoFrameList
■ CSSSWEFrameActHICalendar
■ CSSSWEFrameAlarmListSch
■ CSSSWEFrameGanttActivityFs
■ CSSSWEFrameGanttHiMode
■ CSSSWEFrameInMail
■ CSSSWEFrameInMailBody
Business Component User Properties That Can
Reference the CSSBCActivity Class
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference the
CSSBCActivity class:
■ Adding Contacts to the Action Business Component on page 117
■ Specifying the Manager That Sends Email on page 156
■ Restricting How Siebel CRM Displays Private Activities for Primaries on page 148

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCActivity Class
40
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference the
CSSBCActivity class. Each of these business component user properties is required:
■ Specifying the Status for In Progress Emails on page 155
■ Specifying the Status for Sent Emails on page 155
■ Specifying the Status for Unsent Outbound Emails on page 155
■ Specifying the Status for Rejected Emails on page 155
Methods That the CSSBCActivity Class Can Reference
This topic describes the methods that the CSSBCActivity class can reference. It includes the following
topics:
■ Clear Grid Begin End Date Method on page 40
■ Complete Activity Method on page 40
■ Is Primary In MVG Method on page 41
■ Set Employee Id Method on page 41
■ Set Grid Begin End Date Method on page 42
You can specify each method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSBCActivity class. These methods are mostly defined for coding purposes. Calling a method
directly requires analysis and testing.
Clear Grid Begin End Date Method
The ClearGridBeginEndDate method returns the business component to regular mode after the
SetGridBeginEndDate method sets it to calendar mode. For more information, see "Set Grid Begin
End Date Method" on page 42.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call the ClearGridBeginEndDate method from an applet, business
component, or business service. You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item
described in "Calling a Method" on page 30 except from a custom command or external interface.
Complete Activity Method
The CompleteActivity method saves the activity record and determines the costs associated with an
activity. It then updates the parts, time, and expense records of the activity with the costs of each
item according to the price list, rate list, and cost list.
Siebel CRM calls the Complete Activity business service when it saves an activity. This business
service calls the CompleteActivity method. It typically uses this method with the Action business
component. You can use it with other business components that reference the CSSBCActivity class.
If the applet is in query mode, then Siebel CRM cannot call this method.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCActivity Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 41
You can configure Siebel CRM to call the CompleteActivity method from an applet, business
component, or business service. You can configure Siebel CRM to call it from any item described in
"Calling a Method" on page 30 except from an external interface.
Is Primary In MVG Method
If the user is the primary in the multivalue group of a specified field, then the IsPrimaryInMVG
method returns a value of Y. You can use this method to determine whether or not Siebel CRM allows
the user to do operations that only the primary in the multivalue group can do. For example, only
the primary can modify the primary.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method only from a server script or browser script that
resides on an applet, business component, or business service.
Table 6 describes the arguments that you can use with the IsPrimaryInMvg method.
Set Employee Id Method
The SetEmployeeId method sets the criteria of the next SQL query that resides in the current activity
business component to the row ID and login that Siebel CRM provides as input arguments. This
configuration allows the user to view employee records in the calendar.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method only from a server script or browser script that
resides on an applet, business component, or business service.
Table 7 describes the arguments that you can use with the SetEmployeeId method.
Table 6. Arguments That You Can Use with the IsPrimaryInMvg Method
Argument Description
fieldname Specifies the name of the field that Siebel CRM examines.
Table 7. Arguments That You Can Use with the SetEmployeeId Method
Argument Description
emp_login_id Specifies the row ID of the employee. Siebel CRM returns the calendar records
for this employee.
emp_login_name Specifies the login of the employee. Siebel CRM returns the calendar records
for this employee.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCActivityPlan Class
42
Set Grid Begin End Date Method
The SetGridBeginEndDate method sets the business component to Calendar mode and sets the
beginning and ending dates for the grid.
Siebel CRM requires this method in a script that manipulates the business component in Calendar
mode, such as manipulating an instances of a recurring activity.
CAUTION: To avoid a performance problem, it is recommended that you set the date interval so that
Siebel CRM does not return a large number of records. For example, no more than 1000 records. You
typically set this interval to a month or a week.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method only from a server script or browser script that
resides on an applet, business component, or business service.
Table 8 describes the arguments that you can use with the SetGridBeginEndDate method. Each
argument uses the following format:
mm
/
dd
/
yyyy
You can use the "Clear Grid Begin End Date Method" on page 40 method to modify the mode that the
business component uses when it modifies the mode from Calendar mode to regular mode.
CSSBCActivityPlan Class
This topic describes the CSSBCActivityPlan class. It includes the following topics:
■ Dependencies and Limitations for the CSSBCActivity Class on page 36
■ Business Component User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCActivity Class on page 39
■ Methods That the CSSBCActivity Class Can Reference on page 40
The CSSBCActivityPlan class supports activity plans. It filters the template drop-down list in Activity
Plans views. If the user creates a new activity in one of these views, then Siebel CRM displays activity
templates in the template drop-down list. It only displays activity templates for the current context.
For example, the Activity Plans view in the Service screen only displays the activity templates for
service requests.
The CSSBCActivityPlan class is a specialized class. It is recommended that you do not use it with a
typical business component. For more information, see "Using Specialized Classes" on page 28.
Table 8. Arguments That You Can Use with the SetGridBeginEndDate Method
Argument Description
beginDate Specifies the beginning date for the grid in the time zone that the object manager
uses. Siebel CRM interprets the beginning time for this date as midnight at the
beginning of the day.
endDate Specifies the ending date for the grid. Siebel CRM interprets the ending time for this
date as midnight at the end of the day.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCContactSIS Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 43
The "CSSBusComp Class" on page 30 class is the parent of this class.
Business component user properties that Siebel CRM gets from "CSSBusComp Class" on page 30 can
reference the CSSBCActivityPlan class.
CSSBCContactSIS Class
This topic describes the CSSBCContactSIS class. It includes the following topics:
■ User Properties and Methods That You Can Use with the CSSBCContactSIS Class on page 43
The CSSBCContactSIS class supports contact functionality for the following applications:
■ Siebel Life Sciences. This class supports the following items:
■ Scheduling
■ Displaying all and affiliated contacts
■ Updating position and join fields and making them editable
■ Setting the Last Call date to the later of the call dates for all positions when Siebel CRM
merges contacts
■ Siebel Automotive. This class supports the following items:
■ Calling new correspondence from buttons instead of the application menu bar.
■ Reassigning contacts and any related opportunities and activities.
■ Creating opportunities and sales steps if Siebel CRM creates a new record. For Siebel Dealer
applications only.
This class uses the Pharma Professional Position business component. You must not configure Siebel
CRM to deactivate this business component or remove any fields from it.
The "CSSBCUser Class" on page 60 class is the parent of this class.
User Properties and Methods That You Can Use with the
CSSBCContactSIS Class
This topic describes user properties and methods that you can use with the CSSBCContactSIS class.
User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCContactSIS Class
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference the
CSSBCContactSIS class:
■ Specifying the Business Component for Reassignment in Siebel Automotive on page 161
■ Specifying Positions in Siebel Automotive on page 161
■ Reassigning Contacts in Siebel Automotive on page 161
■ Reassigning Opportunities in Siebel Automotive on page 161

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCFile Class
44
■ Enabling the Dispatch Board on page 170
■ Specifying Opportunity Business Components in Siebel Automotive on page 159
■ Specifying Position Join Fields for Siebel Life Sciences on page 162
The following topics describe field user properties that can reference the CSSBCContactSIS class:
■ Specifying the Field That Stores the Account Id of a Contact on page 95
■ Specifying the Field That Stores Parent Account IDs for Contacts on page 110
Methods That the CSSBCContactSIS Class Can Reference
The CSSBCContactSIS class can reference the following methods:
■ AffiliatedContacts. Display affiliated contacts.
■ AllContacts. Display all contacts.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call these methods from any item described in "Calling a Method" on
page 30 except from an external interface.
You can specify each method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSBCContactSIS class.
CSSBCFile Class
This topic describes the CSSBCFile class. It includes the following topics:
■ Dependencies and Limitations for the CSSBCFile Class on page 44
■ Methods That the CSSBCFileClass Can Reference on page 45
The CSSBCFile class supports file attachments and file replication. Siebel CRM uses it to transfer files
to and from the Siebel File System.
The "CSSBCBase Class" on page 30 class is the parent of this class.
Dependencies and Limitations for the CSSBCFile Class
Table 9 lists the fields that the CSSBCFile class requires. Prefix represents a unique prefix for the field
name. For more information, see "Specifying Field Name Prefixes for File Attachment Business
Components" on page 145.
Table 9. Fields That the CSSBCFile Class Requires
Field Name Value Type
PrefixDockStatus BOOL
PrefixFileAutoUpdFlg BOOL

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCFile Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 45
Methods That the CSSBCFileClass Can Reference
This topic describes the methods that the CSSBCFile class can reference. It includes the following
topics:
■ Create File Method on page 45
■ Get File Method on page 46
■ Put File Method on page 47
■ Update Src From Link Method on page 47
■ Methods That the CSSBCBase Class Can Reference on page 31
You can specify each method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSBCFile class.
Unless noted otherwise, each of these methods returns one of the following strings:
■ Success. The operation succeeded.
■ Error. The operation did not succeed.
Create File Method
The CreateFile method places a copy of an external file into the Siebel File System. It updates the
relevant fields in the business component so that Siebel CRM can attach it to the current record. You
can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item described in "Calling a Method" on page 30
except from a browser script.
PrefixFileDate UTCDATETIME
PrefixFileDeferFlg TEXT
PrefixFileDockReqFlg BOOL
PrefixFileExt TEXT
PrefixFileName TEXT
PrefixFileRev ID
PrefixFileSize NUMBER
PrefixFileSrcPath TEXT
PrefixFileSrcType TEXT
PrefixFileDockStatFlg BOOL
Table 9. Fields That the CSSBCFile Class Requires
Field Name Value Type

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCFile Class
46
Table 10 describes the arguments that you can use with the CreateFile method.
Delete File Method
The DeleteFile method deletes a file that resides in the Siebel File System or an external file. You can
configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item described in "Calling a Method" on page 30
except from a browser script or external interface.
Table 11 describes the arguments that you can use with the DeleteFile method.
Get File Method
The GetFile method copies a file that resides in the Siebel File System that is attached to the current
record into a temporary directory. It allows a user to view or edit a file attachment. It returns one
of the following strings:
■ Success, outFilePath. The operation succeeded. OutFilePath contains the path to the file that
Siebel CRM copied to the temporary directory.
■ Error. Siebel CRM did not copy the file to the temporary directory.
Table 10. Arguments That You Can Use with the Create File Method
Argument Description
srcFilePath Specifies the path to the source file.
keyFieldName Specifies the name of the PrefixFileName field that contains the name of the file
in the Siebel File System. For example, the AcctsFileName field contains the
name of the file for the Account Attachment business component.
keepLink If Y, then Siebel CRM stores the link to the external file.
altSrcFileName Optional. If the file name that Siebel CRM creates in the Siebel File System is
different from the name of the source file that it uses to copy the file, then it
uses the value that the altSrcFileName argument contains as an alternative
name for the source file name.
Table 11. Arguments That You Can Use with the Delete File Method
Argument Description
fileName Specifies the name of the file that Siebel CRM deletes, including the path to this file.
internal Optional. Specifies that the file is an internal file. An internal file is a file that resides
in the Siebel File System. You can use one of the following values:
■ True. The file is an internal file.
■ False. The file is not an internal file.
If you do not specify the internal argument, then Siebel CRM assumes that the file
is not an internal file.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCFile Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 47
■ OutOfDate. Siebel CRM did not copy the file to the temporary directory but this file is not the
most recent version of the file. The most recent version of the file is not available in the File
System.
The TmpDir parameter in the Siebel section of the .cfg file for the Siebel Business Application
specifies the temporary directory.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item described in "Calling a Method" on
page 30 except from a browser script.
Table 12 describes arguments that you can use with the GetFile method.
Put File Method
The PutFile method replaces a file in the Siebel File System that is attached to the current record
with a copy of a file in a directory. It updates the relevant business component fields. You can
configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item described in "Calling a Method" on page 30
except from a browser script.
Table 13 describes the arguments that you can use with the PutFile method.
Update Src From Link Method
The UpdateSrcFromLink method replaces a file that resides in the Siebel File System that is attached
to the current record. Siebel CRM replaces this file with an external file that is linked to the file that
it replaces. If something modifies this external file, then it updates the file attachment. It updates
the relevant business component fields. You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any
item described in "Calling a Method" on page 30 except from a browser script.
Table 12. Arguments That You Can Use with the Get File Method
Argument Description
keyFieldName Specifies the name of the PrefixFileName field that contains the name of the file
in the Siebel File System. For example, the AcctsFileName field contains the name
of the file for the Account Attachment business component.
Table 13. Arguments That You Can Use with the Put File Method
Argument Description
fileName Specifies the name of a file and the path to this file that Siebel CRM updates.
keyFieldName Specifies the name of the PrefixFileName field that contains the name of the file
in the Siebel File System. For example, the AcctsFileName field contains the name
of the file for the Account Attachment business component.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCFINOppty Class
48
Table 14 describes the arguments that you can use with the UpdateSrcFromLink method.
CSSBCFINOppty Class
This topic describes the CSSBCFINOppty class. It includes the following topics:
■ User Properties and Methods That You Can Use with the CSSBCFINOppty Class on page 48
The CSSBCFINOppty class supports opportunities. You can use it to implement a specialized
Opportunity business component that performs specialized behavior. For example:
■ Use a search specification in the business component so that the user can view all Opportunities
in the secure Admin view.
■ Use Secured Opportunities so that only an associated Sales Rep can view these opportunities.
The Siebel Automotive application uses the CSSBCFINOppty class to enable Send Letter (CTRL+L)
functionality directly from the business component.
The CSSBCFINOppty class requires the Name field that contains the name of the opportunity.
The "CSSBCOppty Class" on page 56 class is the parent of this class.
User Properties and Methods That You Can Use with the
CSSBCFINOppty Class
This topic describes user properties and methods that you can use with the CSSBCFINOppty class.
Business Component User Properties That Can Reference The
CSSBCFINOppty Class
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference the
CSSBCFINOppty class:
■ Specifying the Application Name on page 168
■ Specifying Business Components for the Opportunity Sales Step in Siebel Automotive on page 160
■ Specifying Business Components for the Sales Step Admin in Siebel Automotive on page 160
■ Specifying Business Objects for the Sales Step Admin in Siebel Automotive on page 160
■ Calculating Values When Writing Records on page 135
Table 14. Arguments That You Can Use with the Update Src From Link Method
Argument Description
keyFieldName Specifies the name of the PrefixFileName field that contains the name of the file
in the Siebel File System. For example, the AcctsFileName field contains the name
of the file for the Account Attachment business component.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCFINSActivity Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 49
■ Specifying How to Populate Opportunity Sales Steps in Siebel Automotive on page 160
■ Specifying Search Specifications for Nonsales Rep Views on page 129
■ Specifying Values for New Opportunities in Siebel Automotive on page 159
■ Specifying Values for Used Opportunities in Siebel Automotive on page 159
Methods That the CSSBCFINOppty Class Can Reference
The CSSBCFINOppty class can reference the SetSecureAdminView method. If called on a business
component, and if the current business component is in admin mode, then the SetSecureAdminView
method configures the business component to use the Secured Admin view mode. This configuration
removes the search specification from the business component. You can configure Siebel CRM to call
this method from any item described in "Calling a Method" on page 30 except from an external
interface.
You can specify this method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSBCFINOppty class.
CSSBCFINSActivity Class
The CSSBCFINSActivity class supports activities that reside in Siebel Financial Services applications.
Siebel CRM typically uses the Action business component to support activities. It is not typically
necessary to create another Activity business component that requires the CSSBCFINSActivity class.
Many dependencies exist on the field names, list of values, and user properties that this class uses.
The "CSSBCActivity Class" on page 36 class is the parent of this class.
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference the
CSSBCFINSActivity class:
■ Setting the Primary Sales Rep as the Owner on page 147
■ Setting the Current User as the Primary Contact on page 147
■ Updating the Synchronization Status for Activities on page 111
■ Specifying Activities to Synchronize for Siebel Handheld on page 161
■ Identifying Business Components That Siebel Financial Services Uses on page 165
For more information about the methods that the CSSBCFINSActivity class can reference, see
"Methods That the CSSBCActivity Class Can Reference" on page 40.
CSSBCForecast Class
This topic describes the CSSBCFINSActivity class. It includes the following topics:
■ Dependencies and Limitations for Forecast Classes on page 50
■ Business Component User Properties That Can Reference the CSSBCForecast Class on page 50
■ Methods That the CSSBCForecastClass Can Reference on page 51

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCForecast Class
50
The CSSBCForecast class supports forecasts. It can create, modify, display, or delete a forecast. It
can associate a forecast that a subordinate person creates with the forecasts that a manager owns.
It can roll up forecast numbers to the summary records and top-level forecasts. Analysis views, such
as the My Forecast Analysis view or the Subordinates View, allow the user to add or delete a
subordinate forecast from a manager forecast.
The SBCForecastBase class is the parent of this class.
The CSSBCForecast class is a specialized class. It is recommended that you do not use it with a
typical business component. For more information, see "Using Specialized Classes" on page 28.
Dependencies and Limitations for Forecast Classes
The business components whose names begin with Forecast 2000 depend on each other and depend
on revenue business components. If you modify one of these business components, then you must
also modify any dependent business components. For example:
■ If you modify the Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Item Detail business component, then you must
modify the Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Item Detail Flat business component.
■ Siebel CRM uses the Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Item DynCol business component to display the
Forecast Details spreadsheet. Each record that resides in the Forecast Item DynCol business
component corresponds to a row in the spreadsheet, and the child forecast details provide data
for the dynamic columns, such as dates. For more information about the dynamic column user
properties, see Siebel Forecasting Guide.
■ Siebel CRM uses the Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Item Detail Flat business component to join the
Forecast Item and Forecast Item Detail business components. It uses this join to create a flat
view. The Forecast Item business component typically stores the nonnumeric properties that the
child details can share. To support this configuration, you must add new fields and user properties
that reference this field to these business components.
■ If you add a field to a revenue business component, and if a forecast must include data from this
field, then you must add a corresponding field to a forecast business component and you must
add a column to the table that this forecast business component references.
Business Component User Properties That Can
Reference the CSSBCForecast Class
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference the
CSSBCForecast class:
■ Specifying Client Timeouts for Forecasts on page 114
■ Specifying Server Timeouts for Forecasts on page 114
■ Specifying Sleep Time Between Forecast Save Attempts on page 114
■ Specifying Search Specifications for Forecast Rollup on page 115
■ Specifying Search Specifications for Forecasts on page 114

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCForecast Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 51
■ Specifying Revenue Aggregation Fields on page 112
■ Disallowing Users to Pick Dates in the Forecast Date Dialog Box on page 116
The following topic describes a business component user property that can reference the
CSSBCForecast class. It is required:
■ Specifying Business Components for Forecast Analysis on page 115
Methods That the CSSBCForecastClass Can Reference
This topic describes the methods that the CSSBCForecast class can reference. It includes the
following topics:
■ Forecast Generate Method on page 51
■ Rollup Forecast Method on page 53
You can specify each method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSBCForecast class.
Forecast Generate Method
The ForecastGenerate method does the following:
■ Creates the detail and summary records for a Forecast 2000 – Forecast record.
■ Completes a forecast after Siebel CRM creates the record for the top level forecast header.
■ Queries for the correct revenue records, and then creates the detail records and summary
records for the forecast.
Siebel CRM calls the ForecastGenerate method when it saves a new forecast.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item described in "Calling a Method" on
page 30.
Configuring Siebel CRM to Create Forecasts Immediately
Siebel CRM can create detail and summary records in one of the following ways when it initially saves
a new forecast:
■ Immediately. The user must wait while Siebel CRM creates the forecast, by default. To enable
this behavior, the following system preference must be set to FALSE. This setting configures
Siebel CRM to not use the Forecast Service Manager server component:
Forecast: Use Server Task
■ In the background. The user can continue using Siebel CRM while it creates the forecast. To
enable this behavior:
■ The following system preference must be set to TRUE. This setting configures Siebel CRM to
use the Forecast Service Manager server component.
Forecast: Use Server Task

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCForecast Class
52
■ The Forecast Service Manager server component that resides in the Forecast Service
Management component group must be enabled. If it is disabled, then Siebel CRM does not
create detail or summary records and it only creates the top level forecast record.
If the WriteRecord method saves a new forecast header record, then Siebel CRM calls the
ForecastGenerate method to create the detail and summary records. To configure Siebel CRM to
create only the header record, you must write script outside of the WriteRecord method. This script
must use an InvokeMethod that calls the SetWriteRecordsWithGenerate method, and it must use an
input argument of N. If you use this configuration, then Siebel CRM does the following:
■ Does not call the ForecastGenerate method when it saves a new record for any subsequent new
forecast
■ Does not create any detail or summary records unless the script calls the ForecastGenerate
method at some later point
If your script uses an input argument of Y when it calls the SetWriteRecordsWithGenerate method,
then Siebel CRM calls the ForecastGenerate method when it saves any subsequent new forecast.
Not calling the ForecastGenerate method when Siebel CRM saves a forecast is different from allowing
the ForecastGenerate method to run in the background. If you are not required to enable or disable
ForecastGenerate for different forecast scenarios, then it is possible that you will not write script that
calls the SetWriteRecordsWithGenerate method.
Arguments That You Can Use with the Forecast Generate Method
Table 15 describes the arguments that you can use with the ForecastGenerate method.
Table 15. Arguments That You Can Use with the Forecast Generate Method
Argument Description
copyFcstId Specifies the Forecast Row Id of the previous forecast that exists in the same
series. If Siebel CRM copies a forecast to create a forecast from a previous
forecast, then it includes the modifications that it makes to the detail records
of the copied forecast. It includes these modifications in the new forecast. If
the New button references this method, then you must set the copyFcstId
argument to NULL.
bForce If Y, and if this forecast already exists, then Siebel CRM recreates the
forecast.
bAutoForecast If Y, and if a subordinate forecast exists, then Siebel CRM associates this
subordinate forecast with a manager forecast. You typically set this
argument to Y.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCForecastBase Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 53
Rollup Forecast Method
The RollupForecast method creates the summary records for a forecast according to the detail
records. Siebel CRM uses it to create the initial summary records when it creates a forecast. The
Rollup button or a menu item on a forecast applet references the RollupForecast method or the
RollupParentForecast method. Siebel CRM does not automatically update summary records. To
update summary records after Siebel CRM modifies detail records, it must call the RollupForecast
method through a control or programmatically. A current, active row must exist for the
RollupForecast method. This row must exist in the forecast business component that resides at the
top level. You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item described in "Calling a
Method" on page 30.
CSSBCForecastBase Class
This topic describes the CSSBCForecastBase class. It includes the following topics:
■ Methods That the CSSBCForecastBase Class Can Reference on page 54
The CSSBCForecastBase is a base class. You can use it only as a parent class. The "CSSBCForecast
Class" on page 49 is one example of a subclass of the CSSBCForecastBase class. You can use the
CSSBCForecastBase class to add or delete detail or summary records in a forecast.
The CSSBCAdjustable class is the parent of this class.
You must not configure Siebel CRM to create a business component that is an instance of the
CSSBCForecastBase class.
For more information, see "Dependencies and Limitations for Forecast Classes" on page 50.
bNeedRollup You can use one of the following values:
■ Y. Create summary records for the forecast. You typically set this
argument to Y.
■ N. D not create summary records for the forecast until the user manually
chooses Rollup.
bImplicitCreateFcst You can use one of the following values:
■ Y. Create any subordinate forecasts that are missing.
■ N. Disregard any subordinate forecasts that are missing.
If a subordinate forecast is missing, then Siebel CRM displays a dialog box
when it saves the new forecast. This dialog box asks the user if Siebel CRM
must create any subordinate forecasts that are missing.
Table 15. Arguments That You Can Use with the Forecast Generate Method
Argument Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCForecastItem Class
54
Methods That the CSSBCForecastBase Class Can
Reference
This CSSBCForecastBase class can reference the RollupParentForecast method. This method
determines the summary records that a forecast contains. If Siebel CRM modifies line item detail
records, then it does not automatically determine summary records. The RollupParentForecast
method does the same work as the "Rollup Forecast Method" on page 53 with the following difference:
■ Siebel CRM calls the RollupParentForecast method from a child business component that
references the CSSBCForecast class.
■ Siebel CRM calls the RollupForecast method directly from the business component that
references the CSSBCForecast class.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item described in "Calling a Method" on
page 30.
You can specify this method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSBCForecastBase class.
CSSBCForecastItem Class
The CSSBCForecastItem class stores the detail and summary records for a forecast. It stores data
that is relevant to a forecast, such as opportunity, account, and revenue class. Siebel CRM uses
records from one of the following classes:
■ CSSBCForecastItem. Determines each row a spreadsheet contains that resides in a
spreadsheet view.
■ CSSBCForecastItemDetail. Determines the columns that a spreadsheet contains. For more
information, see "CSSBCForecastItemDetail Class" on page 54.
You can only use the CSSBCForecastItem class to add or delete the detail and summary records that
a forecast contains.
The CSSBCAdjustable class is the parent of this class.
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference the
CSSBCForecastItem class:
■ Specifying Pop-up Revenues Lists on page 112
■ Specifying the Field That Siebel CRM Copies for New Revenue Forecasts on page 112
For more information, see "Dependencies and Limitations for Forecast Classes" on page 50.
CSSBCForecastItemDetail Class
This topic describes the CSSBCForecastItemDetail class. It includes the following topics:
■ Methods That the CSSBCForecastItemDetail Class Can Reference on page 55

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCFundReq Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 55
The CSSBCForecastItemDetail class stores the detail and summary records for forecasts. Siebel CRM
uses it with the "CSSBCForecastItem Class" on page 54. The CSSBCForecastItemDetail class stores
data that is relevant to some aspects of the records. For example, quantity, price, and revenue. Many
CSSBCForecastItemDetail records can exist for each CSSBCForecastItem record. Siebel CRM uses
records of the following type:
■ CSSBCForecastItem. Identifies each row of the spreadsheet that the spreadsheet view
displays.
■ CSSBCForecastItemDetail. Identifies each column of the spreadsheet that the spreadsheet
view displays.
You can use the CSSBCForecastItemDetail class to add or delete detail records or summary records
to or from a forecast. You must not use it for other reasons.
The CSSBCAdjustable class is the parent of this class.
The "Specifying the Field That Siebel CRM Copies for New Revenue Forecasts" on page 112 business
component user property can reference the CSSBCForecastItemDetail class.
For more information, see "Dependencies and Limitations for Forecast Classes" on page 50.
Methods That the CSSBCForecastItemDetail Class Can
Reference
The CSSBCForecastItemDetail class can reference the following methods:
■ AutoAdjust. Gets adjustments made to the previous forecast in the series and makes the same
adjustment to the current selection of records.
■ UpdateSelectionFromRevn. Updates a forecast detail record with data from the revenue
record that Siebel CRM associates with the forecast detail record.
■ UpdateSelectionToRevn. Updates the revenue record that Siebel CRM associates with the
forecast detail record with data from this forecast detail record.
Siebel CRM calls these methods for an individual forecast detail record. It can use each method in a
script that buttons and menu items reference from a forecast detail view. You can specify each
method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child of the
CSSBCForecastItemDetail class.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item described in "Calling a Method" on
page 30.
CSSBCFundReq Class
The CSSBCFundReq class supports fund requests. The Fund Request business component references
the CSSBCFundReq class. It includes code that uses the Outbound Communications Manager
business service that sends an email message.
If the following calculated fields in the Fund Request business component evaluate to Y according to
a status modification, then Siebel CRM uses code that sends the mail message:

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCOppty Class
56
■ Status Email Apr Rej
■ Status Email Submit
The Fund Request business component uses specialized code that creates the email message text.
An email template does not provide this text. You cannot configure this text.
The "CSSBCBase Class" on page 30 class is the parent of this class.
Business component user properties that Siebel CRM gets from "CSSBCBase Class" on page 30 can
reference the CSSBCFundReq class. This configuration is true except for the following user property
because of the specialized business component code that the CSSBCFundReq class uses:
Field Read Only Field:
fieldname
For more information, see "Making Fields Read-Only" on page 139.
For more information about the methods that the CSSBCFundReq class can reference, see "Methods
That the CSSBCBase Class Can Reference" on page 31.
CSSBCOppty Class
The CSSBCOppty class supports opportunities. You can use it to call specialized opportunity behavior,
such as estimating compensation.
The "CSSBCBase Class" on page 30 class is the parent of this class.
The business component user property described in "Allowing Only the Primary to Modify Sales
Methods for Opportunities" on page 147 can reference the CSSBCOppty class.
For more information about the methods that the CSSBCOppty class can reference, see "Methods
That the CSSBCBase Class Can Reference" on page 31.
CSSBCOrderMgmtQuoteItem Class
The CSSBCOrderMgmtQuoteItem class supports quote line items that order management uses. The
Quote Item business component references the CSSBCOrderMgmtQuoteItem class. It includes the
Product field that includes multiple drop-down lists, including Product. The drop-down list field for
Product is Name.
The CSSBCOrderMgmtQuoteItem class is a specialized class. It is recommended that you do not use
it with a typical business component. For more information, see "Using Specialized Classes" on
page 28.
For more information about quote line items and order management, see Siebel Order Management
Guide and Siebel eSales Administration Guide.
The CSSBCOrderMgmtPriceableItem class is the parent of this class.
CAUTION: The Product pick map must occur last in the sequence of pick maps to make sure the
pricing engine works correctly. The default sequence is 99.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCPharmaSpecializedAct Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 57
CSSBCPharmaSpecializedAct Class
The CSSBCPharmaSpecializedAct class supports call reporting in Siebel Life Sciences. This class does
following:
■ Creates records in the S_ACT_EMP table for attendee calls.
■ Determines time off according to business hours. Siebel CRM uses values that the User
Preferences contain to determine the working hours for a user. If these User Preferences do not
contain values, then Siebel CRM uses 9 AM to 5 PM.
■ Makes sure that Siebel CRM synchronizes the Start Date, End Date, Duration, Planned, and
Planned Completion fields. If the value in one of these fields is modified, then Siebel CRM
determines the value that the calendar displays for activities.
You can use the CSSBCPharmaSpecializedAct class only with the Pharma business components in
Siebel Life Sciences. Siebel CRM comes predefined with the business component names and field
names hard coded in the class methods.
The CSSBCSubmitBusComp class is a specialized class. It is recommended that you do not use it with
a typical business component. For more information, see "Using Specialized Classes" on page 28.
The CSSBCSubmitBusComp class is the parent of the CSSBCSubmitBusComp class.
The "Updating the Planned Field if the Start Date Field Is Modified" on page 143 business component
user property can reference the CSSBCPharmaSpecializedAct class.
CSSBCPosition Class
This topic describes the CSSBCPosition class. It includes the following topics:
■ Methods That the CSSBCPosition Class Can Reference on page 58
The CSSBCPosition class supports positions in organizations. Siebel CRM uses the specialized
business component code for positions in a transaction because it must update the position record
in the base table and the denormalized hierarchy table in a transaction. To support this feature,
Siebel CRM opens a dedicated database connection. You cannot prevent Siebel CRM from opening
this connection. Siebel CRM does not use the default database connection that it typically uses to
write records.
The specialized code resides in SqlWriteRecord method of the CSSBCPartyDenorm class.
Organizations, groups, and divisions use CSSBCPartyDenorm and use this specialized code.
The "CSSBusComp Class" on page 30 class is the parent of the CSSBCPosition class.
The CSSBCPosition class is a specialized class. It is recommended that you do not use it with a typical
business component. For more information, see "Using Specialized Classes" on page 28.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCProposal Class
58
Methods That the CSSBCPosition Class Can Reference
The CSSBCPosition class can reference the OnGenReportRelClicked method. This method rebuilds the
denormalized relationships that exist in the S_PARTY_RPT_REL table so that the hierarchical view
modes display the correct information. The OnGenReportRelClicked method removes all values from
the S_PARTY_RPT_REL table. This method then examines each record that resides in the S_PARTY
table so that it can recreate the denormalized hierarchical structure in the S_PARTY_RPT_REL table.
This work creates a large number of transactions for a Siebel Remote user and regional nodes. For
more information, see the topics about creating Siebel reporting relationships in Siebel Database
Upgrade Guide and Siebel Enterprise Integration Manager Administration Guide.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call the OnGenReportRelClicked method from any item described in
"Calling a Method" on page 30 except from an external interface.
You can specify this method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSBCPosition class.
CSSBCProposal Class
This topic describes the CSSBCPosition class. It includes the following topics:
■ Methods That the CSSBCProposal Class Can Reference on page 58
The CSSBCProposal class supports proposals and presentations. It creates and copies proposals. It
can create proposal content. It supports the Proposal Generation business service. The
CSSBCProposal class requires the following fields:
■ Name. Name of the Proposal record.
■ Template Name. Name of the Proposal template.
The "CSSBCFile Class" on page 44 class is the parent of this class.
Methods That the CSSBCProposal Class Can Reference
The CSSBCProposal class can reference the RequestAllFiles method. This method identifies proposals
and literature files that Siebel CRM downloads to a Mobile Web Client. It examines the entire content
structure of the current proposal, and then sets the File Dock Request Flag that resides in the
template file and in the literature files that the section components specify. Siebel CRM downloads
the proposal and literature files to the Mobile Web Client the next time the user synchronizes.
You can configure Siebel CRM to call this method from any item described in "Calling a Method" on
page 30 except from an external interface.
You can specify this method in the Method property of a class method. This class method is a child
of the CSSBCProposal class.
CSSBCServiceRequest Class
This topic describes the CSSBCServiceRequest class. It includes the following topics:

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCTaskTransient Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 59
■ Dependencies and Limitations on page 59
The CSSBCServiceRequest class supports service requests. It supports special functionality that
resides in the Service Request module that tracks service data, such as determining warranty
coverage and calculating commit time. A service request uses a lifecycle that begins with an Open
status and ends with a Closed status. The user updates this status. The state model can guide the
user in setting this status.
The "CSSBCBase Class" on page 30 class is the parent of this class.
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference the
CSSBCServiceRequest class:
■ Allowing Users to Update Closed Service Requests on page 116
■ Setting the Field Created Date to the Saved Date on page 143
For more information about the methods that the CSSBCServiceRequest class can reference, see
"Methods That the CSSBCBase Class Can Reference" on page 31.
Dependencies and Limitations
The Entitlement Verification and Commit Time business services depend on the fields and
functionality that the Service Request module provides. The CSSBCEntitlement class and the
CSSCommitTimeService class interact frequently with the CSSBCServiceRequest class.
Siebel CRM sets the contact as the recipient when it creates correspondence for a service request.
To support this configuration, the Primary Contact Address Id field must be active in the Service
Request business component.
The CSSBCServiceRequest class requires the Status field and Sub-Status field.
CSSBCTaskTransient Class
The CSSBCTaskTransient class supports transient data that Siebel CRM requires while a task UI
instance runs. It filters a single record for the current context in a task UI and current business
component. It runs a default query on the first Get or Set function, and then creates a new record
if the Execute method returns no rows.
The "CSSBCTaskTransientBase Class" on page 60 class is the parent of this class.
Siebel CRM uses the CSSBCTaskTransient class only to support a transient business component in a
task UI. You must not use it for any other purpose. To access this class, you must use only the
Transient BusComp new object wizard in Siebel Tools. For more information about transient business
components, see Siebel Business Process Framework: Task UI Guide.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCTaskTransientBase Class
60
CSSBCTaskTransientBase Class
The CSSBCTaskTransientBase class supports a transient business component. It is similar to the
CSSBCTaskTransient class except that it requires you to configure Siebel CRM to manage records.
Siebel CRM does not use the CSSBCTaskTransientBase directly in Siebel Tools. It uses the
CSSBCTaskTransient class. You must not use the CSSBCTaskTransientBase class for typical
configuration purposes. You can use it only to support a transient business component. For more
information, see "CSSBCTaskTransient Class" on page 59.
The "CSSBCBase Class" on page 30 class is the parent of this class.
CSSBCUser Class
This topic describes the CSSBCUser class. It includes the following topics:
■ Guidelines for Using the CSSBCUser Class on page 60
The CSSBCUser class supports users, employees, contacts, and personal contacts. It does the
following:
■ Creates and manages user records
■ Integrates external security adapters
■ Manages the Sync List for personal information manager (PIM) devices
■ Manages personal contact information
■ Manages other typical contact and employee tasks
The "CSSBCBase Class" on page 30 class is the parent of this class.
The following topics describe business component user properties that can reference the CSSBCUser
class:
■ Automatically Assigning Responsibilities to Users on page 118
■ Making Sure the Current Employee Holds a Position on page 119
For more information about the methods that the CSSBCUser class can reference, see "Methods That
the CSSBCBase Class Can Reference" on page 31.
Guidelines for Using the CSSBCUser Class
Siebel CRM uses the CSSBCUser class for business components that contain information about
people. These business components use the S_PARTY table as the base table and the S_CONTACT
table as the primary extension table. To enable this configuration, Siebel CRM sets the value of the
Inner Join Extension Table 1 business component user property to S_CONTACT.
The records in these business components are contacts that Siebel CRM displays in contact views,
including employees where sensitive data might exist. This situation is true except for personal
contacts.

Business Component Classes ■ CSSBCUser Class
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 61
The CSSBCUser class includes integrated support for external authentication systems, such as LDAP
(Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) or ADSI (Active Directory Services Interfaces). You must do
some customization to enable this configuration. After you enable external authentication, Siebel
CRM propagates the users and passwords that it creates to the external authentication systems when
it calls the WriteRecord method.
The CSSBCUser class requires the configurable constraint that the "Making Sure the Current Employee
Holds a Position" on page 119 topic describes. The business component configuration or the database
layer contains other required fields. The following required business component fields store
information about people:
■ First Name
■ Last Name
■ Person UId
If Siebel CRM enters a value in the Login field, then the CSSBCUser class allows it to modify this
value but not to leave the field empty.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component Classes
■ CSSBCUser Class
62

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 63
5 User Properties
This chapter describes user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ Overview of User Properties on page 63
■ Alphabetic List of User Properties on page 66
■ Application User Properties on page 69
■ Applet User Properties on page 71
■ Business Service User Properties on page 86
■ Control User Properties on page 87
■ Field User Properties on page 89
■ Integration Component User Properties on page 97
■ Integration Component Field User Properties on page 98
■ Integration Object User Properties on page 98
■ List Column User Properties on page 99
■ View User Properties on page 100
For information about business component user properties, see Chapter 6, “Business Component User
Properties”.
Overview of User Properties
This topic describes an overview of user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ How This Book Describes the User Property Format on page 64
■ Numbering Instances of a User Property on page 65
A user property is an object definition that Siebel CRM adds as a child to an applet, business
component, control, field, or list column. It configures specialized behavior that the properties of the
parent object cannot provide. The following object types include user properties:
■ Applet
■ Application
■ Assignment
■ Business Component
■ Business Service
■ Business Service Method Argument

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Overview of User Properties
64
■ Control
■ Field
■ Integration Component
■ Integration Component Field
■ Integration Object
■ List Column
■ View
■ Virtual Business Component
Oracle only supports user properties that this book describes. For information about a user property
that is specific to a Siebel Business Application, see the guide for this application. For example, for
a user property that is specific to Siebel Hospitality, see Siebel Hospitality Guide.
For important caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28.
How This Book Describes the User Property Format
You can enter a text string in the Value property to define the value of a user property. Unless noted
otherwise, this book describes the format that you must use in this user property. For example, to
define the value for the following Activity SearchSpec user property, you must use square brackets
to enclose every field name that you include in this search specification, and you must use quotes
and parentheses:
[Status]= LookupValue('EVENT_STATUS', 'Open') AND [Class] =
LookupValue('FS_ACTIVITY_CLASS', 'Sales Activity')
In the following example, to list multiple pairs of fields, you must enclose each pair in single quotes
and use a comma to separate each pair:
Parent: 'Contact.Id', 'Service Request.Contact Id', 'Service Agreement.Contact
Person Id'
Note the following example:
"[
FieldToCheck
]", "[
BusCompName
]", "[
MethodName
]", "[
Condition
]"
This example requires the following format:
■ Square brackets ([]) must enclose each parameter.
■ Double quotes (") must enclose each set of square brackets.
■ A comma and a space must separate each parameter.
Many user properties can contain a value of TRUE or FALSE. In most situations, if a user property
does not exist for an object, then Siebel CRM assumes a value of FALSE. For information about
locating an object, and then examining the user property list to determine if a user property exists
for an object, see “Viewing a Business Component User Property” on page 108.

User Properties ■ Overview of User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 65
Numbering Instances of a User Property
Siebel CRM can use some user properties on multiple instances of a single business component or
applet. If more than one instance of this user property exists, then Siebel CRM runs each instance
sequentially. It uses Name n, such as On Field Update Invoke 1, On Field Update Invoke 2, and so
on to identify multiple instances of a user property. In most situations, if the business component or
applet includes only one instance of the user property, then Siebel CRM does not require this number.
Example of Numbering Instances of a User Property
For example, the Asset Mgmt - Asset (Order Mgmt) business component includes the following user
properties:
On Field Update Invoke "Product Name", "Asset Mgmt - Asset", "CopyXA"
On Field Update Invoke 1 "Product Name", "Asset Mgmt - Asset", "GeneratePartNumber"
On Field Update Invoke 2 "Product Name", "Asset Mgmt - Asset", "SaveCxProd"
On Field Update Invoke 3 "Quantity", "Asset Mgmt - Asset", "SetExtendedQuantity"
If Siebel CRM updates the Product Name field in the Asset Mgmt - Asset (Order Mgmt) business
component, then it calls the following methods that the Asset Mgmt - Asset business component
uses:
■ CopyXA
■ GeneratePartNumber
■ SaveCxProd
If Siebel CRM updates the Quantity field in the Asset Mgmt - Asset (Order Mgmt) business
component, then it calls the SetExtendedQuantity method that resides in the Asset Mgmt - Asset
business component.
If you do not specify FieldToCheck, then Siebel CRM calls the CopyXA method in the Asset Mgmt -
Asset business component when the user saves the record. For example:
On Field Update Invoke "", "Asset Mgmt - Asset", "CopyXA"
Guidelines for Numbering Instances of a User Property
If you configure Siebel CRM to create multiple instances of a user property, then it is recommended
that you use the following guidelines:
■ Number each instance.
■ Use consecutive numbers. For example, use Deep Copy 8, and then Deep Copy 9.
■ Do not include a gap between a number that is greater than 9.
■ Do not append a number that includes more than two digits.
The following examples create unwanted results:
■ You use On Field Update Invoke 10 but no instances exist that use numbers less than 10.
■ You use Deep Copy 9 and Deep Copy 19 but no instances exist that are numbered sequentially
between 9 and 19.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Alphabetic List of User Properties
66
■ You use Named Method 100.
For more information, see How This Book Describes the User Property Format on page 64.
Alphabetic List of User Properties
Table 16 includes an alphabetic list of the user properties that this chapter describes. For a list of
business component user properties, see “Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties” on
page 101.
Table 16. Alphabetic List of User Properties
User Property Topic
Affiliated Account Id Field Specifying the Field That Stores the Account Id of a Contact on
page 95
ApplicationContextType Specifying the Application That Creates Proposals on page 83
AssocFieldName [Field Name] Specifying the Field Name for an MVG on page 98
Association Specifying Association Business Components on page 97
BAPIAdapterService Specifying the BAPI Adapter Service on page 86
BatchSize Specifying the Batch Size for SAP IDOCs on page 87
CanInvokeMethod: MethodName Enabling Methods for Applets on page 75
ClientBusinessServicen Calling Business Services from the Client on page 70
Contact Relationship Type Specifying Relationships in Organization Charts on page 83
DataSourceBuscompName Specifying the Parent Business Component on page 86
Default Applet Method Specifying the Method That the Enter Key Calls on page 85
DefaultAppletFocus Specifying the Default Applet Focus on page 100
DefaultFocus Specifying the Default Applet Focus on page 84
DefaultFocus_Edit Specifying the Default Applet Focus for Base, Edit, or Edit List
Mode on page 84
DefaultFocus_New Specifying the Default Applet Focus for New Mode on page 85
DefaultFocus_Query Specifying the Default Applet Focus for Query Mode on page 85
Disable Buscomp Hierarchy Disabling Hierarchies in List Applets on page 74
DisableNewRecord Disabling New Record Creation on page 75
DisableSearch Disabling Search on Text Fields or Unindexed Fields on page 89
DisableSort Disabling Sort on Business Component Fields on page 90
DisableSort Disabling Sort on List Columns on page 99

User Properties ■ Alphabetic List of User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 67
Display Mask Char Masking Credit Card, Account, and Other Secure Data on
page 93
DocumentContextType Specifying Template Values for Proposals on page 81
Drilldown Visibility Specifying Drilldown Visibility on page 82
EnableSIDataLossWarning Disabling Data Loss Warnings in Standard Interactivity on
page 74
EnableStandardMethods Enabling Record Manipulation in Field Service and Task Views on
page 76
Encrypt Key Field Specifying the Field That Contains the Encryption Key on
page 92
Encrypt ReadOnly Field Setting an Encrypted Field to Read Only if Encryption Fails on
page 92
Encrypt Service Name Specifying the RC2 or AES Encryption Service on page 92
Encrypt Source Field Specifying the Field That Contains Secure Data on page 93
Encrypted Enabling Encryption on a Field on page 92
FINS Query Mode Disabled Method
n
Disabling Methods for FINS Applets in Query Mode on page 75
ForceActive Forcing Controls to Be Active on page 87
ForceActive Forcing Fields That a List Column References to be Active on
page 100
High Interactivity Enabled Enabling High Interactivity for Applets on page 76
Logical Message Type Specifying the IDOC Message Type for SAP on page 99
Major Time Unit Specifying Gantt Chart Behavior on page 78
Minor Time Unit Specifying Gantt Chart Behavior on page 78
MVG Specifying MVG Business Components on page 97
Named Method n Calling Methods from Applets on page 72
NoDataHide Hiding Applets That Contain No Data on page 77
NoDelete Preventing Siebel EAI From Deleting Records on page 98
NoInsert Preventing Siebel EAI From Inserting Records on page 98
NoUpdate Preventing Siebel EAI From Updating Fields on page 98
OverrideViewCachen Disabling the View Cache on page 70
Page Specifying the Goto Web Page on page 88
Parent Id Field Specifying Field Names According to Parent Id on page 82
Table 16. Alphabetic List of User Properties
User Property Topic

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Alphabetic List of User Properties
68
PDQDisabledViewn Disabling Predefined Queries in Views on page 70
Political Analysis Field Specifying Political Influence in Organization Charts on page 82
PostInvokeMethod n Specifying Post Invoke Methods on page 83
PostMainViewData Saving Unsaved Data on page 87
Required Making a Field Required on page 90
Show Required n Making an Applet Control Required on page 77
SleepTime Specifying the Time Out Interval for Receive Requests on
page 87
SubCompCanUpdate Updating Assets on page 93
SubCompUpdate Cascading Asset Updates on page 94
Text Length Override Setting the Field Text Length on page 90
Url Specifying the Goto URL on page 88
Use Literals For Like Using Literals Instead of Bind Variables on page 96
UseExistsForSubQuery Specifying the SQL for EXISTS Search Specifications on page 95
View Specifying the Goto View on page 88
Visibility Type Specifying the Calendar Visibility Filter on page 84
WebGotoPlayerErrorPage Specifying the Error Web Page for SmartScript on page 85
WebGotoView Specifying the Finish or Cancel Web Page for SmartScript on
page 85
X-BC Specifying Gantt Chart Behavior on page 78
X-Color Field
X-Color LOV Name
X-Color Map
X-Date InvokeMethod
X-Display Constraint Map
X-Display Duration
X-DrillDown Field
X-End DateTime Field
X-Join Field
Table 16. Alphabetic List of User Properties
User Property Topic

User Properties ■ Application User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 69
Application User Properties
This topic describes application user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ Calling Business Services from the Client on page 70
■ Disabling Predefined Queries in Views on page 70
■ Disabling the View Cache on page 70
X-Join InvokeMethod Specifying Gantt Chart Behavior on page 78
X-LOV Map
X-Num Slots
X-Num Tool Tips
X-Sort Spec
X-Start DateTime Field
X-Tooltips 1
X-Tooltips 2
X-Tooltips n
Y-BC
Y-BC ViewSet Size
Y-Constraint
Y-DrillDown Field
Y-DrillDown View
Y-Join Field
Y-Label
Y-Legend
Y-SortSpec
Z-BC
Z-Date InvokeMethod
Z-End DateTime Field
Z-Join Field
Z-Join InvokeMethod
Z-Start DateTime Field
Table 16. Alphabetic List of User Properties
User Property Topic

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Application User Properties
70
Siebel CRM sets some of the parameters that it set in the application configuration (.cfg) file prior to
Siebel CRM version 8.0 differently. It now sets them as application user properties in Siebel Tools.
Calling Business Services from the Client
The ClientBusinessServicen user property calls a business service from a browser script. It must
specify the name of the business service that a browser script calls. This value uses the following
format:
ClientBusinessService
n
where:
■ n is a sequential number. If you skip a number, then Siebel CRM cannot call this service from a
browser script. For more information, see “Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
You can use this user property only with Siebel Browser Script.
If a browser script attempts to use this user property to call a business service that is not listed, then
an error that is similar to the following error might occur at runtime:
Cannot get service: <name of service>.(SBL-UIF-00275)
Starting with Siebel CRM version 8.0, you no longer set this user property in the application .cfg file.
You now set it as an application user property in Siebel Tools.
Disabling Predefined Queries in Views
The PDQDisabledViewn user property disables the Predefined Query (PDQ) dropdown list for a view.
The value for this user property must include the name of the view where you must disable the
Predefined Query (PDQ) dropdown list.
If you add this user property to a view, then Siebel CRM does not apply the PDQs in the dropdown
list when it loads this view. The user can still choose the PDQs in the dropdown list, and then Siebel
CRM applies these PDQs.
Starting with Siebel CRM version 8.0, you no longer set this user property in the application .cfg file.
You now set it as an application user property in Siebel Tools.
Disabling the View Cache
The OverrideViewCachen user property disables caching for a view. The value for this user property
must use the following format:
OverrideViewCache
n
where:
■ n is a sequential number between 0 and 99. For more information, see “Numbering Instances of
a User Property” on page 65.

User Properties ■ Applet User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 71
For example, to disable caching if Siebel CRM makes a dynamic modification to a view. For example,
if it modifies a parameter or calls a toggle applet. Starting with Siebel CRM version 8.0, you no longer
set this user property in the application .cfg file. You now set it as an application user property in
Siebel Tools.
To disable the view cache
1
Open Siebel Tools.
2 In the Object Explorer, click Application.
3 In the Applications list, query the Name property for the Siebel Business Application that contains
the view where you must disable the cache.
4 In the Object Explorer, click Application User Prop.
5 In the Application User Props list, create a new application user property using values from the
following table.
6 Compile and test your modifications.
Applet User Properties
This topic describes applet user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ Calling Methods from Applets on page 72
■ Disabling Data Loss Warnings in Standard Interactivity on page 74
■ Disabling Hierarchies in List Applets on page 74
■ Disabling Methods for FINS Applets in Query Mode on page 75
■ Disabling New Record Creation on page 75
■ Enabling Methods for Applets on page 75
■ Enabling High Interactivity for Applets on page 76
■ Enabling Record Manipulation in Field Service and Task Views on page 76
■ Hiding Applets That Contain No Data on page 77
■ Making an Applet Control Required on page 77
■ Specifying Gantt Chart Behavior on page 78
Property Value
Name OverrideViewCache0
You can use OverrideViewCache1, OverrideViewCache2, and so on to disable
the cache for more views.
Value The name of the view where you must disable the cache.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Applet User Properties
72
■ Specifying Template Values for Proposals on page 81
■ Specifying Drilldown Visibility on page 82
■ Specifying Field Names According to Parent Id on page 82
■ Specifying Political Influence in Organization Charts on page 82
■ Specifying Post Invoke Methods on page 83
■ Specifying Relationships in Organization Charts on page 83
■ Specifying the Application That Creates Proposals on page 83
■ Specifying the Calendar Visibility Filter on page 84
■ Specifying the Default Applet Focus on page 84
■ Specifying the Error Web Page for SmartScript on page 85
■ Specifying the Finish or Cancel Web Page for SmartScript on page 85
■ Specifying the Method That the Enter Key Calls on page 85
■ Specifying the Parent Business Component on page 86
Calling Methods from Applets
The Named Method n applet user property calls a business component or business service method,
or sets a field value. You can use it instead of scripting. The value for this user property must include
a value that depends on the following action that Siebel CRM must perform:
■ You can use the following format to set a field value:
"
Name
", "SET", "
Field
", "
Expression
"
If Siebel CRM calls
Name
, then it uses
Expression
to set the value of
Field
.
■ You can use the following format to call a business component method:
"
Name
", "
Action
", "
BusComp
", "
Method
"
If Siebel CRM calls
Name
, then it calls
Method
of the
BusComp
according to the
Action
. For a list
of actions, see Table 17 on page 74.
■ You can use the following format to call a business service method:
"
Name
", "
Action
", "
BusComp
", "
Service
", "
Method
"
If Siebel CRM calls
Name
, then it calls
Method
from the
Service
business service of the
BusComp
business component according to
Action
. For a list of actions, see “Actions That You Can Use with
the Named Method n User Property for Applets” on page 74.
It might be necessary for you to configure Siebel CRM to start an action in reply to a data
modification. For example, if Siebel CRM creates, deletes, or updates a record. You can configure
Siebel CRM to start the reply before or after it applies the date modification. You can use a user
property to create this automated reply without creating a custom script.

User Properties ■ Applet User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 73
You can use this applet user property with the following classes:
■ CSSFrameBase
■ CSSFrameListBase
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65 and “Calling Business Service Methods from
Business Components” on page 148.
Format You Must Use with the Named Method n Applet User Property
You must enclose each item that you include in the value of this user property in double quotation
marks. You must use a comma and a space to separate each item. If a value includes a hyphen or
parenthesis, then you must enclose this value in another set of single quotation marks or two more
sets of double quotation marks. For example, if Siebel CRM must send the O2 Repair - Create
Notification workflow process as a value for a parameter, then you use the following format:
"'O2 Repair - Create Notification'" or """O2 Repair - Create Notification"""
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
You can append more parameters to an expression. If you use a business service action, then Siebel
CRM sends this expression as a property set. You must use a name and value pair instead of an array
of strings. For example:
"
NameExpr
", "
ValueExpr
"
Calling Methods in a Specific Order
You can use the Named Method n applet user property to call methods in a specific order. For
example, you can use it to update a legacy system with new account records after Siebel CRM creates
a new account record. The following code saves the record in Siebel CRM, and then calls a workflow
process that updates the legacy system:
Named Method 2: WriteRecord
'INVOKE', 'WriteRecord', 'INVOKESVC', 'Workflow Process Manager', 'Run Process',
'"ProcessName"', '"Account - New Order"', '"RowId"','[Id]'

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Applet User Properties
74
Actions That You Can Use with the Named Method n User Property for
Applets
Table 17 describes the actions that you can use with the Named Method n user property.
Disabling Data Loss Warnings in Standard Interactivity
The EnableSIDataLossWarning configuration parameter determines whether or not Siebel CRM
displays a warning. It displays this warning if the user attempts to switch context without saving
modifications, and if the client is in standard interactivity (SI) mode. The value for this user property
must include one of the following values:
■ TRUE or no value. Do not display the warning.
■ FALSE or this user property does not exist. Display the warning.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or create a new instance of it.
Disabling Hierarchies in List Applets
The Disable Buscomp Hierarchy applet user property prevents Siebel CRM from displaying a
hierarchical relationship in a list applet. The value for this user property must include a Boolean
value. If TRUE, then Siebel CRM disables the business component hierarchy.
Siebel CRM uses a hierarchical list applet to display records that include a hierarchical relationship.
To display this hierarchy in the client, it uses icons in the first column of this list applet. You can set
the Hierarchy Parent Field property of the parent business component to use this hierarchy.
Table 17. Actions You Can Use with the Named Method n User Property
Action Description Method Type
INVOKE Calls the method. Business component
INVOKESEL Saves the state and calls the method one time for each
chosen record.
INVOKEALL Saves the state, requeries, and then calls the method
one time for each record.
INVOKESAVE Saves the state, requeries, and then calls the method.
INVOKESVC Calls the method. Business service
INVOKESVCSEL Saves the state and calls the method one time for each
chosen record.
INVOKESVCALL Saves the state, requeries, and then calls the method
one time for each record.
INVOKESVCSAVE Saves the state, requeries, and then calls the method.

User Properties ■ Applet User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 75
To disable this hierarchy, you can add this applet user property to the applet with the following
values:
■ Name. Disable Buscomp Hierarchy.
■ Value: TRUE.
Siebel CRM uses this applet user property on predefined list applets, such as Asset Mgmt - Asset List
Applet.
For more information, see the topic about specialized behavior that Web templates support in
Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
Disabling Methods for FINS Applets in Query Mode
The FINS Query Mode Disabled Method n applet user property disables a method if the applet is in
query mode. The value for this user property must include the name of a method.
You can use this applet user property with the CSSSWEFrameFINApplication class.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or create a new instance of it. You can
specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see “Numbering
Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
Disabling New Record Creation
The DisableNewRecord applet user property prevents Siebel CRM from calling NewRecord in the
current applet. The value for this user property must match the application name exactly.
If the application name is the same as the name of the Siebel Business Application that Siebel CRM
is currently running, then Siebel CRM disables NewRecord on this applet. For example, if the Siebel
Sales Enterprise application is currently running, then the following value disables NewRecord on this
applet for this application:
Siebel Sales Enterprise
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Enabling Methods for Applets
The CanInvokeMethod: MethodName applet user property enables or disable a method or a button.
It must include a value or an expression that returns one of the following values:
■ TRUE. Siebel CRM enables the method.
■ FALSE. Siebel CRM disables the method.
MethodName identifies the name of the method that this user property enables or disables.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Applet User Properties
76
For example, Siebel CRM uses the following values to disable the Copy Record method that resides
in the Partner Product List Applet:
■ Name. CanInvokeMethod: CopyRecord.
■ Value. FALSE.
The following example uses an expression for the value in the SIS Account List Applet. It enables the
copy record feature for accounts that include a status but disables it for all other accounts:
■ Name. CanInvokeMethod: CopyRecord.
■ Value. [Account Status] IS NOT NULL.
Siebel CRM disables the method that the button calls. You can do this declaratively at the applet
level. It is easier to use than scripting PreCanInvokeMethod.
Siebel CRM uses this user property in the CSSFrame class, CSSFrameList class, and the subclasses
of these classes.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, modify the value for it, or if an
instance of it is not already defined, then to create a new instance of it.
Enabling High Interactivity for Applets
The High Interactivity Enabled applet user property makes sure that Siebel CRM displays the applet
in high interactivity (HI) mode. A task view requires high interactivity mode. The value for this user
property must include one of the following values:
■ Y. Display the applet in high interactivity mode.
■ N. Display the applet in standard interactivity mode.
You can use this applet user property with the following classes:
■ CSSSWEFrameShuttleBaseAssoc
■ CSSSWEFrameShuttleBaseMvg
Enabling Record Manipulation in Field Service and Task
Views
The EnableStandardMethods applet user property enables record manipulation operations in a field
service or task view. The value for this user property must include one of the following values:
■ Y. Enable record manipulation operations.
■ N. Call this method only if the user does one of the following:
■ Right-clicks and opens an applet menu
■ Uses a shortcut

User Properties ■ Applet User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 77
If you specify the EnableStandardMethods user property on an applet, then the user can use this
applet to do record manipulation operations. For example, the user can run a query, advance the
record pointer, edit multiple records, and so on.
You can use this applet user property with the following classes:
■ CSSFrame
■ CSSFrameList
■ CSSSWEFrameShuttleBaseAssoc
■ CSSSWEFrameShuttleBaseMvg
Hiding Applets That Contain No Data
The NoDataHide applet user property hides the applet if it contains no data. The value for this user
property must include one of the following values:
■ Y. If the applet contains no data, then hide it.
■ N. If the applet contains no data, then do not hide it.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
Making an Applet Control Required
The Show Required n applet user property requires a control on an applet. Siebel CRM makes sure
that the field that this control references is required and resides on an applet. The value for this user
property must specify the name of an applet control.
If you specify this user property, then the business component that the applet references must use
the CSSBCUser class.
If the control that you specify does not reside in the applet, then the user cannot enter a value for
the required control. For example, if you create an applet user property named Show Required 1 with
a value of EmailAddress, then Siebel CRM requires the user to use the EmailAddress control in the
applet.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property. If more than one instance of this user
property exists, then Siebel CRM runs each instance sequentially. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Applet User Properties
78
Specifying Gantt Chart Behavior
Table 18 describes the applet user properties that Siebel CRM uses for the eGanttChart Busy Free
Time Applet. To view the values that you can use for each of these user properties, locate the
predefined eGanttChart Busy Free Time Applet in the Applets list in Siebel Tools, and then examine
the Value property in the Applet User Properties list.
Table 18. User Properties for the eGanttChart Busy Free Time Applet
Applet User Property Description
Major Time Unit Specifies the major time unit in the X-axis of the Gantt chart. You can
use one of the following values:
■ Day
■ Week
■ Month
■ Year
Minor Time Unit Specifies the minor time unit in the X-axis of the Gantt chart. You can
use one of the following values:
■ Hour
■ Day
■ Week
■ Month
You can use the following combinations of major and minor time units:
■ Day, Hour
■ Week, Day
■ Month, Day
■ Month, Week
■ Year, Month
X-BC Specifies the business component for the X-axis of the Gantt chart.
X-Color Field Specifies the cells of the Gantt chart that Siebel CRM can color
differently. This applet user property specifies the field in the X business
component that determines the coloring. For the field that you choose,
make sure a corresponding list of values exists. For more information,
see the description for the X-Color LOV Name applet user property.
X-Color LOV Name Specifies the list of values that defines the values of the field that you
choose for the X-Color Field applet user property. From this list of values,
you can specify the Language Independent Code (LIC) that Siebel CRM
uses for the field value.

User Properties ■ Applet User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 79
X-LOV Map Specifies the Language Independent Code of the list of values that Siebel
CRM can map to colors.
X-Color Map Specifies the colors of the different values of the Language Independent
Code. These values must use the same order that the values in the X-
LOV Map applet user property uses. For example, 2-High maps to
GanttChartBlue.
The values of the X-Color Map applet user property are the style sheet
classes that the Gantt.css defines.
X-Date InvokeMethod Specifies to map to an internal X-business component method that
determines the date-time range for the X-business component data. You
must not modify this applet user property.
X-Display Constraint
Map
Specifies the lower and upper bounds of the time that Siebel CRM
displays in the Gantt chart instead of displaying a 24-hour interval. It
applies only if the minor time unit is Hour.
X-Display Duration Specifies the number of minutes to increment each cell in the Gantt
chart.
X-DrillDown Field Specifies the field in the X business component that Siebel CRM uses as
the drill down field. A corresponding Drilldown Object must exist for the
applet in Siebel Tools.
X-End DateTime Field Specifies the field in the X business component that specifies the end of
the date and time range.
X-Join Field Specifies the field in the X business component that links it to the Y
business component. If you do not specify the X-Join InvokeMethod
applet user property, then Siebel CRM uses the value in the X-Join Field
applet user property in a search specification.
X-Join InvokeMethod Specifies how to map to an internal X business component method to link
the Y and X business components. You must not modify this applet user
property.
X-Num Slots Specifies the number of slots for a cell. For example, assume multiple
activities include the same start and end times. If X-Num Slots is 3, then
Siebel CRM splits the cell that contains the time range into a maximum
of three slots. These cells contain the conflicting activities.
Table 18. User Properties for the eGanttChart Busy Free Time Applet
Applet User Property Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Applet User Properties
80
X-Num Tool Tips Specifies the number of tooltips that the applet contains. For example,
assume that the following tooltip is the last tooltip that the applet
defines:
X-Tooltip 12
In this example, you set the value of the X-Num Tool Tips applet user
property to 12.
If the applet does not contain an X-Tooltip n applet user property, then
you set the value of the X-Num Tool Tips applet user property to 0 (zero).
X-Sort Spec Specifies the sort specification for the X business component.
X-Start DateTime Field Specifies the field in the X business component that contains the start
for the date and time range.
X-Tooltips 1 Specifies the First control that Siebel CRM displays in the tooltip.
X-Tooltips 2 Specifies the Second control that Siebel CRM displays in the tooltip.
X-Tooltips n You can define more applet user properties for more tooltip controls.
Y-BC Specifies the business component that Siebel CRM uses for the Y-axis of
the Gantt chart.
Y-BC ViewSet Size Specifies the maximum number of records that the Y-axis can include.
Y-Constraint Specifies the search specification for the Y business component in the
base Gantt chart. Siebel CRM does not include any value for this user
property, by default. If this user property does not include a value, then
it uses a link in a parent and child relationship to constrain the Y business
component.
Y-DrillDown Field Specifies the source field that Siebel CRM uses for the Y drilldown.
Y-DrillDown View Specifies the destination view of the Y drilldown. You can modify this
user property.
Y-Join Field Specifies the field in the Y business component that Siebel CRM uses to
link this field to the X and Z business components.
Y-Label Specifies the label for the Y-axis.
Y-Legend Specifies a field in the Y business component that Siebel CRM displays in
the Gantt chart.
Y-SortSpec Specifies the sort specification for the Y business component.
Table 18. User Properties for the eGanttChart Busy Free Time Applet
Applet User Property Description

User Properties ■ Applet User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 81
Specifying Template Values for Proposals
The DocumentContextType applet user property specifies the context of a proposal. The value for
this user property must include a string that defines a proposal template category. This value must
match exactly a value that the PROPOSAL_TEMPLATE_TYPE list of values contains.
If the value you specify matches a value in the PROPOSAL_TEMPLATE_TYPE list of values, then Siebel
CRM uses the templates that include the same category value in this applet. It displays these values
in the Template drop-down list. For example, the following value filters proposal templates so that
Siebel CRM displays only some proposal templates in the Template drop-down list in this applet in
the client:
Account Proposal
The Account Proposal that Siebel CRM defines for the Category field determines the templates that
Siebel CRM displays.
Z-BC Specifies the business component that determines the background that
Siebel CRM draws for the Z-axis of the Gantt chart. For example, assume
the working schedule of each employee is Monday through Friday, 8:00
AM to 5:00 PM. In this example, Siebel CRM uses a white background
where it displays the schedule and a gray background where it does not
display the schedule.
One of the following Z business components determines the display:
■ GanttStateNone. No schedule.
■ GanttStateOff. A schedule exists.
■ GanttStateOn. Color of the cell that the X-Color Map controls.
Z-Date InvokeMethod Specifies how to map the internal Z business component method that
determines the date and time range for the Z business component data.
You must not modify this user property.
Z-End DateTime Field Specifies the field in the Z business component that specifies the end of
the date and time range.
Z-Join Field Specifies the field in the Z business component that links to the Y
business component. If the Z-Join InvokeMethod property does not
include a value, then Siebel CRM uses the Z-Join Field property as a
search specification.
Z-Join InvokeMethod Specifies how to map an internal Z business component method to link
the Y and Z business components with each other. You must not modify
this user property.
Z-Start DateTime Field Specifies the field in the Z business component that determines the start
of the date and time range.
Table 18. User Properties for the eGanttChart Busy Free Time Applet
Applet User Property Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Applet User Properties
82
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Specifying Drilldown Visibility
The Drilldown Visibility applet user property determines the visibility that Siebel CRM uses for a new
view during a single record drill down. Earlier versions of Siebel CRM use this applet user property.
The Visibility Type property of the drilldown object replaces this applet user property in later
versions. For more information, see “Specifying the Calendar Visibility Filter” on page 84.
Specifying Field Names According to Parent Id
The Parent Id Field applet user property specifies the name of a field that resides in the current
business component. For example, the PS Project Team OrgChart Applet specifies the Parent Team
Member Id field that resides in the PS Project Team business component. If the user drags and drops
one box over another box in an organization chart to create a parent and child relationship, then
Siebel CRM populates this field with the parent row ID.
If you do not specify a field, then Siebel CRM uses the default value from the Manager Id field that
resides in the Contact business component.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, but not to modify the value for it or
to create a new instance of it.
Specifying Political Influence in Organization Charts
The Political Analysis Field applet user property specifies the name of a field that resides in the
current business component. Siebel CRM uses it in the organization chart to display the level of
influence for each contact. It shades the box of the contact with the appropriate level of gray.
If you do not specify a field, then Siebel CRM uses Political Analysis as the default value.
You can map this field only to a list of values that includes the following values:
■ Low. No Color.
■ Political Structure (Medium). Light Grey.
■ Inner Circle (High). Dark Grey.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify this user property or modify the values for it, but not to
deactivate it or create a new instance of it.

User Properties ■ Applet User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 83
Specifying Post Invoke Methods
The PostInvokeMethod n user property sets a value in some predefined applets. For example, the
FINS FSW Service Request List Applet references the Service Request business component. It
includes the following user property:
■ Name. PostInvokeMethod 1
■ Value. NewRecord:SetFieldValue:INS Product:[INS Product Predefault Calc]
If the user creates a new record in this applet, then this user property sets the INS Product field to
the value that the INS Product Predefault Calc calculated field returns. In this example, it overrides
the predefault value that Siebel CRM sets in the business component field.
Specifying Relationships in Organization Charts
The Contact Relationship Type applet user property specifies a list of relationship types that indicate
the contact possesses a line of influence. The value for this user property must specify one or more
relationship types. You can use a comma and a space to separate multiple relationship types. For
example:
Influencer, TAS Influencer
The CONTACT_RELATIONSHIP_TYPE list of values typically provides these types.
If the user presses and holds down the CTRL key, and then drags one box in an organization chart
and drops it on another box, then the value of this applet user property populates the
RELATION_TYPE_CD column of the S_CONTACT_REL table. This table is the intersection table that
resides between the Contact and Contact Relationship business components. For example, if the user
drags and drops Box A in an organization chart onto Box B, then:
■ The CONTACT_ID column identifies the row ID of Box A.
■ The REL_CONTACT_ID column identifies the row ID of Box B.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the values for this user property, but not to deactivate it or
create a new instance of it.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
Specifying the Application That Creates Proposals
The ApplicationContextType applet user property specifies the Microsoft application that Siebel CRM
uses to create proposal and presentation documents. It must include one of the following values:
■ MSWord. Use Microsoft Word for a proposal.
■ MSPpt. Use Microsoft PowerPoint for a presentation.
You cannot configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, modify the value for it, or create
a new instance of it.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Applet User Properties
84
Specifying the Calendar Visibility Filter
The Visibility Type applet user property sets the visibility filter in a calendar applet. The value for this
user property must include one of the following values:
■ My. The Owner static drop-down list displays the name of the user who is logged in. This user
can view only their personal calendar.
■ My Direct Reports. The Owner static drop-down list displays the direct reports of the user who
is logged in. This user can view the calendars for all people who report directly to this user. Siebel
CRM typically uses this value in the eCalendar my direct reports applets.
■ All. The user who is logged in can view the calendars of other people that Siebel CRM allows this
user to access even if these other people are not direct reports.
Specifying the Default Applet Focus
The DefaultFocus applet user properties set the focus for a field or control that resides in an applet
before a user interacts with this field or control. It can override this focus behavior as determined by
the applet mode. An applet web template determines the modes that an applet can use.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate each of these user properties, to modify the value for
each them, or to create a new instance of each of them, but you must not configure Siebel CRM to
create more than one instance of each them for an applet.
Setting the Default Focus for an Object That Siebel CRM Does Not
Display
If you set the default focus to a field or control that Siebel CRM does not display in the visible portion
of the client, then one of the following situations might occur. This behavior might confuse the user:
■ The user might not be able to identify the object that is in focus.
■ Siebel CRM might attempt to adjust the vertical position of the view so that it can display the
field or control that is in focus.
Specifying the Default Applet Focus for Base, Edit, or Edit List Mode
The DefaultFocus_Edit applet user property sets the focus for a field or control in an applet if the
applet is in Base, Edit, or Edit List mode. The value for this user property must include the name of
a field or control that resides in the applet. You must not enclose this value with quotes. For example,
you can use the following value to set the default focus for the Last Name field on an applet that is
in Edit mode:
Last Name
If you do not add the DefaultFocus_Edit user property to an applet, and if the applet is in Base, Edit,
or Edit List mode, then Siebel CRM does not set the focus on any field or control.

User Properties ■ Applet User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 85
Specifying the Default Applet Focus for New Mode
The DefaultFocus_New applet user property sets the focus for a field or control that resides in an
applet if the applet is in New mode. The value for this user property must include the name of a field
or control that resides in the applet. You must not enclose this value with quotes. For example, you
can use the following value to set the default focus to the New button on an applet that the user uses
to add a new record:
NewRecord
If you do not add the DefaultFocus_New user property to an applet, and if the applet is in New mode,
then Siebel CRM sets the focus on the first field in the applet.
Specifying the Default Applet Focus for Query Mode
The DefaultFocus_Query applet user property sets the focus for a field or control that resides in an
applet if the applet is in Query mode. The value for this user property must include the name of a
field or control that resides in the applet. You must not enclose this value with quotes. For example,
you can use the following value to set the default focus for the First Name field on an applet that is
in Query mode:
First Name
If you do not add the DefaultFocus_Query user property to an applet, and if this applet is in Query
mode, then Siebel CRM sets the focus to the first field that it displays in this applet.
Specifying the Error Web Page for SmartScript
The WebGotoPlayerErrorPage applet user property specifies the name of the Web page that Siebel
CRM displays if an error occurs while it runs a SmartScript in Siebel eMarketing. This error page
includes a control that returns navigation to the eSmartScript page that caused the error.
Specifying the Finish or Cancel Web Page for
SmartScript
The WebGotoView applet user property specifies the name of the view that Siebel CRM displays if it
calls the FINISH event or the CANCEL event in the Siebel SmartScript player applet.
Specifying the Method That the Enter Key Calls
The Default Applet Method user property specifies the method that Siebel CRM runs if the user
presses the Enter key in an applet. The value for this user property must include the name of a
method that Siebel CRM accesses from the applet.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it. Only one instance can exist on each applet.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Business Service User Properties
86
Specifying the Parent Business Component
The DataSourceBuscompName applet user property specifies the name of the business component
that the business object references as the parent business component. It must specify the name of
a business component that the current business object references.
If the Document Server receives a request to create a proposal or presentation, then it tries to
restore the request context before it processes this request. It does this so that Siebel CRM positions
the business component on the correct record set. The Proposal business component gets data from
this business component according to the link specification. The first record is the record that the
user used to submit the proposal request.
Note the following:
■ It is typically not necessary to specify this applet user property because Siebel CRM defaults to
the parent business component of the Proposal business component. This is typically the parent
business component.
■ You can specify this applet user property only if the parent business component that the current
business object references is not the same as the parent business component of the Proposal
business component.
■ If you use this applet user property, then the link to the business component that the user
property defines restricts the data that Siebel CRM gets from the business components instead
of the default value of the parent of the proposal.
■ You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not
to create a new instance of it
Business Service User Properties
This topic describes business service user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ Specifying the BAPI Adapter Service on page 86
■ Specifying the Batch Size for SAP IDOCs on page 87
■ Specifying the Time Out Interval for Receive Requests on page 87
For information about using business component user properties to specify business services, see
“Specifying Business Services” on page 148.
Specifying the BAPI Adapter Service
The BAPIAdapterService business service user property specifies the name of the BAPI (Business
Application Programming Interface) adapter business services. It must specify one of the following
values:
■ BAPI Adapter
■ EAI
■ SAP

User Properties ■ Control User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 87
Specifying the Batch Size for SAP IDOCs
The BatchSize business service user property specifies the number of IDOCs (Intermediate
Documents) that Siebel CRM reads from SAP in a single call. The value for this user property must
include an integer. The value you use depends on the resources that are available in your
environment. A high value might degrade performance. The default value is 3000.
Specifying the Time Out Interval for Receive Requests
The SleepTime business service user property specifies the time out interval, in seconds, that Siebel
CRM uses for a receive request. The value for this user property must include an integer. The default
value is 20 seconds.
CAUTION: If you set the SleepTime user property to a low value or zero, then a serious negative
impact on performance might result. It can cause SAP to flood the SAP system buffers and to retry
sending IDOCs to Siebel CRM because the connector does not "receive" them.
Control User Properties
This topic describes control user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ Forcing Controls to Be Active on page 87
■ Saving Unsaved Data on page 87
■ Specifying the Goto URL on page 88
■ Specifying the Goto View on page 88
■ Specifying the Goto Web Page on page 88
Forcing Controls to Be Active
The ForceActive control user property that resides on a control in a form applet forces the field that
the control references to be active even if Siebel CRM does not display this field in the client. The
value for this user property must include a Boolean value. If Y, then this field is active even if Siebel
CRM does not display it in the client.
A field is typically active only if Siebel CRM displays it in the client. For more information, see “Forcing
Fields That a List Column References to be Active” on page 100.
Saving Unsaved Data
The PostMainViewData control user property prevents Siebel CRM from losing unsaved data if a
control calls a method that modifies the main view before Siebel CRM saves any new data that resides
in the current record. The value for this user property must include one of the following values:
■ TRUE. If the current record contains modified data:

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Control User Properties
88
■ In a high interactivity view. Siebel CRM saves the current record before the control
modifies the focus.
■ In a standard interactivity view. Siebel CRM displays a message that warns that unsaved
data might be lost. This message does not display unless you also add the following
parameter to the InfraUIFramework section of the application .cfg file:
EnableSIDataLossWarning = TRUE
■ FALSE or this user property does not exist. Siebel CRM calls the control method and does
not write unsaved data to the current record.
It is recommended that you set the PostMainViewData user property on each control that affects how
Siebel CRM saves data, such as the Attach button. For example, if the All Service Requests view is
the main view, then the user can click the Search button before Siebel CRM saves the current record.
If the user runs a search, and then clicks the Attach button for a record, then Siebel CRM drills down
on the Results list into the active record. This configuration modifies the applet that resides in the
main view and Siebel CRM might lose the new data that resides in the unsaved service request.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, modify the value for it, or if an
instance of it is not already defined, then to create a new instance of it.
Specifying the Goto URL
The Url control user property specifies the URL that Siebel CRM uses when it calls the GotoUrl method
for an applet control. If the value of the Method Invoked property on a control is GotoUrl, then you
must use the Url control user property to specify the URL.
Siebel CRM typically uses the GotoUrl method with the CancelQuery control. It uses the following
value for the Url:
JavaScript:history.back()
Specifying the Goto View
The View control user property specifies the name of the view that Siebel CRM displays when it calls
the GotoView method for an applet control. For example:
Account List View
If the value of the Method Invoked property on a control is GotoView, then you must use the View
control user property to specify the view.
Specifying the Goto Web Page
The Page control user property specifies the Web page that Siebel CRM displays when it calls the
GotoPage method for an applet control.

User Properties ■ Field User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 89
If you set the Method Invoked property of a control to GotoPage, then you must use the Page control
user property to specify the Web page.
Siebel CRM typically uses the GotoPage method with the Main Menu control that Siebel Wireless uses
where the value of Page is SLWS Start Page.
Field User Properties
This topic describes field user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ Disabling Search on Text Fields or Unindexed Fields on page 89
■ Disabling Sort on Business Component Fields on page 90
■ Making a Field Required on page 90
■ Setting the Field Text Length on page 90
■ Specifying Encryption for Fields on page 91
■ Updating Assets on page 93
■ Cascading Asset Updates on page 94
■ Specifying the Field That Stores the Account Id of a Contact on page 95
■ Specifying the SQL for EXISTS Search Specifications on page 95
■ Using Literals Instead of Bind Variables on page 96
For information about using business component user properties to control fields, see “Controlling
Fields” on page 138.
Disabling Search on Text Fields or Unindexed Fields
The DisableSearch field user property prevents the user or the Siebel query engine from running a
query on a field that is not indexed or that is a text field. The value for this user property must include
one of the following values:
■ TRUE. Disable wildcard search on the field. For example, if the user enters the following value,
then Siebel CRM displays an error message:
[Name] LIKE 'S*'
Siebel CRM does allow an exact search. For example, it allows the following search:
[Name] = 'Siebel'
■ FALSE or this user property does not exist. Allow wildcard or exact match search.
Siebel CRM enforces this user property in the following situations:
■ Query by example
■ Query Assistant

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Field User Properties
90
■ Search Center
■ Query started in a programmatic or message interface
■ Predefined query
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, modify the value for it, or if an
instance of it is not already defined, then to create a new instance of it.
Disabling Sort on Business Component Fields
The DisableSort field user property specifies whether a user can sort a result set on a business
component field. It must include one of the following values:
■ TRUE. Disable all sorting on any field in any applet that references the business component.
Siebel CRM does the following:
■ Does not display the sort icons or tool tips in the list column header.
■ Does not display the field in the Advanced Sort window.
■ If a user attempts to sort on the Name field in any applet that references this business
component, then Siebel CRM displays an error message.
■ FALSE or this user property does not exist. Enable sort on the field.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, modify the value for it, or if an
instance of it is not already defined, then to create a new instance of it.
For more information, see “Disabling Sort on List Columns” on page 99.
Making a Field Required
The Required field user property makes the parent field a required field in some situations. The value
for this user property must include a calculated expression. If Siebel CRM evaluates this expression
to Y, then the field is required.
You can use this applet user property only with a business component that references the CSSBCBase
class.
Setting the Field Text Length
The Text Length Override field user property configures Siebel CRM to use the text length of a field
instead of the database column to determine the maximum field length. You can use this field user
property only for a text field. The value for this user property must include text. If this user property:
■ Exists. The Text Length property of this field determines the maximum field length regardless
of the value that the user property contains. This situation is true even if the value is empty.
■ Does not exist. The size of the database column determines the maximum field length.

User Properties ■ Field User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 91
Specifying Encryption for Fields
This topic describes user properties that handle encryption. It includes the following topics:
■ Overview of Encryption User Properties on page 91
■ Upgrading Encryption on page 91
■ Enabling Encryption on a Field on page 92
■ Specifying the Field That Contains the Encryption Key on page 92
■ Specifying the RC2 or AES Encryption Service on page 92
■ Setting an Encrypted Field to Read Only if Encryption Fails on page 92
■ Masking Credit Card, Account, and Other Secure Data on page 93
■ Specifying the Field That Contains Secure Data on page 93
Overview of Encryption User Properties
Siebel CRM comes predefined with the following business services that it uses to encrypt data fields
according to RSA (Rivest Shamir Adleman) encryption:
■ Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Encryptor
■ RC2 Encryptor
To encrypt a field, you set the encryption flag, identify the encryption service, and specify the
encryption key. To disable encryption on a field, you set the Encrypted user property of the field to N.
If encryption is enabled, then Siebel CRM writes data to the field in the encrypted format and reads
decrypted data from the field. Encryption must be enabled for each business component field that
Siebel CRM maps to the same database column, and the user property specifications for these
objects must be consistent.
Siebel CRM typically encrypts credit card number fields. However, it might be necessary for you to
disable encryption in these fields in the following screens so that the user can view this information:
■ Order Entry -- Orders
■ Quote
■ Agreements
For more information about setting up or upgrading encryption, see Siebel Security Guide. For more
information about encryption keys and how to manage them, see Siebel System Administration
Guide.
Upgrading Encryption
To do one of the following, you must run an upgrade script that modifies the encryption for the field:
■ Use the RSA or AES encryptor service on a field that Siebel CRM previously did not encrypt or
that the Standard Encryptor encrypted. Siebel CRM no longer supports Standard Encryptor.
■ Use a stronger version of RC2 encryption than Siebel CRM previously used on the field.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Field User Properties
92
For more information, see the upgrade guide for the operating system you are using.
Enabling Encryption on a Field
The Encrypted field user property specifies whether Siebel CRM encrypts a field. The value for this
user property must include a Boolean value. If Y, then Siebel CRM enables encryption. To enable
encryption on a field, you must set this field user property to Y and you must configure the Encrypt
Service Name and Encrypt Key Field user properties. For more information, see Siebel Security
Guide.
Specifying the Field That Contains the Encryption Key
The Encrypt Key Field field user property specifies the name of the business component field that
contains the encryption key index. The keyfile.bin file in the following directory contains indexed
encryption keys:
\
Siebel_Root
\Admin
The Encrypt Key Field user property specifies the business component field that contains the
numbered encryption key index that Siebel CRM uses to decrypt the parent field.
For example, the Credit Card Number field that resides in the Quote business component is an
encrypted field that contains credit card numbers. The Credit Card Number Key Index field contains
the index of the encryption key that Siebel CRM uses to decrypt the Credit Card Number field. Siebel
CRM sets the Credit Card Number field in the Encrypt Key Field user property to a value that the
Credit Card Number Key Index contains.
Specifying the RC2 or AES Encryption Service
The Encrypt Service Name field user property specifies the encryption service name. It must specify
one of the following values:
■ RC2 Encryptor
■ AES Encryptor
You can set this field user property on an encrypted field to specify the embedded encryption service
that Siebel CRM applies.
Setting an Encrypted Field to Read Only if Encryption Fails
If decryption fails, then the Encrypt ReadOnly Field field user property sets an encrypted field to
read-only. It must specify the name of a calculated business component field whose Calculated Value
property is empty.
The calculated field that this field user property specifies determines whether Siebel CRM sets the
data in the encrypted field to read-only. Preserving the data in read-only form allows someone to
recover it later without modifying this data. This calculated field can use one of the following values:
■ Y. Decryption fails on the encrypted field. Siebel CRM sets this encrypted field to read-only.
■ N. Decryption succeeds on the encrypted field. Siebel CRM sets this encrypted field to readable.

User Properties ■ Field User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 93
For example, the Quote business component includes the encrypted Credit Card Number field. Siebel
CRM sets the Encrypt ReadOnly Field user property for this field to the value that the Credit Card
Number - Read Only calculated field contains.
Masking Credit Card, Account, and Other Secure Data
The Display Mask Char field user property displays a masked version of secure data, typically a credit
card number or account number. The value for this user property must include a character that Siebel
CRM uses to mask characters. Siebel CRM sets this value to x, by default.
Siebel CRM uses this field user property with the Encrypt Source Field user property to display only
the last 4 digits of a credit card number or account number. For example, xxxxxxxxxxxx9999. You
set this field user property on a separate calculated field that Siebel CRM displays in the client instead
of on the field that contains the entire credit card number or account number.
For example, Siebel CRM uses the Credit Card Number field in the Quote business component as the
encrypted field that stores the credit card number. The properties of the Credit Card Number -
Display calculated field include the following values:
■ Display Mask Char. This user property contains x.
■ Encrypt Source Field. This user property contains the following value. The applet field that
displays the masked credit card number must reference the Credit Card Number - Display field:
Credit Card Number
The field that the Encrypt Source Field property identifies must be encrypted. If it is not encrypted,
then the masking functionality does not work.
For more information, see “Specifying the Field That Contains the Encryption Key” on page 92.
Specifying the Field That Contains Secure Data
The Encrypt Source Field field user property specifies the name of the business component field that
contains an encrypted credit card number or account number. For more information, see “Masking
Credit Card, Account, and Other Secure Data” on page 93.
Updating Assets
The SubCompCanUpdate field user property updates asset records. The value for this user property
must include one of the following values:
■ TRUE. Update any nonroot asset record.
■ FALSE. Set asset records to read only.
For more information, see “Allowing Users to Update Assets” on page 116 and “Cascading Asset
Updates” on page 94.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Field User Properties
94
Cascading Asset Updates
The SubCompUpdate field user property cascades modifications that occur to an asset record. It
cascades these modifications to child asset records. The value for this user property must include
one of the following values:
■ TRUE. Cascade modifications to child asset records.
■ FALSE. Do not cascade modifications.
Configuring Siebel CRM to Cascade Asset Updates
This topic describes how to configure Siebel CRM to cascade modifications that it makes to an asset
record. The example in this topic describes how to configure Siebel CRM to cascade modifications
that it makes to the Ship Date field that resides in the Asset Mgmt - Asset business component. It
cascades these modifications to the Ship Date field that resides in the Asset Mgmt - Asset -
SubCompUpdate Processing business component.
To configure Siebel CRM to cascade asset updates
1
Log in to Siebel Tools.
2 In the Object Explorer, click Business Component.
3 In the Business Components list, query the Name property for the following value:
Asset Mgmt - Asset
4 In the Object Explorer, expand the Business Component tree, and then click Field.
5 In the Fields list, query the Name property for the following value:
Ship Date
6 In the Object Explorer, expand the Field tree, and then click Field User Prop.
7 In the Field User Props list, create a new field user property using values from the following table.
8 In the Field User Props list, create a new field user property using values from the following table.
9 In the Object Explorer, click Business Component.
Property Value
Name SubCompCanUpdate
Value FALSE
Property Value
Name SubCompUpdate
Value TRUE

User Properties ■ Field User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 95
10 In the Business Components list, query the Name property for the following value:
Asset Mgmt - Asset - SubCompUpdate Processing
11 In the Object Explorer, click Field.
12 In the Fields list, query the Name property for the following value:
Ship Date
13 Set the following property using values from the following table.
Specifying the Field That Stores the Account Id of a
Contact
The Affiliated Account Id Field user property specifies the name of the business component field that
stores the account ID of affiliated contacts. Siebel Life Sciences applications use it to display affiliated
contacts. If you do not define this field user property, then Siebel CRM searches for the Account Id
field in the parent business component.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
For more information, see “Specifying the Field That Stores Parent Account IDs for Contacts” on
page 110.
Specifying the SQL for EXISTS Search Specifications
The UseExistsForSubQuery field user property determines the type of SQL clause that Siebel CRM
uses if it encounters an EXISTS search specification in a business component. If it encounters an
EXISTS search specification, and if the value for this user property is:
■ TRUE. Siebel CRM uses the SQL EXISTS clause.
■ FALSE or this user property does not exist. Siebel CRM uses the SQL IN clause.
In some situations, using the SQL EXISTS clause instead of the IN clause can improve query
performance, particularly for IBM DB2 390.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, to modify the value for it, or to create
a new instance of it, but no more than one instance for a single business component.
Property Value
Force Active TRUE

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Field User Properties
96
Using Literals Instead of Bind Variables
The Use Literals For Like field user property uses a literal instead of a bind variable as the criteria
for a LIKE predicate in the SQL code that Siebel CRM uses to query a field. The value for this user
property must include one of the following values:
■ TRUE. Siebel CRM uses a literal instead of a bind variable. For example:
LIKE "ABC%"
where:
■ The % (percentage symbol) specifies the exact location of the wildcard.
■ FALSE or this field user property does not exist. Siebel CRM uses a bind variable. If a search
string includes a wildcard, such as * or ?, then Siebel CRM creates the following predicate to
represent this wildcard:
LIKE ?
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, to modify the value for it, or to create
a new instance of it, but no more than one instance for a single field.
How Siebel CRM Handles Wildcards
To include a wildcard in a search string, the user can explicitly include it. For example, "ABC*" or
"*ABC?". Siebel CRM can also append a trailing wildcard (*) if all of the following items are true:
■ The search string does not contain any wildcard. For example: "ABC".
■ The = (equal) sign does not precede the search string.
■ The AutomaticTrailingWildcards parameter in the InfraUIFramework section of the application
CFG file is set to TRUE or does not exist. The uagent.cfg file is an example of an application CFG
file. If this parameter is:
■ TRUE. Siebel CRM automatically creates a trailing wildcard or adds a LIKE predicate. If you
use a script, and if this script creates a query, then Siebel CRM adds a LIKE statement to the
SQL that this script creates.
■ FALSE or does not exist. Siebel CRM does not automatically create a trailing wildcard or
add a LIKE predicate. It typically sets this parameter to FALSE to avoid using the Use Literals
For Like user property.
Guidelines for Using Literals Instead of Bind Variables
CAUTION: Avoid or minimize using the Use Literals For Like field user property. It can use resources
because it requires more SQL code parsing that can cause a package cache overflow. It is
recommended that you use it only after testing indicates that a significant performance improvement
will result.
Using the Use Literals For Like user property can impact performance when compared to using a bind
variable for some searches. For example:

User Properties ■ Integration Component User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 97
■ A search string that includes a wildcard in a trailing position, such as "ABC*", can improve
performance because Siebel CRM can choose a more appropriate index.
■ A search string that includes a wildcard in a leading position, such as "*ABC", can degrade
performance. The Use Literals For Like field user property does not improve performance for this
search because it does not significantly reduce the number of rows that Siebel CRM must scan.
If you configure the Use Literals For Like field user property, then use the following guidelines:
■ If poor performance exists, or if a DB2 UDB utility indicates that the optimizer does not choose
indexes efficiently, then it is recommended that you use the Use Literals For Like field user
property. If performance improves significantly, then deploy this configuration to your production
environment.
■ Do not use the Use Literals For Like field user property to improve performance with a case-
insensitive query.
■ Use a literal in a query that includes a LIKE predicate. This configuration can improve query
performance on DB2 UDB. It provides information that the database optimizer can use to choose
indexes for the query.
Integration Component User Properties
This topic describes integration component user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ Specifying Association Business Components on page 97
■ Specifying MVG Business Components on page 97
■ Preventing Siebel EAI From Deleting Records on page 98
■ Preventing Siebel EAI From Inserting Records on page 98
Specifying Association Business Components
The Association integration component user property indicates that the integration component is an
association business component. The value for this user property must include a Boolean value. If Y,
then the integration component is an association integration component.
Specifying MVG Business Components
The MVG integration component user property specifies that the integration component is a
multivalue group business component. The value for this user property must include a Boolean value.
If Y, then the integration component is a multivalue group business component.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ Integration Component Field User Properties
98
Preventing Siebel EAI From Deleting Records
The NoDelete integration component user property restricts the Siebel EAI connector from
performing a delete on the corresponding business component. The value for this user property must
include a Boolean value. If Y, then the Siebel EAI connector does not perform deletes in the business
component that the integration component references.
Preventing Siebel EAI From Inserting Records
The NoInsert integration component user property restricts the Siebel EAI connector from inserting
on the corresponding business component. The value for this user property must include a Boolean
value. If Y, then the Siebel EAI connector does not perform inserts in the business component that
the integration component references.
Integration Component Field User
Properties
This topic describes integration component field user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ Specifying the Field Name for an MVG on page 98
■ Preventing Siebel EAI From Updating Fields on page 98
Specifying the Field Name for an MVG
The AssocFieldName [Field Name] integration component field user property specifies the name of
the business component field that Siebel CRM displays on the multivalue group business component.
Preventing Siebel EAI From Updating Fields
The NoUpdate integration component field user property restricts the Siebel EAI connector from
updating the corresponding field. The value for this user property must include a Boolean value. If
Y, then the Siebel EAI connector updates the field that the integration component field references.
Integration Object User Properties
This topic describes integration object user property. It includes the following topics:
■ Specifying the IDOC Message Type for SAP on page 99

User Properties ■ List Column User Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 99
Specifying the IDOC Message Type for SAP
The Logical Message Type integration object user property specifies the logical message type that
corresponds to the IDOC (Intermediate Document). The value for this user property must include a
logical message type that corresponds to the IDOC. For example, DEBMAS or MATMAS. If you use
this integration object user property with an SAP product, then the SAP Connector:
■ Ignores it when it receives each IDOC from SAP.
■ Uses the value that it contains to populate the control segment MESTYP field before it sends each
IDOC to SAP.
List Column User Properties
This topic describes list column user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ Disabling Sort on List Columns on page 99
■ Forcing Fields That a List Column References to be Active on page 100
Disabling Sort on List Columns
The DisableSort list column user property specifies whether a user can sort a result set on a list
column. It prevents the user and the Siebel query engine from sorting data that is not indexed. The
value for this user property must include a Boolean value. If TRUE, then Siebel CRM does the
following:
■ Disables sort on the list column.
■ Does not display the sort icons or tool tips in the list column header.
■ Does not display the field in the Advanced Sort window.
For example, if you set the DisableSort user property of the Name list column to TRUE, then Siebel
CRM does the following:
■ Does not display the sort icons or Sortable tool tip in the Name list column.
■ Does not display the Name field in the Advanced Sort window.
■ If a user attempts to sort on the Name field, then it displays an error message. For more
information, see “Disabling Sort on Business Component Fields” on page 90.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, modify the value for it, or if an
instance of it is not already defined, then to create a new instance of it.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
User Properties
■ View User Properties
100
Forcing Fields That a List Column References to be
Active
The ForceActive list column user property forces the field that the list column references to be active
even if Siebel CRM does not display it. A field is typically active only if Siebel CRM displays it in the
client. The value for this user property must include a Boolean value. If Y, then the field is active
even if Siebel CRM does not display it in the client. For more information, see “Forcing Controls to Be
Active” on page 87.
View User Properties
This topic describes view user properties.It includes the following topics:
■ Specifying the Default Applet Focus on page 100
Specifying the Default Applet Focus
The DefaultAppletFocus view user property identifies an applet in a view. Siebel CRM sets the focus
to this applet before the user interacts with the view. This user property overrides the applet that
receives the default focus.
The value for this user property must include the name of an applet that the view displays. You must
not enclose this value in quotes. For example, Siebel CRM sets the value of the DefaultAppletFocus
user property of the Account Screen Homepage View to the following value:
Account Home Search Virtual Form Applet
It sets the focus for this view to the Account Home Search Virtual Form Applet the first time the user
accesses this view.
If the DefaultAppletFocus user property does not exist on a view, then the screen view determines
the default focus. If the Type property of the screen view is:
■ Detail View, and if the view includes more than one applet, then Siebel CRM places the focus on
the second applet.
■ Not Detail View, or if the view includes only one applet, then Siebel CRM places the focus on the
first applet.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, to modify the value for it, or to create
a new instance of it, but no more than one instance for a single view.
For more information, see “Setting the Default Focus for an Object That Siebel CRM Does Not Display”
on page 84.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 101
6 Business Component User
Properties
This chapter describes business component user properties. It includes the following topics:
■ Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties on page 101
■ Viewing a Business Component User Property on page 108
■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data on page 108
■ Controlling Search and Sort on page 121
■ Controlling Visibility Filters on page 130
■ Controlling Records on page 132
■ Controlling Fields on page 138
■ Controlling Primaries on page 146
■ Specifying Business Services on page 148
■ Controlling Parent and Child Relationships on page 149
■ Controlling Email on page 154
■ Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications on page 158
■ Doing Other Work on page 167
For brevity, this chapter uses the term user property to represent the term business component user
property, unless noted otherwise. A business component is the parent of a business component user
property.
Alphabetic List of Business Component
User Properties
Table 19 includes an alphabetic list of business component user properties.
Table 19. Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties
User Property Topic
Active Field Making Fields Active on page 138
Active Value
Activity SearchSpec Specifying Search Specifications for the Action Business
Component on page 129
Admin Mode Field Allowing Administrators to Modify Records on page 133

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Alphabetic List of Business Component User
Properties
102
Admin NoDelete Preventing Administrators from Deleting Records on page 134
Admin NoUpdate Preventing Administrators from Updating Records on page 134
All Mode Sort Overriding Sort Specifications on Business Components on
page 123
Always Enable Child:
buscompname
Enabling Service Request Updates in Child Business
Components on page 154
Always Enable Field n Allowing Users to Update Closed Service Requests on page 116
Application Name Specifying the Application Name on page 168
Aspect BC NoInsert: Aspect Using Aspects to Control Read Only, Insert, and Other
Behavior on page 168
Aspect BC ReadOnly: Aspect
Aspect Child BC ReadOnly: Aspect
Aspect Default Value: Aspect
Assignment Object Specifying Assignment Objects on page 120
Associate: Completion Timeout Specifying Server Timeouts for Forecasts on page 114
Associate: Completion Timeout
(Client)
Specifying Client Timeouts for Forecasts on page 114
Associate: Sleep Time Between
Attempts
Specifying Sleep Time Between Forecast Save Attempts on
page 114
AutoPopulateResponsibility Automatically Assigning Responsibilities to Users on page 118
BC eAuto Sales Step Specifying Business Components for the Opportunity Sales Step
in Siebel Automotive on page 160
BC eAuto Sales Step Admin Specifying Business Components for the Sales Step Admin in
Siebel Automotive on page 160
BC Opportunity Specifying the Business Component for Reassignment in Siebel
Automotive on page 161
BC Position Specifying Positions in Siebel Automotive on page 161
BC Read Only Field Making Records Read-Only According to a Field Value on
page 133
BO eAuto Sales Step Admin Specifying Business Objects for the Sales Step Admin in Siebel
Automotive on page 160
Calc Actual OnWriteRecord Calculating Values When Writing Records on page 135
ChargeBusinessService Determining Charges for Service Activities on page 111
ChargeBusinessServiceMethodn Specifying the Business Service Method for Activity Charges on
page 111
Table 19. Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties
User Property Topic

Business Component User Properties ■ Alphabetic List of Business Component User
Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 103
CloseOutFlag Setting the Close Out Flag Field on page 119
Contact MVG PreDefault
Expression
Adding Contacts to the Action Business Component on page 117
Contact-Activity BC Name Reassigning Contacts in Siebel Automotive on page 161
Contact-Opportunity BC Name Reassigning Opportunities in Siebel Automotive on page 161
Copy Contact Copying Contacts to Campaigns on page 113
Credit Card Expired Month Specifying Credit Card User Properties on page 167
Credit Card Expired Year
Credit Card Number
Credit Card Type
Credit Check Enabling Credit Check on page 166
Credit Check Workflow Specifying the Workflow Process for Credit Check on page 166
Currency Field n Modifying the Currency That a Field Uses on page 145
Day Number: Arrival Date Field Specifying the Arrival Date Field for the Day Number Business
Service on page 166
Day Number: Function BC Name Specifying the Business Component for the Function Space on
page 166
Day Number: Room Block BC
Name
Specifying the Business Component for the Room Block on
page 166
DB2 Optimization Level Specifying the DB2 Optimization Level for SQL Statements on
page 172
Deep Copy Copying and Deleting Child and Grandchild Records on page 150
Deep Copy/Delete Link Buscomp
Deep Delete
Default Aspect Using Aspects to Control Read Only, Insert, and Other
Behavior on page 168
Default Bookmark View Specifying the Default Bookmark View on page 170
DefaultPrefix Specifying Field Name Prefixes for File Attachment Business
Components on page 145
Disable Automatic Trailing
Wildcard Field List
Disabling Automatic Trailing Wildcards in Queries on page 125
DisplayType Overriding the Type for Fields That Users Read from Right-To-
Left on page 143
Duplicate Elimination Removing Duplicate Records From Queries on page 122
Table 19. Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties
User Property Topic

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Alphabetic List of Business Component User
Properties
104
Dynamic Hierarchy Parent Field Id Controlling Global Account Visibility on page 130
DynHierarchy Hierarchy Id Field
DynHierarchy Visibility
Organization Id Field
DynHierarchy Visibility Position Id
Field
eAuto Enable Create Sales Step Specifying How to Populate Opportunity Sales Steps in Siebel
Automotive on page 160
Email Activity Accepted Status
Code
Specifying Statuses for Outgoing Email on page 155
Email Activity New Status Code
Email Activity Rejected Status
Code
Email Activity Sent Status Code
Email Manager Compatibility Mode Specifying the Manager That Sends Email on page 156
Employee Link Controlling My Visibility Filters on page 131
Enable Dispatch Board Enabling the Dispatch Board on page 170
Extended Quantity Field Extending Quote Quantities on page 118
Field Read Only Field: fieldname Making Fields Read-Only on page 139
FileMustExist Making Sure an Attachment File Exists on page 170
Forecast Analysis BC Specifying Business Components for Forecast Analysis on
page 115
Forecast Rollup Specifying Search Specifications for Forecast Rollup on
page 115
Group Visibility Specifying Group Plus Team Visibility in Campaigns on page 113
Group Visibility Only Specifying Group Only Visibility in Campaigns on page 113
Inner Join Extension Table n Specifying Joins to the S_PARTY Table on page 172
Maintain Master Account Maintaining the Master Account in Account Hierarchies on
page 110
Manager List Mode Controlling Manager Visibility Filters on page 132
Master Account Field Specifying the Master Account Field on page 110
MVG Set Primary Restricted:
visibility_mvlink_name
Specifying Who Can Modify Primary Team Members on page 146
Table 19. Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties
User Property Topic

Business Component User Properties ■ Alphabetic List of Business Component User
Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 105
Named Method n Calling Business Service Methods from Business Components on
page 148
Named Search: Forecast Series
Date Range
Specifying Search Specifications for Forecasts on page 114
No Change Field n Disabling Modifications to Saved Records on page 133
No Clear Field n Disallowing Empty Fields on page 139
NoDelete Field Disabling Field Deletion on page 140
Non-SalesRep View Mode
SearchSpec
Specifying Search Specifications for Nonsales Rep Views on
page 129
On Condition Set Field Value Setting Field Values According to Conditions on page 140
On Field Update Invoke n Calling Methods When Siebel CRM Updates Fields on page 142
On Field Update Set n Updating Fields When Siebel CRM Updates Other Fields on
page 141
OnAddAssocUpdateParent:
buscompname
Updating the Parent Business Component if Siebel CRM Modifies
Children on page 152
Opportunity Name Specifying Opportunity Business Components in Siebel
Automotive on page 159
Parent Account Field Specifying the Field That Stores Parent Account IDs on page 110
Parent Read Only Field Setting Business Components to Read-Only According to a Field
Value on page 136
Parent Read Only Field:
buscompname
Setting Business Components to Read-Only According to a
Name on page 137
ParentBC Account Id Field Specifying the Field That Stores Parent Account IDs for
Contacts on page 110
Picklist Pre Default Field n Setting Default Values for Fields That Use Drop-Down Lists on
page 144
Position Join Fields Specifying Position Join Fields for Siebel Life Sciences on
page 162
Post Default Created Date To Date
Saved
Setting the Field Created Date to the Saved Date on page 143
Primary Position Modification Allowing Only the Primary to Modify Sales Methods for
Opportunities on page 147
Private Activity Search Spec Restricting How Siebel CRM Displays Private Activities for
Primaries on page 148
Protect Seed Data Protecting Seed Data on page 120
Table 19. Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties
User Property Topic

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Alphabetic List of Business Component User
Properties
106
PSP: Active Specifying Business Components for Product Selection and
Pricing on page 163
PSP: Buscomp Name
PSP: Eligibility Fields
PSP: Eligibility Group
PSP: Eligibility Signal
PSP: Enabled BO: busobjname
PSP: Mode
PSP: Prepick Groups
PSP: Price Fields
PSP: Price Signal
QueryAssistantNumQueries Adding Search Criteria to the Query Assistant on page 126
RBFields Specifying Room Types for Siebel Hospitality on page 165
Recipient Email Address Field Sending Email Packages to Recipients on page 156
Recipient Fax Address Field
Recipient First Name Field
Recipient Id Field n
Recipient Last Name Field
Recipient Preferred Medium Field
Recursive Link Specifying Recursive Links Between Parent and Child Business
Components on page 153
Remote Source Specifying External Data Sources for Business Services on
page 149
Required Position MVField Making Sure the Current Employee Holds a Position on page 119
Response Type Call Back Responding to Email or Web Offers on page 158
Response Type More Info
Response Type Unsubscribe
Revenue Aggregation Field n Specifying Revenue Aggregation Fields on page 112
Revenue Associate List Specifying Pop-up Revenues Lists on page 112
Revenue Field Map: fieldname Specifying the Field That Siebel CRM Copies for New Revenue
Forecasts on page 112
Revision Condition n Enabling the Revise Button According to Conditions on page 171
Table 19. Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties
User Property Topic

Business Component User Properties ■ Alphabetic List of Business Component User
Properties
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 107
Revision Copy Field n Creating Numbered Revisions of Quotes, Orders, or
Agreements on page 117
Sequence Field Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records on
page 135
Sequence Use Max Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records According
to Maximum Values on page 135
Service Name Specifying Business Services for Virtual Business
Components on page 149
Service Parameters Specifying Business Service Parameters on page 149
Set Primary Sales Rep As Owner Setting the Primary Sales Rep as the Owner on page 147
Set User As Contact Setting the Current User as the Primary Contact on page 147
Skip Existing Forecast Series Date Disallowing Users to Pick Dates in the Forecast Date Dialog
Box on page 116
Sort Field Map n Specifying How to Sort Predefined Queries for Opportunities on
page 127
Sort Search Optimization Optimizing Sort Searches on page 121
State Model Specifying State Models on page 120
SubCompUpdate On Save Allowing Users to Update Assets on page 116
TargetProp n Saving Query Results in Target Lists on page 127
TypeRetailNew Specifying Values for New Opportunities in Siebel Automotive on
page 159
TypeRetailUsed Specifying Values for Used Opportunities in Siebel
Automotive on page 159
Update Parent BC Specifying the Parent Business Component for Accounts on
page 109
Update Planned Field On Set:
StartDate
Updating the Planned Field if the Start Date Field Is Modified on
page 143
Update Status To Synchronized Updating the Synchronization Status for Activities on page 111
Update Status To Synchronized
Types
Specifying Activities to Synchronize for Siebel Handheld on
page 161
Use Literals For Merge:
table_name
Using Literals Instead of Bind Variables When Merging
Records on page 137
Validate Parent Account Validating Parent Account IDs on page 109
Table 19. Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties
User Property Topic

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Viewing a Business Component User Property
108
Viewing a Business Component User
Property
This topic describes how to view a business component user property.
To view a business component user property
1
Open Siebel Tools.
2 Choose the View menu, and then click Options.
Siebel Tools displays the Development Tools Options dialog box.
3 In the Object Explorer Hierarchy window, make sure the Business Component User Prop option
contains a check mark, and then click OK.
4 In the Object Explorer, click Business Component.
5 In the Business Components list, locate the business component you must modify.
For example, locate the Activity Plan business component.
6 In the Object Explorer, expand the Business Component tree, and then click Business Component
User Prop.
The Business Component User Properties list displays the user properties that exist for this
business component.
Controlling Siebel CRM Data
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control Siebel CRM data.
It includes the following topics:
■ Controlling Accounts on page 109
■ Controlling Activities on page 110
View Aspect Using Aspects to Control Read Only, Insert, and Other
Behavior on page 168
View Aspect 1
View Aspect 2
View Aspect: View Name
ViewMode Sort: mode_num Sorting According to the View Mode That the Business
Component Uses on page 124
WorkFlow Behaviour Identifying Business Components That Siebel Financial Services
Uses on page 165
Table 19. Alphabetic List of Business Component User Properties
User Property Topic

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 109
■ Controlling Revenues on page 111
■ Controlling Campaigns on page 113
■ Controlling Forecasts on page 113
■ Allowing Users to Update Closed Service Requests on page 116
■ Allowing Users to Update Assets on page 116
■ Adding Contacts to the Action Business Component on page 117
■ Creating Numbered Revisions of Quotes, Orders, or Agreements on page 117
■ Extending Quote Quantities on page 118
■ Automatically Assigning Responsibilities to Users on page 118
■ Making Sure the Current Employee Holds a Position on page 119
■ Setting the Close Out Flag Field on page 119
■ Specifying State Models on page 120
■ Specifying Assignment Objects on page 120
■ Protecting Seed Data on page 120
Controlling Accounts
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control accounts.
Validating Parent Account IDs
The Validate Parent Account user property validates the parent account ID when Siebel CRM modifies
an account hierarchy. It can contain one of the following values:
■ Y. Validate the parent account ID.
■ N. Do not validate the parent account ID.
It is recommended that you do not modify the default value of this user property. You cannot
configure Siebel CRM to deactivate or create a new instance of this user property.
Specifying the Parent Business Component for Accounts
The Update Parent BC user property specifies the name of the parent business component that Siebel
CRM updates when it updates an account hierarchy. The value of this user property must contain the
name of an active business component.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, to modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
110
Specifying the Field That Stores Parent Account IDs
The Parent Account Field user property specifies the name of the business component field that
stores the parent account ID. The CSSBCAccountSIS class uses this value as the parent account ID
for the record.
It is recommended that you do not modify the default value of this user property. You cannot
deactivate or create a new instance of this user property.
Specifying the Field That Stores Parent Account IDs for Contacts
The ParentBC Account Id Field user property specifies the name of the field in the parent business
component that stores the account ID that Siebel CRM uses to display affiliated contacts. For
example:
Account ID
Siebel CRM uses this value in a Siebel Life Sciences application. If this user property does not exist,
and if the user clicks the Affiliated Accounts button, then Siebel CRM creates an error.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Specifying the Master Account Field
The Master Account Field user property specifies the name of the field that stores the master account
ID. The value for this user property must contain the name of a business component field. The
CSSBCAccountSIS class uses this value as the master account ID for the record.
It is recommended that you do not modify the value of this user property. You cannot deactivate or
create a new instance of this user property.
Maintaining the Master Account in Account Hierarchies
The Maintain Master Account user property maintains the master account ID in an account hierarchy.
The value for this user property must contain one of the following values:
■ Y. Maintain the master account ID.
■ N. Do not maintain the master account ID.
You cannot deactivate or create a new instance of this user property.
Controlling Activities
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control activities.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 111
Determining Charges for Service Activities
The ChargeBusinessService user property specifies the name of the business service that Siebel CRM
uses to determine charges for a service activity. You must not enclose this name in quotes. For
example:
FS Service Charge
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Specifying the Business Service Method for Activity Charges
The ChargeBusinessServiceMethodn user property specifies the name of the business service method
that Siebel CRM uses to determine charges for a service activity. You must not enclose this name in
quotes and it must identify a business service method that resides on the business service that the
ChargeBusinessService user property specifies. For example, ChargeBusinessServiceMethod1 can
contain a value of CreateServiceCharges. This value identifies a method of the FS Service Charge
business service.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Updating the Synchronization Status for Activities
The Update Status To Synchronized user property sets the status of some activities to Synchronized
during a handheld synchronization. It can contain one of the following values:
■ Y. Modify the activity status to Synchronized.
■ N or this user property does not exist. Do not modify the activity status to Synchronized.
The Update Status To Synchronized Types user property determines the types of activities that Siebel
CRM updates.
An activity that includes the Status field set to Synchronized in a Siebel Industry Application is read-
only in the Activities view.
Siebel CRM supports this user property in the CSSBCFINSActivity class but not subclasses of this
class.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Controlling Revenues
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control revenues.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
112
Specifying Revenue Aggregation Fields
The Revenue Aggregation Field n user property specifies the business component field that Siebel
CRM rolls up into the summary record from the detail records. Details and summaries reside in the
same business component. A summary record sums the values from one or more fields that reside
in the detail records for the summary date range. The value of this user property must contain the
name of a field that resides in the Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Item Detail business component. For
example, if you use the following value, then Siebel CRM sums the Amount Revenue field from the
detail records, and then stores this sum in the summary record:
Amount Revenue
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property.
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
Specifying Pop-up Revenues Lists
The Revenue Associate List user property displays an association list if the user clicks New to create
a new detail. The value for this user property is a Boolean value. If Y, and if the user clicks New to
create a new detail, then Siebel CRM displays a pop-up list that lists revenues. The associated search
specification for the current forecast series identifies the revenues that Siebel CRM displays. The user
must associate one of these revenues with the forecast instead of adding free text data.
You define this user property on the Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Item business component.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, but not to deactivate it or
to create a new instance of it.
Specifying the Field That Siebel CRM Copies for New Revenue
Forecasts
The Revenue Field Map: fieldname user property specifies the field that Siebel CRM copies from the
Revenue business component to one of the following business components. It copies this value if the
user creates a detail in the Forecast Item business component:
■ Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Item
■ Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Item Detail
Note the following:
■ The value of this user property must contain the name of a field that resides in the Revenue
business component.
■ The fieldname must identify the name of a field that resides in the Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Item
business component.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 113
For example, assume you define the user property that Table 20 describes. You define it on the
Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Item business component. In this example, Siebel CRM copies the value
of the Sales Rep Organization Id field of the Revenue business to the Organization Id field.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it
for each field that Siebel CRM must copy, or deactivate it.
Controlling Campaigns
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control campaigns.
Copying Contacts to Campaigns
The Copy Contact user property copies contact associations to a campaign if the user modifies the
status of the campaign from Planned to Active. Siebel CRM uses this user property with the DBM
Campaign business component. The value for this user property must contain a Boolean value. If
TRUE, and if a user modifies the status of a campaign from Planned to Active, then Siebel CRM copies
all of the contact associations for the planned campaign to the active campaign.
Specifying Group Only Visibility in Campaigns
The Group Visibility Only user property specifies that Siebel CRM use only group visibility in the
campaign. The value for this user property must contain a Boolean value. If TRUE, then Siebel CRM
uses only group visibility and you must set the Group Visibility user property to FALSE. Setting the
Group Visibility user property to FALSE makes sure Siebel CRM deactivates the Buscomp View Mode
user property so that it does not cause an inner join to the S_SRC_POSTN table.
Specifying Group Plus Team Visibility in Campaigns
The Group Visibility user property uses group plus team visibility in a campaign. The value for this
user property must contain a Boolean value. If TRUE, then Siebel CRM uses group plus team visibility.
Controlling Forecasts
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control accounts. It
includes the following topics:
■ Specifying Client Timeouts for Forecasts on page 114
■ Specifying Server Timeouts for Forecasts on page 114
Table 20. Example of the Revenue Field Map: fieldname User Property
User Property Value
Revenue Field Map: Organization Id Sales Rep Organization Id

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
114
■ Specifying Sleep Time Between Forecast Save Attempts on page 114
■ Specifying Search Specifications for Forecasts on page 114
■ Specifying Search Specifications for Forecast Rollup on page 115
■ Specifying Business Components for Forecast Analysis on page 115
■ Disallowing Users to Pick Dates in the Forecast Date Dialog Box on page 116
Specifying Client Timeouts for Forecasts
The Associate: Completion Timeout (Client) user property specifies the maximum number of seconds
that Siebel CRM waits on the client for a subordinate forecast to finish before it skips the association
and creates an error. If Siebel CRM does not create the association, then the user can manually
associate the subordinate forecast. Siebel CRM uses this user property in synchronous mode. The
value for this user property must contain an integer that is greater than 0.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it. If you deactivate this user property, then Siebel CRM uses the default
value.
Specifying Server Timeouts for Forecasts
The Associate: Completion Timeout user property for the server specifies the maximum number of
seconds that Siebel CRM waits for the Siebel Server for a subordinate forecast to finish before it skips
the association and creates an error. The description of the value that you use for this user property
is the same as the description of the value that you use for the Associate: Completion Timeout user
property for the client. For more information about this description, see “Specifying Client Timeouts
for Forecasts” on page 114.
Specifying Sleep Time Between Forecast Save Attempts
The Associate: Sleep Time Between Attempts user property specifies the number of seconds that
Siebel CRM waits after each attempt it makes to determine if a subordinate forecast is complete. The
description for the value that you use is the same as the description for the Associate: Completion
Timeout user property for the client. For more information, see “Specifying Client Timeouts for
Forecasts” on page 114.
Specifying Search Specifications for Forecasts
The Named Search: Forecast Series Date Range user property specifies the search specification that
Siebel CRM applies on the Revenue business component when it creates a forecast. It makes sure
that the revenues that the search returns occur in the Forecast Date range, by default.
The value for this user property must contain a valid search specification. This search specification
and the Auto and Assoc search specifications can use special variables that the Forecast Series and
Forecast Series Date business components define. For example, consider the following default value
of this user property:
[Date] >= '&FCST_DATE_LOWER_BOUND' and [Date] <= '&FCST_END_DATE'

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 115
This search specification returns the values that exist between the Date - Lower Bound field and the
End Date field of the Forecast 2000 -- Forecast Series Date business component. In this situation,
the &FCST_DATE_LOWER_BOUND variable represents the Date - Lower Bound field. If this field:
■ Contains a value. Siebel CRM sets the value of the History View Date to the value that the Date
- Lower Bound field contains.
■ Does not contain a value. If the History Edit field:
■ Contains a value. Siebel CRM sets the Date - Lower Bound field to the value that the History
Edit field contains.
■ Does not contain a value. Siebel CRM sets the Date - Lower Bound field to the value that
the Start Date contains.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it. If you
deactivate it, then you must make sure that the Siebel CRM limits the revenues in the forecast
according to date. To do this, you can modify the Auto and Assoc search specifications of the Forecast
Series. You cannot configure Siebel CRM to create a new instance of this user property.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
Specifying Search Specifications for Forecast Rollup
The Forecast Rollup user property contains a search specification that Siebel CRM applies to the
Forecast Detail business component during a forecast rollup. Siebel CRM rolls up only the detail
records that satisfy the search specification. It rolls up these records into the summary record. The
value for this user property must contain a valid search specification.
For example, the following search specification returns forecast details that the current user owns.
It also returns any subordinate records that exist that Siebel CRM rolls into this forecast:
[Link Type] = LookupValue('FCST_FCSTITEM_LINK_TYPE','Own Item') OR [Link Type] =
LookupValue('FCST_FCSTITEM_LINK_TYPE','Item')
To restrict this search specification according to a series, you can use the Forecast 2000 -- Forecast
Series business component.
It is recommended that you do not modify the value of this user property for a predefined business
component that Siebel CRM uses for forecasting.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
Specifying Business Components for Forecast Analysis
The Forecast Analysis BC user property specifies the name of the business component that provides
the records that Siebel CRM displays in the lower applet of a forecast analysis view. This type of view
allows the user to choose multiple forecasts, and then to view an aggregate summary of records in
a lower applet. The value for this user property must contain the name of a business component. For
example:
Forecast 2000 – Forecast Item Detail Flat

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
116
It is recommended that you do not modify the value of this user property for a predefined business
component that Siebel CRM uses for forecasting.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the values for this user property, but not to deactivate it or
create a new instance of it.
Disallowing Users to Pick Dates in the Forecast Date Dialog Box
The Skip Existing Forecast Series Date user property configures Siebel CRM to not allow the user to
pick a date in the Forecast Date dialog box in a Forecast view. It applies this restriction only if a
forecast already exists for the current user for the current date. It can contain one of the following
values:
■ Y. Do not display the date. The user cannot pick another date.
■ N. Display the date and allow the user to pick it.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, but not to deactivate it or
to create a new instance of it.
Allowing Users to Update Closed Service Requests
The Always Enable Field n user property updates the fields that reside in a closed service request. It
must contain the name of the field that Siebel CRM must update.
If a user sets the Status field on a service request to Closed, then Siebel CRM sets the Sub-Status
field to Resolved and makes the record read-only except for the Status and Sub-Status fields. The
CSSBCServiceRequest specialized business component class controls this behavior. For important
caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28.
If the business component includes:
■ One instance of this user property. This instance must not include the numeric suffix.
■ More than one instance of this user property:
■ The first instance must not include the numeric suffix.
■ Subsequent instances must include the numeric suffix, numbered sequentially.
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property, modify the values for it, or to create
a new instance of it.
Allowing Users to Update Assets
The SubCompUpdate On Save user property specifies whether the user can update an asset record.
It can contain one of the following values:
■ TRUE. The user can update an asset record.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 117
■ FALSE. The user cannot update an asset record and Siebel CRM disables any
SubCompCanUpdate and SubCompUpdate field user properties that exist on fields that the
business component contains. For more information, see “Updating Assets” on page 93 and
“Cascading Asset Updates” on page 94.
Adding Contacts to the Action Business Component
The Contact MVG PreDefault Expression user property identifies the predefault contact record that
Siebel CRM adds to the Contact multivalue field of the Action business component. The value for this
user property must use the following format:
Parent: 'Contact.Id', 'Service Request.Contact Id', 'Service Agreement.Contact
Person Id'
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
Siebel CRM supports this user property for business components that reference a CSSBCActivity
class, such as CSSBCFINSActivity. The business component where you add this user property must
include a multivalue field named Contact Id or Contact Id (Thin).
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
Creating Numbered Revisions of Quotes, Orders, or
Agreements
The Revision Copy Field n user property and Revision Field property creates a numbered revision of
a quote, order, agreement, and so on. If the user clicks Revise to create a new record as a copy of
the current record, then this user property copies the value that resides in a field of the current
record to the new record. Note the following:
■ This user property must contain the name of a business component field.
■ You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance
of it, or deactivate it.
■ You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
For more information, “Revise Method” on page 33.
In the following example, you use the Revision Copy Field and Revision Field user properties to create
an updated revision of a quote.
To create numbered revisions of quotes, orders, or agreements
1
Open the Business Component User Properties list for the Quote business component.
For more information, see “Viewing a Business Component User Property” on page 108.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
118
2 Add a user property using values from the following table.
3 Add a user property using values from the following table.
4 Add a user property using values from the following table.
5 Compile your modifications.
6 Open the client, and then use the Revise button to create a new quote.
The Revision field contains the next number that occurs in the revision sequence. This number
is one more than the maximum number that the current record contains. The Quote Number and
Credit Card Number fields contain the same values that the current record contains.
Extending Quote Quantities
The Extended Quantity Field user property defines the line item business component that Siebel CRM
uses for a quote. For example, Quote Item. The value for this user property must contain the field
name for the Extended Quantity in the line item. For example:
Extended Quantity Requested
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, but not to deactivate it or
create a new instance of it.
Automatically Assigning Responsibilities to Users
The AutoPopulateResponsibility user property associates a responsibility with a new user when Siebel
CRM creates a record. It must contain a Boolean value. If TRUE, then Siebel CRM associates a
responsibility with a new user when it creates a record. The New Responsibility field for the current
user identifies this responsibility. Note the following:
■ This user property requires that the responsibility multivalue field is named Responsibility.
■ If Siebel CRM uses the business component in the EAI or Siebel Adapter context, then it ignores
this user property.
Property Value
Revision Copy Field 1 Quote Number
Property Value
Revision Copy Field 2 Credit Card Number
Property Value
Revision Field Revision

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 119
■ You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance
of it, or deactivate it.
Making Sure the Current Employee Holds a Position
The Required Position MVField user property modifies the behavior of the WriteRecord method to
require that the current employee must hold at least one position. The value for this user property
must use the following format:
"[
employee_flag
]", "[
position multivalue field
]"
where:
■ employee flag identifies the employee flag field that references the EMP_FLG column of the
S_CONTACT table.
■ position multivalue field identifies the multivalue field that contains the positions that the
employee holds. You must make sure that the relationship that this multivalue field uses
references the S_PARTY_PER table. You must not use the relationship that Siebel CRM uses with
the positions that reference the employee or contact record that references the S_POSTN_CON
table.
The code that Siebel CRM runs during a WriteRecord event determines whether it sets the value of
the Employee Flag to Y:
■ If it is Y, and if a position is associated with the current employee record, then no error occurs.
■ If it is not Y, or if a position is not associated with the current employee record, then the
WriteRecord event does not start and Siebel CRM creates an error.
If the EAI or Siebel Adapter context uses the business component, then Siebel CRM ignores this user
property.
You can use this user property only with a business component that stores employee information.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
Setting the Close Out Flag Field
The CloseOutFlag user property specifies the value of the CloseOut Flg field for the parent business
component. It must contain a Boolean value of Y or N. You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate
this user property or modify the value for it, but not to create a new instance of it.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Siebel CRM Data
120
Specifying State Models
The State Model user property adds a business component to the business components that a multi-
value group applet displays. This applet resides in the State Model business component. The value
for this user property must contain a Boolean value. If Y, then Siebel CRM adds the business
component where you define this user property to the multi-value group applet. For more
information about the State Model, see Siebel Applications Administration Guide.
Specifying Assignment Objects
The Assignment Object user property identifies the assignment object that Siebel CRM uses when it
sets the Assignment Object Name (AsgnObjectName) parameter of the Assignment Manager server
component when it runs an interactive assignment. The value for this user property must contain the
name of an assignment object that is a child of a workflow policy object. You must enclose this
assignment object in quotes.
For example, the Activity List View references the Action business component. If you set the
Assignment Object user property on the Action business component to Activity, and if the user
chooses Assign from the Tools menu while the user is in a child form applet in the Activity List View,
then Siebel CRM adds the activity instead of some other object to the Assignment Manager queue
for reassignment to a new owner.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property only if you disable interactive
assignment, and only if you also remove any related controls from the client. You can configure
Siebel CRM to modify the values for this user property, but not to create a new instance of it.
Protecting Seed Data
The Protect Seed Data user property prevents Siebel CRM from modifying seed data records of a
business component. You can set it to one of the following values:
■ Y. The user cannot modify or delete seed data records.
■ N. The user can modify or delete seed data records.
For example, if you add this user property with a value of Y to the Responsibility business component,
then the user cannot modify or delete any seed data responsibility record that starts with zero (0).
you can start the client in one of the following ways to override this user property:
■ Append the following parameter to the command line that opens Siebel CRM, as defined in the
properties dialog box for Siebel CRM shortcut in Windows:
/editseeddata
■ Append the following parameter to the UNIX command line that opens Siebel CRM:
/editseeddata
You can configure Siebel CRM to create a new instance of this user property, but not to modify the
value for it or deactivate it.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Search and Sort
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 121
Controlling Search and Sort
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control search and sort.
It includes the following topics:
■ Optimizing Sort Searches on page 121
■ Removing Duplicate Records From Queries on page 122
■ Overriding Sort Specifications on Business Components on page 123
■ Sorting According to the View Mode That the Business Component Uses on page 124
■ Disabling Automatic Trailing Wildcards in Queries on page 125
■ Adding Search Criteria to the Query Assistant on page 126
■ Saving Query Results in Target Lists on page 127
■ Specifying How to Sort Predefined Queries for Opportunities on page 127
■ Specifying Search Specifications for the Action Business Component on page 129
■ Specifying Search Specifications for Nonsales Rep Views on page 129
Optimizing Sort Searches
The Sort Search Optimization user property helps a database work with a rules-based optimizer
(RBO). You can set it to one of the following values:
■ TRUE. Enable sort search optimization.
■ FALSE. Disable sort search optimization.
The Sort Search Optimization user property chooses an index from multiple indexes. To do this, it
adds a search term to the SQL statement that does not modify the search result but that provides
the rules-based optimizer with more information to help it choose the correct index. The Sort Search
Optimization user property sets the column in this search term to the first column of the sort
specification. For example, assume a query includes the following sort:
ORDER BY
NAME, START_DT
In this example, the Sort Search Optimization user property adds the following search term to the
SQL statement:
NAME >= '\1'
where:
■ '\1' represents the ASCII 0 character.
Searching for values that are greater than ASCII 0 does not remove any information from the search
result, but this search term helps the optimizer to choose the most effective index. This configuration
improves the query performance when the business component specifies a sort specification and if
the optimizer fails to choose the correct index. This access requires Sales Rep or Organization
visibility, because All or All Across Organization visibility typically overrides sort specifications.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Search and Sort
122
The Sort Search Optimization user property works only with Oracle 8 databases or with Oracle 9i
databases that support a rules-based optimizer. It does not work with cost-based optimizers. Siebel
CRM does not support it starting with Siebel CRM release 8.x. Siebel CRM disables Sort Search
Optimization for DB2. For more information about rules-based optimizers, see Oracle9i Database
Performance Tuning Guide and Reference.
Removing Duplicate Records From Queries
The Duplicate Elimination user property removes duplicate records from the result set of a query on
a business component that runs in ForwardOnly mode. This result set might include multiple copies
of the same record if one of the following situations exists:
■ The intersection table includes duplicate rows. For example, Start Date is part of the association,
and associations with different start dates are logically unique.
■ The join references one or more destination columns that are not unique, and no join constraints
or run-time search specifications exist.
You can use the Duplicate Elimination user property to determine how Siebel CRM handles these
multiple copies. The value for this user property must contain a Boolean value. If:
■ TRUE. Siebel CRM only aggregates the set of unique records that the memory currently contains.
Do not do this aggregation as part of the SQL in the database layer.
■ FALSE or this user property does not exist on the business component. Siebel CRM
aggregates the set of unique records as part of the SQL that runs in the database layer. This
aggregation provides superior performance. However, if any of the following conditions apply,
then the Siebel Object Manager does this aggregation after Siebel CRM reads all rows from the
database:
■ The Database Aggregation Flag parameter in the Server Datasource section of the
configuration file is FALSE. This configuration sets Siebel CRM to server mode.
■ The DBAggregation parameter in the application .cfg file on the Mobile Web Client is FALSE.
■ A search specification includes a clause that the database cannot evaluate. Siebel CRM must
evaluate this specification in memory.
■ Aggregation in the database fails for some reason.
This user property determines how Siebel CRM does aggregation. You must first make multiple
settings in Siebel Tools to enable aggregation on a list column or for a multivalue link.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it. No more than one instance can exist for each business component.
For more information about:
■ Setting parameters in the configuration file, see Siebel System Administration Guide.
■ Account hierarchies, see Siebel Applications Administration Guide.
■ Configuring a list applet to display totals or to display totals in a separate applet for a multivalue
link, see Configuring Siebel Business Applications.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Search and Sort
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 123
■ ForwardOnly mode, see Siebel Object Interfaces Reference.
Using Duplicate Elimination with a Denormalized Relationship
A situation might exist where Siebel CRM might denormalize the relationship and view that it uses
for associations that exist in the context of the parent record. It might repeat the same parent row
in the result set as an association to different child records that reside in the intersection table even
if no duplicate associations exist. In this situation, it might be preferable to configure Siebel CRM to
not reject duplicates.
Overriding Sort Specifications on Business Components
The All Mode Sort user property overrides the default sort specification that a business component
contains. It can contain one of the following values:
■ Normal. Use the Sort Specification property of the business component. This value allows the
user to run a predefined query that incorporates a SORT. Any query that Siebel CRM does in a
workflow process uses this Sort Specification property even if no visibility is set for the view.
■ TRUE. Override the Sort Specification property of the business component. Use the U1 index.
This index is the predefined user key. If Siebel CRM defines this user key on the primary
extension table, especially for a business component that references the S_PARTY table, then
this behavior reverts to Normal.
■ FALSE. Remove all sorting.
Guidelines for Overriding Sort Specifications on Business Components
Siebel CRM overrides the sort specification on the business component for some visibility types to
force the view to use an ORDER BY sort with the predefined user key. The All Mode Sort user property
determines whether Siebel CRM overrides this sort specification. If it does do this override, then this
user property determines the sort that Siebel CRM applies, if any, to the business component for the
affected views.
If you set the Visibility Applet Type property of the view to one of the following values, then the All
Mode Sort user property affects this view:
■ All
■ Catalog
■ Group
■ Manager
■ Organization
■ Sub-Organization
Note the following:
■ If you set this user property to Personal or Sales Rep, then the All Mode Sort user property does
not affect the view.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Search and Sort
124
■ If you configure the default sort order so that it sorts one of these views, then this configuration
might display a large amount of data that Siebel CRM typically sorts only according to a user key.
■ If you use All Mode Sort to override the default sort behavior, then it is recommended that you
contact your database administrator to get guidance on how the database indexes the sort-by
fields.
■ It is recommended that you performance test the view and any reports that use the view.
Sorting According to the View Mode That the Business
Component Uses
The ViewMode Sort: mode_num user property specifies a sort specification on a business component
that is in view mode. The value for this user property must use the following format:
field name1
,
field nameN
where:
■ field name identifies the name of a business component field.
The order that you use in this value determines the priority that Siebel CRM uses for each field that
the sort uses.
CAUTION: To avoid a performance problem, any sort that you define must reference an indexed
column. The items in this sort sorts must occur in the same sequential order that this index uses.
This configuration includes any sort that you define with the ViewMode Sort user property.
mode_num contains an integer that identifies a view mode. Table 21 describes the integers that you
can use. For information about these integers, see Siebel Object Interfaces Reference.
You can use the ViewMode Sort user property to sort items in a view that uses visibility other than
the Personal or Sales Rep visibility. You can use it with the following views:
■ All
■ Catalog
Table 21. View Modes That You Can Use with the View Mode Sort User Property
Integer View Mode
1 ManagerView
3 AllView
5 OrganizationView
7 GroupView
8 CatalogView
9 SubOrganizationView

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Search and Sort
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 125
■ Group
■ Manager
■ Organization
■ Sub-Organization
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
Example of Configuring the View Mode Sort User Property
If you set the All Mode Sort user property to FALSE for a business component, and if Siebel CRM
displays this business component in a view mode that the ViewMode Sort user property supports,
then Siebel CRM ignores all other sort specifications. For example, assume Siebel CRM must sort the
records in a business component according to the Last Name field, and then by First Name, and that
it must do this sort only if it displays this business component in an All view mode. Table 22 describes
the user properties that you can add to the business component to support this example. For more
information, see “Overriding Sort Specifications on Business Components” on page 123.
Disabling Automatic Trailing Wildcards in Queries
The Disable Automatic Trailing Wildcard Field List user property disables the automatic trailing
wildcards that Siebel CRM uses in a query on a field. You cannot disable this user property for a
DTYPE_PHONE field.
The value for this user property must contain a list of fields separated by commas. You can add this
user property to a business component to disable automatic trailing wildcards for individual fields.
For example:
■ Name. Disable Automatic Trailing Wildcard Field List.
■ Value. First Name, Last Name.
To disable automatic trailing wildcards
1
In the Siebel Web Client, navigate to the Administration - Server Configuration screen, Enterprises,
and then the Component Definitions view.
2 In the Component Definitions list, locate the relevant component.
For example, to disable automatic trailing wildcards for Siebel Sales, locate the following
component:
Table 22. Example of Configuring the View Mode Sort User Property
User Property Value
All Mode Sort FALSE
ViewMode Sort:3 Last Name, First Name

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Search and Sort
126
Sales Object Manager (ENU)
3 Click Menu, and then click Start Reconfiguration.
4 In the Component Parameters list, locate Automatic Trailing Wildcard, and then set the Value field
to FALSE.
5 In the Component Parameters list, click Menu, and then click Commit Reconfiguration.
6 Restart the server component.
For more information about starting and stopping server components, see Siebel System
Administration Guide.
Adding Search Criteria to the Query Assistant
The QueryAssistantNumQueries user property adds a search criterion to the Query Assistant. The
predefined Query Assistant uses four search criteria in a query. Siebel CRM displays them as four
rows that the user can choose. It also includes an operator for the query and the value that Siebel
CRM must query.
Table 23 lists the predefined fields in the Query Assistant business component that correspond to
each other for each criteria.
To add search criteria to the Query Assistant
1
In the Business Component User Properties list, locate the QueryAssistantNumQueries user
property, and then set the Value property to 5.
For more information, see “Viewing a Business Component User Property” on page 108.
2 In the Object Explorer, click Field.
3 In the Fields list, click the Field4 field, choose the Edit menu, and then click Copy Record.
4 Set the Name property to Field5.
5 In the Fields list, click the Operator4 field, choose the Edit menu, and then click Copy Record.
6 Set the Name property to Operator5.
7 In the Fields list, click the Value4 field, choose the Edit menu, and then click Copy Record.
8 Set the Name property to Value5.
Table 23. Fields That Correspond to Each Other for Each Criteria
Query Field Operator Field Value Field
Field1 Operator1 Value1
Field2 Operator2 Value2
Field3 Operator3 Value3
Field4 Operator4 Value4

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Search and Sort
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 127
9 Add a control for each field that maps to the Query Assistant applet.
10 Display the controls in the Web layout.
Saving Query Results in Target Lists
The TargetProp n user property specifies a target list for a business component. It uses the following
format:
"
EntityDisplayName
", "
MVFName
", "
ListCategory
"
where:
■ EntityDisplayName identifies a language-independent code value that the SLM_FIELD_DISPLAY
list of values contains.
■ MVFName identifies the name of the multivalue field that stores the target list.
■ ListCategory identifies one of the display values that the SLM_LST_CATEGORY list of values
contains. These values are Account, Contact, Employee, Position, or Prospect.
For example:
"Accounts", "List Mgmt List Id", "Accounts"
Targeting is a type of query that allows the user to save query results in a target list, and then apply
this list to other views.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it
for each target list, or deactivate it.
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
For more information about how to configure a target list, see the topic about global target list
management in the Siebel Applications Administration Guide.
Specifying How to Sort Predefined Queries for
Opportunities
The Sort Field Map n user property determines how Siebel CRM sorts a predefined query on a
business component that stores opportunity data. It uses the following format:
"
field
", "
redirect field
"
where:
■ field is the name of a multivalue field that resides in the current business component. This field
stores opportunity data that Siebel CRM maps to a field that resides in the Revenue business
component. The Revenue field and the Close Date field are examples of this field.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Search and Sort
128
■ redirect field is the name of a single-value field that resides in the current business component.
This field stores opportunity data. Siebel CRM maps it to the same revenue field that resides in
the primary revenue record for the opportunity. The Primary Revenue Amount field and the
Primary Revenue Close Date field are examples of a redirect field.
A one-to-many relationship exists between a business component that handles opportunity data and
the Revenue business component. This relationship enables the master and detail view that displays
the revenue records that Siebel CRM associates with an opportunity. The Opportunity business
component and the Global Account Opportunity business component are examples of business
components that handle opportunity data.
Opportunities typically include multivalue fields that reference fields that reside in the Revenue
business component. For example, the Revenue field that resides in the Opportunity business
component references the Revenue field that resides in the Revenue business component. An
existing predefined query on opportunities might include a sort specification that references one or
more of these multivalue revenue fields. The Sort Field Map user property redirects this sort to the
corresponding single-value field in the opportunity at runtime. For example, it redirects a sort
specification that resides on the Revenue multivalue field in the Opportunity business component to
the Primary Revenue Amount field. This field contains the revenue amount for the primary revenue
record of the opportunity. You can use the Sort Field Map n user property to specify how Siebel CRM
does this redirect.
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. However, you typically add
multiple instances to redirect multiple revenue fields. The numeric suffix differentiates these
instances. For more information, see “Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
You must not configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but
you can configure Siebel CRM to create a new instance of it.
For information about configuring a sort specification in a predefined query, see Configuring Siebel
Business Applications. For information about the primary revenue record for an opportunity, see
Siebel Applications Administration Guide.
Example of Configuring the Sort Field Map User Property
For an example of configuring the Sort Field Map user property, assume you define the user
properties that Table 24 describes in the Opportunity business component.
In this example, the following sort specification in a predefined query provides a result set that Siebel
CRM sorts in descending order according to the revenue amounts that exist in the primary revenue
records of the opportunities:
'Opportunity'.Sort = "Revenue (Descending)"
Table 24. Example of Configuring the Sort Field Map User Property
User Property Value
Sort Field Map 1 "Revenue","Primary Revenue Amount"
Sort Field Map 2 "Close Date","Primary Revenue Close Date"

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Search and Sort
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 129
The following sort specification in a predefined query provides a result set that Siebel CRM sorts
according to the revenue close dates that exist in the primary revenue records:
'Opportunity'.Sort = "Close Date "
Alternative to Configuring the Sort Field Map User Property
For a new predefined query, it is recommended that you do not configure the sort specification to
reference a multivalue field. You can configure the sort specification to reference a single-value field
instead of using the Sort Field Map user property to do a redirect. For example, you can use the
corresponding Primary Revenue field. You can use the following instead of using
'Opportunity'.Sort = "Close Date ":
'Opportunity'.Sort = "Primary Revenue Close Date"
Specifying Search Specifications for the Action Business
Component
The Activity SearchSpec user property specifies a search specification for the Action business
component. The value for this user property must contain a valid search specification. For example:
[Status]= LookupValue('EVENT_STATUS', 'Open') AND [Class] =
LookupValue('FS_ACTIVITY_CLASS', 'Sales Activity')
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it. For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property
Format” on page 64.
Specifying Search Specifications for Nonsales Rep
Views
The Non-SalesRep View Mode SearchSpec user property specifies the search specification that Siebel
CRM uses on a business component if it is not in Sales Rep mode. The value for this user property
must contain a valid search specification for the business component.
The fields that you include in this search specification must exist in the business component and the
values for the fields must be valid. For example, the following search specification is valid:
"[Secure Flag] = 'N' OR [Secure Opty Id] IS NOT NULL"
This specification references the Secure Flag field and the Secure Opty Id field. It configures Siebel
CRM to display business component records that are not secure. It also displays records that include
a value in the Secure Opty Id field. This configuration indicates that the current record is not secure.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Visibility Filters
130
Controlling Visibility Filters
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control visibility filters.
It includes the following topics:
■ Controlling Global Account Visibility on page 130
■ Controlling My Visibility Filters on page 131
■ Controlling Manager Visibility Filters on page 132
Controlling Global Account Visibility
The dynamic hierarchy user properties define relationships that control visibility in Global Accounts
views that the Accounts screen contains. The value for these user properties must contain the name
of a field that resides in the current business component, not enclosed in quotes.
Siebel CRM provides default values for this user property for the business components that the
following items in Global Account views reference:
■ Subaccounts
■ Contacts
■ Activities
■ Opportunities
■ Sales teams
If your Siebel CRM implementation does not use global accounts, then you can deactivate this user
property. It is recommended that you seek technical assistance because inactivating this user
property might affect the account reporting hierarchy relationship. For more information, see
“Getting Help From Oracle” on page 20.
You must not configure Siebel CRM to create a new instance of this user property.
Dynamic Hierarchy Id Field
The DynHierarchy Hierarchy Id Field user property specifies a business component field that defines
a join to an account hierarchy. This relationship determines the business component records that
Siebel CRM displays in the flat list that it associates with an account hierarchy in Global Accounts
views.
For example, the value of this user property in the Global Account Action business component is
Dynamic Hierarchy Id. The content of the Dynamic Hierarchy Id field on the Global Account Action
business component is the ID of a record that resides in the table that defines account hierarchies.
Siebel CRM associates a Global Account Action record with the account hierarchy where the activity
account resides. Siebel CRM displays this record in the flat list of activities for the parent account
and for any other account that exists in the hierarchy.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Visibility Filters
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 131
Dynamic Hierarchy Parent Field Id
The Dynamic Hierarchy Parent Field Id user property specifies a business component field that stores
the ROW_ID of the parent account for the account hierarchy. For example, Account. This field must
be active or the Force Active property of the field must be TRUE.
Dynamic Hierarchy Visibility Organization Id Field
The DynHierarchy Visibility Organization Id Field user property specifies a business component field
that defines the join between accounts and organizations. This relationship identifies the records that
Siebel CRM displays in the flat list of the business component if the user clicks All Global Accounts
or All Global Accounts Across Organizations.
For example, the value of this user property on the Global Account Contact business component is
DynHierarchy Visibility Organization Id. The default value of the DynHierarchy Visibility Organization
Id field is the alias of the join that joins accounts and organizations. Siebel CRM associates a Global
Account Contact record to the same organization that it associates with the account.
If the user sets visibility to All Global Accounts, then the hierarchy only displays accounts that
reference the same organization that the user position references. This organization includes only
the contact records that the account contains that Siebel CRM displays in the flat list of contacts for
a hierarchy.
Dynamic Hierarchy Visibility Position Id Field
The DynHierarchy Visibility Position Id Field user property specifies the business component field that
specifies the join to positions. This relationship defines the records that Siebel CRM displays in the
flat list of the business component if the user clicks My Global Accounts.
For example, the value of this user property on the Global Account Opportunity business component
is DynHierarchy Visibility Position Id. The default value of the DynHierarchy Visibility Position Id field
is the alias of the join that joins positions or team members and accounts. Siebel CRM associates a
Global Account Opportunity record with the team members that exist on the account. If the user
clicks My Global Accounts, then the hierarchy displays only the accounts that include the user
position on the account team. It displays the opportunity records in the flat list of opportunities for
an account hierarchy. It displays an opportunity only if the current user is on the account team that
includes this opportunity.
Controlling My Visibility Filters
The Employee Link user property restricts data visibility to the data that Siebel CRM associates with
the user login. The value for this user property must contain the name, not enclosed in quotes, of a
link that includes the following items:
■ Parent business component is Employee.
■ Child business component is the current business component.
For example:
Employee/My Competitor

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Records
132
Siebel CRM uses the business component where you set this user property to configure the My view
that restricts data according to the user name that the user enters during the login instead of the
position.
For example, the My Competitor business component provides data for the SI Com Tracked
Competitors View in Siebel Briefings. Siebel CRM labels this view as My Tracked Competitors in the
client. It sets the Employee Link user property that resides on the My Competitor business
component to Employee/My Competitor. This view only lists competitor records that the Employee/
My Competitor link associates with the user. These are the competitors that the user enters.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it. No more than one instance can exist for each business component.
Controlling Manager Visibility Filters
The Manager List Mode user property specifies the records that Siebel CRM displays in a manager
view. The value for this user property must contain one of the following values:
■ Primary. Display only the records that are related to the primary team members who report to
this manager.
■ Team. Display the records for all people who report to the manager. Siebel CRM does a subquery
for the My Team's view so that it can get and display the accounts, opportunities, and so on for
all members that the team contains, and not only for the primary team members. Performance
is slower but this query yields more data.
Controlling Records
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control records. It
includes the following topics:
■ Making Records Read-Only According to a Field Value on page 133
■ Disabling Modifications to Saved Records on page 133
■ Allowing Administrators to Modify Records on page 133
■ Preventing Administrators from Deleting Records on page 134
■ Preventing Administrators from Updating Records on page 134
■ Calculating Values When Writing Records on page 135
■ Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records on page 135
■ Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records According to Maximum Values on page 135
■ Setting Business Components to Read-Only According to a Field Value on page 136
■ Setting Business Components to Read-Only According to a Name on page 137
■ Using Literals Instead of Bind Variables When Merging Records on page 137

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Records
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 133
Making Records Read-Only According to a Field Value
The BC Read Only Field user property specifies the business component field that determines
whether a record is read-only. If the value that this field contains is TRUE, then the current record
is read-only.
If you set the Admin Mode Flag property to TRUE, then this setting overrides the BC Read Only Field
user property. For information, see “Allowing Administrators to Modify Records” on page 133.
Disabling Modifications to Saved Records
The No Change Field n user property disallows modifying a field value after Siebel CRM saves the
record. It must specify the name of a business component field, not enclosed in quotes.
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
Allowing Administrators to Modify Records
The Admin Mode Field user property determines whether a business component is currently in Admin
mode. It allows an administrator to delete, insert, merge, or update records regardless of how you
set the following business component properties:
■ No Delete
■ No Insert
■ No Merge
■ No Update
Siebel CRM typically sets the Admin Mode Flag property of an administrative view to TRUE to allow
an administrator to configure Siebel CRM to do these operations regardless of how you set these
properties.
Requirements for Using Admin Mode
If you set the Admin NoDelete user property on a business component, then Siebel CRM cannot
delete records in any view that references this business component. This situation also applies for
the Admin NoUpdate user property. For more information about Admin Mode, see Siebel Security
Guide and Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
The value for this user property must contain the name of a field, not enclosed in quotes. This field
must possess the following characteristics:
■ Reside in the current business component
■ Active

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Records
134
■ Calculated
■ Of type DTYPE_BOOL
■ Contain a value of ""
Siebel CRM uses the value of the Admin Mode Flag property of the current view to determine the
business component behavior at runtime. For example, assume you create a calculated business
component field and name it IsAdminMode. It is recommended that you use this naming format, but
it is not required. You add the Admin Mode Field user property with a value of IsAdminMode to the
business component.
CAUTION: All views and drilldowns that a screen contains that are enabled for Admin Mode also
work in Admin Mode because of their subordinate relationship to the screen. This behavior applies
even if you set the Admin Mode Flag property of a view to False.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, deactivate it, or create a
new instance of it, but no more than one instance for each business component.
Using a Script to Set the Admin Mode
You can use the Admin Mode Field user property in a script to determine if a business component is
currently in Admin mode. The following example displays Y only if the business component is
currently in Admin mode:
function BusComp_NewRecord ()
{
var isAdmin = this.GetFieldValue("IsAdminMode");
var WshShell = COMCreateObject("WScript.Shell");
WshShell.Popup(isAdmin);
}
Preventing Administrators from Deleting Records
The Admin NoDelete user property prevents Siebel CRM from deleting business component records
if a view is Admin mode. It must contain a Boolean value of Y or N. If a business component does
not include this user property, then Siebel CRM defaults this value to N.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it. No more than one instance can exist for each business component.
For more information, see “Allowing Administrators to Modify Records” on page 133.
Preventing Administrators from Updating Records
The Admin NoUpdate user property prevents Siebel CRM from updating business component records
if a view is in Admin mode. It must contain a Boolean value of Y or N. If a business component does
not include this user property, then Siebel CRM defaults this value to N.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it. No more than one instance can exist for each business component.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Records
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 135
For more information, see “Allowing Administrators to Modify Records” on page 133.
Calculating Values When Writing Records
The Calc Actual OnWriteRecord user property calculates a number when Siebel CRM writes a record.
It can contain one of the following values:
■ Y. Calculate the Actual Number.
■ N. Do not calculate the Actual Number.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records
The Sequence Field user property configures a sequence field to create a sequential line number
when Siebel CRM creates a new record or copies a record. This user property must contain the name
of the business component field that corresponds to the sequence number column that resides in the
table that this business component references. This field is typically Line Number or Sequence
Number. Note the following:
■ The business object must reference a sequence business component.
■ You must set the Insert Position property to LAST for each applet that displays a record from the
numbered detail business component. If this user property is empty, then unexpected behavior
might result in the line numbers that Siebel CRM creates in the applet.
■ You must do other configuration work. For more information, see the topics that describe creating
a sequence field in Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
For information about how Siebel CRM uses a sequenced field to number a new record, see
“Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records According to Maximum Values” on page 135.
Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records
According to Maximum Values
The Sequence Use Max user property creates a sequence number for a new or copied record. It must
specify one of the following values:
■ Y. Set the sequence number to the maximum existing sequence number plus 1.
■ N or this user property does not exist. Set the sequence number to the sequence number of
the current record plus 1. Renumber other records, if necessary.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Records
136
For example, Table 25 describes a configuration that defines the Line Number field as the sequence
field and sets the sequence for any new or copied record to the value of the maximum existing
sequence plus 1. For more information, see “Specifying Sequential Line Numbers for New Records” on
page 135.
Setting Business Components to Read-Only According
to a Field Value
The Parent Read Only Field user property sets a business component to read-only according to the
value that a field contains. It restricts the detail records that Siebel CRM displays in a multivalue
group. The value for this user property must use the following format:
buscompname
.
fieldname
where:
■ buscompname specifies the name of the parent business component.
■ fieldname specifies the name of a field that resides in the parent business component. If Siebel
CRM evaluates the value of this field to TRUE or Y, then it sets the current business component
to read-only. Note the following:
■ The business component that contains this field must be a parent or grandparent of the
business component that Siebel CRM sets to read-only. A link or a series of links must create
this relationship.
■ The Link Specification property of this field must be set to TRUE. If it is FALSE, then this user
property does not work correctly. The exception is if Siebel CRM displays the child record in
the multivalue field in the parent business component, then you can set this Link
Specification property to FALSE.
To restrict the detail records that Siebel CRM displays in a master and detail view, you must make
sure that some other business object does not use the business component that Siebel CRM sets to
read-only.
You add this user property to the business component that Siebel CRM must set to read-only.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
For more information about the Parent Read Only Field user property, see Configuring Siebel Business
Applications.
Table 25. Example of the Sequence User Properties
User Property Value
Sequence Field Line Number
Sequence Use Max Y

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Records
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 137
Setting Business Components to Read-Only According
to a Name
The Parent Read Only Field: buscompname user property specifies the name of a field that resides
in a parent business component. This business component contains a calculated field that Siebel CRM
evaluates to TRUE or FALSE or Y or N. This behavior is similar to “Setting Business Components to
Read-Only According to a Field Value” on page 136, except that the name instead of the value specifies
the name of the parent business component. If the calculated field evaluates to TRUE or Y, then
Siebel CRM sets the child business component to read-only.
The value for this user property must contain a field name.
This user property uses multiple fields as part of the decision to make the current record read only.
For example, Table 26 describes a configuration that makes a contact read-only in a parent service
request, account, or opportunity according to different fields that reside in these parents. If the
current record that resides in the Contact business component includes a parent of Service Request,
Account, or Opportunity, and if Siebel CRM evaluates the field that the Value property identifies to
TRUE, then it sets the record to read-only.
Using Literals Instead of Bind Variables When Merging
Records
The Use Literals For Merge: table_name user property creates a literal in an SQL statement for
predicates that reside on a column that possesses low cardinality. It can contain one of the following
values:
■ TRUE. Use a literal value instead of a bind variable as criteria in an SQL statement where the
predicate resides on a column that is a foreign key to table_name.
■ FALSE or the user property does not exist. Use a bind variable instead of a literal value.
table_name identifies the name of a table. The current business component includes a field that is a
foreign key column to this table.
For example, assume you add the following user property and set the value for it to TRUE:
Use Literals For Merge:S_BU
In this example, Siebel CRM uses literals instead of bind variables in SQL statements whose
predicates reside on a column that is a foreign key to S_BU.
Table 26. Example of Using the Parent Read Only Field: buscompname User Property
User Property Name Value
Parent Read Only Field: Service Request field name
Parent Read Only Field: Account field name
Parent Read Only Field: Opportunity field name

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Fields
138
Siebel CRM uses a bind variable for all predicates when it merges records. In some situations, if the
cardinality of the column is low, and if using an index is more efficient, then DB2 does table scans.
You add this user property to the business component where Siebel CRM merges records.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
Controlling Fields
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control fields. It includes
the following topics:
■ Making Fields Active on page 138
■ Making Fields Read-Only on page 139
■ Disallowing Empty Fields on page 139
■ Disabling Field Deletion on page 140
■ Setting Field Values According to Conditions on page 140
■ Updating Fields When Siebel CRM Updates Other Fields on page 141
■ Calling Methods When Siebel CRM Updates Fields on page 142
■ Setting the Field Created Date to the Saved Date on page 143
■ Updating the Planned Field if the Start Date Field Is Modified on page 143
■ Overriding the Type for Fields That Users Read from Right-To-Left on page 143
■ Setting Default Values for Fields That Use Drop-Down Lists on page 144
■ Modifying the Currency That a Field Uses on page 145
■ Specifying Field Name Prefixes for File Attachment Business Components on page 145
For information about using field user properties to control fields, see “Field User Properties” on
page 89.
Making Fields Active
The following user properties together determine if a record is active:
■ Active Field. Specifies the business component field that Siebel CRM uses as the active flag for
this business component.
■ Active Value. Specifies how to interpret the value of this flag.
The value for the Active Field user property must contain the name of a field that resides in the
current business component and that Siebel CRM uses as the active flag for this business component.
You must enclose this value in quotes.
If the value of the active flag for a record is:

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Fields
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 139
■ Y. This record is active in any of the following situations:
■ The value of the Active Value user property is Y.
■ The Active Value user property does not exist for a business component.
■ N. If the value of the Active Value user property is N, then this record is active.
Consider the following example:
■ The value of the Active Field user property on the Quote business component is Active.
■ The Active Value user property does not exist on the Quote business component.
In this situation, if the value of the Active field on a record is Y, then this record is active.
Consider the following example:
■ The value of the Active Field user property of the Fund business component is Locked Flag.
■ The value of the Active Value user property of the Fund business component is N.
In this situation, if the value of the Locked Flag field on a record is N, then this record is not locked.
Siebel CRM can update an active record. It cannot update a record that is not active.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it. No more than one instance can exist for each business component.
Making Fields Read-Only
The Field Read Only Field: fieldname user property sets a business component field to read-only. The
fieldname value for this user property must contain the name of a business component field. This
field must contain a Boolean value.
If Siebel CRM evaluates the field that this user property references to TRUE at runtime, then it sets
the field that fieldname specifies to read-only.
For example, if Field Read Only Field: Sales Rep contains a value of Calculated Primary Flag, and if
the Calculated Primary Flag field is TRUE, then Siebel CRM sets the Sales Rep field to read-only.
CAUTION: You must not use this user property with the Abstract field of the Service Request
business component. If you do this, then Siebel CRM examines the Abstract field to determine if it
is read-only. If it is read-only, then the entire Service Request business component becomes read-
only and the user cannot add an activity or attachment to a service request.
This user property does not work correctly on the Fund Request business component because of the
specialized business component code that the parent CSSBCFundReq class contains. For important
caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28.
Disallowing Empty Fields
The No Clear Field n user property disallows setting a field value to an empty value. It must specify
the name of a business component field, not enclosed in quotes.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Fields
140
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
Disabling Field Deletion
The NoDelete Field user property restricts the records that Siebel CRM deletes. It must specify the
name of a business component field.
Siebel CRM does not delete records that contain a value of Y in the business component field that
you specify. For example, assume the following configuration exists on the Contact business
component:
■ The NoDelete Field user property contains a value of Protect Internal Employee Flag.
■ The Protect Internal Employee Flag field of a record is Y.
In this example, Siebel CRM cannot delete this record.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it. No more than one instance can exist for each business component.
Setting Field Values According to Conditions
The On Condition Set Field Value user property specifies the value for a field according to a condition.
The value for this user property must use the following format:
"
Condition
", "
FieldName
", "
FieldValue
"
where:
■ Condition specifies the condition that Siebel CRM evaluates.
■ FieldName specifies the name of a business component field.
■ FieldValue specifies the value.
If Siebel CRM evaluates Condition to TRUE, then it sets the FieldName to the FieldValue.
If the condition is TRUE in the following example, then Siebel CRM sets the Employee Flag field to Y:
"[Primary Held Position Id] is not null and [Primary Held Position Id] <> ""No Match
Row Id""", "Employee Flag", "Y"
Double quotes (") must enclose each parameter. A comma and a space must separate each
parameter.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Fields
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 141
Updating Fields When Siebel CRM Updates Other Fields
The On Field Update Set n user property sets the value of a business component field when Siebel
CRM updates another field. The value for this user property must use the following format:
"
FieldToCheck
", "
FieldToSet
", "
Value
", "
Condition
"
where:
■ Value and Condition are optional parameters.
Note the following:
■ If Siebel CRM updates FieldToCheck, then it sets FieldToSet to Value.
■ If you do not include the Value parameter, then it sets FieldToSet to the value that FieldToCheck
contains.
■ If you include Condition, then it updates FieldToSet only if Condition
evaluates to TRUE.
■ Double quotes (") must enclose each parameter. A comma and a space must separate each
parameter.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
Setting the Value Parameter of On Field Update Set
The Value parameter can contain an expression. If Siebel CRM updates the Done Flag in the following
example, then it uses an IIF expression to set the Done field:
"Done Flag", "Done", "IIF ([Done Flag] = "Y", Today (), "")"
Any expression you use must evaluate to the same data type that the target field uses. In the
following example, Siebel CRM uses the ToChar function to convert the date to a string before it
concatenates it with another string and sets the field value:
"Agreement Start Date", "Name", "ToChar([Agreement Start Date]) + [Agreement Type]"
Setting the Condition Parameter of On Field Update Set
In the following example, if Siebel CRM updates the Primary Revenue Amount field, then it sets the
Revenue field of the Opportunity business component, but only if the IsParentBCRevn field contains
a value of N:
"Primary Revenue Amount", "Revenue", "[Primary Revenue Amount]", "[IsParentBCRevn]
= 'N'"
Using On Field Update Set with An Address Business Component

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Fields
142
Siebel CRM concatenates street address, city, and state so that it can populate the Address Name
field of an address business component, such as Business Address. If the user updates the street
address, city, or state, then Siebel CRM uses multiple instances of the On Update Field Set user
property to set the value of a calculated field. In the following example, if the user updates a city,
then Siebel CRM uses an On Update Field Set user property that contains the following value:
"City", "Address Name", "IIF( [Address Name Locked Flag] = ""N"", [Calculated
Address Name], [Address Name])"
If the user updates the street address or the state, then Siebel CRM uses similar user property
instances to update the Address Name field.
Guidelines for Updating Fields When Siebel CRM Updates Other Fields
If you configure the On Field Update Set n user property, then use the following guidelines:
■ Do not use this user property to set a multivalue or calculated field. If FieldToSet is a multivalue
or calculated field, then Siebel CRM does not update it when it examines FieldToCheck.
■ Do not define FieldToCheck as a field on a multivalue group. This user property does not
recognize modifications that Siebel CRM makes in a multivalue group field, including modifying
the primary field by modifying the primary record of a multivalue group. For example, assume
you use the following value for the On Field Update Set user property on the Contact business
component:
"Primary Address Id", "Email Address", "my@oracle.com"
If the user modifies the primary of the Street Address multivalue group, then Siebel CRM does
not update the Email Address field.
Calling Methods When Siebel CRM Updates Fields
The On Field Update Invoke n user property calls a business component method when Siebel CRM
updates a field. The value for this user property must use the following format:
"[
FieldToCheck
]", "[
BusCompName
]", "[
MethodName
]", "[
Condition
]"
If Siebel CRM updates FieldToCheck, then it calls the MethodName that the BusCompName contains.
If you do not include FieldToCheck, then it calls this method when the user saves the record.
You can optionally include a condition. If you define a condition, then Siebel CRM calls this method
only if the condition evaluates to TRUE.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Fields
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 143
Setting the Field Created Date to the Saved Date
The Post Default Created Date To Date Saved user property sets the Created Date of a field to the
Saved Date when Siebel CRM saves a record. You can set this user property to one of the following
values:
■ TRUE. Set the Created Date to the Saved Date.
■ FALSE. Do not modify the Created Date.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Updating the Planned Field if the Start Date Field Is
Modified
The Update Planned Field On Set: StartDate, StartTime user property automatically updates the
Planned field when Siebel CRM updates the Start Date field. It can include one of the following
values:
■ Y. Update the Planned field.
■ N or this user property does not exist. Do not update the Planned field.
Siebel CRM uses this user property with the CSSBCPharmaSpecializedAct class. For important
caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Overriding the Type for Fields That Users Read from
Right-To-Left
The DisplayType user property overrides the Type property of a field that Siebel CRM configures for
right-to-left (RTL) display. It is applicable only if Siebel CRM uses this right-to-left configuration. It
displays text fields as data types from left to right. For example, DTYPE_ID, DTYPE_PHONE, and so
on.
The value for this user property must contain one of the following values:
■ DTYPE_CURRENCY
■ DTYPE_DATE
■ DTYPE_ID
■ DTYPE_INTEGER
■ DTYPE_NUMBER
■ DTYPE_PHONE

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Fields
144
Displaying data from right to left for some fields does not make sense. For example, a service request
number must always display from left to right. Siebel CRM sets the Type property for the SR Number
field to DTYPE_TEXT. It sets the DisplayType user property for this field to DTYPE_ID to make sure
the service request number displays left to right.
Setting Default Values for Fields That Use Drop-Down
Lists
The Picklist Pre Default Field n user property sets default values for fields in a new record of the child
business component. To set these values, CRM gets values from the parent business component
record. The value for this user property must use the following format:
"
field
", "'
buscomp1.field1','buscomp2.field2
',' . . .'"
where:
■ field is a field that resides in the current business component.
■ buscompn.fieldn is the name of a field that resides in the parent business component.
For example, assume a view references a parent Action business component. The user can use a
drop-down list that references the child Opportunity business component to create a new record.
Note the following format requirements:
■ You must include a space after the first comma.
■ You must use double quotes (") to enclose the list of buscompn.fieldn entries.
■ You must use single quotes to enclose each buscompn.fieldn entry.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
Using Multiple Instances of Picklist Pre Default Field
You can configure Siebel CRM to use multiple instances of the Picklist Pre Default Field n user
property. For example, to create a new opportunity, the user can use an Opportunity drop-down list
in each of the following applets:
■ Activity Form Applet that references the Action business component
■ Comm Outbound Item Form Applet that references the Comm Outbound Email business
component
If the user creates a new opportunity from the drop-down list in each of these applets, then Siebel
CRM sets a default value for the Account for the opportunity and the Account Id field. It uses the
corresponding field value from the parent record to get these default values.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Fields
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 145
Table 26 describes user properties that this example uses on the Opportunity business component.
For more information, see “Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
Modifying the Currency That a Field Uses
The Currency Field n user property specifies the name of a field that stores currency data. If the user
modifies the currency code, then Siebel CRM does a currency exchange operation on the data that
this field contains, and then updates the field value.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it. You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more
information, see “Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
Specifying Field Name Prefixes for File Attachment
Business Components
The DefaultPrefix user property specifies the unique field name prefix for each business component
that Siebel CRM uses for file attachments. It must specify a string that Siebel CRM uses for the prefix
in the names of the required fields that these business components contain. You do not enclose this
value with quotes.
Each business component that Siebel CRM uses for file attachments includes a unique field name
prefix. For example, the value of the DefaultPrefix user property for the Account Attachment business
component is Accnt because the required fields for this business component are named
AccntDockStatus, AccntFileDate, AccntFileName, and so on. For more information, see Table 9 on
page 44.
To create the entire field name for the required fields in any file attachment business component, a
method uses the default prefix that this user property specifies. A method can use this prefix to
access the required fields without using the literal name of each field.
You can modify the value for this user property. You cannot create more than one instance of this
user property, and you cannot deactivate this user property.
Table 27. Example of Using the Picklist Pre Default Field n User Property
User Property Name Value
Picklist Pre Default Field 1 "Account", "'Action.Account Name', 'Comm Outbound
Email.Account Name'"
Picklist Pre Default Field 2 "Account Id", "'Action.Account Id', 'Comm Outbound
Email.Account Id'"

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Primaries
146
Controlling Primaries
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control primaries. It
includes the following topics:
■ Specifying Who Can Modify Primary Team Members on page 146
■ Setting the Primary Sales Rep as the Owner on page 147
■ Setting the Current User as the Primary Contact on page 147
■ Allowing Only the Primary to Modify Sales Methods for Opportunities on page 147
■ Restricting How Siebel CRM Displays Private Activities for Primaries on page 148
Specifying Who Can Modify Primary Team Members
The MVG Set Primary Restricted: visibility_mvlink_name user property determines who can modify
the primary team member of an opportunity, account, or contact. The value for this user property
must contain one of the following values:
■ TRUE or this user property does not exist. Only a Siebel Administrator in Admin view mode
or a Manager in Manager view mode can modify the primary team member.
■ FALSE. Someone other than the Manager or Siebel Administrator can modify the primary team
member.
visibility_mvlink_name identifies the name of a multivalue link that resides in the BusComp View
Mode child object of the business component where you must configure this visibility.
The following example describes how to control who can modify the primary sales team members for
contacts.
To specify who can modify primary team members
■ Create the following user property on the Contact business component:
User Property Name Value
MVG Set Primary Restricted: Position
where:
■ Position is the value of the Visibility MVLink property of the Sales Rep
business component view mode that resides on the Contact business
component.
FALSE

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Primaries
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 147
Setting the Primary Sales Rep as the Owner
The Set Primary Sales Rep As Owner user property identifies the Primary Sales Rep that Siebel CRM
assigns to the user who is currently logged in, and then assigns all new activities to this Primary
Sales Rep. It can contain one of the following values:
■ Y. Assign the current user as the Primary Sales Rep for all new activities.
■ N or this user property does not exist. Do not assign all new activities.
This user property is applicable only if the business component name is Action (Web), and only if
Siebel CRM uses it for the Professional Portal LS application.
Siebel CRM supports this user property with the CSSBCFINSActivity class but not for any subclass of
CSSBCFINSActivity.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Setting the Current User as the Primary Contact
The Set User As Contact user property assigns the current user as the Primary Contact for all new
activities. It can contain one of the following values:
■ Y. Assign the current user as the Primary Contact for all new activities.
■ N or this user property does not exist. Do not assign all new activities.
This user property is applicable only if the business component name is Action (Web), and only if
Siebel CRM uses it for the Professional Portal LS application.
Siebel CRM supports this user property with the CSSBCFINSActivity class but not for any subclass of
CSSBCFINSActivity.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Allowing Only the Primary to Modify Sales Methods for
Opportunities
The Primary Position Modification user property specifies who can modify the Sales Method of an
opportunity. You can set this user property to one of the following values:
■ Y. Only the primary position can modify the Sales Method.
■ N. Anyone can modify the Sales Method.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Specifying Business Services
148
Restricting How Siebel CRM Displays Private Activities
for Primaries
The Private Activity Search Spec user property includes a search specification that restricts the
activities that Siebel CRM displays to activities that include one of the following:
■ The Private flag is not set.
■ The user who is currently logged in is the primary owner.
You can define other restrictions, as necessary.
The value for this user property must include a valid search specification. For example:
[Private] = 'N' OR [Private] IS NULL OR [Primary Owner Id] = LoginId ()
This value supports typical search specification functionality, such as the following:
IIf(
condition
,
search spec 1
,
search spec 2
)
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
Specifying Business Services
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to specify business
services. It includes the following topics:
■ Calling Business Service Methods from Business Components on page 148
■ Specifying Business Service Parameters on page 149
■ Specifying External Data Sources for Business Services on page 149
■ Specifying Business Services for Virtual Business Components on page 149
For information about using business service user properties, see “Business Service User Properties”
on page 86.
Calling Business Service Methods from Business
Components
The Named Method n business component user property calls a business component or business
service method, or sets a field value. You can use it instead of scripting. The value that this user
property can contain and the usage for it is similar to the value and usage that you can use for the
Named Method n applet user property. For more information, see “Calling Methods from Applets” on
page 72.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Parent and Child Relationships
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 149
Specifying Business Service Parameters
The Service Parameters user property specifies parameters for a business service. The value for this
user property must use the following format:
ParamName1
=
ParamValue2
;
ParamName2
=
ParamValue2
;
ParamNameN
=
ParamValueN
where:
■ ParamName specifies the name of a parameter.
■ ParamValue specifies the value for the parameter that Siebel CRM sends to the business service.
For example:
DLLName=VirtualBusCompODBC.dll
The Pre_Invoke method typically parses these parameters. A virtual business component typically
uses these values in a workflow process. For more information about configuring a business service
in a workflow process, see the Siebel Business Process Framework: Workflow Guide.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
Specifying External Data Sources for Business Services
The Remote Source user property specifies an external data source that a business service uses. The
value for this user property identifies the name of this external data source. For example:
DSN=EXCELABCCust
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it.
Specifying Business Services for Virtual Business
Components
The Service Name user property specifies a business service that a virtual business component uses.
The value for this user property must contain the name of a business service.
Controlling Parent and Child
Relationships
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control parent and child
relationships. It includes the following topics:
■ Copying and Deleting Child and Grandchild Records on page 150
■ Updating the Parent Business Component if Siebel CRM Modifies Children on page 152
■ Specifying Recursive Links Between Parent and Child Business Components on page 153
■ Enabling Service Request Updates in Child Business Components on page 154

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Parent and Child Relationships
150
Copying and Deleting Child and Grandchild Records
The Deep Copy and Deep Delete user properties copy or delete a record. For example, a deep copy
user property can copy the detail records that a child business component contains from the original
record to a new record that the parent business component contains. If Siebel CRM uses one of these
user properties, then it examines sources according to the following order to determine the parent
and child link that it must use:
1 The parent and child reside in the same business component. The Recursive Link user
property that resides in the business component must define the relationship. Siebel CRM uses
this link to identify child records. For more information, see “Specifying Recursive Links Between
Parent and Child Business Components” on page 153.
2 The Deep Copy/Delete Link user property is set on the parent business component.
Siebel CRM uses the link that the Deep Copy/Delete Link user property specifies. For more
information, see “Specifying the Link for Deep Copy and Delete” on page 152.
3 The parent and child business components are of the same Siebel object, and the
parent is the primary business component in the business object. Siebel CRM determines
whether a link from the parent to the child exists. If it exists, then Siebel Tools displays it in the
Link property in the Business Object Component list.
4 Step 1, Step 2, or Step 3 do not provide a link between the parent component and the
child business component. Siebel CRM determines whether a link named parent business
component/child business component exists. For example, Opportunity/Revenue. If this link
exists, then Siebel CRM uses it.
Each business component that Siebel CRM modifies during a deep copy uses the configuration that
resides on each of these business components. The parent business component includes deep copy
properties for each child, and each child business component includes deep copy properties for each
grandchild. This configuration is the same for deep delete.
Siebel CRM supports deep copy only for a business component that references the CSSBCBase class
and that gets data from this class. The CSSBusComp class resides in the parent of the CSSBCBase
class. Siebel CRM does not support deep copy for the CSSBusComp class. You can write a script or
a workflow process that uses deep copy with the CSSBusComp class.
You must not use Deep Copy or Deep Copy/Delete Link with the Quote business components or the
Order Entry – Orders business component. The copy functionality for these business components
uses the Data Transfer Utilities business service. For more information, see Siebel Order Management
Infrastructure Guide.
Using Deep Copy to Copy Records in Child Business Components
The Deep Copy n user property specifies a child business component. If a user chooses the Copy
option, then Siebel CRM copies the records that this child business component contains. This option
typically copies only one level. The Deep Copy n user property copies records in multiple levels,
similar to a cascade copy. You typically use Deep Copy and Deep Delete together.
The value for this user property must contain the name of a child business component if you define
the parent and child link in one of the ways that the “Copying and Deleting Child and Grandchild
Records” on page 150 topic describes.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Parent and Child Relationships
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 151
You must not use Deep Copy if the parent-child relationship is a many-to-many (M:M) relationship.
Instead, you can set the No Copy property to FALSE in the link that Siebel CRM uses for this parent-
child relationship.
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65 and “Specifying the Link for Deep Copy and
Delete” on page 152.
To use deep copy to copy records in child business components
1
In the parent business component, create the user properties for each child business component
that Siebel CRM must include in the deep copy. Use values from the following table.
2 Add a multivalue link in the parent business component for each child business component.
3 Set the No Copy property of the multivalue link to TRUE.
This configuration prevents an error that is similar to the following from occurring:
A Duplicate Record Exists SQL
4 Create a multivalue field in the parent business component from each child business component.
Using Deep Delete to Delete Records in Child Business Components
The Deep Delete n user property specifies a child business component. The value for this user
property must contain the name of a child business component if you define a parent and child link
in one of the ways that the “Copying and Deleting Child and Grandchild Records” on page 150 topic
describes.
If a user chooses the Delete option, then Siebel CRM deletes the records that this child business
component contains. This option typically deletes records in only one level. The Deep Delete n user
property deletes records in multiple levels, which is similar to a cascade delete. You typically use
Deep Copy and Deep Delete together.
To use deep delete, do “Using Deep Copy to Copy Records in Child Business Components” on page 150
with the following differences:
■ In Step 1 on page 151, use Deep Delete 1 and Deep Delete 2 for the names.
■ In Step 3 on page 151, set the No Delete property of the multivalue link to TRUE.
You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65 and “Specifying the Link for Deep Copy and
Delete” on page 152.
User Property Name Value
Deep Copy 1 child business component name
Deep Copy 2 child business component name

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Parent and Child Relationships
152
Specifying the Link for Deep Copy and Delete
The Deep Copy/Delete Link Buscomp user property specifies the link that Siebel CRM uses for a deep
copy or deep delete of the child business component. It resides in the parent business component.
The value for this user property must contain the name of a link that exists between the parent
business component and the child business component.
The Link object defines a one-to-many parent and child relationship that exists between these
business components. For information about links, see Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
CAUTION: If you deactivate a predefined instance of this user property in a production environment,
then thoroughly plan and test this configuration to confirm that Siebel CRM no longer copies or
deletes child records, and that your configuration does not affect records from other business
components that are related to these child records.
Specifying Links for More Than One Business Component
Buscomp is an optional parameter. You use it if you must specify the link for more than one business
component. It must identify the business component that Siebel CRM uses as the child in a link where
the current business component is the parent. You set the deep copy or deep delete user properties
in the parent business component. For example, to configure Siebel CRM to do a deep copy or deep
delete of the revenues that Siebel CRM associates with an opportunity, you add the Deep Copy/
Delete Link: Revenue user property with a value of Opportunity/Revenue. You add this user property
to the Opportunity business component. Opportunity is the parent business component and Revenue
is the child business component of the Opportunity/Revenue link.
Updating the Parent Business Component if Siebel CRM
Modifies Children
The OnAddAssocUpdateParent: buscompname user property updates a parent business component
with the value that Siebel CRM sets in a child business component if it associates an account or
contact with this child business component. The value for this user property must use the following
format:
"
Condition1
", "
ParentBCField1
", "[
ChildBCField1
]" or "
Expression1
",
"
ParentBCField2
", "
[ChildBCField2]
" or "
Expression2
", ...
where:
■ ParentBCFieldn identifies a field that resides in the parent business component that Siebel CRM
updates if it evaluates Conditionn to TRUE.
■ ChildBCFieldn identifies the business component field where you set this user property. Siebel
CRM uses the value of this field to update the parent business component field.
■ Expressionn contains an expression that determines the value that Siebel CRM uses to update
the parent business component field. An IIf statement is an example of this expression.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Parent and Child Relationships
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 153
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
Example of Updating the Parent Business Component if Siebel CRM
Modifies Children
For example, the OnAddAssocUpdateParent: Action user property on the Contact business
component contains the following value:
"[Account Id] IS NULL", "Account Id", "IIf([Account Id] IS NULL OR [Account Id] =
'No Match Row Id','',[Account Id])"
If a user chooses a contact for an activity, and if Siebel CRM does not already associate an account
with the parent activity, then Siebel CRM also chooses the account from the contact for the activity.
If an account is associated with the contact, then Siebel CRM does not set an account for the activity.
In this example, the OnAddAssocUpdateParent: Contact user property that resides in the Account
business component contains the following value:
"[Account Id] IS NULL OR [Account Id] = 'No Match Row Id'", "Account Id", "[Id]",
"Primary Address Id", "[Primary Address Id]"
If Siebel CRM associates an account with a contact, then it sets the primary address of this account
as the primary address for the contact.
Specifying Recursive Links Between Parent and Child
Business Components
The Recursive Link user property specifies a parent and child relationship between a business
component and itself.
If Siebel CRM copies or deletes a record that resides in a parent business component, then the Deep
Copy, Deep Delete, or Update Foreign Key Field user properties can copy or delete records that reside
in child business components. If the parent and child are the same business component, then the
Recursive Link user property must specify the link that defines this parent and child relationship.
The value for this user property must contain the name of a link that resides between the parent
business component and itself. For example, to delete catalog subcategories if Siebel CRM deletes a
category, you can use Deep Delete with the Recursive Link user property set to the following value:
Catalog Category/Catalog Category
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it. No more than one instance can exist for each business component.
For more information, see “Copying and Deleting Child and Grandchild Records” on page 150 and
“Specifying the Parent Business Component for Accounts” on page 109.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Email
154
Naming a Link
A link name uses the following format:
parent business component
/
child business component
This format is optional. The value that the Recursive Link user property contains might include
different names on each side of the slash. For example, Action/Action - Deep. However, the parent
and child business components of this link must be the same business component.
For more information about the Link object type, see Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
Enabling Service Request Updates in Child Business
Components
The Always Enable Child: buscompname user property determines whether Siebel CRM can update
a child business component of a service request after it closes this service request. It must contain
a Boolean value. If TRUE, then Siebel CRM can update the child business components of a service
request even if this service request is closed.
You can also modify the service request status to Open to modify a closed service request and child
business component.
Enabling Service Request Updates in Child Business Components with
Customer Surveys
The Always Enable Child: Customer Survey user property of the Service Request business component
enables or disables customer surveys. Closing a service request does not prevent Siebel CRM from
updating the child Customer Satisfaction business component. You can survey your customers even
if the service request is resolved.
To allow Siebel CRM to update other business components, you can add user properties to the Service
Request business component, and then substitute the appropriate business component name for
Customer Survey.
Controlling Email
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control email. It includes
the following topics:
■ Specifying Statuses for Outgoing Email on page 155
■ Specifying the Manager That Sends Email on page 156
■ Sending Email Packages to Recipients on page 156
■ Responding to Email or Web Offers on page 158

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Email
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 155
Specifying Statuses for Outgoing Email
The email activity user properties handle the status for outbound email messages.
Specifying the Status for In Progress Emails
The Email Activity Sent Status Code user property specifies the code that Siebel CRM uses in the
EVENT_STATUS_LOV list of values that correspond to an outbound email that is in progress. The
eMail Response client uses it to set the status of an outbound email that is in process or that is
waiting for the Communications Outbound Manager or Email Manager to send this email. The value
for this user property must contain a language-independent value that the EVENT_STATUS_LOV list
of values contains. For example:
Queued
You must not deactivate this user property. You can modify the values for this user property. You
cannot create a new instance of this user property.
Specifying the Status for Sent Emails
The Email Activity Accepted Status Code user property specifies the code that Siebel CRM uses in the
EVENT_STATUS_LOV list of values that corresponds to sent outbound email. The eMail Response
client uses it to set the status of an outbound email that Siebel CRM finished processing. The value
for this user property must contain a language-independent value that the EVENT_STATUS_LOV list
of values contains. For example:
Done &&
You must not deactivate this user property. You can modify the values for this user property. You
cannot create a new instance of this user property.
Specifying the Status for Unsent Outbound Emails
The Email Activity New Status Code user property specifies the code that Siebel CRM uses in the
EVENT_STATUS_LOV list of values that corresponds to an outbound email that Siebel CRM has not
sent or has not processed. The eMail Response client uses it to set the status of an outbound email
that Siebel CRM has not yet sent. The value for this user property must contain a language-
independent value that the EVENT_STATUS_LOV list of values contains. For example:
Not Started
You must not deactivate this user property. You can modify the values for this user property. You
cannot create a new instance of this user property.
Specifying the Status for Rejected Emails
The Email Activity Rejected Status Code user property specifies the code that Siebel CRM uses in the
EVENT_STATUS_LOV list of values that corresponds to an unsuccessful outbound email. The eMail
Response client uses it to set the status of an outbound email that Siebel CRM rejects because it
cannot send this email for some reason. The value for this user property must contain a language-
independent code that the EVENT_STATUS_LOV list of values lists. For example:

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Email
156
Cancelled
You must not deactivate this user property. You can modify the values for this user property. You
cannot create a new instance of this user property.
Specifying the Manager That Sends Email
The Email Manager Compatibility Mode user property specifies how to send email messages. It must
specify one of the following values:
■ Y. The business component uses Mail Manager to send email messages.
■ N. The Outbound Communications Manager sends email messages.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Sending Email Packages to Recipients
The recipient communications user properties send email packages. A generic recipient is a generic
name for a person instead of the actual name, email address, or fax number. Service Request Owner
is an examples of a generic recipient. Contact Name is another example. Siebel CRM gets values for
these generic recipients from user properties, and then displays them as a list of recipients in the
Pick Recipient applet.
You can configure this list of generic recipients. This configuration is similar to the set of templates
that Siebel CRM lists in the Body drop-down list in the Send Email or Send Fax dialog boxes except
that Siebel CRM adds recipients through child user properties.
For example, the user can choose Service Request Owner or Service Request Contact for recipients
when this user creates an email or fax for a service request. For a contact record, the user might
choose only Contact Name. Siebel CRM does not list the actual name in the Pick Recipient applet.
Instead, it gets the name and corresponding fax number or email address from fields that reside in
the current business component record. For example, a contact can include a name, email address,
and a fax number.
Siebel CRM can also use a join to get the recipient information from a record that resides in another
business component. For example, Siebel CRM gets recipient information for the Service Request
Owner in a service request from an employee record and recipient information for the Service
Request Contact from a contact record. These fields reference joins from the service request record.
Recipient First Name Field
The Recipient First Name Field user property identifies the first name of the recipient of an email,
fax, or page. It specifies the name of the business component field that contains this first name.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Email
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 157
Recipient Last Name Field
The Recipient Last Name Field user property identifies the last name of the recipient of an email, fax,
or page. It specifies the name of the business component field that contains this last name.
Recipient Email Address Field
The Recipient Email Address Field user property identifies the email address of the recipient. It
specifies the name of the business component field that contains this email address.
Recipient Fax Address Field
The Recipient Fax Address Field user property identifies the fax address of the recipient. It specifies
the name of the business component field that contains this fax address. This address must use a
format that your fax server can understand. For more information about driver parameters for the
Internet SMTP/POP3 Server, see Siebel CTI Admin Guide.
Recipient Preferred Medium Field
The Recipient Preferred Medium Field user property identifies the communications channel that the
recipient prefers for email or fax. It specifies the name of the business component field that contains
the name of this channel.
If Siebel CRM uses the Only Send Preference setting for a communication request, and if the template
channel type:
■ Corresponds to the value that exists in the field that this user property specifies, then it sends a
communications template to the recipient.
■ Does not correspond to the value that exists in the field that this user property specifies, or if
this user property does not exist, and if the business component includes the Preferred
Communications field, then it gets the preference from this Preferred Communications field.
Recipient Id Field
The Recipient Id Field n user property specifies properties for email recipients when Siebel CRM sends
an email or fax. The value for this user property contains the following items:
■ ID field name. Identifies the foreign key field that resides in the parent business component
that references records that reside in the joined business component.
■ Business component. Identifies the joined business component.
■ Label. Specifies the text for the label that Siebel CRM displays in the Pick Recipient dialog box
for this generic recipient. For example:
Service Request Owner
■ Field in the target business component. You can include this optional item if the field name
is not an ID field.
A comma must separate each item. For more information, see “Numbering Instances of a User
Property” on page 65.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications
158
Responding to Email or Web Offers
The response type user properties specify how Siebel CRM creates new email or Web offers. You can
use them with offer, email offer, and Web offer business components.
Response Type Call Back
The Response Type Call Back user property creates a Call Back response type if the user creates a
new email or Web offer. If you set this user property to Y, then it creates a Call Back response.
Response Type More Info
The Response Type More Info user property creates a More Info response type if the user creates a
new email or Web offer. If you set this user property to Y, then it creates a More Info response.
Response Type Unsubscribe
The Response Type Unsubscribe user property creates an Unsubscribe response type if the user
creates a new email or Web offer. If you set this user property to Y, then it creates an Unsubscribe
response.
Controlling Specific Siebel Business
Applications
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control specific Siebel
Business Applications. It includes the following topics:
■ Controlling Siebel Automotive on page 159
■ Specifying Activities to Synchronize for Siebel Handheld on page 161
■ Specifying Position Join Fields for Siebel Life Sciences on page 162
■ Specifying Business Components for Product Selection and Pricing on page 163
■ Identifying Business Components That Siebel Financial Services Uses on page 165
■ Specifying Room Types for Siebel Hospitality on page 165
■ Specifying Arrival Dates, Room Blocks, and Function Spaces for Siebel Hospitality on page 165
■ Enabling Credit Check on page 166
■ Specifying the Workflow Process for Credit Check on page 166
■ Specifying Credit Card User Properties on page 167

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 159
Controlling Siebel Automotive
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to control Siebel
Automotive. It includes the following topics:
■ Specifying Opportunity Business Components in Siebel Automotive on page 159
■ Specifying Values for New Opportunities in Siebel Automotive on page 159
■ Specifying Values for Used Opportunities in Siebel Automotive on page 159
■ Specifying Opportunity Sales Steps in Siebel Automotive on page 160
■ Specifying the Sales Step Admin in Siebel Automotive on page 160
■ Specifying Reassignment in Siebel Automotive on page 161
■ Specifying Positions in Siebel Automotive on page 161
Specifying Opportunity Business Components in Siebel Automotive
The Opportunity Name user property specifies the name of the business component that Siebel CRM
uses to create opportunities in a Siebel Automotive application. The value for this user property must
contain the name of a business component. For example:
Opportunity
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Specifying Values for New Opportunities in Siebel Automotive
The TypeRetailNew user property specifies the value that Siebel CRM uses in the Opportunity Type
field that indicates that an opportunity is a new retail opportunity.
The CSSBCFINOppty business component class uses this user property when it calculates the Actual
Number for new retail opportunities. For example, if you add the TypeRetailNew user property with
a value of Retail New, then the CSSBCFINOppty class includes only the opportunities that include an
Opportunity Type of Retail New.
If the TypeRetailNew user property does not exist, then Siebel CRM uses a value of New.
Siebel CRM uses this user property with Siebel Automotive.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
Specifying Values for Used Opportunities in Siebel Automotive
The TypeRetailUsed user property specifies the value that Siebel CRM uses in the Opportunity Type
field that indicates that an opportunity is a used retail opportunity. The description for this user
property is the same as the description for the TypeRetailNew user property except that it applies
only to used opportunities. For more information, see “Specifying Values for New Opportunities in
Siebel Automotive” on page 159.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications
160
Specifying Opportunity Sales Steps in Siebel Automotive
This topic describes the user properties that Siebel CRM uses to specify opportunity sales steps in
Siebel Automotive.
Specifying Business Components for the Opportunity Sales Step in Siebel Automotive
The BC eAuto Sales Step user property specifies the name of the business component for eAuto
Opportunity Sales Step. This business component must reference the Opportunity business object.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
Specifying How to Populate Opportunity Sales Steps in Siebel Automotive
The eAuto Enable Create Sales Step user property specifies how to populate opportunity sales steps
for a Siebel Automotive application. The value for this user property must use the following format:
"
ApplicationName
", "
bPopulate
"
where:
■ ApplicationName specifies the name of a Siebel Business Application.
■ bPopulate is Y or N. If Y, then Siebel CRM populates the opportunity sales steps.
For example, the following code configures Siebel CRM to populate the Opportunity Sales Step for
the Siebel Dealer application:
"Siebel Dealer", "Y"
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it.
Specifying the Sales Step Admin in Siebel Automotive
This topic describes the user properties that Siebel CRM uses to specify the Sales Step Admin in
Siebel Automotive.
Specifying Business Objects for the Sales Step Admin in Siebel Automotive
The BO eAuto Sales Step Admin user property specifies the name of the business object that Siebel
CRM uses for eAuto Sales Step Admin. It defines the view to set for Sales Steps. You can configure
Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it, or deactivate it.
Specifying Business Components for the Sales Step Admin in Siebel Automotive
The BC eAuto Sales Step Admin user property specifies the name of the business component that
Siebel CRM uses for eAuto Sales Step Admin. This business component must reference the eAuto
Sales Step Admin business object. You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user
property, create a new instance of it, or deactivate it.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 161
Specifying Reassignment in Siebel Automotive
This topic describes the user properties that Siebel CRM uses to specify reassignment in Siebel
Automotive.
Specifying the Business Component for Reassignment in Siebel Automotive
The BC Opportunity user property specifies the name of the Opportunity business component that
Siebel CRM uses during reassignment in a Siebel Automotive application. This business component
must reference the Opportunity business object. You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user
property or modify the value for it, but not to create a new instance of it.
Reassigning Opportunities in Siebel Automotive
The Contact-Opportunity BC Name user property specifies the name of the business component that
Siebel CRM uses to reassign an opportunity in a Siebel Automotive application. For example:
Opportunity
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Reassigning Contacts in Siebel Automotive
The Contact-Activity BC Name user property specifies the name of the business component that
Siebel CRM uses when it reassigns an activity to another contact in a Siebel Automotive application.
For example:
Action
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Specifying Positions in Siebel Automotive
The BC Position user property specifies the name of a business component that stores Position data.
Siebel CRM uses this business component when it creates an opportunity in a Siebel Automotive
application. You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it,
but not to create a new instance of it.
Specifying Activities to Synchronize for Siebel Handheld
The Update Status To Synchronized Types user property determines the types of activities that Siebel
CRM updates during handheld synchronization. It uses the following format:
,
type1
,
type2
,
typeN
,
where:
■ type identifies an activity type.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications
162
For example, assume you set the Update Status To Synchronized user property to Y and the Update
Status To Synchronized Types to the following value:
,Account Call,Professional Call,Attendee Call,
In this example, Siebel CRM updates the Status fields to Synchronized for activities of type Account
Call, Professional Call, and Attendee Call.
A comma must prefix and suffix each activity type. For more information, see “How This Book
Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.
You must also set the Update Status To Synchronized user property to Y. For more information, see
“Updating the Synchronization Status for Activities” on page 111.
An activity with the Status field set to Synchronized in a Siebel Industry Application is read-only in
the Activities view.
Siebel CRM supports this user property in the CSSBCFINSActivity class but not in subclasses of this
class.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Specifying Position Join Fields for Siebel Life Sciences
The Position Join Fields user property specifies the position join fields that Siebel CRM uses for an
update in a Siebel Life Sciences application. The value for this user property includes one or more
field names. For example:
"Rep Specialty", "Rep TOP", "Primary Address Id"
There is no limit to the number of field names you can specify.
Double quotes (") must enclose each parameter. A comma and a space must separate each
parameter.
If you add a new field to this user property, then you must also create a field that includes the same
name in the Pharma Professional Position business component and that references the same column
that resides in the S_POST_CON table.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on page 64.

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 163
Specifying Business Components for Product Selection
and Pricing
The product selection and pricing user properties control how Siebel CRM integrates product business
components with the Production Selection and Pricing (PSP) engine. Table 28 describes these user
properties. For more information, see Siebel Order Management Infrastructure Guide.
Table 28. Production Selection and Pricing User Properties
User Property Value Description
PSP: Active Y or N Turns PSP integration on or off.
PSP: Buscomp Name Business
component name
Specifies the business component that instructs
Siebel CRM to call the PSP engine. For example:
Internal Product PSP Integration
It is recommended that you do not modify the
value for this user property.
PSP: Eligibility Fields Business
component field
Specifies the fields that the PSP Eligibility group
contains. For example, you can use one of the
following values:
■ Eligibility Reason
■ Eligibility Status
A PSP group is a group of fields that the PSP
engine populates if the same signals call these
fields.
PSP: Eligibility Group PSP group name Specifies the name of the PSP group that calls
eligibility. This value is typically Eligibility.
PSP: Eligibility Signal Signal name Specifies the signal name that Siebel CRM calls to
populate all field values that the PSP Eligibility
group contains. For example:
GetUserProdEligibility
PSP: Enabled BO:
busobjname
Y or N Determines whether PSP is active in the business
object. Siebel CRM enables PSP integration only if
the following is true:
■ PSP: Active is Y.
■ PSP: Enabled BO: busobjname is Y.
This configuration allows Siebel CRM to use the
same product business component with multiple
business objects or in a Siebel Business
Application that does not use PSP.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications
164
Using the Product Selection and Pricing User Properties
You can use the product selection and pricing user properties with a product business component
that references the CSSBCPecBase class or subclass, such as CSSBCProdBuyNow. For example,
assume Siebel CRM must use the GetProdEligibility signal to populate the Eligibility Status and
Eligibility Reason fields, but only in the Order Entry business object. Table 29 describes the user
properties that you can add that configures this example. You add them to the following business
component:
Internal Product by Price List Optional 2
PSP: Mode PSP mode Specifies the PSP Mode that Siebel CRM uses to
create a PSP signal. For example:
Product
Siebel CRM uses this value as an input to the
context service that determines the variable map
mode.
PSP: Prepick Groups PSP group name or
names
Specifies the prepick group. You can use one of
the following values:
■ Price
■ Eligibility
PSP: Price Fields Business
component field
Specifies the fields that the PSP Price group
contains. For example:
Deals, List Price, and Net Price
PSP: Price Signal Signal name Specifies the signal name that Siebel CRM calls to
populate all field values that the PSP Price group
contains. For example:
GetUserProdPrice
Table 29. Example of Using the Product Selection and Pricing User Properties
User Property Value
PSP: Active Y
PSP: Buscomp Name Internal Product PSP Integration
PSP: Eligibility Fields Eligibility Reason, Eligibility Status
PSP: Eligibility Group Eligibility
PSP: Eligibility Signal GetProdEligibility
PSP: Enabled BO: Order Entry Y
Table 28. Production Selection and Pricing User Properties
User Property Value Description

Business Component User Properties ■ Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 165
Identifying Business Components That Siebel Financial
Services Uses
The WorkFlow Behaviour user property identifies a business component that the Siebel Financial
Services application uses. It can include one of the following values:
■ Y. Use this business component in a Siebel Financial Services application.
■ Empty or this user property does not exist. Do not use this business component in a Siebel
Financial Services application.
This user property helps the Workflow Process Object Manager to identify a Siebel Financial Service
application from other types of Siebel Industry Applications.
Siebel CRM supports this user property for use in the CSSBCFINSActivity class, but not in the
subclasses of this class. It does support this user property for custom configuration.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Specifying Room Types for Siebel Hospitality
The RBFields user property specifies fields that reside in the Room Block business component that
represent types of rooms. The value for this user property includes the names of fields that exist in
the Room Block business component. For example:
RB Single, RB Double, RB Triple, RB Quad, 100
A comma must separate each field. An integer must terminate the value. It indicates the sum of the
values for the specified fields. The integer is typically 100.
You can modify the value for this user property and create a new instance of it. You cannot deactivate
this user property. For more information, see “How This Book Describes the User Property Format” on
page 64.
Specifying Arrival Dates, Room Blocks, and Function
Spaces for Siebel Hospitality
The day and number user properties define day and number values.
PSP: Mode Product
PSP: Prepick Groups Eligibility
Table 29. Example of Using the Product Selection and Pricing User Properties
User Property Value

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Controlling Specific Siebel Business Applications
166
Specifying the Arrival Date Field for the Day Number Business Service
The Day Number: Arrival Date Field user property specifies the name of the Arrival Date field that
Siebel CRM uses in the Day Number business service. If the user modifies the value of this field, then
this business service sends this modification to the date fields that reside in the Function Space and
Room Block business components.
You can modify the value for this user property. You cannot deactivate or create a new instance this
user property.
Specifying the Business Component for the Function Space
The Day Number: Function BC Name user property specifies the name of the business component
that Siebel CRM uses for the Function Space. Siebel CRM uses it with the Day Number: Arrival Date
Field user property. For more information, see “Specifying the Arrival Date Field for the Day Number
Business Service” on page 166.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, but not to deactivate it or
to create a new instance of it.
Specifying the Business Component for the Room Block
The Day Number: Room Block BC Name user property specifies the name of the business component
that Siebel CRM uses for the Room Block. Siebel CRM uses it with the Day Number: Arrival Date Field
user property. For more information, see “Specifying the Arrival Date Field for the Day Number
Business Service” on page 166.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, but not to deactivate it or
to create a new instance of it.
Enabling Credit Check
The Credit Check user property enables or disables Credit Check during verification. It must contain
one of the following values:
■ Y. Do credit check.
■ N. Do not do credit check.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property or modify the value for it, but not to
create a new instance of it.
Specifying the Workflow Process for Credit Check
The Credit Check Workflow user property specifies the name of the workflow process that Siebel CRM
uses if Credit Check is enabled. For example, Credit Check – Quotes. If you set the Credit Check user
property to Y, then the Credit Check Workflow user property is required.
You can configure Siebel CRM to deactivate this user property only if you set the Credit Check user
property to N. You can modify the value for this user property. You cannot create a new instance of it.

Business Component User Properties ■ Doing Other Work
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 167
Specifying Credit Card User Properties
The following credit card user properties store information in the Mod 10 (LUHN) algorithm for credit
card validation:
■ Credit Card Expired Month on page 167
■ Credit Card Expired Year on page 167
■ Credit Card Number on page 167
■ Credit Card Type on page 167
These user properties are valid only:
■ For a business component that references the CSSBCBase class or that gets data from a class
that references the CSSBCBase class, such as CSSBCQuote.
■ With the Validate method of the Credit Card Transaction Service business service. This is an
exception to the typical user property behavior of the specialized business component class. For
important caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28. For more information
about payment validation, see Siebel Order Management Guide.
All four of the fields that these user properties reference must contain data to allow validation.
Credit Card Expired Month
The Credit Card Expired Month user property stores the expiration month of the credit card.
Credit Card Expired Year
The Credit Card Expired Year user property stores the expiration year of the credit card.
Credit Card Number
The Credit Card Number user property stores the credit card number.
Credit Card Type
The Credit Card Type user property stores the credit card type.
Doing Other Work
This topic describes business component user properties that you can use to do other work. It
includes the following topics:
■ Specifying the Application Name on page 168
■ Using Aspects to Control Read Only, Insert, and Other Behavior on page 168
■ Specifying the Default Bookmark View on page 170
■ Enabling the Dispatch Board on page 170

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Doing Other Work
168
■ Making Sure an Attachment File Exists on page 170
■ Enabling the Revise Button According to Conditions on page 171
■ Specifying Joins to the S_PARTY Table on page 172
■ Specifying the DB2 Optimization Level for SQL Statements on page 172
■ Capturing User Drilldown Behavior on page 173
Specifying the Application Name
The Application Name user property specifies the name of the application. It must reference a valid
application name.You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a
new instance of it, or deactivate it.
Using Aspects to Control Read Only, Insert, and Other
Behavior
An aspect determines how Siebel CRM displays data from a business component. You can use one of
the aspect user properties to configure business component behavior according to the applet that
Siebel CRM uses to display data from this business component. For example, the applets that
reference the Action business component might contain different predefault values for the Type field.
An aspect user property is optional.
Aspect User Properties for the CSSBCBase Class
If Siebel CRM sets an aspect for an applet that references the CSSBCBase class, then it modifies the
behavior of this class according to the following user property setting. These settings assume the
current aspect is Aspect and the value of Field Name is Y:
■ Aspect BC ReadOnly: Aspect. The current record becomes read-only.
■ Aspect Child BC ReadOnly: Aspect. The child business components of the current record
become read-only.
■ Aspect BC NoInsert: Aspect. The user cannot insert a new record. You must make sure that
Siebel CRM does not modify the [Field Name] value if the user steps off the record. If it does
modify this value, then the behavior in the client might confuse the user. An incorrect
configuration makes an insert that depends on the state of the current record. This configuration
is probably not what your implementation requires.

Business Component User Properties ■ Doing Other Work
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 169
■ Aspect Default Value: Aspect. If you define Aspect Default Value: Aspect for a business
component field, and if the current aspect is Aspect, then the predefault value for this field
becomes the expression that the value of the user property defines. For example, the Action
business component handles activities. If it includes a Planned field, and if you define the Aspect
Default Value: Planned field user property for this field, and if the value of this user property is
Timestamp(), then the predefault value for the planned start date and time of the activity
becomes Timestamp().
You cannot use Aspect Default Value with a multivalue field because a multivalue field does not
use a predefault value.
Table 30 lists the aspect user properties that you can use with a business component.
Table 31 lists the aspect user properties that you can use with a field.
Aspect User Properties for the CSSSWEFrameBase or
CSSSWEFrameListBase Class
You must configure Siebel CRM to set and send the aspect name to the business component that the
view references in the following situations. This business component uses the CSSSWEFrameBase or
CSSSWEFrameListBase class:
■ You define a View Aspect* user property for the current view.
■ You do not define View Aspect* for the current view but you do define the Default Aspect.
Table 32 lists the aspect user properties that you can use with a view.
Table 30. Aspect User Properties That You Can Use With a Business Component
User Property Name Value
Default Aspect Aspect
Aspect BC ReadOnly: Aspect Field Name
Aspect Child BC ReadOnly: Aspect Field Name
Aspect BC NoInsert: Aspect Field Name
Table 31. Aspect User Properties That You Can Use With a Field
User Property Name Value
Aspect Default Value: Aspect Expression
Table 32. Aspect User Properties That You Can Use With a View
User Property Name Value
View Aspect: View Name Aspect Name
View Aspect "View Name", "Aspect Name"

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Doing Other Work
170
Specifying the Default Bookmark View
The Default Bookmark View user property specifies the default view that Siebel CRM uses to access
a business component when it creates a bookmark for this business component. The value for this
user property must contain the name of a view, not enclosed in quotes.
The Communications Server uses this user property to create a bookmark when it sends a package,
and if the Attach Bookmark field of this package contains a check mark. For example, this user
property exists on the predefined Opportunity business component that the Opportunity List View
references. Assume the Communications Server creates an email message, and that a bookmark that
references an opportunity record is attached to this message. If the user clicks this bookmark, and
if the responsibility that this user uses includes this view, then Siebel CRM displays the linked record
in the Opportunity List View. For more information about bookmarks, see Siebel CTI Admin Guide.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it,
or deactivate it. No more than one instance can exist for each business component.
Enabling the Dispatch Board
The Enable Dispatch Board user property enables the Dispatch Board views that reference the
business component that contains this user property. The value for this user property must contain
one of the following values:
■ TRUE. Enable the Dispatch Board views that reference this business component.
■ FALSE or this user property does not exist. Disable the Dispatch Board views that reference
this business component.
You can modify this user property. You cannot deactivate or create a new instance of this user
property.
For more information, see Siebel Field Service Guide.
Making Sure an Attachment File Exists
The FileMustExist user property determines whether a file must already exist before the user can add
it as an attachment. The value for this user property must contain a Boolean value. If TRUE, then
the file must already exist before the user can add it as an attachment.
View Aspect 1 "View Name", "Aspect Name"
View Aspect 2 "View Name", "Aspect Name"
Default Aspect Aspect Name
Table 32. Aspect User Properties That You Can Use With a View
User Property Name Value

Business Component User Properties ■ Doing Other Work
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 171
Enabling the Revise Button According to Conditions
The Revision Condition n user property enables the Revise button that Siebel CRM displays in a list
applet.
Table 33 describes typical values for this user property. In this example, if the Active flag is Y and
the Order Status is Open, then Siebel CRM enables the Revise button.
Note the following:
■ You can use this user property with order management and loyalty programs in Siebel Industry
Applications.
■ You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For more information, see
“Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
You can configure Siebel CRM to modify the value for this user property, create a new instance of it
if an instance does not already exist, or deactivate it.
Using the Revision Condition User Property
In this example, you configure Siebel to enable the Revise button if the status is Open or Failed.
To use the Revision Condition user property
1
Add a new calculated field using values from the following table.
2 Modify the Value property of the Revision Condition 2 user property to the following value:
"Status Rev", "Y"
Table 33. Example of the Revision Condition n User Property
User Property Value
Revision Condition 1 "Active", "Y"
Revision Condition 2 "Status", LookupValue("FS_ORDER_STATUS","Open")
Property Value
Name Status Rev
Calculated Value IIf([Status]=LookupValue("FS_ORDER_STATUS","Open") OR
[Status]=LookupValue("FS_ORDER_STATUS","Failed"), "Y", "N")

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Doing Other Work
172
Specifying Joins to the S_PARTY Table
The Inner Join Extension Table n user property specifies a table. The value for this user property
must contain the name of a table, not enclosed in quotes. This table must be an extension table of
the S_PARTY table. Siebel CRM uses an inner-join to join this table to the S_PARTY table. Some
business components use the Siebel Party Model to control access and visibility. For example,
organization, account, and position. These business components use one or more inner joins to the
base S_PARTY table.
If you create a new business component that references the Siebel Party Model, then you must use
the Inner Join Extension Table n user property to define one or more tables that Siebel CRM implicitly
joins to the S_PARTY base table. For example, to configure visibility for a group that does not fit any
of the predefined Siebel Party Model business components, you might need to create a new business
component.
You must not deactivate this user property or modify the value. You can create a new instance of this
user property, if necessary. You can specify this user property with or without the numeric suffix. For
more information, see “Numbering Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
CAUTION: You must be careful if you use the S_PARTY table in a custom configuration. For more
information, see Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
Numbering Instances of the Inner Join Extension Table User Property
If you add multiple Inner Join Extension Table n user properties to a business component, then you
can append a value to this user property. The lowest value indicates the primary extension table. For
example, the predefined Employee business component includes the following user properties:
■ Inner Join Extension Table 1 includes a value of S_CONTACT.
■ Inner Join Extension Table 2 includes a value of S_USER.
■ Inner Join Extension Table 3 includes a value of S_EMP_PER.
In this example, S_CONTACT is the primary extension table. For more information, see “Numbering
Instances of a User Property” on page 65.
Specifying the DB2 Optimization Level for SQL
Statements
The DB2 Optimization Level user property modifies the optimization level that Siebel CRM uses for
the SQL statements that a business component creates. The value for this user property must contain
an integer that indicates the level of optimization that Siebel CRM uses. The DB2 connector uses an
optimization level of 3 for each client SQL statement.
CAUTION: The value that you use for the DB2 Optimization Level user property affects the entire
business component. Modifying it can adversely affect the performance of other SQL statements that
this business component creates. It is extremely important that you analyze SQL statements that
Siebel CRM performs slowly, and that you use other tuning options before you modify the DB2
Optimization Level user property.

Business Component User Properties ■ Doing Other Work
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 173
To specify the DB2 optimization level for SQL statements
1
Use other tuning options:
■ Make sure an index exists that addresses the needs of the WHERE conditions and the ORDER
BY clause on the tables that Siebel CRM uses in the query.
■ Remove one or more columns from the ORDER BY clause.
■ If the business component is customized, then simplify this customization.
2 If Step 1 does not fix the problem, then proceed to Step 3.
3 Analyze performance.
You can use the /s <filename> option when you start the client. This option causes Siebel CRM
to log all SQL statements. This log file includes the time that Siebel CRM spends to run each SQL
statement. You can use it to identify the statements that run slowly. Note that the DB2 SQL
generator adds the following clause to the end of the SQL statement. This clause does not display
in the SQL log:
optimize for 1 row
4 If a DB2 Optimization Level user property already exists on the business component that creates
the SQL statement, then examine this optimization level to determine if it causes the slow SQL
query.
5 Paste the suspected slow query into one of the explain utilities, add the following clause, and
then set the optimization level to the appropriate value:
optimize for 1 row
6 Create a query plan for the statement, and then analyze it. If you conclude that modifying the
optimization level is the best way to improve query performance, then use a different
optimization level.
7 If the new optimization level fixes the slow query, then add the user property to the business
component.
Capturing User Drilldown Behavior
You can use the business component user properties that this topic describes to capture user
drilldown behavior so that Siebel CRM can store values for the business component fields where the
drilldown occurs. It can store these values in an attribute in a user profile, which is a type of attribute
that Siebel CRM creates at run time to allow it to modify the Siebel application behavior in reply to
a user action. It can store one business component field for each of these attributes. For more
information about these attributes, see the topic about the SetProfileAttr method for an application
in Siebel Object Interfaces Reference, and the topic about dynamic user profile attributes in Siebel
Personalization Administration Guide.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Doing Other Work
174
Example of Capturing User Drilldown Behavior
In this example, the Com Invoice Profile comes predefined with Siebel CRM starting with Siebel CRM
release 8.1.1.10. It tracks the parent Account Id when the user navigates away from the Account
Summary View. This view displays the following information:
■ Account details in a form applet that references the CMU Com Invoice Profile business component
■ Invoice profiles in a list applet that references the Com Invoice Profile business component
These business components reference the same database table, but no link exists that Siebel CRM
can use that allows the CMU Com Invoice Profile business component to access the Account business
component. Assume your implementation must get billing details from an external system when the
user drills down on a billing profile. To support this requirement, Siebel CRM must send an integration
object message that includes the following data:
■ Data from the CMU Com Invoice Profile business component, including values for the Invoice
Profile Name field and the Account Id field that Siebel CRM uses as key fields to get billing
information for the SOAP and HTTP Web service call. This billing information includes invoices,
payment adjustments, balance, and so on.
■ The Account Id of the account that Siebel CRM displays in the Account Summary View when the
user drills down on the Profile Name field of the business component record that Siebel CRM
displays in the Com Invoice Profile list applet.
Siebel CRM includes the following predefined objects to capture this Account Id:
1 Adds the Profile Name drilldown object to the CMU Com Invoice Profile List Applet. The View
property of this drilldown object references the CMU Billing Invoice View. The business
component property of this applet references the Com Invoice Profile business component.
2 Adds the following user properties to the Com Invoice Profile business component.
ProfileAttributeValue1 and ProfileAttributeValue2 each provide the name of a business
component field. In this example, ProfileAttributeValue must contain the name of a business
component field that currently exists. ProfileAttributeName can contain a text string.
Name Value
DrilldownObject0 Profile Name
Profile Name:ProfileAttributeName1 Service Account Id
Profile Name:ProfileAttributeName2 Service Account
Profile Name:ProfileAttributeValue1 Account Id
Profile Name:ProfileAttributeValue2 Account Name

Business Component User Properties ■ Doing Other Work
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 175
3 Adds the following fields to the CMU Com Invoice Profile business component:
DrilldownObject User Property
The DrilldownObject n user property identifies the name of a drilldown object. This drilldown object
resides in an applet. It references a business component.
Table 34 describes typical values for this user property.
Profile Name: attributename User Property
The Profile Name: attributename user property identifies the name of the profile attribute that Siebel
CRM sets when the user clicks a drilldown object.
Table 35 describes typical values for this user property.
Profile Name: attributevalue User Property
The Profile Name: attributevalue user property identifies the name of a business component field.
Siebel CRM sets the value for this field according to the results of the drilldown.
Name Calculated Value
Service Account GetProfileAttr("Service Account")
Siebel CRM uses the value of the ProfileAttributeName2 profile defined
in Step 2 to calculate the Service Account.
Service Account Id GetProfileAttr("Service Account Id")
Siebel CRM uses the value of the ProfileAttributeName1 profile defined
in Step 2 to calculate the Service Account Id.
Table 34. Example of the DrilldownObject n User Property
User Property Value
DrilldownObject0 Name of the drilldown object. For example:
Profile Name
Table 35. Example of the ProfileAttributeName User Property
User Property Value
Profile Name:ProfileAttributeName1 Name of the profile attribute. For example:
Service Account Id

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Business Component User Properties
■ Doing Other Work
176
Table 36 describes typical values for this user property.
Table 36. Example of the ProfileAttributeValue User Property
User Property Value
Profile Name:ProfileAttributeValue1 Value of the profile attribute. For example:
Account Id

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 177
7 Siebel Web Engine Tags
This chapter describes Siebel Web Engine (SWE) tags. It includes the following topics:
■ About SWE Tags on page 177
■ Applet Tags on page 178
■ Form and Web Page Tags on page 184
■ Frame Tags on page 185
■ Navigation Control Tag on page 187
■ Program Logic Tags on page 189
■ Referential Tags on page 193
■ Screen Tags on page 196
■ Subview Tags on page 198
■ Threadbar Tags on page 200
■ Togglebar Tags on page 203
■ Toolbar Tags on page 205
■ Tree Tags on page 207
■ View Tags on page 209
■ Tags That Support a Specific Feature on page 215
■ Tags That Are for Oracle Internal Use Only on page 217
About SWE Tags
A Siebel Web Engine (SWE) tag is an HTML tag that you can insert in a Siebel Web Template file. It
specifies how to format and display a repository object that resides in an HTML page in the client.
Siebel CRM locates Siebel Web Template Files (SWT) in the WEBTEMPL directory of the Siebel Server
installation directory. For more information, see Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
A SWE tag includes the following prefix:
swe:
For brevity, this chapter includes this prefix only in the format description and code example.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Applet Tags
178
Applet Tags
This topic describes tags that you can use to configure how SWE displays an applet. It includes the
following topics:
■ Applet Tag on page 178
■ Applet Layout Tag on page 178
■ Control Tag on page 179
■ Form Applet Layout Tag on page 180
■ Master and Detail Applet Tags on page 180
■ Select Row Tag on page 182
Applet Tag
The applet tag references an applet that SWE displays in a view. It uses the following format:
<swe:applet id="1" var="Parent"/>
where:
■ id. References an applet that uses the View Web Template Item list.
■ var. Allows you to use a variable in the applet template that configures the if-var tag to
conditionally display HTML. For example, you can use the applet tag to display the Applet Title
in the applet template only if the applet is a top applet.
You can use the applet tag only in a view Web template.
Applet Layout Tag
The applet layout tag controls the layout of an applet. You can use it to determine the HTML content
that SWE displays according to the current view layout mode and layout preferences. It uses the
following format. You must specify at least one attribute:
<swe:layout viewDisplayMode="
view_mode
" appletDisplayMode="
applet_mode
"
appletDisplaySize="
size
"/>
where:
■ viewDisplayMode. Optional. You can use one of the following values:
■ Layout. SWE displays the tag only if Siebel CRM is in Edit View Layout mode.
■ Show. SWE displays the tag only if Siebel CRM is not in Edit View Layout mode.
If you do not include the viewDisplayMode attribute, then SWE displays the tag regardless of the
Edit View Layout mode.
■ appletDisplayMode. Optional. You can use one of the following values:

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Applet Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 179
■ Show. SWE displays the tag only if the applet is visible.
■ Hide. SWE displays the tag only if the applet is hidden.
If you do not include the appletDisplayMode attribute, then SWE displays the tag regardless of
applet visibility.
■ appletDisplaySize. Optional. You can use one of the following values:
■ Min. SWE displays the tag only if the applet is minimized.
■ Max. SWE displays the tag only if the applet is maximized.
If you do not include the appletDisplaySize attribute, then SWE displays the tag regardless of
applet display size.
Control Tag
The control tag provides a placeholder in an applet Web template for a control or list column. It uses
the following format:
<swe:control id="1" property="
property_name
" />
where:
■ id. Maps a child applet, control, or list column to this placeholder tag.
■ property. Optional. If you include this attribute, then it identifies the property of the control or
list item that SWE displays on the Web page.
You can use this tag only in an applet Web template of type Base, Edit, New, or Query.
You cannot nest the control tag. For example, SWE does not support following usage:
<swe:control id = "1"> <!-- the "parent" control
<swe:this property = "displayname"/>
<swe:this property = "formattedHtml"/>
<swe:control id = "2" property="formattedHtml">
<!-- A child control gets context or gets properties from its "parent">
</swe:control> <!-- End of parent -->
Defining the Property Attribute of the Control Tag
Table 37 describes the values that you can use for the property attribute. You can use this attribute
only in a singleton tag. A singleton tag is a tag that does not include a required end tag.
If you do not include this attribute, then:
■ This tag displays the body only if the ID attribute maps the control ID.
■ You can use the following tag to display this user property in the body of the control tag:

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Applet Tags
180
this
Form Applet Layout Tag
The form-applet-layout tag contains the controls that reside in the main body of a form applet. It
uses the following format:
<swe:form-applet-layout>
</swe:form-applet-layout>
This tag does not include any attributes. You cannot use the idgroup tag in this template. For more
information, see “Map Siebel Object to SWE Tag” on page 194.
Master and Detail Applet Tags
The for-each-child and child-applet tags display a view that includes master and detail applets. This
view is similar to the layout that a catalog uses. SWE can interweave the records that it displays in
these applets instead displaying only master records in the master applet and only detail records in
the detail applet.
You can configure the master and detail applets as list applets to create a layout that is similar to a
catalog. To define a relationship between these applets, you can use the Position attribute of the view
web template item. This attribute is similar to the Position attribute of a tree node:
■ The master applet uses a first-level position value, such as 1 or 2.
■ A child applet uses a second-level position value, such as 1.1 or 1.2.
■ A grandchild applet uses a third-level position value, such as 1.1.1 or 1.1.2.
SWE can display more than one set of master and detail relationships in a view where more than one
master applet can exist.
Table 37. Values You Can Use for the Property Attribute
Value Description
FormattedHtml Displays the data for a control or list item in HTML.
DisplayName Displays the caption property of the control or list item.
ListHeader Displays a column header for a list column that includes links that the user
can use to sort the column. You can use this value only with a control tag that
Siebel CRM maps to a list column that resides in the Base template of a list
applet.
RequiredIndicator Displays an icon if the control is required. For example, assume the user must
enter a value for the control before Siebel CRM can save the record to the
database. The RequiredIndicator parameter that resides in the SWE section
of the application configuration file identifies this icon.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Applet Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 181
Siebel CRM only maps the master applets to the applet tags that the view template contains. It does
this mapping in the view web template item. It does not assign IDs to the other applets that the view
web template item contains. It specifies the layout of nonmaster applets in the applet template of
the master applet. It does not specify this layout in the view template.
Siebel CRM supports this layout only for an applet that is in base mode.
The catalog style layout works only in standard interactivity mode. You must not use these tags in
high interactivity mode.
Example of Using Master and Detail Applet Tags
In the example that this topic describes, assume a master and detail view includes the Category
Items List Applet as the master applet and the Sub Category Items List Applet as the detail applet.
The following table lists the view web template items that this view uses.
The base template for the Category Items List Applet contains the following code:
<table>
<swe:for-each-row>
<tr>
<td>
<swe:control id ="5001" /> </td><!-- field value similar to "Small Business" -->
<td>
<swe:for-each-child>
<swe:child-applet> <!-- Display the child applet -->
</swe:for-each-child>
</td>
</tr>
</swe:for-each-row>
</table>
The base template for the Sub Category Items List Applet contains the following code:
<table><tr>
<swe:for-each-row>
<td>
<swe:control id="5001"/> </td><!-- field value similar to "Desktop" -->
</swe:for-each-row>
</tr></table>
Iterate Child Applets Tag
The for-each-child tag iterates each of the child applets that Siebel CRM defines for this applet
according to the position value of the view web template that resides in the view that references this
applet. It uses the following format:
New Identifier Applet Applet Mode Position
101 Category Items List Applet Base 1
Sub Category Items List Applet Base 1.1

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Applet Tags
182
<swe:for-each-child> ...... </swe:for-each-child>
SWE can use this tag only in the base template of an applet. If the applet does not contain a child
applet, then SWE ignores this tag.
Child Applet Tag
The child-applet tag places a child applet in a parent applet. The base template of this child displays
the child at the point where SWE places this tag.
The child-applet tag uses the following format:
<swe:child-applet/>
You can set the HTML Number of Rows property of the Sub Category Items List Applet to the number
of values that SWE must display in each category.
You must configure the appropriate drilldown objects to allow the user to drill down from the category
and subcategory values.
Select Row Tag
The select-row tag displays check boxes in a multiselect list applet. This applet allows the user to
choose multiple items for a transaction. To make these choices, the user clicks the check boxes that
SWE displays in the left column.
This tag uses the following format:
<swe:select-row property="FormattedHtml" />
where:
■ property. If the applet is enabled for multirecord selection in Siebel Tools, and:
■ If you set the property attribute to FormattedHtml in the select-row tag or in this tag, then
SWE displays the check box. For more information, see “This Tag” on page 195.
■ If you do not include the property attribute, then SWE displays the body of this select-row
tag.
For example:
<swe:select-row property="FormattedHtml" />
For example:
<swe:select-row>
<swe:this property="FormattedHtml" />
</swe:select-row>
You can set the HTML Multi Row Select property of the list object of the applet to TRUE to enable
multirecord selection in Siebel Tools.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Applet Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 183
Using the Select Row Tag
You can use the select-row tag to create a generic list applet template that SWE can use with a list
applet that does or does not support multirecord selection in the following locations:
■ In the list header. You can use the select-row tag to conditionally add a td tag for the header
for the row selection check box column.
■ In the list body. You can use the select-row tag with the this tag to conditionally add a td tag
that contains the check box.
You must place list applet controls and list columns in a form tag when you enable multirecord
selection. Any method that resides on the applet requires that SWE submit the form that contains
the row selection check boxes. For more information, see “Form Tag” on page 184.
If the user chooses multiple records, then Siebel CRM does not disable a control that does not
support calling a method. This situation occurs because Siebel CRM does not call the Siebel Server
if the user chooses multiple records. Instead, if the control is activated, then Siebel CRM sends a
message to the user that states that it cannot do the action if multiple records are chosen.
How the Select Row Tag Positions the Current Record
The select-row tag positions the current record differently than how the PositionOnRow control
positions this record. A single list applet can contain the PositionOnRow control and the Multiple Row
Selection. Siebel CRM chooses the record where the business component is currently positioned
when the user navigates to a list applet. The user can use the check box to remove the check mark
for this record.
Unlike PositionOnRow, no round trip occurs to the Siebel Server when the user uses a check box to
choose rows. Siebel CRM identifies the records as chosen on the business component only if it calls
a method that resides on the applet. The user can choose records across multiple pages. The user
can use the Next and Previous controls and can also choose records from different working sets.
How the HTML Client Framework Chooses Records
If Siebel CRM calls a method that resides on an applet, then the HTML Client framework sets the
chosen records in the business component. This configuration occurs in the PrepareToInvokeMethod
method before it calls the DoInvokeMethod method. These methods reside in the CSSSWEFrame
class. Siebel CRM does the following work when the framework uses a command to call a method
that resides on an applet:
1 Positions the parent business component of the applet, if it exists, on the correct records.
2 Positions the business component that the applet references in the currently active record, if
necessary.
3 If Siebel CRM identifies multiple records, then it calls the SelectRowById method of the
CSSBusComp class to choose these records in the business component.
4 To call the method on the applet, Siebel CRM calls the DoInvokeMethod method of the
CSSSWEFrame class.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Form and Web Page Tags
184
The CSSSWEFrame class does not include any methods that support multiple records. If a specialized
applet supports this feature, then the DoInvokeMethod method must be specialized. The
DoInvokeMethod method calls the IsMultiRecSelected method of the CSSSWEFrame class to
determine if multiple records are chosen. If TRUE, then it calls the EnumAllSelections of the
CSSBusComp class to get all the records that are currently chosen in the business component. For
important caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28.
Form and Web Page Tags
This topic describes tags that you can use to configure how SWE displays a form and how it uses a
web page. It includes the following topics:
■ Form Tag on page 184
■ Web Page Item Tag on page 184
Form Tag
The form tag creates an HTML form that allows the user to input information. It uses the following
format:
<swe:form name="
form_name
" htmlAttr="
attribute_names
"> ... </swe:form>
where:
■ name. Optional. Specifies the HTML form name. If not specified, then SWE uses a name that it
creates internally.
■ htmlAttr. Optional. The value for this attribute must contain the names of valid attributes that
the HTML form tag contains. SWE applies these attributes to the HTML form that it creates. You
cannot use the following values:
■ method
■ name
■ action
Web Page Item Tag
The pageitem tag provides a placeholder in a web page for a web page item. It uses the following
format:
<swe:pageitem id="1" property="FormattedHTML" />
where:
■ id. Identifies a web page item.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Frame Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 185
■ property. Optional. Identifies the property of the Web page item that SWE displays on the Web
page. You can use this attribute only in a singleton tag.
You can use one of the following values.
■ FormattedHtml. Display the data for the Web page item in HTML.
■ DisplayName. Display the caption property of the Web page item that the repository
contains.
If you do not include the property attribute, then:
■ SWE displays the body only if the Web page item ID is mapped.
■ SWE can use the this tag to display the property in the body of the pageitem tag. For more
information, see “This Tag” on page 195.
You can use this tag only in a Web page.
Frame Tags
This topic describes tags that you can use to configure how SWE uses frames. It includes the
following topics:
■ Frame Tag on page 186
■ Frameset Tag on page 186
The frame tags allow SWE to control how it refreshes URLs. You can use them in the following
situations:
■ Container page template. Creates the frame definition document for SWE. Note the following:
■ It is recommended that you define the contents of the frame that uses the include tag, but
it is not required. You can place these contents in the body of the frame tag. For more
information, see “Include Tag” on page 193.
■ The contents of the frame tag must include the entire HTML document. It must include the
HTML document structure tags, such as the html, head, and body tags, and so on. This
content must include the view templates.
■ If the type is View, then the contents of the frame tag must contain only the current-view
tag. For more information, see “Current View Tag” on page 211.
■ View template. Used in a View template to create a frame definition document that displays the
applets that the view contains. SWE refreshes these frames only if one or more of these applets
contains new data. Note the following:
■ SWE can use a frame in a View template only if it also uses this frame in the container page,
and only if a separate frame exists in the container page for the View.
■ If you place an applet in a frame, then you must make sure that Siebel CRM maps at least
one applet tag in this frame to an applet. If you do not do this, then an empty frame might
occur. For more information, see “Applet Tag” on page 178.
■ If a frame tag contains an applet tag, then you must set the type attribute of this tag to
Applet.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Frame Tags
186
Frame Tag
The frame tag identifies the beginning and end of the contents that SWE places in a frame. SWE
displays this tag as an HTML frame tag, with the src attribute of this tag set to a SWE URL that gets
the contents of the frame.
The frame tag uses the following format:
<swe:frame type="
frame_type
" name="
frame_name
"> .... </swe:frame>
where:
■ type. Identifies the frame type. SWE uses this information to determine when to refresh this
frame. You can use one of the values that the following table describes.
■ name. Optional. Specifies a name for the frame. You can use this attribute only if the type of the
frame is Page. SWE creates a typical name for other frame types.
You must place the frame tag in the body of the frameset tag.
SWE can support a nested frameset where:
■ The frame tag contains a frameset tag.
■ the Type attribute of the outer frame tag is Page.
Frameset Tag
The frameset tag defines the set of frames that the document contains. It uses the following format:
Value Description
Screenbar In a container page template, specifies that the frame contains the primary tab
bar.
Viewbar In a container page template, specifies that the frame contains Siebel CRM
menus, a visibility drop-down list, and a search drop-down list.
View In a container page template, specifies that the frame contains the current view
that includes the content area.
Page In a container page template, specifies that the frame contains a Web page. SWE
does not refresh these frames after initial loading.
Applet In a View template, specifies that the frame contains an applet.
Content Creates a frameset that includes view frames. It supports how Siebel CRM
displays multiple views in some features, such as Search Center. The Content
frame typically includes a frameset that contains only the View frame. Other
content frames can include framesets that include two or more frames, the View
frame, and frames that display other views, such as the Search View.
AltView Configures subframes to display one or more alternate views in the content
frame, such as Search Center, in addition to the view in the View frame.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Navigation Control Tag
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 187
<swe:frameset htmlAttr="
attribute_names
"> ... </swe:frameset>
where:
■ htmlAttr. Specifies the attributes for the HTML frameset tag.
SWE displays the frameset tag as an HTML frameset tag. The body of the frameset tag can only
contain frame tags.
Navigation Control Tag
The nav-control tag implements navigation control. It uses the following format:
■ Screenbar that first-level navigation uses:
<swe:nav-control type="Screen With Category" style="Tab" indentWidth="
integer
"/>
■ Drop-down list that second-level navigation uses:
<swe:nav-control type="Category View" style="Select"/>
■ Detail view that third-level navigation uses:
<swe:nav-control type="
type
" style="Tab" indentWidth="
integer
"
anchorTab="
Enabled or Disabled
"/>
where:
■ type, style. Specifies the type and style. You can use the values that the following table
describes.
■ indentWidth. Specifies the number of pixels to indent the row of tabs. Applies to screen and
detail view tabs.
Type Style Description
Category View Select Displays a visibility dropdown list. Applies to visibility
control.
Detail Category Tab Displays view navigation control that includes category
tabs but no links below the tabs.
Applies to separate view and subview navigation control.
Detail Category View Tab Displays subview navigation control that includes view
tabs. Applies to separate view and subview navigation
control.
Detail Category With
View
Tab Displays view navigation control that includes category
tabs and a set of links below the tabs. Applies to view
navigation control.
Screen With Category Tab Displays screen tabs that includes category links below the
tabs. Applies to view navigation control.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Navigation Control Tag
188
■ anchorTab. Enables or disables smart view anchoring.
First-Level Navigation Example
The CCScreenbar_Tabs.swt template includes the following code:
<swe:if condition="Web Engine State Properties, IsHighInteractive">
<swe:switch>
<swe:case condition="Web Engine State Properties, IsHtmlMarkup">
<swe:nav-control type="Screen With Category" style="Tab" indentWidth="8"/>
</swe:case>
...
</swe:switch>
</swe:if>
Second-Level Navigation Example
The CCFormButtonsTop.swt template includes the following code:
<swe:if-var name="Parent">
<swe:if condition="Web Engine State Properties, IsHighInteractive">
<swe:switch>
<swe:case condition="Web Engine State Properties, IsViewPosition, 'Position:2'">
<td><img src="images/spacer.gif" width="1" height="1"></td>
<td class="AppletTitle" nowrap>
<swe:nav-control type="Category View" style="Select"/>
</td>
</swe:case>
...
</swe:switch>
</swe:if>
</swe:if-var>
Third-Level Navigation Example
The CCViewbar_Tabs_DropList.swt template includes the following code:
<swe:if condition="Web Engine State Properties, IsHighInteractive">
<swe:switch>
<swe:case condition="Web Engine State Properties, IsHtmlMarkup">
<swe:switch>
<swe:case condition="Web Engine State Properties, IsViewPosition,
'Position:3'">
<table class="tier3Back" width="100%" align="center" cellpadding="0"
cellspacing="0" border="0"><tr valign="top"><td><img src="images/spacer.gif"
width="1" height="3"></td></tr></table>
<swe:nav-control type="Detail Category With View" style="Tab"
indentWidth="30" anchorTab="Enabled"/>
</swe:case>

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Program Logic Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 189
</swe:switch>
</swe:case>
</swe:switch>
...
</swe:if>
Support for the Navigation Control Tag Across Siebel CRM Versions
This book describes support for the nav-control tag starting with Siebel CRM version 7.7 in high
interactivity mode. Before Siebel CRM version 7.5.3.6, if a user action or navigation causes Siebel
CRM to refresh the current view or to display a new view, then it anchors the result at the top of the
page, by default. This behavior might disorient the user in some situations. For example, assume the
user clicks a view tab to navigate to a new view and this user expects that Siebel CRM will display
detail information, such as attachments, in the bottom part of the target view. Assume the user views
the lower part of a view where the parent applet uses more than a full window height. In this
situation, the user must scroll to display the view details.
Starting with Siebel CRM version 7.5.3.6 in high interactivity mode:
■ The smart view anchoring feature solves these problems. It anchors and adjusts the scroll
position in a view after the user does something that causes Siebel CRM to modify or refresh a
view. For example, if the user clicks a view tab, then Siebel CRM does not modify the location
where it displays this tab.
■ Siebel CRM enables view anchoring, by default. You can disable this behavior for third or fourth
level view navigation that the user starts when the user clicks a view tab. To do this, you set the
anchorTab property of the SWE template that the view uses to Disabled.
Program Logic Tags
This topic describes tags that you can use to control program logic, such as how SWE handles errors
or does conditional branching. It includes the following topics:
■ Error Tag on page 189
■ JavaScript Tag on page 190
■ If Tag on page 191
■ Iterate Tag on page 192
■ Iterate Rows Tag on page 192
■ Switch, Case, and Default Tags on page 192
Error Tag
The error tag displays an error message. If an error occurs on the Siebel Server when Siebel CRM:
■ Submits a form. SWE displays the same page again and it includes the error message.
■ Does not submit a form. SWE continues to use the application error page.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Program Logic Tags
190
You can use one of the following formats:
■ Format one:
swe:error
■ Format two:
<swe:error property="FormattedHtml" />
■ Format three:
<swe:error>
<swe:this property="FormattedHtml" />
<swe:error/>
For example:
<swe:form>
<swe:error>
<b> <font color="red"> <swe:this property="FormattedHtml"/> </font> </b>
</swe:error>
.....
</swe:form>
Note the following:
■ You can use the error tag in any form tag.
■ If you do not use an error tag in a Siebel Web template file, then the code creates a
CSSSWEErrorSWX instance as an error node. It inserts this error node as the first child of the
enclosing page or form node.
■ If no errors exist when SWE displays a form, then it ignores the contents of the error tag.
■ SWE displays the error message in plain text in a new paragraph. If the error message font uses
the same color as the background, then it is not visible. You can use the enclosing HTML tags to
modify the font and style that Siebel CRM uses for the error message.
■ You can use the error tag in a form tag in an applet template only if Siebel CRM uses standard
interactivity. Siebel CRM uses a dialog box to display an error in high interactivity mode.
■ You must use the error tag instead of using the pageitem tag mapped to the _SWEErrMsg item
in the application error page. Siebel CRM does not support the _SWEErrMsg item. For more
information, see “Web Page Item Tag” on page 184.
JavaScript Tag
The scripts tag specifies where to place any JavaScript that SWE creates for the page. It uses the
following format:
<swe:scripts/>
This tag does not include any attributes.
Note the following:

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Program Logic Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 191
■ SWE includes some JavaScript code in every page that it sends to the browser. This code must
occur after all the Siebel content that the page contains, and it must reside in the HTML body tag.
■ The scripts tag must be the last Siebel SWE tag that the template contains, and it must reside
in the HTML body tag.
■ SWE determines the correct placement of this tag, repositions it, if necessary, and removes any
scripts tags that it does not require.
■ If you do not specify the scripts tag, then SWE places the JavaScript code immediately after the
last tag that the page contains, by default. In some situations, this configuration might occur in
an HTML formatting tag that is similar to td … /td. This configuration might cause a minor
formatting problem when the browser displays the page.
If Tag
The if tag implements a simple IF THEN conditional branch. It uses the following format:
<swe:if
condition="
business_service
,
business_service_method
,
argument1
:
value1
,
argument2
:
val
ue2
,..."> ... </swe:if>
where:
■ condition. Defines the condition.
■ argument:value defines an argument and value pair.
If SWE evaluates the condition to:
■ TRUE. It processes the body of the if tag.
■ FALSE. It ignores the body of the if tag.
You can use the if tag with any business service, such as a custom business service that examines
an HTTP header. The output arguments for this business service must contain a property that
includes the name of the business service method and a value of 1 or 0 that indicates if the condition
is true or false.
The predefined Web Engine State Properties business service supports the following conditions:
■ IsEvenRow
■ IsOddRow
■ IsCurrentRow
■ IsErrorRow
■ IsRowMultipleOf
■ IsRowPositionOf
■ IsLastDisplayedRow
■ IsHighInteractive
■ IsHighInteractiveApplet

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Program Logic Tags
192
■ IsLowInteractive
■ Invalid
Iterate Tag
The for-each tag iterates a tag according to the number of times that you specify. It can reduce the
size of template files if SWE uses the same HTML tags, and if Siebel tags contain controls or page
items that include different values for the ID parameter.
This tag uses the following format:
<swe:for-each count="
integer
" iteratorName="
interator_name
" startValue="
integer
"/>
where:
■ count. Specifies the number of times the tag iterates the tag contents.
■ iteratorName. Specifies the name of the iterator. You can use the following format to get the
value of the iterator during the iteration:
swe:
iteratorName
You must replace the iteratorName attribute with the actual name of the iterator. For example,
if you set the value of the iteratorName to CurrentID, then you must use the following format:
swe:CurrentID
■ startValue. Specifies the value that SWE assigns to the iterator at the start of the iteration. To
do the iteration, SWE assigns this start value to the iterator, and then increments the iterator by
one for each iteration.
Iterate Rows Tag
The for-each-row tag iterates each record that SWE displays in a list applet. It creates columns of
data that SWE displays in a list applet. It uses the following format:
<swe:for-each-row count="
integer
"/>
where:
■ count. Specifies the maximum number of records to iterate. If the number of records that the
list applet contains is less than this count, then the tag only iterates for the number of records
that the list applet contains.
You can use this tag only in a Base template for a list applet.
Switch, Case, and Default Tags
The switch, case, and default tags provide conditional branching that is similar to the switch, case,
and default statements in the C++ language. For example, they can use the following format:

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Referential Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 193
<swe:switch>
<swe:case condition="
case_tag_attribute
">
...
</swe:case>
<swe:case condition="
case_tag_attribute
">
...
</swe:case>
<swe:default>
...
</swe:default>
</swe:switch>
where:
■ condition. Is an attribute of the case tag that specifies the condition that SWE examines. The
condition attribute uses the same format that the if tag uses. If any case tag:
■ Satisfies the condition. SWE ignores all subsequent case tags and default tags. It
processes the body of the if tag.
■ Does not satisfy the condition. SWE processes the body of the default tag.
For more information, see “If Tag” on page 191.
Note the following:
■ The switch tag is a container tag that SWE uses for the case and default tags. SWE ignores any
other type of tag that the body of the switch tag contains.
■ SWE examines the case tags starting with the first case tag it encounters.
■ SWE allows only one default tag in the body of a switch tag.
Referential Tags
This topic describes tags that you can use to configure SWE to reference objects. It includes the
following topics:
■ Include Tag on page 193
■ Map Siebel Object to SWE Tag on page 194
■ This Tag on page 195
■ This Id Tag on page 196
■ This Table Id Tag on page 196
Include Tag
The include tag includes another template or HTML file in the current template file. It uses the
following format:
<swe:include file="
file_name
.swt"/>

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Referential Tags
194
where:
■ File. Identifies the name of the file that SWE must include. This file must reside in the same
folder as the other template files that SWE uses. It must use an .swt extension even if it is an
HTML file.
Map Siebel Object to SWE Tag
The idgroup tag maps a Siebel object to SWE. It uses the following format:
<swe:idgroup name="
namespace_ID
">
where:
■ name. Identifies the namespace ID. You must identify the namespace to support mapping.
SWE can apply the namespace to other mappings, such as an applet or page item.
Example of Mapping Siebel Objects to SWE
For example, assume Siebel CRM must display an applet that includes a DHTML menu in Internet
Explorer 5.0, and that it must use regular controls instead of the menu that other browsers use. All
other controls that the applet contains are the same for all browsers. To use mappings that are
specific to the browser, you can include each mapping in an idgroup tag. For example:
<swe:switch>
<swe:case condition="Web Engine User Agent, IsMemberVirtualUA,
'VirtualAgent:IE5'">
<swe:idgroup name="IE5">
<swe:menu>
...
</swe:menu>
</swe:idgroup>
</swe:case>
<swe:default>
<swe:idgroup name="NonIE5">
<swe:control id="1" ..>
<swe:control id="2" ..>
</swe:idgroup>
</swe:default>
</swe:switch>
<swe:control id="3" ..>
<swe:control id="4" ..>
In this situation, the NonIE5 namespace identifies the 1 and 2 IDs when SWE maps applet controls
to the control tags. The Namespace property of the applet web template item stores the namespace
value. The Web Layout Editor in Siebel Tools automatically populates this attribute. The mappings to
the control tags that include IDs 3 and 4 reside outside of the namespace. This attribute is empty
for these mappings. For more information, see “Control Tag” on page 179.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Referential Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 195
This Tag
The this tag references the object that contains it:
■ If it is nested in another tag, then it references a property of the parent tag.
■ If it resides outside of a tag, then it references the property of an applet, view, or application
according to the type of the template where it resides.
This tag uses the following format:
<swe:control id="1" >
<td> <swe:this property="DisplayName"/>: </td>
<td> <swe:this property="FormattedHtml"/> </td>
</swe:control>
where:
■ property. Identifies the name of the property that this tag references. You can use this tag in
any SWE tag that includes a property attribute.
Table 38 describes how you can use the this tag. You can use this tag only as a singleton tag except
when it references a viewlink tag or a screenlink tag. For more information, see “Screen Tags” on
page 196 and “View Tags” on page 209.
Table 38. How You Can Use the This Tag
Where the This Tag
Resides
What it
References
Property Attribute Values
Applet Web Template Applet The property attribute can contain the following
values:
■ Title. Display the title of the applet.
■ RowCounter. Display a row counter. You can
use the SWE_ROW_COUNTER_MAP list of
values to customize the display format of the
row counter.
View Web Template View The property attribute can contain the following
values:
■ Title. Display the title of the View.
Web Page Application The property attribute can contain the following
values:
■ Title. Display the title of the application object.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Screen Tags
196
This Id Tag
The this.Id tag creates scrollable tab bars for a screen or view. It creates a unique ID for the HTML
td tag that contains each tab. It uses the following format:
<swe:screenlink>
<td id="swe:this.Id" ...>
...
</td>
</swe:screenlink>
You can use this tag only in the HTML td tag that contains a screen, view, or subview tab. You can
add it to any one of the following tags:
■ “Screen Link Tag” on page 197
■ “View Link Tag” on page 214
This Table Id Tag
The this.TableId tag creates scrollable tab bars for a screen or view. It creates a unique ID for the
HTML table tag that contains the tabs. It uses the following format:
<swe:screenbar>
...
<table ID="swe:this.TableId" ...>
<swe:for-each-screen>
...
</swe:for-each-screen>
</table>
...
</swe:screenbar>
You can use the this.TableId tag only in the HTML table tag that contains the screen, view, or subview
tabs. You can add it any one of the following tags:
■ Screenbar Tag on page 197
■ Subview Bar Tag on page 198
■ View Bar Tag on page 212
Screen Tags
This topic describers tags you can use that affect screen behavior. It includes the following topics:
■ For Each Screen Tag on page 197
■ Screenbar Tag on page 197
■ Screen Link Tag on page 197
■ Screen Name Tag on page 198

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Screen Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 197
Starting with Siebel CRM version 7.7, Oracle supports these tags only for standard interactivity
mode. A view that runs in high interactivity mode use the nav-control tag. For more information, see
“Navigation Control Tag” on page 187.
For Each Screen Tag
The for-each-screen tag creates a screen bar. It iterates the screens that the Page Tab property of
the application object defines. The sequence value of each screen determines the tab order. This tag
uses the following format:
<swe:for-each-screen>
... HTML ...
<swe:screenlink property property="
property_name
" state="
property_state
">
... HTML ....
<swe:screenname/>
... HTML ...
</swe:screenlink>
... HTML ...
</swe:for-each-screen>
This tag does not include any attributes.
Screenbar Tag
The screenbar tag defines the section of the template that displays the screen bar. It identifies the
beginning and end of the screen bar section of the template. It uses the following format:
<swe:screenbar>
... HTML ...
<swe:for-each-screen>
... HTML ...
<swe:screenlink property property="
property_name
" state="
property_state
"
... HTML ...
<swe:screenname/>
... HTML ...
</swe:screenlink>
... HTML ...
</swe:for-each-screen>
... HTML ...
</swe:screenbar>
Screen Link Tag
The screenlink tag defines the link that the user clicks to navigate to the screen. It uses the following
format:
<swe:screenlink state="
value
" property="
value
" htmlAttr="
value
"/>
where:

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Subview Tags
198
■ state. Optional. Can include one of the following values:
■ Active. Use this tag only if the current view name identifies the currently active view.
■ Inactive. Use this tag only if the current view name does not identify the currently active
view.
If you do not include the state attribute, then SWE uses this tag for all views.
■ property. Optional. You can only use FormattedHtml as the value for this attribute. It creates
the HTML that defines the link. If you do not include this attribute, then SWE creates no output.
■ htmlAttr. Optional. Add more HTML attributes to the HTML tag.
To conditionally display different HTML for active and inactive views, you can specify the screenlink
tag without the property attribute but with a value for the state attribute. If you do not include the
property attribute, then you can use the this tag to display the property in the body of the screenlink
tag. For more information, see “This Tag” on page 195.
Screen Name Tag
The screenname tag displays the screen name. It uses the following format:
swe:
screen_name
Subview Tags
This topic describes subview tags. It includes the following topics:
■ Subview Bar Tag on page 198
■ For Each Subview Tag on page 200
Starting with Siebel CRM version 7.7, SWE uses these tags only in standard interactivity mode. High
interactivity mode uses the nav-control tag. For more information, see “Navigation Control Tag” on
page 187.
Subview Bar Tag
The subviewbar tag configures a subcategory View drop-down list. It can also display a second
horizontal tab bar beneath the detail view bar. It uses the following format:
<swe:subviewbar type="
type
" property="
value
">
where:
■ type. If set to:
■ Select. SWE displays the subview bar as an HTML select control that displays the set of views
that are available in the category that the user chooses.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Subview Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 199
■ Any value other than Select. SWE uses the viewlink tag and the viewname tag in the body
of the subviewbar tag. The behavior of these tags is similar to how SWE uses them in the
viewbar tag. For more information, see “View Tags” on page 209.
■ property. If set to FormattedHtml, then SWE displays the HTML Select control. You can use this
attribute only if you set the type attribute to Select.
If you do not include the property attribute, and if a subview exists, then SWE displays the
contents of this subviewbar tag.
How SWE Uses the Subview Bar Tag
If the user chooses a category name in the detail view bar, and if the subviewbar tag:
■ Exists. SWE sets the default view in this category as the active view, and then displays the
subcategory drop-down list or tab bar in this default view. It expands to list all the views that
reside in the category that the user chooses.
■ Does not exist. SWE displays the default view for the category. The default view is the view that
contains the lowest sequence number in the category that the user can view.
If the user chooses a noncategory view from the detail view bar, then the subviewbar tag displays
nothing.
Example of Using the Subview Bar Tag as a Control
The following code configures the subviewbar tag as an HTML select control in a subcategory drop-
down list. It references the CCViewDetail.swt file and the CCSubViewbar_Drop.swt file:
<swe:form>
<swe:subviewbar type="Select">
<tr class="tier4On">
<td> </td>
<td valign="top"><swe:pageitem id="2" property="DisplayName" /></td>
<td ><swe:this property="FormattedHtml" /></td>
<td width="100%"> </td>
</tr>
</swe:subviewbar>
</swe:form>
Example of Using the Subview Bar Tag as a Tab or Link
The following code configures the subviewbar tag as a tab or link in a subcategory tab bar. It
references the CCSubViewbar_Tabs.swt file:
<td class='tier4Off'><img src="images/nav/left_cap.gif" align="absmiddle" width="6"
height="19" border="0" alt=""/></td>
<swe:subviewbar>
<swe:viewlink state="Active" property="FormattedHtml" >
<td><img src="images/nav/tabon_arrw.gif" align="absmiddle"
width="6" height="19" border="0" alt=""/></td>

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Threadbar Tags
200
<td class='tier4OnLabel' background="images/nav/
tabon_back.gif"><nobr> <swe:viewname/> </nobr></td>
<td><img src="images/nav/tabon_rightcap.gif" align="absmiddle" width="6"
height="19" border="0" alt="" /></td>
</swe:viewlink>
<swe:viewlink state="Inactive" property="FormattedHtml" >
<td class='tier4Off'><nobr> <swe:viewname/> img src="images/nav/
tab_rightcap.gif" align="absmiddle" width="6" height="19" border="0" alt=""/></
nobr></td>
</swe:viewlink>
</swe:subviewbar>
<td width="100%" class="tier4Back"> </td>
For Each Subview Tag
The for-each-subview tag iterates each subview. It uses the following format:
swe:for-each-subview
SWE uses this tag if you do not set the type attribute of the subviewbar tag to Select. This behavior
is similar to the for-each-view tag. For more information, see “This Tag” on page 195 and “For Each
View Tag” on page 212.
Threadbar Tags
This topic describes tags that you can use to configure the threadbar. It includes the following topics:
■ About Threadbar Behavior on page 201
■ For Each Thread Tag on page 201
■ Step Separator Tag on page 201
■ Thread Link Tag on page 202
■ About Link Navigation on page 202
■ Example of Using the Threadbar Tags on page 202
The threadbar tracks user navigation among views. The following is an example of the threadbar.
The right-angle bracket (>) is a separator:
Home > Consumer:PCs > PCs:Laptops > Laptops:Pentium III
where:
■ Home, Consumer:PCs, and so on, are the thread buttons.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Threadbar Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 201
About Threadbar Behavior
If the user clicks the thread button, then SWE creates a new bookmark, and then displays a
bookmarked view. The bookmark ID for the new view is the current SWE count plus 1. Siebel CRM
sends this count to the Siebel Server in the request. The threadbar does the following:
■ If Siebel CRM requests a new screen, then SWE creates a new thread that replaces the current
thread.
■ If a user clicks a view button, then SWE replaces the last thread step with the view that the user
requests.
■ If the user clicks a link, then SWE appends a new step to the threadbar for the view that the tag
references.
■ If the user clicks a thread button, then SWE deletes all the thread buttons that exist to the right
of the button that the user clicks. It deletes the thread up to the step view according to the value
of the SWEBMCount parameter.
■ If a thread applet or thread field is not defined for a view, and if Siebel CRM displays this view,
then SWE does not update the thread button.
The bookmark ID assignment policy does not modify the bookmark deletion policy. Siebel CRM keeps
the 20 bookmarks that it created most recently and deletes previous bookmarks, by default. If the
SWE count in the user request is less than the SWE count on the Siebel Server, then Siebel CRM
deletes all the bookmarks that contain a SWE count that is larger than the count in the user request.
Usage for the threadbar tags is similar to behavior of the following tags:
■ “Screenbar Tag” on page 197
■ “View Bar Tag” on page 212
For Each Thread Tag
The for-each-thread tag iterates each of the thread steps to display the contents of these steps. It
uses the following format:
swe:for-each-thread
Step Separator Tag
The stepseparator tag specifies the symbol that separates thread buttons. You include it at the
beginning or the end of the threadbar tag. It uses the following format:
<swe:stepseparator>
separator_symbol
</swe:stepseparator>
You can use the threadlink and step separator tags only in the threadbar tag.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Threadbar Tags
202
Thread Link Tag
The threadlink tag identifies the thread button on the threadbar. It uses the following format:
<swe:threadlink property="
value
" title="
value
">...</swe:threadlink>
where:
■ formattedhtml. Include an HTML link.
■ title. Display the title=value pair of the thread button.
About Link Navigation
The thread button can contain a link that navigates the user to a previous page. Separators separate
the thread buttons. This link requires the following GotoBookmarkView command:
SWECmd=GotoBookmarkView&SWEBMCount=2SWECount =3
where:
■ SWEBMCount = 2 indicates that SWE uses bookmark #2 to create the view.
■ SWECount=3 is the bookmark ID for the current view.
For example, SWE translates a thread button for the AK Parker account into the following HTML:
<a href = "www.siebel.com/start.swe?SWECmd=GotoBookmarkView&SWEBMCount=2&
SWECount=3> Account: AK Parker </a>
Example of Using the Threadbar Tags
To use a threadbar, you insert threadbar tags in an appropriate SWT file. For example:
<swe:threadbar>
... HTML ...
<swe:for-each-thread>
... HTML...
<swe:threadlink property="FormattedHtml">
<span class="threadbar"><nobr><swe:this property="Title"/></nobr></span>
</swe:threadlink>
... HTML ...
<swe:stepseparator>
<span class="threadbardiv"> > </span>
</swe:stepseparator>
... HTML ...
</swe:for-each-thread>
... HTML ...
</swe:threadbar>
This code creates the following threadbar:
Home > Consumer:PCs > PCs:Laptops

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Togglebar Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 203
If your Siebel Business Application:
■ Uses frames. Put the tags in the swt file that contains the view bar frame or the swt file that
contains the view frame.
■ Does not use frames. Put the tags in a container page, such as the CCPageContainer.swt file.
Togglebar Tags
This topic describes tags you can use to configure the togglebar.
For Each Toggle Tag
The for-each-toggle tag iterates the number of toggle applets. It displays the contents of these
toggle applets. It uses the following format:
swe:for-each-toggle
This tag does not include any attributes.
Toggle Bar Tag
This topic describes tags that you can use to configure the toggle bar. It includes the following topics:
■ For Each Toggle Tag on page 203
■ Toggle Bar Tag on page 203
■ Toggle Link Tag on page 204
■ Toggle Name Tag on page 204
■ Examples of Using the Togglebar Tags on page 204
The togglebar tag displays the toggle selection control in an applet template. It works similarly to
how the viewbar tag and the for-each-screen tag works. For more information, see “View Bar Tag”
on page 212 and “For Each Screen Tag” on page 197.
It uses the following format:
<swe:togglebar type="
value
" property="
value
">
where:
■ type. If you set this attribute to:
■ Select. SWE displays the togglebar as an HTML Select control. This control lists applet titles
that the user can click to toggle applets.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Togglebar Tags
204
■ Any value other than Select. To create a toggle link or tab, SWE can use the for-each-
toggle, togglelink, and togglename tags in the body of the togglebar tag. This configuration
is similar to how SWE uses the for-each-view, viewlink, and viewname tags. For more
information, see “View Tags” on page 209.
■ property. If you set this attribute to FormattedHtml, then SWE displays the HTML Select control.
If you do not include this attribute, and if toggle applets are defined, then SWE uses the this tag
in the body of this togglebar tag to display the select control. For more information, see “This
Tag” on page 195.
You can use the property attribute only if you set the type attribute to Select.
If a toggle applet is not defined for the applet, then SWE ignores the togglebar tag.
Toggle Link Tag
The togglelink tag creates a toggle link. It uses the following format:
<swe:togglelink state="
active or inactive
" property="
value
">
where:
■ state. Optional. You can use one of the following values:
■ Active. Use this tag only if the current applet title identifies the currently active applet.
■ Inactive. Use this tag only if the current applet title does not identify the currently active
applet.
If you do not include the state attribute, then SWE displays this tag in all applets.
■ property. Optional. If you set this attribute to FormattedHtml, then SWE creates the HTML that
creates a link that the user can use to toggle the applet. If you do not include this attribute, then
SWE does nothing.
Toggle Name Tag
The togglename tag displays the applet title. It uses the following format:
<swe:togglename/>
Examples of Using the Togglebar Tags
The following code displays toggle applets as a select control:
<swe:togglebar type="Select" >
<table>
<tr>
<td> <swe:control id="1" property="DisplayName"> </td>
<td> <swe:this property="FormattedHtml"/> </td>

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Toolbar Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 205
</tr>
</table>
</swe:togglebar>
where:
■ SWE uses the control to create a label that is similar to the following. It places this control before
the select control:
Show:
The following code displays the toggle applets as tabs or links:
<swe:togglebar>
<table>
<tr>
<td><swe:togglelink property="FormattedHtml"> <swe:togglename> </swe:togglelink>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</swe:togglebar>
Toolbar Tags
This topic describes toolbar tags. It includes the following topics:
■ Configuring an HTML or Java Toolbar on page 205
■ Toolbar Tag on page 206
■ Toolbar Item Tag on page 206
A toolbar or toolbar item allows the user to start an action. Siebel CRM displays the toolbar in a
separate frame near the top of the client. Siebel CRM maps a command object definition to:
■ A toolbar item or toolbar icon that resides in an application-level menu or menu item.
■ An applet method menu item that resides in an applet menu.
A toolbar icon or toolbar menu item can reference a method name, a method handler, or a service.
This service can reside in one of the following locations:
■ On the Browser or the Siebel Server
■ In an applet class, business component class, SWE frame manager, or business component data
in the Browser or Siebel Server.
Configuring an HTML or Java Toolbar
Siebel CRM supports the following types of toolbars:
■ HTML toolbar. Resides in the top frame in the template. To add an HTML toolbar, you add the
following code to the SWT file:

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Toolbar Tags
206
<swe:toolbar name=
value
>
//
any HTML here
...
<swe:toolbaritem>
//
any HTML here
...
</swe:toolbar>
where:
■ value is the toolbar name that exists in the repository.
To configure a box item, you must configure the command so that it references a service.
■ Java toolbar. Resides in the frame below the top frame in Siebel Call Center and other
applications that use (CTI) computer telephony integration. If a Siebel Business Application does
not use any Java toolbar, then Siebel CRM does not include this lower frame.
To add a Java toolbar, you add the following code to the SWT file:
<swe:toolbar name="
name
" javaapplet="true" />
The Java applet calls the ShellUIInit method on the service that the command references when
the Java applet attempts to start. This applet calls the ShellUIExit method when it exits. Siebel
CRM uses a set of communication protocols that it defines for the communication between the
Java applet and the service.
Siebel CRM implements the toolbar as a Java applet that includes all the toolbar controls and the
threads that interact with the Siebel Server.
Toolbar Tag
The toolbar tag specifies a toolbar. It uses the following format:
<swe:toolbar name="
name
" javaapplet="
Boolean
" />
where:
■ name. Name of the toolbar object definition that resides in the repository.
■ javaapplet. You can use one of the following values:
■ TRUE. Use a Java toolbar.
■ FALSE or this attribute does not exist. Use an HTML toolbar.
Toolbar Item Tag
The toolbaritem tag resides between the toolbar start and end tags. It gets all of the toolbar items
for this toolbar from the repository. It uses the following format:
<swe:toolbaritem>
This tag does not include any attributes.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Tree Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 207
Tree Tags
This topic describes tags that you can use to configure an explorer view that contains a tree applet
and a list applet that allows the user to view tree details. This view style displays hierarchically
structured information in an expandable tree control. It includes the following topics:
■ Applet Tree List Tag on page 207
■ For Each Indent Tag on page 208
■ For Each Node Tag on page 208
■ Indent Image Tag on page 208
■ Node Tag on page 208
SWE does the following:
■ Displays the tree control in a vertical frame on the left side of the applet.
■ Displays detailed information for the item that the user chooses in the tree. It displays these
details in a detail applet in a vertical frame on the right side of the applet.
These vertical frames allow the user to scroll the tree applet independently of the detail applet. This
configuration allows the tree to grow in length and width.
SWE does the following to display a tree:
■ Iterates each item of the tree.
■ Displays each item top-down, depth-first.
■ Displays one item at time.
■ Indents each tree item so that the text displays at the correct indent level relative to the master,
and to display the expand and collapse button, the text of the item, and the links.
■ It uses one of the following to display the indentation, the expand button, the collapse button,
and the item:
■ A series of GIF images.
■ Text if in text-only mode.
■ Displays the list applet that is associated with the currently chosen tree node as part of the view.
Applet Tree List Tag
The applet-tree-list tag is a placeholder for the list applet that SWE displays if the user chooses or
expands a tree item. This list applet depends on the type of the item that is currently chosen.
This tag uses the following format:
swe:applet-tree-list
This tag does not include any attributes.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Tree Tags
208
For Each Indent Tag
The for-each-indent tag creates an indentation. It iterates each level of a tree item. It does not
include any attributes.
This tag uses the following format:
swe:for-each-indent
For Each Node Tag
The for-each-node tag display tree nodes and field values. It iterates each visible item in the tree
control top-down and depth-first. If you do not specify the count attribute, then this tag iterates all
nodes in the tree. This tag uses the following format:
swe:for-each-node
Indent Image Tag
The indent-img tag provides a placeholder for the GIF image that corresponds to the current
indentation level of a tree item. SWE identifies the GIF file it uses in the img tag at each level. The
GIF image in this file can be an empty space or a vertical bar.
This tag uses the following format:
swe:indent-img
This tag does not include any attributes.
Node Tag
The node tag provides a placeholder for a tree item. This item can be one of the following:
■ Tree node. SWE displays the display name.
■ Field value. SWE creates the field value.
This tag uses the following format:
<swe:node state="
value
" type="
value
"/>
where:
■ state. You can use one of the following values:
■ Active. A chosen node.
■ Inactive. A nonchosen node.
■ type. You can use one of the following values:
■ DisplayName. Display the Display Name property of the tree node.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ View Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 209
■ FieldValue. Display the field value.
The expand and collapse button, the item icon, and the links are part of a tree item. Depending on
settings in the configuration file, SWE displays the expand and collapse button as a GIF image or as
text. It displays the expand and collapse button only if the tree item includes a child item.
The following links are associated with each item:
■ A link for the expand and collapse button that expands or collapses the item.
■ A link for the item image that allows the user to choose the item or to navigate to the next or
previous workset.
This tag uses the this tag as a child tag. For more information, see “This Tag” on page 195.
View Tags
This topic describes tags that you can use to configure how SWE displays a view. It includes the
following topics:
■ Overview of Using View Tags on page 209
■ Current View Tag on page 211
■ For Each View Tag on page 212
■ View Tag on page 212
■ View Bar Tag on page 212
■ View Link Tag on page 214
■ View Name Tag on page 215
■ Predefined Query Tag on page 215
Overview of Using View Tags
SWE can display the following views on a single page:
■ Main view. The user uses the level 2 or level 3 view bar to choose the main view. A page can
include only one main view.
■ Alternate views. Any other view. For example, the Search view that displays applets.
SWE can display views in the following ways:
■ Each view in a separate HTML frame.
■ All views in a single frame.
■ Multiple views in the main browser window or in a dialog box.
The examples in this book describe multiple view layouts that use SWE frames. The description for
usage without frames is similar except you can use HTML tables to position the views instead of
frames and framesets.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ View Tags
210
To support multiple views, you must modify frames, framesets, and the Content Container. The
Content Container is the container page for the content area.
Starting with Siebel CRM version 7.7, SWE supports the viewbar, for-each-view, viewlink, and
viewname tags only for standard interactivity. High interactivity uses the nav-control tag. For more
information, see “Navigation Control Tag” on page 187.
Modifications That Occurred Starting with Siebel CRM Version 8.x
Siebel CRM version 8.x includes an outer content frame. If you configured a view frame in the
application container page, then you must replace this view frame with a content frame. In prior
versions, the application container page template that includes the view frame without the outer
content frame does not create any errors, but it does allow you to configure Siebel CRM to display
multiple views.
if you configured a view frame in the application container page in a version prior to Siebel CRM
version 8.x, then you must replace this view frame with a content frame. This content frame defines
the area where Siebel CRM can load one or more views. This frame contains a frameset that includes
a view frame. The structure of this container template must be similar to the following example:
<swe:frameset htmlAttr="rows='80,50,50,*' border='0' frameborder='No'">
<swe:frame type="Page" htmlAttr="marginheight='0' marginwidth='0' noresize
scrolling='No'">
<swe:include file="CCBanner.swt"/>
</swe:frame>
<swe:frame type="Screenbar" htmlAttr="marginheight='0' marginwidth='0' noresize
scrolling='No'">
<swe:include file="CCScreenbar.swt"/>
</swe:frame>
<swe:frame type="Viewbar" htmlAttr="marginheight='0' marginwidth='0' noresize
scrolling='No'">
<swe:include file="CCViewbar.swt"/>
</swe:frame>
<swe:frame type="Content" htmlAttr="marginheight='0' marginwidth='0' noresize
scrolling='Yes'">
<swe:include file="CCMainView.swt"/>
</swe:frame>
</swe:frameset>
The following code from the CCMainView.swt file defines a frameset that contains the main view:

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ View Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 211
<swe:frameset htmlAttr="cols='100%' border='0' frameborder='No'">
<swe:frame type="View" htmlAttr=" noresize scrolling='Yes'">
<swe:current-view/>
</swe:frame>
</swe:frameset>
Displaying More Views in the Content Area
To display more views in the content area, you can configure Siebel CRM to load a different content
container page in the content frame. To do this, you can configure SWE to call the
LoadContentContainer method from a control or page item. The User Property Container sends this
content container.You set this to the Web Template Name of the content container page and not to
the SWT file name.
For example, to display the search view with the main view, you can configure SWE to create a
content container page, such as CCSMainAndSearchView.swt, and then use the
LoadContentContainer method to load it. The following code from the CCSMainAndSearchView.swt
file contains the tags that load the main view and search view into two frames:
<swe:frameset htmlAttr="cols='100%' border='0' frameborder='No'">
<swe:frame type="View" htmlAttr="noresize scrolling='Yes'">
<swe:current-view/>
</swe:frame>
<swe:frame type="AltView" name="Search" htmlAttr="noresize scrolling='Yes'">
<swe:view name="Search View" id="Search" />
</swe:frame>
</swe:frameset>
The current-view tag references the main view. The view tag references alternate views.
Current View Tag
The current-view tag identifies the location or zone that an alternate view occupies. It uses the
following format:
swe:current-view
This tag allows the user to navigate to other views when multiple view zones exist. In the example
in the “Displaying More Views in the Content Area” on page 211 topic, SWE navigates to the Search
view the first time it displays the search view zone. During any subsequent display of this zone, the
specialized frame code in the Search view can call the BuildViewAsync method or it can display
controls that the GotoView method references that allow the user to navigate to other views. For
important caution information, see “Using Specialized Classes” on page 28.
The main view contains an empty view ID.
If you configure SWE to make a call from:
■ The BuildViewAsync method. You must set the pViewId parameter to the View ID of the view
that SWE must display.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ View Tags
212
■ A frame. You must use the view ID of the frame that the m_cszViewId data member of the frame
sets. This data member is part of the CSSSWEFrame class. It identifies the view where the frame
resides. This configuration causes Siebel CRM to display another view in the same view zone.
To configure the main view to navigate to another view, you can configure SWE to call the
BuildViewAsync method and set the pViewId parameter to NULL.
You can use the following code to get a view:
CSSSWEFrameMgr::GetView (const SSchar* pViewId = NULL);
where:
■ GetView is a method that resides in the CSSSWEFrameMgr class.
You can use the following code to get the main view:
m_pFrameMgr->GetView()
You can use the following code to get the search view:
m_pFrameMgr->GetView ("Search")
For Each View Tag
The for-each-view tag iterates the views that SWE displays in the view bar. It uses the following
format:
swe:for-each-view
This tag does not include any attributes.
View Tag
The view tag identifies alternate views in a frame set. It uses the following format:
<swe:view name="
name
" id="
ID
">
where:
■ name. Name of the alternate view.
■ id. An ID that identifies the location or zone that this view occupies. This ID replaces this view
with another view.
View Bar Tag
The viewbar tag implements a drop-down list or a detail view list. It uses the following format:
<swe:viewbar type="
value
" mode="
context
" property="
value
">
where:

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ View Tags
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 213
■ type. You can use one of the following values:
■ Select. If the user chooses this control, then display the view that this control references.
■ A value other than Select. Display the view bar as an HTML select control that includes the
set of context or noncontext views, depending on the value of the mode attribute.
■ mode. You can use one of the following values:
■ Context. Display only context views.
■ NonContext. Display only noncontext views.
If you do not specify the mode attribute, then SWE displays all views.
■ property. You can use this attribute only if you set the type attribute to Select. If:
■ You set this attribute to FormattedHtml, then SWE displays the HTML select control.
■ You do not specify this attribute, and if no views exist that SWE can display, then SWE
displays the contents of this viewbar tag.
How the Viewbar Tag Implements Drop-Down Lists and Tabs
The viewbar tag implements the drop-down list that Siebel CRM uses for second-level navigation and
the detail view list that Siebel CRM uses for third-level navigation. You can use it to implement one
of the following items:
■ Drop-down list. SWE populates each item in the drop-down list with the display name of a
context view. It displays the visibility drop-down list in the view bar frame. To implement this
drop-down list as a viewbar tag, the following code in the CCPageContainer.swt file or the
CCFrameViewbar.swt file sets the Type attribute to Select and the Mode attribute to Context:
<swe:form>
<td nowrap>
<swe:viewbar type="Select" mode="Context">
<swe:this property="FormattedHtml"/>
</swe:viewbar>
</td>
</swe:form>
■ Tabs. SWE creates a horizontal view bar that includes tabs. It sets each tab label to the display
name of a noncontext view. To implement this view bar, the following code in the
CCViewbar_Tabs.swt file does not include the Type attribute and it sets the Mode attribute to
NonContext:
<swe:viewbar>
... HTML ...
<swe:for-each-view>
... HTML ...
<swe:viewlink state="Active">
... HTML ....
<swe:this property="FormattedHtml">
... HTML ....
<swe:viewname/>
... HTML ...
</swe:this>

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ View Tags
214
... HTML ...
</swe:viewlink>
<swe:viewlink state="InActive">
... HTML ....
<swe:this property="FormattedHtml">
... HTML ....
<swe:viewname/>
... HTML ...
</swe:this>
... HTML ...
</swe:viewlink>
... HTML ..
</swe:for-each-view>
... HTML ..
</swe:viewbar>
The detail view bar requires the following tags. The drop-down list does not require these tags:
■ child for-each-view
■ viewlink
■ viewname
View Link Tag
The viewlink tag displays a link that the user can click to display a view. It uses the following format:
<swe:viewlink state="
value
" property="
value
" htmlAttr="
value
"/>
where:
■ state. Optional. You can use one of the following values:
■ Active. Use this tag only if the current view name identifies the currently active view.
■ Inactive. Use this tag only if the current view name does not identify the currently active
view.
If you do not include the state attribute, then SWE displays this tag in all views.
■ property. Optional. You can only use FormattedHtml as the value for this attribute. It creates
the HTML that defines the link. If you do not include this attribute, then SWE creates no output.
■ htmlAttr. Optional. Add more HTML attributes to the HTML tag.
To display HTML for an active view that is different than the HTML for an inactive view, you can use
the viewlink tag without specifying the property attribute but with a value for the state attribute. If
you do not include the property attribute, then you can use the this tag to display the property in
the body of the viewlink tag. For more information, see “This Tag” on page 195.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Tags That Support a Specific Feature
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 215
View Name Tag
The viewname tag displays the view name. It uses the following format:
swe:viewname
Predefined Query Tag
The pdqbar tag displays the list of predefined queries for a view, runs a predefined query, and sends
the query result. It uses the following format:
<swe:pdqbar>
...HTML code...
<swe:pageitem id="##"/>
...HTML code...
<swe:this property="FormattedHtml" />
</swe:pdqbar>
To display a label, you can use a pageitem tag in the view bar or a control tag in the view. You include
these tags in the pdqbar tag. For more information, see “Web Page Item Tag” on page 184 and
“Control Tag” on page 179.
Tags That Support a Specific Feature
This topic describes tags that you can use to configure how SWE displays a particular feature. It
includes the following topics:
■ Language Conversion Tag on page 215
■ Training Tag on page 216
■ Wireless Tag on page 216
■ XSL Stylesheet Tag on page 216
Language Conversion Tag
The dir tag creates a template that can work with a bidirectional language. If SWE displays:
■ A language that the reader reads from right to left (rtl), then it converts the dir tag to dir="rtl".
■ A language that the reader reads from left to right, it does nothing.
This tag uses the following format:
<HTML dir="swe:dir">
You can use this tag only in an HTML tag that includes the dir attribute.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Tags That Support a Specific Feature
216
Training Tag
A training tag is a SWE tag that SWE uses only with Siebel Training Test. Table 39 describes these
tags.
Wireless Tag
The screenoptionlink tag creates links that use a phone style so that the client displays phone
numbers for list items. You can use it only with an application that uses Wireless Markup Language.
It uses the following format:
swe:screenoptionlink
XSL Stylesheet Tag
The xsl-stylesheet tag specifies the name of the XSLT stylesheet (EXtensible Stylesheet Language)
on the XML output document. It uses the following format:
<swe:xsl-stylesheet name= "table.xsl" mode= "process"/>
where:
■ name. Specifies the name of the stylesheet.
■ mode. You can use one of the following values:
■ Process. SWE processes XSLT on the XML output, and then sends the transformed document
back to the client.
Table 39. Training Tags
SWE Tag Description
swe:answer Display an answer.
swe:answerList Display the list of answers for the test.
swe:questionList Display all the questions that the test contains.
swe:questionPoints Display the maximum number of points for the test question.
swe:questionPointsReceived Display the points that the user earned.
swe:questionSequence Display the test question sequence.
swe:questionText Display the text of the test questions.
swe:test Display the name of the test.
swe:userAnswer Display the answers that the user provided.

Siebel Web Engine Tags ■ Tags That Are for Oracle Internal Use Only
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 217
■ Embed. SWE inserts an XML processing instruction in the beginning of the XML document
that Siebel CRM uses for external XSLT processing.
For more information, see the topic about manipulating Siebel XML with XSL stylesheets and
XSLT in XML Reference: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration.
The style sheet must reside in the following directory:
\webtempl
Each view template contains only one xsl-stylesheet tag. If the view contains more than one xsl-
stylesheet tag, then SWE uses the last tag that this view contains.
Tags That Are for Oracle Internal Use
Only
This topic describes tags that only Oracle personnel can modify. It includes the following topics:
■ All Applets, All Controls, and List Control Tags on page 217
■ Calendar Tags on page 217
■ Gantt Chart Tags on page 218
You must not modify these tags without assistance from Oracle. For more information, see “Getting
Help From Oracle” on page 20.
All Applets, All Controls, and List Control Tags
SWE uses the following tags with the XML to SWE interface if SWE is in No Template mode. They are
only for Oracle internal use:
■ swe:all-applets
■ swe:all-controls
■ swe:list-control
Calendar Tags
The SWE calendar tags are specialized SWE tags that SWE uses only with a calendar applet. They
are only for Oracle internal use. They include the following tags:
■ swe:calendar
■ swe:calendarActivity
■ swe:calendarActivityLoop
■ swe:CurrentDayHeader
■ swe:calendarInterval

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Web Engine Tags
■ Tags That Are for Oracle Internal Use Only
218
■ swe:calendarIntervalLoop
■ swe:calendarMultiDayActivity
■ swe:calendarNotCurrentlyDayHeader
■ swe:printHr
■ swe:printTr
Gantt Chart Tags
The Gantt chart tags are specialized SWE tags that SWE uses only with a Gantt chart. They are only
for Oracle internal use. The following tags are Gantt tags:
■ swe:ganttChart
■ swe:ganttChartMajorAxisLegend
■ swe:ganttChartMinorAxisLegend
■ swe:ganttChartXObjectExtendedOT
■ swe:ganttChartXObjectLoop
■ swe:ganttChartXObjectMutiple
■ swe:ganttChartXObjectNone
■ swe:ganttChartXObjectOT
■ swe:ganttChartXObjectOff
■ swe:ganttChartXObjectOn
■ swe:ganttChartYObjectLoop

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 219
8 Siebel Templates for Employee
Applications
This chapter describes the predefined templates that Siebel CRM uses in an employee application. It
includes the following topics:
■ Overview of Configuring Siebel Templates for Employee Applications on page 219
■ Form Templates on page 221
■ List Templates on page 240
■ Calendar Templates on page 255
■ Chart Templates on page 263
■ Container Templates on page 267
■ Popup Templates on page 269
■ Search Templates on page 276
■ Tree Templates on page 287
■ View Templates on page 292
■ Specialized Employee Templates on page 319
■ Wizard, Error, and Smart Script Templates on page 333
Overview of Configuring Siebel
Templates for Employee Applications
This topic describes an overview of configuring Siebel templates for employee applications. It
includes the following topics:
■ Guidelines for Configuring Applet Templates on page 219
■ About Mapping IDs to Placeholders on page 220
■ Elements in the Client of an Employee Application on page 220
Guidelines for Configuring Applet Templates
If you configure an applet template, then use the following guidelines:
■ Never map a native HTML button to a list or form. You can set the properties for a MiniButton the
same way you set the properties for most controls.
■ To save time during configuration, you can place the button divider after the menu button and
before the previous record button.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Overview of Configuring Siebel Templates
for Employee Applications
220
■ To maximize the potential for vertical alignment, place taller fields, such as text area fields, at
the bottom of the form. Siebel CRM displays each column of fields independently of the other
columns. This configuration maximizes form layout options and minimizes gaps that might occur
between fields in the same column but where the alignment of fields across columns might not
remain vertical.
■ To define the text that Siebel CRM displays in the client, you can map the control on a label and
use the Caption property of the control. A form section is not a control. It is a label that groups
related fields. The FormSection control implements a form section. Siebel CRM expands the
FormSection label to fit the region where you place it. To set it apart from the background color,
the label displays against the FormSection color that the cascading style sheet defines. For more
information about this control, see Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
■ If you configured Siebel CRM in an earlier version to use the Previous or Next text labels, then
you must reconfigure this customization to use the RecNavPrv and RecNavNxt controls. All record
navigation must map to these controls. For more information about these controls, see
Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
About Mapping IDs to Placeholders
Siebel CRM can map an ID to a placeholder. For example, the first row in Table 41 on page 227
describes that you can map ID 2 to the Back placeholder. The Placeholder column in this table lists
the placeholder that you can map to an ID. It displays the exact label that Siebel Tools displays in
the Web Layout Editor. If you can map an ID to more than one placeholder, then this column lists
each item. For example, Table 41 on page 227 describes that you can map any ID in the range of
1296 through 1300 to a Required, Label, or 2-Column Wide Field placeholder.
Note that Siebel CRM does the following:
■ Uses ID 580 to map a New control. It displays this control only in standard interactivity mode.
■ Uses ID 599 to map a Save control. It displays this control only in high interactivity mode.
Elements in the Client of an Employee Application
Table 40 describes an overview of user interface elements that Siebel CRM uses in the Siebel Web
Client for an employee application.
Table 40. Description of User Interface Elements
User Interface Element Description
Application menu An application-level menu that includes menu items, such as File,
Edit, View, Navigate, Tools, and Help.
Branding area The area where Siebel CRM displays the Oracle logo.
Application toolbar A toolbar that includes icons for items, such as Site Map, Customer
Dashboard, and iHelp items.

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 221
The mode that an applet Web template uses determines the kind of work the user can do in this
applet. It also determines the buttons that Siebel CRM displays in a web template. For example, it
displays the Edit button in an applet that is in Edit mode but it does not display this button in an
applet that is in Base mode.
Form Templates
This topic describes applet form templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Overview of Using Applet Form Templates on page 222
■ Form Template for Edit, New, or Query Mode on page 227
■ One Column Form Template on page 229
■ One Column Form, Light Template on page 229
■ One Column Form, Light Template for Base, Edit, or New Mode on page 230
■ Four Column Form Template for Base Mode on page 231
■ Four Column Form Template for Edit or New Mode on page 234
Applet control banner An area that contains a menu and buttons for a form or list.
Primary applet The first form or list on the page that displays the primary record or
record set.
Detail applet An applet that displays different sets of data according to the
individual primary record. If Siebel CRM modifies the primary
record, then it also updates data.
First-level navigation Set of tabs that allow the user to navigate to screens.
Second-level navigation Links that allow the user to navigate to views. Siebel CRM can
display these links directly under the screen tabs or in the visibility
filter.
Third-level navigation View tabs in the view bar that Siebel CRM displays below the first
applet in a view.
Fourth-level navigation Links that Siebel CRM displays under the third-level tabs, view tabs
on a grandchild applet, or links in a drop-down list.
Record navigation An area that displays the record set and allows the user to navigate
forward and backward in the record set.
Search A button that integrates search and global find.
Favorites A list of saved and predefined queries for the view.
iHelp frame An area that displays links that the user can click to navigate
through steps in a task.
Table 40. Description of User Interface Elements
User Interface Element Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Form Templates
222
■ Four Column Form Template With No Record Navigation on page 236
■ Grid Layout Form Template on page 239
Overview of Using Applet Form Templates
This topic describes an overview of using applet form templates.
About Form Layouts That Use a Grid
A grid layout template does not use placeholder tags. It uses the following Siebel tags in a single
location for all controls that reside in the main body of the form:
swe:form-applet-layout
/swe:form-applet-layout
A grid layout template includes the following items:
■ Body. The following tag defines the body. It contains no placeholder tags:
swe:form-applet-layout
■ Header or footer. You must not use placeholder tags for items such as buttons in a header or
footer. You cannot use the Web Layout Editor to modify the layout of a header or footer.
An applet Web template that uses a grid is different from an applet Web template that does not use
a grid in the following ways:
■ To modify a form layout, you can use a grid template in the Web Layout Editor in Siebel Tools
without modifying the web template that the form references.
■ Labels and controls in a grid template are separate items in the Web Layout Editor. You can place
them independently in the applet layout. However, a label and the control that it references are
actually a single object in the repository with one set of shared properties.
■ A grid template does not compress empty space in a column. The browser compresses horizontal
space as much as possible without modifying the size of any field on the form applet.
For examples of grid layout templates, see “Grid Layout Form Template” on page 239 and “Popup Form,
Grid Layout Template” on page 271.
About Form Layouts That Do Not Use a Grid
This topic describes form layouts that do not use a grid that are available but that no longer come
predefined with Siebel CRM. Siebel CRM versions before version 7.7 use form applets that do not use
a grid in Edit mode in standard interactivity mode. Starting with Siebel CRM version 7.7, most form
applets use a grid layout.
The four column form templates define a set of layout regions. A region can include one or more label
and field pairs. You can use Siebel Tools to place a control in a region and to resize the control. The
four column form includes regions that are different in height. It can accommodate controls that span
one, two, or four columns.

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 223
Siebel CRM groups these regions. This grouping helps make sure that each region uses only the
minimum vertical space that Siebel CRM requires to display it. If Siebel CRM does not map any
control to a region, then it collapses this region and moves the next region up in the form.
To create a wide variety of form designs while maintaining only one form template, you can combine
horizontally proportioned regions with grouped regions.
Figure 1 displays the master template for layout regions.
Figure 2 includes an example of a layout that Siebel CRM creates from the master template. Each X
indicates a region that does not contain any mapped control.
Figure 1. Master Template for Layout Regions
Figure 2. Example of a Layout That Siebel CRM Creates From the Master Template

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 225
How Siebel CRM Maps Controls for Forms That Do Not Use a Grid
Figure 4 displays the ID ranges that Siebel CRM uses for the controls that it displays in each region.
It is recommended that you configure Siebel CRM to map each control to the lowest ID that is
available in each region.
About the Style That Some Four Column Form Templates Use
The following templates create the same layout for a form that includes four columns. They also
support child and grandchild styles.
■ Four Column Form Template for Base Mode on page 231
■ Four Column Form Template for Edit or New Mode on page 234
■ Form Template for Edit, New, or Query Mode on page 227
Figure 4. How Siebel CRM Maps Controls for Forms That Do Not Use a Grid

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Form Templates
226
Figure 5 includes a parent style that these templates display.
Figure 6 includes a child style that these templates display.
Capabilities of Four Column Form Templates
Form templates that include four columns can do the following:
■ Define a large number of control placeholders. Some of these placeholders can span one column,
two columns, or four columns.
■ Map fields up to four columns.
■ Display labels above field values.
■ Display validation errors at the top of the form.
■ Support text in ID 91 that spans all four columns.
■ Support the predefined applet styles.
Figure 5. Example of the Parent Style That Some Four Column Templates Use
Figure 6. Example of the Child Style That Some Four Column Templates Use

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 227
Form Template for Edit, New, or Query Mode
The Applet List Edit (Edit/New/Query) template uses the CCAppletList_E_N_Q.swt file.Figure 7
includes the generic layout that this template uses. For more information, see “About the Style That
Some Four Column Form Templates Use” on page 225.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletList_E_N_Q.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCFormButtonsTop.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCFormButtonsTopRight.swt
CCList4ColBody.swt
Table 41 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 7. Generic Layout of the Applet List Edit (Edit/New/Query) Template
Table 41. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletList_E_N_Q.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Form Templates
228
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
125 Info-Button
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 152 Control
160 through 164 Control
192 Label
194 Label
580 New
599 Save
1001 through 1009 FormSection
1020 FormSection
1296 through 1300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1301 through 1310 Required or Label
1311 through 1315 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1316 through 1330 Required or Label or Field
1331 through 1335 Required or Label or 4-Column Wide Field
1336 through 1340 Required or Label or 4-Column Wide Field
1360 through 1374 Required or Label or Field
1500 Required or Legend
1801 through 1810 Required or Label or Field
Table 41. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletList_E_N_Q.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 229
One Column Form Template
The Applet Form 1-Col (Base/Edit/New) template uses the CCAppletForm1Col_B_E_N.swt file. It also
supports the child and grandchild styles.
Figure 8 includes an example of this template.
One Column Form, Light Template
The Applet Form 1-Col Light (Base/Edit/New) template uses the CCAppletForm1ColLight_B_E_N.swt
file. You can use it on a portal page where you require a light, single-column form.
1816 through 1830 Required or Label or Field
1860 through 1874 Required or Label or Field
2001 through 2009 FormSection
2296 through 2300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2301 through 2310 Required or Label or Field
2311 through 2315 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2316 through 2330 Required or Label or Field
2331 through 2335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2360 through 2374 Required or Label or Field
2801 through 2810 Required or Label or Field
2816 through 2830 Required or Label or Field
2860 through 2874 Required or Label or Field
Figure 8. Example of the Applet Form 1-Col (Base/Edit/New) Template
Table 41. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletList_E_N_Q.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Form Templates
230
Figure 9 includes an example of this template.
One Column Form, Light Template for Base, Edit, or New
Mode
The Applet Form 1 Column Light (Base/Edit/New) template uses the
CCAppletForm1ColLight_B_E_N.swt file. This template does the following:
■ Supports a required field indicator for each field.
■ Supports narrow columns, such as the columns that a home page view displays.
■ Supports parent, child, and grandchild styles.
■ Displays a label above the field value.
■ Displays buttons at the bottom of the applet.
■ Gets the applet title from the Title property of the applet.
Figure 10 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletForm1ColLight_B_E_N.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
Figure 9. Example of the Applet Form 1-Col Light (Base/Edit/New) Template
Figure 10. Generic Layout of the Applet Form 1 Column Light (Base/Edit/New) Template

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 231
CCTitle.swt
CCForm1ColBodyLight.swt
dCCFormButtonsBottom.swt
dCCButtons_Form.swt
Table 42 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Four Column Form Template for Base Mode
The predefined Applet Form 4 Column (Base) template uses the CCAppletForm4Col_B.swt file.
Table 42. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletForm1ColLight_B_E_N.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 110 Control
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
151 through 155 Control
156 Control
157 through 158 Control
1301 through 1330 Required or Label or Field
1500 Required or Legend

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Form Templates
232
Figure 11 includes the generic layout that this template uses. For more information, see “About the
Style That Some Four Column Form Templates Use” on page 225.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletForm4Col_B.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCFormButtonsTop.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCFormButtonsTopRight.swt
CCForm4ColBody.swt
Table 43 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 11. Generic Layout of the Applet Form 4 Column (Base) Template
Table 43. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletForm4Col_B.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 233
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
125 Info Button
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 152 Control
160 through 164 Control
192 Label
194 Label
580 New
599 Save
1001 through 1009 FormSection
1020 FormSection
1296 through 1300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1301 through 1310 Required or Label or Field
1311 through 1315 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1316 through 1330 Required or Label or Field
1331 through 1335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1336 through 1340 Required or Label or 4-Column Wide Field
1360 through 1374 Required or Label or Field
1500 Required or Legend
1801 through 1810 Required or Label or Field
1816 through 1830 Required or Label or Field
1860 through 1874 Required or Label or Field
Table 43. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletForm4Col_B.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Form Templates
234
Four Column Form Template for Edit or New Mode
The predefined Applet Form 4 Column (Edit/New) template uses the CCAppletForm4Col_E_N.swt file.
Figure 12 includes the generic layout that this template uses. For more information, see “About the
Style That Some Four Column Form Templates Use” on page 225.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletForm4Col_E_N.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCFormButtonsTop.swt
CCButtons.swt
2001 through 2009 FormSection
2296 through 2300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2301 through 2310 Required or Label or Field
2316 through 2330 Required or Label or Field
2331 through 2335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2360 through 2374 Required or Label or Field
2801 through 2810 Required or Label or Field
2811 through 2815 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2816 through 2830 Required or Label or Field
2860 through 2874 Required or Label or Field
Figure 12. Generic Layout of the Applet Form 4 Column (Edit/New) Template
Table 43. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletForm4Col_B.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 235
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCFormButtonsTopRight.swt
CCForm4ColBody.swt
Table 44 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 44. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletForm4Col_E_N.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
125 Info Button
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 152 Control
160 through 164 Control
192 Label
194 Label
580 New
599 Save

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Form Templates
236
Four Column Form Template With No Record Navigation
The predefined Applet Form 4-Col (No Record Nav) template uses the
CCAppletForm4Col_NoRecNav.swt file. For more information, see “Capabilities of Four Column Form
Templates” on page 226. This template does not support record navigation.
1001 through 1009 FormSection
1020 FormSection
1296 through 1300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1301 through 1310 Required or Label or Field
1311 through 1315 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1316 through 1330 Required or Label or Field
1331 through 1335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1336 through 1340 Required or Label or 4-Column Wide Field
1360 through 1374 Required or Label or Field
1500 Required or Legend
1801 through 1810 Required or Label or Field
1816 through 1830 Required or Label or Field
1860 through 1874 Required or Label or Field
2001 through 2009 FormSection
2296 through 2300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2301 through 2310 Required or Label or Field
2316 through 2330 Required or Label or Field
2331 through 2335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2360 through 2374 Required or Label or Field
2801 through 2810 Required or Label or Field
2811 through 2815 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2816 through 2830 Required or Label or Field
2860 through 2874 Required or Label or Field
Table 44. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletForm4Col_E_N.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 237
Figure 13 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletForm4Col_NoRecNav.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCFormButtonsTopNoRecNav.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCFormButtonsTopRight.swt
CCForm4ColBody.swt
Table 45 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 13. Generic Layout of the Applet Form 4-Col (No Record Nav) Template
Table 45. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletForm4Col_NoRecNav.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
131 New

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Form Templates
238
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 152 Control
160 through 164 Control
580 New
599 Save
1001 through 1009 FormSection
1020 FormSection
1296 through 1300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1301 through 1310 Required or Label or Field
1311 through 1315 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1316 through 1330 Required or Label or Field
1331 through 1335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1336 through 1340 Required or Label or 4-Column Wide Field
1360 through 1374 Required or Label or Field
1500 Required or Legend
1801 through 1810 Required or Label or Field
1816 through 1830 Required or Label or Field
1860 through 1874 Required or Label or Field
2001 through 2009 FormSection
2296 through 2300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2301 through 2310 Required or Label or Field
2316 through 2330 Required or Label or Field
2331 through 2335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2360 through 2374 Required or Label or Field
2801 through 2810 Required or Label or Field
2811 through 2815 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
Table 45. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletForm4Col_NoRecNav.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 239
Grid Layout Form Template
The Applet Form Grid Layout template uses the CCAppletFormGridLayout.swt file. It uses the
following tag as a placeholder for all controls on a form applet. This tag allows you to use the Web
Layout Editor in Siebel Tools to modify the layout of the controls:
swe:form-applet-layout
Figure 14 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletFormGridLayout.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCFormButtonsTop.swt
CCButtons.swt
Table 46 lists the controls that Siebel CRM can map to the header region of the Applet Form Grid
Layout template. For more information, see “About Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
2816 through 2830 Required or Label or Field
2860 through 2874 Required or Label or Field
Figure 14. Generic Layout of the Applet Form Grid Layout Template
Table 46. Items That Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletFormGridLayout.swt
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
Table 45. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletForm4Col_NoRecNav.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ List Templates
240
List Templates
This topic describes applet list templates. It includes the following topics:
■ List Template for Base or Edit List Mode on page 241
■ Inverted Axis List Template on page 243
■ Message List Template on page 245
■ Portal List Template on page 248
■ Portal List Template With Graphics on page 250
■ Totals List Template for Base or Edit List Mode on page 253
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
125 Info-Button
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 152 Control
160 through 164 Control
192 Label
194 Label
580 New
599 Save
1500 Required or Legend
Table 46. Items That Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletFormGridLayout.swt
ID Placeholder
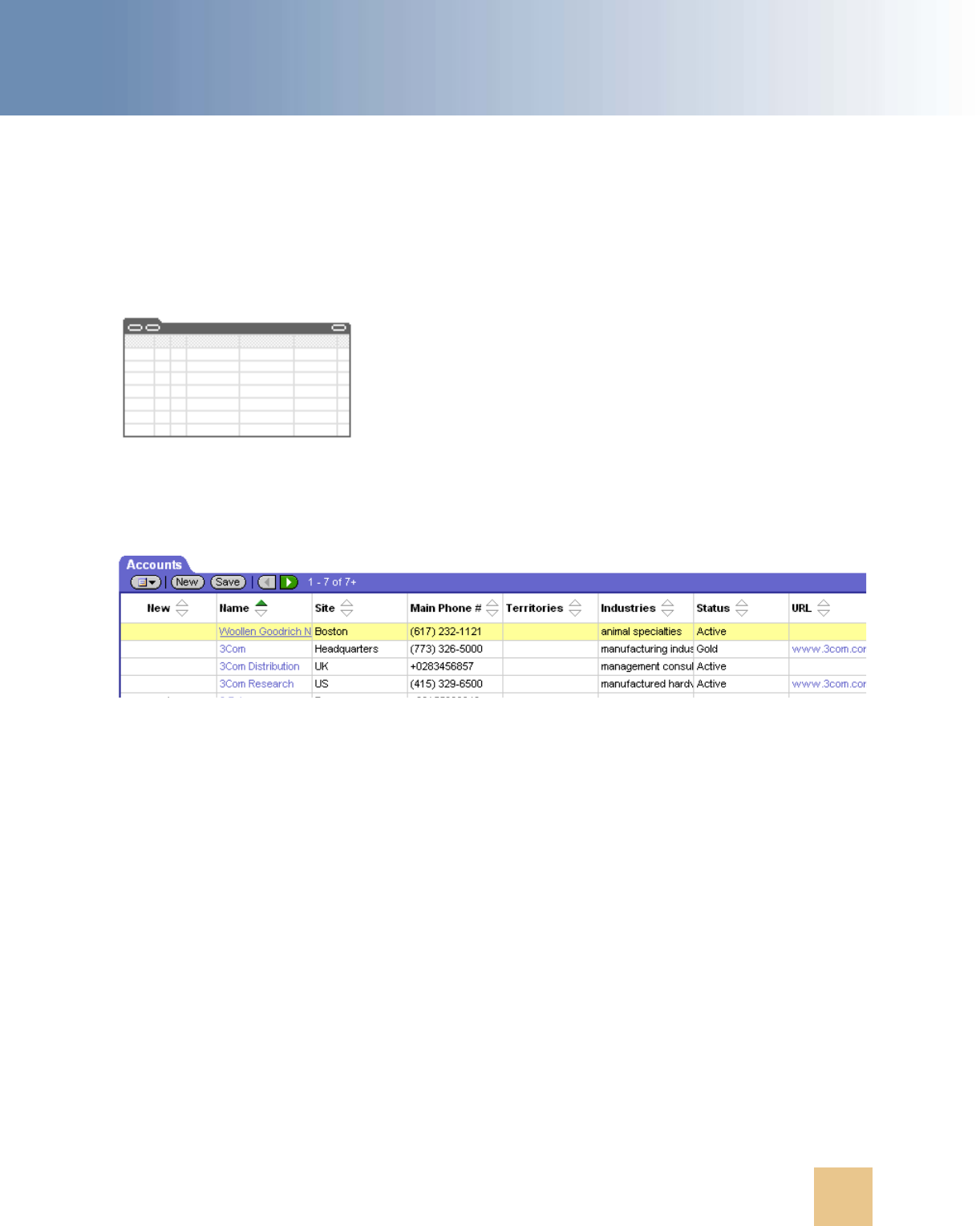
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 241
List Template for Base or Edit List Mode
The Applet List (Base/EditList) template uses the CCAppletList_B_EL.swt file. You can use it for a
read-only or editable list. It supports the parent, child, and grandchild styles.
Figure 15 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 16 includes an example that uses a single row layout that the user can edit.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletList_B_EL.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCListButtonsTop.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
CCListHeader.swt
CCListBody.swt
Figure 15. Generic Layout of the Applet List (Base/EditList) Template
Figure 16. Example of the Applet List (Base/EditList) Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ List Templates
242
Table 47 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 47. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletList_B_EL.swt File
ID Placeholder
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
142 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Save
147 Pick Control
150 through 151 Control
160 through 164 Control
501 through 540 Field
580 New
598 Save
599 Save
611 through 650 Field

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 243
Configuring How Siebel CRM Uses the Columns Displayed Feature
A list can typically display between seven and ten visible columns. To make sure all columns are
visible, and to avoid unwanted text-wrapping or horizontal scrolling, it is recommended that you do
not configure Siebel CRM to map more than ten columns. This template can map up to 80 fields. You
typically set the majority of these fields to available but hidden. Siebel CRM does not display hidden
fields in the list, by default. It displays them in the Columns Displayed dialog box.
Siebel CRM can set the Columns Displayed menu item of the Menu drop-down list to gray to indicate
that it is not available. If the applet mode is not Edit List, then this menu item is not visible. For more
information, see “List Template for Base or Edit List Mode” on page 241.
To display the Columns Displayed menu item, the following objects must be in Edit List mode:
■ The applet.
■ The view web template items of the parent view.
Inverted Axis List Template
The Applet List Inverted template uses the CCAppletListInverted.swt file. This is a specialized list
applet that creates a comparison list. To display column headers down the left side of the list, Siebel
CRM inverts the x-axis and y-axis of this list. It is recommended that you configure this list to display
three to five records. The user can use this list to page through larger record sets.
Figure 17 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletListInverted.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
1500 Required or Legend
Figure 17. Generic Layout of the Applet List Inverted Template
Table 47. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletList_B_EL.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ List Templates
244
CCTitle.swt
CCListButtonsTop.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
CCListBodyInverted.swt
Table 48 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 48. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListInverted.swt File
ID Placeholder
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 152 Control
160 through 164 Control
499 Record Title Row
501 through 520 Control
580 New

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 245
Message List Template
The Applet List Message template uses the CCAppletListMessage.swt file. Siebel CRM uses it on a
home page to display news or timely information. Each record displays a round bullet and provides
a placeholder for a link and short descriptive text. It supports a title that you can map to ID 90 or
ID 184 and layout controls.
Figure 18 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
599 Save
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
1500 Required or Legend
Figure 18. Generic Layout of the Applet List Message Template
Table 48. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListInverted.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ List Templates
246
Figure 19 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletListMessage.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCLayoutTitlePortal.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
CCTitle_Portal.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCListButtonsTopNoRecNav.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
CCListBodyBullet.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Figure 19. Example of the Applet List Message Template

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 247
Table 49 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 49. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListMessage.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
90 Title
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 151 Control
157 Label
160 through 164 Control
184 Drilldown Title
203 MinimizeApplet
204 MaximizeApplet
207 MoveAppletUp
208 MoveAppletDown
211 ShowApplet
212 HideApplet
501 Field
502 through 511 Field
555 Label
580 New

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ List Templates
248
Portal List Template
The Applet List Portal template uses the CCAppletListPortal.swt file. Siebel CRM uses it on a portal
page. It displays a title, layout controls, and an optional line of buttons beneath the title. It supports
a title that you can map to ID 90 or 184.
Figure 20 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletListPortal.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCLayoutTitlePortal.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
CCTitle_Portal.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCListButtonsTopNoRecNav.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
CCListHeaderNoSort.swt
CCListBodyNoRowHilite.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
599 Save
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
Figure 20. Generic Layout of the Applet List Portal Template
Table 49. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListMessage.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 249
Table 50 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 50. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListPortal.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
90 Title
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
142 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Save
147 Pick Control
150 through 151 Control
157 Label
160 through 164 Control
184 Drilldown Title
203 MinimizeApplet
204 MaximizeApplet
207 MoveAppletUp
208 MoveAppletDown
211 ShowApplet
212 HideApplet

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ List Templates
250
Portal List Template With Graphics
The Applet List Portal (Graphical) template uses the CCAppletListPortalGraphical.swt file. It displays
a title, layout controls, and an optional line of buttons beneath the title. This is a specialized list
template in that it can display a graphical applet title. You can map the:
■ Applet image to ID 89.
■ Applet title to ID 90 or 184.
Figure 21 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 22 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletListPortalGraphical.swt
501 through 540 Field
555 Label
580 New
599 Save
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
Figure 21. Generic Layout of the Applet List Portal (Graphical) Template
Figure 22. Example of the Applet List Portal (Graphical) Template
Table 50. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListPortal.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 251
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCLayoutTitlePortal.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
CCTitle_PortalGraphical.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCListButtonsTopNoRecNav.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
CCListHeaderNoSort.swt
CCListBodyNoRowHilite.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Table 51 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 51. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListPortalGraphical.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
89 Image
90 Title
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ List Templates
252
142 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Save
147 Pick Control
150 through 151 Control
157 Label
160 through 164 Control
184 Drilldown Title
203 MinimizeApplet
204 MaximizeApplet
207 MoveAppletUp
208 MoveAppletDown
211 ShowApplet
212 HideApplet
501 through 540 Field
555 Label
580 New
599 Save
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
Table 51. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListPortalGraphical.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 253
Totals List Template for Base or Edit List Mode
The Applet List Totals (Base/EditList) template uses the CCAppletListTotals_B_EL.swt file. You can
map up to 40 fields in this template. For more information about configuring these fields, see
“Configuring How Siebel CRM Uses the Columns Displayed Feature” on page 243.
This template supports the parent, child, and grandchild styles.
Figure 23 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 24 illustrates how you can use this template for a read-only or editable list that displays
column totals in the last row. You must make sure you apply a Totals label to the placeholder in the
first column.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletListTotals_B_EL.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCListButtonsTop.swt
Figure 23. Generic Layout of the Applet List Totals Template
Figure 24. Example of the Applet List Totals (Base/EditList) Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ List Templates
254
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
CCListHeaderTotals.swt
CCListBodyTotals.swt
Table 52 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 52. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListTotals_B_EL.swt File
ID Placeholder
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
142 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Save
147 Pick Control
150 through 151 Control
160 through 164 Control

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Calendar Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 255
Calendar Templates
This topic describes calendar templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Daily Calendar Template on page 255
■ Daily Calendar Template for Portals on page 257
■ Weekly Calendar Template on page 259
■ Monthly Calendar Template on page 260
■ Service Calendar Template on page 262
Daily Calendar Template
The eCalendar Daily Applet template uses the CCAppletCalendarDaily.swt file. It supports the parent,
child, and grandchild applet styles.
Figure 25 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
199 Totals Label
501 through 540 Control
580 New
599 Save
611 through 650 Control
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
1500 Required or Legend
Figure 25. Generic Layout of the Calendar Daily Applet Template
Table 52. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListTotals_B_EL.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Calendar Templates
256
Figure 26 includes an example of this template that uses the parent style.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletCalendarDaily.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Table 53 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 26. Example of the Calendar Daily Applet Template
Table 53. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletCalendarDaily.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Owner Label
102 Owner Field
103 Date Label
104 Date Field (Day)
105 Date Field (Month)
106 Date Field (Year)
107 Time Zone Label
108 Time Zone Field
130 Go
131 Previous
132 Next
133 New Appt
996 Owner Selector
997 Owner Field 2

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Calendar Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 257
Daily Calendar Template for Portals
The Applet Calendar Daily (Portal) template uses the CCAppletCalendarDailyPortal.swt file. It
displays a condensed calendar that you can use on a home page. It supports a graphical header that
you can map to ID 89.
Figure 27 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletCalendarDailyPortal.swt
CCLayoutTitlePortal.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
CCCalendarAppletTitleGraphical.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
998 Today
10000 through 10002 Optional Control
20000 through 20002 Optional Control
Figure 27. Generic Layout of the Applet Calendar Daily (Portal) Template
Table 53. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletCalendarDaily.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Calendar Templates
258
Table 54 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 54. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletCalendarDailyPortal.swt File
ID Placeholder
89 Image
90 Title
101 Owner Label
102 Owner Field
103 Date Label
104 Date Field (Month)
105 Date Field (Day)
106 Date Field (Year)
107 TimeZoneLabel
108 TimeZone
130 Go
131 Previous
132 Next
133 New Appt
157 Label
158 GoToWeeklyView
159 GoToMonthlyView
184 DrillDown Title
203 MinimizeApplet
204 MaximizeApplet
207 MoveAppletUp
208 MoveAppletDown
211 ShowApplet
212 HideApplet
555 Label
999 GoToToday

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Calendar Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 259
Weekly Calendar Template
The eCalendar Weekly Applet template uses the CCAppletCalendarWeekly.swt file. It displays days
of the week down the side of the applet. It embeds daily activities next to each day. This template
supports the predefined applet styles. You must map the applet title to ID 90.
Figure 28 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 29 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletCalendarWeekly.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Figure 28. Generic Layout of the Calendar Weekly Applet Template
Figure 29. Example of the Calendar Weekly Applet Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Calendar Templates
260
Table 55 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Monthly Calendar Template
The eCalendar Monthly Applet template uses the CCAppletCalendarMonthly.swt file. It supports the
predefined applet styles. You must map the applet title to ID 90.
Table 55. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletCalendarWeekly.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Owner Label
102 Owner Field
103 Date Label
104 Date Field (Day)
105 Date Field (Month)
106 Date Field (Year)
107 Time Zone Label
108 Time Zone Field
130 Go
131 Previous
132 Next
133 New Appt
141 New Appt Bitmap
142 Repeat Bitmap
145 Print
301 Start Time
302 End Time
303 Description
996 Owner Selector
997 Owner Field 2
998 Today
10000 through 10002 Optional Control
20000 through 20002 Optional Control

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Calendar Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 261
Figure 30 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 31 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletCalendarMonthly.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCCalendarMonthly_weekday.swt
CCCalendarMonthly_weekend.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Figure 30. Generic Layout of the Calendar Monthly Applet Template
Figure 31. Example of the Calendar Monthly Applet Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Calendar Templates
262
Table 56 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Service Calendar Template
The Service Calendar Applet template uses the CCAppletCalendarService.swt file. It supports the
predefined applet styles. IDs 301 through 307 map the days of the week that display as column
headers.
Table 56. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletCalendarMonthly.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Owner Label
102 Owner Field
103 Date Label
104 Date Field (Day)
105 Date Field (Month)
106 Date Field (Year)
107 Time Zone Label
108 Time Zone Field
130 Go
131 Previous
132 Next
133 New Appt
145 Print
301 through 305 Weekday labels for Monday through Friday.
306 Sat/Sun Label
996 Owner Selector
997 Owner Field 2
998 Today

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Chart Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 263
Figure 32 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletCalendarService.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Table 57 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Chart Templates
This topic describes chart templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Chart Template on page 263
■ Gantt Chart Template on page 265
■ Gantt Chart Activity Template on page 266
■ Gantt Chart Template for Portals on page 266
Chart Template
The Applet Chart template uses the CCAppletChart.swt file. It supports the parent, child, and
grandchild styles. You can map chart controls to ID ranges 501 through 520 and 551 through 555.
You map the chart to ID 599.
Figure 32. Generic Layout of the Service Calendar Template
Table 57. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletCalendarService.swt File
ID Placeholder
301 through 307 Day labels for Sunday through Saturday.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Chart Templates
264
This template can work with a toggle applet relationship. Siebel CRM displays the other toggle
applets in a drop-down list. It maps the drop-down label to ID 2.
Figure 33 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 34 includes an example of this template that uses the child style.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletChart.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCChartBasic.swt
CCTogglebar_drop2.swt
Figure 33. Generic Layout of the Applet Chart Template
Figure 34. Example of the Child Style

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Chart Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 265
Table 58 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Gantt Chart Template
The eGantt Chart Applet template uses the CCAppletGanttChart.swt file. It supports the parent,
child, and grandchild styles. It supports drag-and-drop starting with Internet Explorer 5. It supports
optional controls that you can map to IDs 306 through 314.
Other Gantt chart templates use the eGantt Chart Applet template.
Figure 35 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletGanttChart.swt
CCGanttAppletTitle.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Table 59 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 58. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletChart.swt File
ID Placeholder
501 through 520 Control
551 through 555 Control
599 Chart
1500 Required or Legend
Figure 35. Example of the Applet Gantt Chart Template
Table 59. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletGanttChart.swt File
ID Placeholder
301 through 302 Employee Header
303 Previous
304 Next

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Chart Templates
266
Gantt Chart Activity Template
The eActivityGanttChart Applet template uses the CCAppletActivityGanttChart.swt file. It includes
specialized Gantt code that prevents Siebel CRM from using it outside the context of a Gantt applet.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletActivityGanttChart.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCGanttAppletTitle.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Table 60 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Gantt Chart Template for Portals
The eGanttChart Applet (Portal) template uses the CCAppletGanttChartPortal.swt file. It supports a
title that can map to a drilldown. You can use it to map layout controls on a portal page. You can use
IDs 203 through 212 to map these controls.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletGanttChartPortal.swt
306 through 314 Label or Control
405 Control
2101 through 2130 Control
Table 60. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletActivityGanttChart.swt File
ID Placeholder
301 through 302 Employee Header
303 Previous
304 Next
306 through 314 Label or Control
405 Control
2101 through 2130 Control
Table 59. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletGanttChart.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Container Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 267
CCLayoutTitlePortal.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCTitle_Portal.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Table 61 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Container Templates
This topic describes page container templates. It includes the following topics:
Table 61. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletGanttChartPortal.swt File
ID Placeholder
90 Title
157 Label
184 DrillDown Title
203 MinimizeApplet
204 MaximizeApplet
207 MoveAppletUp
208 MoveAppletDown
211 ShowApplet
212 HideApplet
301 through 302 Employee Header
303 Previous
304 Next
306 through 314 Label or Control
405 Control
555 Label
2101 through 2130 Control

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Container Templates
268
■ Container Template on page 268
■ CC Container Logic Template on page 269
Container Template
The Page Container template uses the CCPageContainer.swt file. It defines the setup for frames. An
employee application requires frames. The employee container templates create frames for the
banner, screen bar, view bar, and content. Some employee applications might also use frames for a
toolbar, a message bar, the search center, the persistent customer dashboard, and the iHelp pane.
To display an optional frame, Siebel CRM calls a predefined UI method at run time.
This template uses the following structure:
CCPageContainer.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCFrameBanner.swt
CCFrameViewbar.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCFrameToolbar.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCFrameThreadbar.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCFrameScreenbar.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCScreenbar_Tabs.swt
CCFrameMsgbar.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
Table 62 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 62. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCPageContainer.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Show Label
21 through 22 Page Item

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Popup Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 269
CC Container Logic Template
The CC Container Page Logic template uses the CCFrameContent_Logic.swt file. It examines
preferences and sends the logical frameset.
This template uses the following structure:
CCFrameContent_Logic.swt
CCFrameContent_VSDT.swt
CCFrameContent_VSD.swt
CCFrameContent_VST.swt
CCFrameContent_VS.swt
CCFrameContent_VDT.swt
CCFrameContent_VD.swt
CCFrameContent_VT.swt
CCFrameContent_V.swt
Popup Templates
This topic describes popup templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Popup Form Template on page 270
■ Popup Form, Grid Layout Template on page 271
■ Popup List Template on page 273
■ Popup Spell Checker Template on page 275
■ Popup Query Template on page 276
23 Page Item (History Label)
33 through 34 Control
35 Favorites Label
36 through 38 Control
Table 62. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCPageContainer.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Popup Templates
270
Popup Form Template
The Popup Form template uses the CCPopupForm.swt file. It defines a one column form that Siebel
CRM uses in base or edit pop-up mode.
Figure 36 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCPopupForm.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCButtons_Popup.swt
Table 63 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 36. Generic Layout of the Popup Form Template
Table 63. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCPopupForm.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Popup Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 271
Popup Form, Grid Layout Template
The Applet Popup Form Grid Layout template uses the CCAppletPopupFormGridLayout.swt file. It
uses the following tag as a placeholder for all controls in a popup form applet that Siebel CRM
displays in a grid:
swe:form-applet-layout
Figure 37 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
139 through 143 Control
152 OK
153 Cancel
154 through 158 Control
580 New
599 Save
1001 through 1009 FormSection
1090 through 1099 Required or Label or Field
1100 Label With Rule
1101 through 1110 Required or Label or Field
1111 through 1115 Required or Label or Field
1150 Label With Rule
1151 through 1160 Required or Label or Field
1500 Required or Legend
2001 through 2002 FormSection
2101 through 2110 Required or Label or Field
2111 through 2115 Required or Label or Field
Figure 37. Generic Layout of the Applet Popup Form Grid Layout Template
Table 63. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCPopupForm.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Popup Templates
272
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletPopupFormGridLayout.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCButtons_Popup.swt
Table 64 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template to the footer of the Applet Popup
Form Grid Layout template. For more information, see “About Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on
page 220.
Table 64. Items That Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletPopupFormGridLayout.swt
ID Placeholder
2 Back
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
152 OK
153 Cancel
154 through 158 Control
580 New
599 Save

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Popup Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 273
Popup List Template
The Popup List template uses the CCPopupList.swt file. It defines how Siebel CRM displays a list in
Base or Edit List pop-up mode.
Figure 38 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 39 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
CCPopupList.swt
CCListButtonsTop.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
CCListHeader.swt
CCListBody.swt
CCButtons_Popup.swt
Figure 38. Generic Layout of the Popup List Template
Figure 39. Example of the Popup List Applet Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Popup Templates
274
Table 65 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 65. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCPopupList.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Save (Optional)
147 Pick
150 through 151 Control
152 OK
153 Cancel
154 through 158 Control
160 through 164 Control
501 through 540 Field
580 New
598 Save- displays only in standard interactivity mode

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Popup Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 275
Popup Spell Checker Template
The Spell Checker Popup Applet template uses the CCAppletSpellCheck.swt file. It is a specialized
salutation applet that creates the spell check pop-up list.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletSpellCheck.swt
Table 66 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
599 Save
611 through 650 Control
Table 66. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletSpellCheck.swt File
ID Placeholder
91 Inside Applet Help Text
132 through 133 Control
134 Div
135 through 136 Control
137 Div
138 through 139 Control
140 Div
141 through 142 Control
143 Div
144 through 145 Control
146 Div
152 through 153 Control
154 Div
155 Control
156 Control
1201 Replacement Word Label
1211 Suggested Word Label
Table 65. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCPopupList.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Search Templates
276
Popup Query Template
The Popup Query template uses the CCPopupQuery.swt file. Figure 40 includes an example of this
template.
Search Templates
This topic describes search templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Search Center, Top Template on page 277
■ Search Center, Bottom Template on page 277
■ Advanced Search Template on page 278
■ Find Template on page 279
■ Save Search Template on page 280
■ Search Preference Template on page 281
■ Search Results Templates on page 283
1221 Dictionary Label
1300 Text Segment
Figure 40. Example of the Popup Query Applet Template
Table 66. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletSpellCheck.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Search Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 277
Search Center, Top Template
The Applet Form Search Top template uses the CCAppletFormSearchTop.swt file. It defines a
specialized applet that Siebel CRM uses to display the top part of the Search Center. You can map
the Search Center title only to ID 90. You can map the control that hides the Search Center frame
only to ID 141.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletFormSearchTop.swt
CCFormSearch.swt
Table 67 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Search Center, Bottom Template
The Search Applet template uses the CCAppletSearchBasic.swt file. It defines a specialized applet
that Siebel CRM uses to display the bottom part of the Search Center.
Figure 41 includes the Search Center.
Table 67. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletFormSearchTop.swt File
ID Placeholder
91 Inside Applet Help Text
141 Hide Icon. For high interactivity mode only.
142 Hide Icon. For standard interactivity mode only.
1201 through 1230 Label
1301 through 1330 Field
Figure 41. Example of the Search Applet Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Search Templates
278
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletSearchBasic.swt
CCFormSearch.swt
Table 68 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Advanced Search Template
The Advanced Search template uses the CCAppletSearchAdvanced.swt file. It defines a specialized
applet that displays advanced search.
This template uses the following structure:
AdvancedSearch.swt
Figure 42 includes the Advanced Search applet.
Table 68. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletSearchBasic.swt File
ID Placeholder
91 Inside Applet Help Text
132 Menu
133 New
141 through 142 Control
143 Control
1101 through 1130 Label or Field
Figure 42. Example of the Advanced Search Template

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Search Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 279
Table 69 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Find Template
The Applet Find template uses the CCAppletSearchFind.swt file. It defines a specialized applet that
determines the bottom of the search applet. The bottom of the Search Center displays the fields that
the user can choose to do an applet query.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletSearchFind.swt
CCFormSearch.swt
Table 69. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the AdvancedSearch.swt File
ID Placeholder
100 Label
105 ClearAll
115 Go
120 Label
125 Label
130 Control
135 Field
145 Label
150 Control
155 Label
160 HTML Checkbox
165 Label
170 Field
175 Label
180 Field
185 Label
190 HTML Checkbox
195 Label
200 HTML Checkbox

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Search Templates
280
Table 70 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Save Search Template
The Save Search template uses the SaveSearchApplet.swt file. It defines a specialized applet that
displays searches that the user saves.
Figure 43 includes the Save Search applet.
This template uses the following structure:
SaveSearchApplet.swt
Table 70. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletSearchFind.swt File
ID Placeholder
91 Inside Applet Help Text
132 Menu
133 New
141 through 142 Control
143 Control
1101 through 1130 Label or Field
Figure 43. Example of the Save Search Template

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Search Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 281
Table 71 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Search Preference Template
The Search Preference template uses the SearchPreference.swt file. It sets search preferences.
Figure 44 includes the Search Preference applet.
This template uses the following structure:
SearchPreference.swt
Table 71. Items That Siebel CRM Can Map for the SaveSearchApplet.swt
ID Placeholder
1000 Label
1005 Field
1010 Label
1015 Field
1020 Control
1025 Control
Figure 44. Example of the Search Preference Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Search Templates
282
Table 72 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 72. Items That Siebel CRM Can Map for the SearchPreference.swt
ID Placeholder
1000 Search Preferences (Label)
1001 Default
1002 Save Preference
1003 Number of Records (Label)
1004 Display records per page (Label)
1005 Select drop-down menu
1006 Results Window (Label)
1007 HTML Checkbox
1008 Open search results in new browser window (Label)
1009 Default Sort (Label)
1010 HTML RadioButton
1018 Context Sensitivity (Label)
1019 HTML RadioButton
1020 Criteria Reservation (Label)
1021 HTML RadioButton

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Search Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 283
Search Results Templates
The Search Results Header, Search Results Body, and Search Refine Category applets are specialized
applets that display search results. Figure 45 includes an example of these applets.
Search Results Header
The Search Results Header applet uses the SearchHeaderResults.swt file. It includes a summary of
search results.
This template uses the following structure:
SearchHeaderResults.swt
Table 73 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 45. Example of the Search Results Applets Template
Table 73. Items That Siebel CRM Can Map for the SearchHeaderResults.swt
ID Placeholder
2001 Label
2002 Field
2003 Label
2004 Field
2005 Label
2006 Field
2007 Field

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Search Templates
284
Search Results Body
The Search Results Body applet uses the SearchResults.swt file. It displays search result details.
This template uses the following structure:
SearchResults.swt
Search_ListHeader.swt
Search_ListBodySearchResults.swt
SearchResultsFooter
Table 74 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Search Refine Category
The Search Refine Category applet uses the Search_RefineCategoryApplet.swt file. It allows the user
to refine a search.
This template uses the following structure:
2008 Field
2009 Field
2010 Label
2011 Label
2012 Label
Table 74. Items That Siebel CRM Can Map for the SearchResults.swt
ID Placeholder
151 Label
152 Field
153 Field
502 ListHeader
503 ListHeader
504 ListHeader
2010 Label
3000 Label
Table 73. Items That Siebel CRM Can Map for the SearchHeaderResults.swt
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Search Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 285
Search_RefineCategoryApplet.swt
Table 75 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Search Results List Template
The Applet List Search Results template uses the CCAppletListSearchResults.swt file. It defines the
search results list that Siebel CRM displays in the Search Center pane. To conserve vertical space, it
embeds the applet title in the button bar, to the right of the menu button.
Figure 46 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletListSearchResults.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCListHeader.swt
CCListBodySearchResults.swt
Table 75. Items That Siebel CRM Can Map for the Search_RefineCategoryApplet.swt
ID Placeholder
1000 Label
1005 Hide Icon
1010 Label
1015 Hide Icon
Figure 46. Generic Layout of the Applet List Search Results Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Search Templates
286
Table 76 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Search Results View Template
The Search Results View template uses the Search_View.swt file. It a specialized view template that
Siebel CRM uses to display search results.
Table 76. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletListSearchResults.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
142 through 143 Control
144 Select
145 Control
146 Control
147 Pick
501 through 540 Control
580 New
599 Save
611 through 640 Control

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Tree Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 287
Figure 45 on page 283 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
Search_View.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
Table 77 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Tree Templates
This topic describes tree templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Applet Tree Template on page 287
■ Applet Tree, Marketing Template on page 289
■ View Tree Template on page 289
■ View Tree Two Template on page 291
Applet Tree Template
The Applet Tree 2 template uses the CCAppletTree2.swt file. It determines applet tabs and borders.
Figure 47 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletTree2.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
Table 77. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the Search_View.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 through 3 Applet
Figure 47. Generic Layout of the Applet Tree 2 Template
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Tree Templates
288
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCListButtonsTopNoRecNav.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
Table 78 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 78. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletTree2.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 Control
151 Control
160 through 164 Control
580 New
599 Save
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
1500 Required or Legend

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Tree Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 289
Applet Tree, Marketing Template
The Applet Tree Marketing template uses the CCAppletTreeMarketing.swt file. It is a specialized tree
applet that determines tabs and borders. It supports a toggle bar.
Figure 48 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletTreeMarketing.swt
CCTitle.swt
Table 79 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View Tree Template
The View Tree template uses the CCViewTree.swt file. It supports multiple columns:
■ The first column uses 25 percent of the window width and contains a tree applet.
■ The second column uses 75 percent of the window width and contains a list applet.
Figure 48. Generic Layout of the Applet Tree Marketing Template
Table 79. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletTreeMarketing.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Label
102 Control
132 Control
133 Control
142 through 143 Control
201 Field
1500 Required or Legend

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Tree Templates
290
It can use noncontext views as tabs.
Figure 49 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewTree.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbarAll_Tabs_DropList.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 80 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 49. Generic Layout of the View Tree Template
Table 80. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewTree.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Top (Parent) Applet
3 Parent Applet
4 Bottom (Child) Applet

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Tree Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 291
View Tree Two Template
The View Tree 2 template uses the CCViewTree2.swt file. It supports the following columns:
■ The first column uses 25 percent of the window width and contains a tree applet.
■ The second column uses 75 percent of the window width and contains a list applet.
It can display noncontext views as tabs.
Figure 50 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewTree2.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
6 Child or Grandchild Applet
8 Child or Grandchild Applet
10 Child or Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet
Figure 50. Generic Layout of the View Tree 2 Template
Table 80. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewTree.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
292
Table 81 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View Templates
This topic describes view templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Overview of Using View Templates on page 293
■ View 1 Over 2 Over 1 Template on page 293
■ View 25 - 50 – 25 Template on page 295
■ View 25 – 75 Template on page 296
■ View 25 – 75 Framed Template on page 297
■ View 25 – 75 Framed Two Template on page 298
■ View 50 – 50 Template on page 299
■ View 66 – 33 Template on page 300
■ View Admin Template on page 302
■ View Admin Template With Grandchild Indented Applets on page 303
■ View Basic Template on page 304
■ View Catalog Admin Template on page 305
■ View Detail Template on page 306
■ View Detail Template With Grandchild Indented Applets on page 308
■ View Detail Two Template on page 309
■ View Detail Two Template With Grandchild Indented Applets on page 311
■ View Detail Three Template on page 312
■ View Detail Three Template With Grandchild Indented Applets on page 314
■ View Detail Three Multichild Template on page 315
■ View Detail Multichild Template on page 316
■ View Parent List With Tabs Template on page 317
Table 81. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewTree2.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Applet
3 Applet
201 Mini-Applet

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 293
Overview of Using View Templates
Each gray area in the view diagrams in “View Templates” on page 292 represents an area where you
can place one or more applets. Siebel CRM expands each applet horizontally to fit the column where
you place this applet. The amount of data that it displays determines the amount of vertical space
the applet uses.
Siebel Tools does not determine style. It might display color schemes and applet titles differently
than Siebel CRM displays them in the client.
Guidelines for Using View Templates
If you configure a view template, then use the following guidelines:
■ Map a tree applet map on a view other than the view tree. Siebel CRM does not call a tree
applet in a template and the applet that this tree references the same way it calls a predefined
applet. You cannot map one of these tree applet as a predefined applet. You can use the View
Tree or View Tree 2 applet.
■ Increase the number of applets that Siebel CRM displays in a region. To define the number
of applets that Siebel CRM can map to a region, most regions use a swe:for-each loop. To
increase the number of applets, you can increase the count attribute of the swe:for each tag.
■ Use a subframe view. The View 25 – 75 (Framed) template is a subframe view. It displays some
applets in the left frame and other applets in the right frame.
■ Reuse applets. Each applet placeholder that resides in a view template specifies a style. To
determine the color scheme that the applet displays and the applet title visibility, Siebel CRM
evaluates this style at run time.
To reuse one applet object definition in many situations, you can apply styles in the view
template, and then code the applet template so that it evaluates styles. This configuration reuses
code and reduces the number of applet copies that you must maintain.
View templates support parent, child, and grandchild styles.
View 1 Over 2 Over 1 Template
The View 1 Over 2 Over 1 template uses the CCView_1Over2Over1.swt file. It includes multiple
regions:
■ The first region uses the full window width.
■ The second and third regions each use 50 percent of the window width.
■ The last region uses the full window width.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
294
Figure 51 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCView_1Over2Over1.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 82 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 51. Generic Layout of the 1 Over 2 Over 1 Template
Table 82. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCView_1Over2Over1.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet
102 through 106 Applet
201 Mini-Applet
202 through 206 Applet
302 through 306 Applet
402 through 406 Applet

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 295
View 25 - 50 – 25 Template
The View 25 - 50 – 25 template uses the CCView_25_50_25.swt file. It includes the following
columns:
■ The first column uses 25 percent of the window width.
■ The second column uses 50 percent of the window width.
■ The third column uses 25 percent of the window width.
Figure 52 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCView_25_50_25.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
502 through 506 Applet
602 through 606 Applet
Figure 52. Generic Layout of the View 25 - 50 - 25 Template
Table 82. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCView_1Over2Over1.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
296
Table 83 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View 25 – 75 Template
The View 25 – 75 template uses the CCView_25_75.swt file. It includes the following columns:
■ The first column uses 25 percent of the window width.
■ The second column uses 75 percent of the window width.
Figure 53 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCView_25_75.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
Table 83. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCView_25_50_25.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet
102 through 111 Applet
201 Mini-Applet
202 through 211 Applet
302 through 311 Applet
Figure 53. Generic Layout of the View 25 - 75 Template

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 297
CCThreadbar.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 84 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View 25 – 75 Framed Template
The View 25 – 75 Framed template uses the CCView_25_75_Framed.swt file. It includes the following
columns:
■ The first column uses 25 percent of the window width.
■ The second column uses 75 percent of the window width.
■ The first and second columns reside in separate frames.
Figure 54 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Table 84. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCView_25_75.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet
102 through 106 Applet
108 through 112 Applet
201 Mini-Applet
202 through 211 Applet
Figure 54. Generic Layout of the View 25 - 75 (Framed) Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
298
This template uses the following structure:
CCView_25_75_Framed.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 85 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View 25 – 75 Framed Two Template
The View 25 75 Framed 2 template uses the CCView_25_75_Framed2.swt file. It includes the
following columns:
■ The first column uses 25 percent of the window width.
■ The second column uses 75 percent of the window width.
■ The first column includes two frames. One applet can reside in each frame. The second column
is in a single frame.
Table 85. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCView_25_75_Framed.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet
102 through 106 Applet
108 through 112 Applet
201 Mini-Applet
202 through 211 Applet

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 299
Figure 55 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCView_25_75_Framed2.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 86 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View 50 – 50 Template
The View 50 – 50 template uses the CCView_50_50.swt file. It includes the following columns:
■ The first column uses 50 percent of the window width.
Figure 55. Generic Layout of the View 25 75 Framed 2 Template
Table 86. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCView_25_75_Framed2.swt File
ID Placeholder
102 through 103 Applet
201 Mini-Applet
202 through 211 Applet

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
300
■ The second column uses 50 percent of the window width.
Figure 56 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCView_50_50.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 87 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View 66 – 33 Template
The View 66 – 33 template uses the CCView_66_33.swt file. It includes the following columns:
Figure 56. Generic Layout of the View 50 - 50 Template
Table 87. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCView_50_50.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet
102 through 106 Applet
201 Mini-Applet
202 through 206 Applet

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 301
■ The first column uses 66 percent of the window width.
■ The second column uses 33 percent of the window width.
Figure 57 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCView_66_33.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 88 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 57. Generic Layout of the View 66 - 33 Template
Table 88. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCView_66_33.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet
102 through 121 Applet
201 through 220 Applet
901 Layout Controls

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
302
View Admin Template
The View Admin 1 template uses the CCViewAdmin1.swt file. It displays subviews as tabs across the
top of the view.
Figure 58 includes the generic layout that this template uses. You can use it in an administrative view
that must display nonrelated views that are difficult to categorize.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewAdmin1.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCSubViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 89 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 58. Generic Layout of the View Admin 1 Template
Table 89. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewAdmin1.swt File
ID Placeholder
5 Child Applet With Pointer
6 Child Applet
7 through 9 Grandchild Applet
13 through 15 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 303
View Admin Template With Grandchild Indented Applets
The View Admin 1 (Grandchild Indented) template uses the CCViewAdmin1_GrndchldIndnt.swt file.
It is similar to the View Admin 1 template except that Siebel CRM indents the second and subsequent
applets. You can use this template to display a hierarchical relationship or to display an
administrative view that must include nonrelated views that are difficult to categorize. For more
information, see “View Admin Template” on page 302.
Figure 59 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewAdmin1_GrndchldIndnt.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCSubViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 90 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 59. Generic Layout of the View Admin 1 (Grandchild Indented) Template
Table 90. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewAdmin1_GrndchldIndnt.swt File
ID Placeholder
5 Child Applet With Pointer
6 Child Applet
7 Grandchild Applet With Pointer
8 through 9 Child or Grandchild Applet
10 through 12 Grandchild Applet
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
304
View Basic Template
The View Basic template uses the CCViewBasic.swt file. All applets use the full window width and are
stacked on top of each other.
Figure 60 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewBasic.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
13 through 15 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet
Figure 60. Generic Layout of the View Basic Template
Table 90. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewAdmin1_GrndchldIndnt.swt File
ID Placeholder
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 305
Table 91 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View Catalog Admin Template
The View Catalog Admin template uses the CCViewCatalog.swt file. It is a specialized view template
that Siebel CRM uses only in a catalog view.
Figure 61 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewCatalog.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
Table 91. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewBasic.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 through 20 Applet
101 Salutation Applet
201 Mini-Applet
901 Layout Controls
Figure 61. Generic Layout of the View Catalog Admin Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
306
CCViewbar_Tabs_DropList.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 92 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View Detail Template
The View Detail template uses the CCViewDetail.swt file or the CCViewDetail_ParentPntr.swt file. It
displays the following items:
■ Parent applet
■ Noncontext views that it displays as tabs
■ Categorized subviews that it displays in a drop-down list
■ Child applet
■ Multiple grandchild applets
Table 92. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewCatalog.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Grandchild Applet
3 Grandchild Applet
4 through 5 Child Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet
8 through 9 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 307
Figure 62 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewDetail.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbar_Tabs_DropList.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 93 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 62. Generic Layout of the View Detail Template
Table 93. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewDetail.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet
3 through 5 Child or Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet
8 through 9 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
308
View Detail Template With Grandchild Indented Applets
The View Detail (Grandchild Indented) template uses the CCViewDetail_GrandchldIndnt.swt file. It
displays the same items as the View Detail template except that it indents grandchild applets. This
indentation indicates a hierarchy. For more information, see “View Detail Template” on page 306.
Figure 63 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewDetail_GrndchldIndnt.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbar_Tabs_DropList.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 94 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 63. Generic Layout of the View Detail (Grandchild Indented) Template
Table 94. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewDetail_GrandchldIndnt.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 309
View Detail Two Template
The View Detail 2 template uses the CCViewDetail2.swt file. It displays the following items:
■ Parent applet
■ Noncontext views that it displays as tabs
■ Child applet
■ Categorized subviews that it displays as tabs
■ Multiple grandchild applets
Figure 64 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewDetail2.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
3 through 5 Child or Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet
8 through 9 Grandchild Applet
88 Tree Applet
201 Mini-Applet
Figure 64. Generic Layout of the View Detail 2 Template
Table 94. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewDetail_GrandchldIndnt.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
310
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCSubViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 95 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 95. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewDetail2.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet
3 Grandchild Applet
4 through 5 Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet
8 through 9 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 311
View Detail Two Template With Grandchild Indented
Applets
The View Detail 2 (Grandchild Indented) template uses the CCViewDetail2_GrndchldIndnt.swt file. It
displays the same items as the View Detail Two template except that it indents grandchild applets.
This indentation indicates a hierarchy. For more information, see “View Detail Two Template” on
page 309.
Figure 65 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewDetail2_GrndchldIndnt.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCSubViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Figure 65. Generic Layout of the View Detail 2 (Grandchild Indented) Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
312
Table 96 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View Detail Three Template
The View Detail 3 template uses the CCViewDetail3.swt file. It is a specialized view template that
does the following:
■ Displays all views as tabs
■ Displays a child applet beneath these tabs
■ Displays categorized subviews in a drop-down list
■ Displays multiple grandchild applets beneath the child applet
You can use it to display an administrative view that must include a collection of views that are not
grouped and that visibility rules do not affect.
Table 96. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewDetail2_GrndchldIndnt.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet
3 Grandchild Applet
4 through 5 Child or Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet
8 through 9 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 313
Figure 66 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewDetail3.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbarAll_Tabs.swt
CCSubViewbar_Drop.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 97 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 66. Generic Layout of the View Detail 3 Template
Table 97. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewDetail3.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet
3 through 5 Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
314
View Detail Three Template With Grandchild Indented
Applets
The View Detail 3 (Grandchild Indented) template uses the CCViewDetail3_GrndchldIndnt.swt file. It
displays the same items as the View Detail Three template except that it indents grandchild applets.
This indentation indicates a hierarchy. For more information, see “View Detail Three Template” on
page 312.
Figure 67 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewDetail3_GrndchldIndnt.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbarAll_Tabs_DropList.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
8 through 9 Child or Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet
Figure 67. Generic Layout of the View Detail 3 (Grandchild Indented) Template
Table 97. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewDetail3.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 315
Table 98 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View Detail Three Multichild Template
The View Detail 3 Multi Child template uses the CCViewDetail3MultiChild.swt file. It is a specialized
view template that displays the following items:
■ Displays all views as tabs
■ Displays a child applet beneath these tabs
■ Displays categorized subviews in a drop-down list
■ Displays multiple grandchild applets in a bounded box.
You can use it to display an administrative view that must include a collection of views that are not
grouped and that visibility rules do not affect.
Figure 68 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewDetail3MultiChild.swt
Table 98. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewDetail3_GrndchldIndnt.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet
3 through 5 Child or Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet
8 through 9 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet
Figure 68. Generic Layout of the View Detail 3 Multi Child Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
316
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbarAll_Tabs_DropList.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 99 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View Detail Multichild Template
The View Detail Multi-Child template uses the CCViewDetailMultiChld.swt file. It displays the same
items as the View Detail Three Multichild template. This indentation indicates a hierarchy. For more
information, see “View Detail Three Multichild Template” on page 315.
Figure 69 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Table 99. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewDetail3MultiChild.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet
3 through 5 Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Child or Grandchild Applet
8 through 9 Child or Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet
Figure 69. Generic Layout of the View Detail Multi-Child Template

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 317
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewDetailMultiChild.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbarAll_Tabs_DropList.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 100 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
View Parent List With Tabs Template
The View Parent List With Tabs template uses the CCViewParentListWithTabs.swt file. It displays the
following items:
■ Parent applet
■ Noncontext views that it displays as tabs
■ Categorized subviews that it displays in a drop-down list
■ Child applet
■ Multiple grandchild applets
Table 100. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewDetailMultiChld.sw File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet
3 through 5 Grandchild Applet
6 through 11 Child or Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ View Templates
318
Figure 70 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewParentListWithTabs.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCSubordinateAppletsBorderStart.swt
CCViewBar_Tabs_DropList_Always.swt
CCSubViewbar_Drop.swt
dCCViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCSubViewbar_Drop.swt
CCSubordinateAppletsBorderEnd.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Figure 70. Generic Layout of the View Parent List With Tabs Template

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Specialized Employee Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 319
Table 101 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Specialized Employee Templates
This topic describes specialized templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Columns Displayed Template on page 320
■ Dashboard Template on page 321
■ Email Response Template for Inbound Messages on page 322
■ Email Response Template for Outbound Messages on page 324
■ Salutation Applet Template on page 326
■ Salutation Applet Template With Graphics on page 326
■ Screen Links Template on page 327
■ Send Mail Template on page 329
■ Send Mail Template for Picking Recipients on page 330
■ Site Map Template on page 331
■ View Dashboard Template on page 331
■ View Segment Detail Template on page 332
Table 101. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewParentListWithTabs.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet
3 through 5 Child or Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet
8 through 9 Grandchild Applet
10 through 20 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet
702 Child Applet (displays only in high interactivity mode)
703 through 705 Child or Grandchild Applet (displays only in high interactivity mode)

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Specialized Employee Templates
320
Columns Displayed Template
The Applet Items Displayed template uses the CCAppletItemsDisplayed.swt file. It is a specialized
template that displays the Columns Displayed dialog box that is available on most lists through the
applet menu. It includes specialized code that prevents Siebel CRM from using it for any other
purpose. For more information, see “Configuring How Siebel CRM Uses the Columns Displayed Feature”
on page 243.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletItemsDisplayed.swt
Table 102 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 102. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletItemsDisplayed.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Save
2 Reset
3 Cancel
10 Available Items Label
11 Available Items Combobox
12 Available Items Hidden Field
20 Move Item to Selected
21 Move All to Selected
22 Move Item to Available
23 Move All to Available
30 Selected Items Label
31 Selected Items Combobox
32 Selected Items Hidden Field
40 Move Item to Top
41 Move Item Up
42 Move Item Down
43 Move Item to Bottom
91 Inside Applet Help Text
100 Error Message
1100 Outside Applet Help Text

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Specialized Employee Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 321
Dashboard Template
The Applet Dashboard template uses the CCAppletDashboard.swt file. It defines a lightweight version
of the dashboard applet that displays the customer context in a call center application. It supports
three rows. Each of these rows can include up to four columns. It displays labels above fields. You
can use ID 211 to map a button that closes the dashboard.
Figure 71 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletDashboard.swt
Table 103 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 71. Example of the Applet Dashboard Template
Table 103. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletDashboard.swt File
ID Placeholder
211 Hide
1200 Label
1201 Label
1202 Label
1300 Field
1301 Field
1302 Field
1700 Label
1701 Label
1702 Label
1800 Field
1801 Field
1802 Field
2200 Label
2201 Label
2202 Label
2300 Field

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Specialized Employee Templates
322
Email Response Template for Inbound Messages
The Applet Email Response - Inbound template uses the EmailRespAppletInboundMsg.swt file.
This template uses the following structure:
EmailRespAppletInboundMsg.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCFormButtonsTop.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCFormButtonsTopRight.swt
CCEmailRespFormInBound.swt
2301 Field
2302 Field
2700 Label
2701 Label
2702 Label
2800 Field
2801 Field
2802 Field
2901 Button
2902 Button
Table 103. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletDashboard.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Specialized Employee Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 323
Table 104 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 104. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the EmailRespAppletInboundMsg.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
125 Info-Button
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 152 Control
160 through 164 Control
192 Label
194 Label
580 New
599 Save
1131 Field
1221 through 1226 Label
1321 through 1326 Field
1500 Required or Legend

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Specialized Employee Templates
324
Email Response Template for Outbound Messages
The Applet Email Response - Outbound template uses the EmailRespAppletOutboundMsg.swt file.
This template uses the following structure:
EmailRespAppletOutboundMsg.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCFormButtonsTop.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCFormButtonsTopRight.swt
CCEmailRespFormOutBound.swt
CCEmailRespFormButtonsBottom.swt
CCEmailRespButtonsBottom.swt
Table 105 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 105. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the EmailRespAppletOutboundMsg.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
125 Info-Button
131 New
132 Edit

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Specialized Employee Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 325
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
145 through 152 Control
160 through 164 Control
192 Label
194 Label
580 New
599 Save
1200 From
1201 To
1202 CC
1203 Subject
1204 Category
1205 Body
1207 Attachments
1220 SR #
1221 Opportunity
1222 Contact
1223 Account
1224 Category
1225 Closing
1300 Label
1301 through 1305 Field
1306 Message Body
1307 Field
1320 through 1325 Field
1401 Addr Book Icon
1402 BCC
Table 105. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the EmailRespAppletOutboundMsg.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Specialized Employee Templates
326
Salutation Applet Template
The Applet Salutation template uses the CCAppletSalutation.swt file. It defines the salutation applet
that Siebel CRM displays on a home page that includes a personal greeting.
Figure 72 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletSalutation.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
Table 106 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Salutation Applet Template With Graphics
The Applet Salutation (Graphical) template uses the CCAppletSalutationGraphical.swt file. It defines
a specialized salutation applet that Siebel CRM displays on a home page that includes a personal
greeting. You can use ID 89 to map an image to this template.
1407 Icon
1500 Required or Legend
1502 Field
1507 Icon
Figure 72. Example of the Applet Salutation Template
Table 106. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletSalutation.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Salutation
Table 105. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the EmailRespAppletOutboundMsg.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Specialized Employee Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 327
Figure 73 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletSalutationGraphical.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
Table 107 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Screen Links Template
The Applet Screen Links template uses the CCAppletScreenLinks.swt file. You can use it to manually
map controls, such as GoToView links. You can define a collection of these links that constitute a
table of contents that the user can use to access information.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletScreenLinks.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCFormButtonsTop.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCFormButtonsTopRight.swt
CCScreenLinks.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Figure 73. Generic Layout of the Applet Salutation (Graphical) Template
Table 107. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletSalutationGraphical.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Salutation
89 Image

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Specialized Employee Templates
328
Table 108 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 108. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletScreenLinks.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
125 Info-Button
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 152 Control
160 through 164 Control
192 Label
194 label
580 New
599 Save
1100 Group Label
1101 through 1120 Link
1200 Group Label
1201 through 1220 Link
1300 Group Label

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Specialized Employee Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 329
Send Mail Template
The Applet Send Mail template uses the CCAppletSendMail.swt file. It defines a specialized applet
that Siebel CRM uses to create the send mail pop-up list.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletSendMail.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCPopupButtonsBottom.swt
Table 109 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
1301 through 1320 Link
1400 Group Label
1401 through 1420 Link
1500 Required or Legend
2100 Group Label
2101 through 2120 Link
2200 Group Label
2201 through 2220 Link
2300 Group Label
2301 through 2320 Link
2400 Group Label
2401 through 2420 Link
Table 109. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletSendMail.swt File
ID Placeholder
152 OK
153 Cancel
154 through 158 Control
300 through 301 Icon
1200 From: Label
Table 108. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletScreenLinks.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Specialized Employee Templates
330
Send Mail Template for Picking Recipients
The Applet Send Mail Pick template uses the CCAppletSendEmailPick.swt file. It defines a specialized
applet that the user can use to choose email recipients.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletSendEmailPick.swt
CCButtons.swt
CCPopupButtonsBottom.swt
1201 To: Label
1202 Cc: Label
1203 Bcc Field
1204 Subject: Label
1205 Body: Label
1206 Optional Label
1207 Attachments: Label
1300 From Field
1301 To field
1302 CC Field
1303 Bcc Field
1304 Subject Field
1305 Templates Field
1306 Body Field
1307 Attachments Field
1400 Optional Control
1401 AB Control
1404 Control
Table 109. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletSendMail.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Specialized Employee Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 331
Table 110 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Site Map Template
The Site Map template uses the CCSiteMap.swt file. It creates a table of contents for the screens and
views that exist in Siebel CRM.
This template uses the following structure:
CCSiteMap.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
You cannot map items for this template.
View Dashboard Template
The View Dashboard template uses the CCViewDashboard.swt file. It defines a specialized view that
Siebel CRM uses for the Dashboard applet. It can contain one applet that uses the full window width.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewDashboard.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
Table 110. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletSendEmailPick.swt File
ID Placeholder
142 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Save
147 Pick Control
152 OK
153 Cancel
154 through 158 Control
501 through 540 Field
598 Save
1200 Label

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Specialized Employee Templates
332
CCHTMLFooter.swt
You cannot map items for this template.
View Segment Detail Template
The View SME Segment Detail template uses the CCViewSegmentDetail.swt file. It defines a
specialized view that Siebel CRM uses in a tree and the expression builder.
Figure 74 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCViewSegmentDetail.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
CCViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
Figure 74. Generic Layout of the View SME Segment Detail Template

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Wizard, Error, and Smart Script Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 333
Table 111 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Wizard, Error, and Smart Script
Templates
This topic describes other templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Applet Wizard Template on page 333
■ Error Page Template on page 334
■ Smart Script Player Template on page 335
■ Smart Script Player Template With Tree Only on page 336
Applet Wizard Template
The Applet Wizard template uses the CCAppletFormWizard.swt file. It defines wizards and
SmartScript applets. It displays buttons at the bottom of the form that allow the user to navigate
through a procedure. You can use ID 90 to map the applet title so that each step in the wizard can
include a unique title. You can map text that occurs outside of the applet, such as the name of the
running script, to ID 1100.
Figure 75 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletFormWizard.swt
CCTitle_Mapped.swt
Table 111. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCViewSegmentDetail.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Tree Applet
3 Java Applet
Figure 75. Generic Layout of the Applet Wizard Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Wizard, Error, and Smart Script Templates
334
CCForm1ColBody.swt
CCButtons.swt
Table 112 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Error Page Template
The Error Page template uses the CCError.swt file. It displays system errors.
This template uses the following structure:
Table 112. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCAppletFormWizard.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
90 Title
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
184 Title
580 New
599 Save
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
1301 through 1350 Required or Label or Field
1500 Required or Legend
2301 through 2350 Required or Label or Field

Siebel Templates for Employee Applications ■ Wizard, Error, and Smart Script Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 335
CCError.swt
CCHTMLHeader.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
CCHTMLFooter.swt
You cannot map items for this template.
Smart Script Player Template
The SmartScript Player Applet (Player Only) template uses the CCSmartScriptPlayerApplet.swt file.
It defines SmartScript applets. It displays buttons at the bottom of the form that allow the user to
navigate through a procedure.
Figure 76 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCSmartScriptPlayerApplet.swt
Table 113 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 76. Generic Layout of the SmartScript Player Applet (Player Only) Template
Table 113. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the CCSmartScriptPlayerApplet.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Finish Script
2 Cancel Script
3 Previous Section
4 Next Section
5 Save Script
6 Save Answers
1500 Required Label

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Employee Applications
■ Wizard, Error, and Smart Script Templates
336
Smart Script Player Template With Tree Only
The Smart Script Player Applet (Tree Only) template uses the CCAppletTree.swt file. It defines a tree
applet that does not include an applet title or border.
Figure 77 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
CCAppletTree.swt
You cannot map items for this template.
Figure 77. Generic Layout of the Smart Script Player Applet (Tree Only) Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 337
9 Siebel Templates for Customer
Applications
This chapter describes the predefined templates that Siebel CRM uses in a customer application. It
includes the following topics:
■ Overview of Configuring Siebel Templates for Customer Applications on page 337
■ Customer Form Templates
■ Customer List Templates
■ Customer View Templates on page 391
■ Customer Container Templates on page 405
■ Specialized Customer Templates on page 408
Overview of Configuring Siebel
Templates for Customer Applications
Most customer applications, such as Siebel eSales and Siebel eService, use a set of customer
templates in standard interactivity mode for general functionality and a subset of employee
templates in high interactivity mode for messages and greetings.
The following types of applications exist for partner relationship management:
■ PRM Manager. Uses high interactivity mode. Templates that Siebel CRM displays in PRM
Manager use the functionality described in Chapter 8, “Siebel Templates for Employee
Applications.”
■ PRM Portal. Uses standard interactivity mode. Templates that Siebel CRM displays in PRM Portal
use the functionality described in this chapter.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Overview of Configuring Siebel Templates
for Customer Applications
338
Overview of User Interface Elements
Table 114 describes an overview of user interface elements that Siebel CRM uses in the Siebel Web
Client for a customer application.
Table 114. User Interface Elements in Customer Applications
Element Description
Header A framed area at the top of the page that remains visible while the user scrolls
the content area. It includes the following elements:
■ Banner
■ Screen bar
■ View bar
Banner A top frame of the header that includes site branding and navigation. It includes
the company logo on the left side and the global navigation links in the lower
right corner.
Global
navigation
links
Links that Siebel CRM displays in the lower right corner of the banner frame.
These links provide functionality that the primary tabs do not provide. Customer
applications and partner applications include the following global navigation
links:
■ Shopping Cart
■ My Account
■ Help
■ Contact Us
■ Log In/Out
Screen bar A bar that displays the primary tabs that provide access to screens.
View bar The bottom frame of the header that Siebel CRM uses to display the simple
search applet in most customer applications. In eChannel, the view bar displays
the second-level navigation and favorites drop-down list controls.
Simple Search
applet
A small applet in the right side of the view bar that can do a simple search. This
applet also contains an icon that links to the Search Center page where the user
can do an advanced search.
Content area The largest frame of the page that contains a view template and one or more
applet templates. The user can scroll this content area vertically without affecting
the position of the header frames.
Salutation and
personal
greeting
Area at the top of the content area that displays text messages. The message
area typically displays a personal greeting on an application home page and a
threadbar on pages lower in the application hierarchical structure.
Thread bar A set of links in the message area that displays the path the user takes through
the application hierarchical structure. It allows for easy navigation to previously
visited pages.

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 339
Customer Form Templates
This topic describes customer form templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Basic Form Template on page 339
■ One Column Form Template on page 340
■ Two Column Form Template on page 342
■ Four Column Form Template on page 344
■ Item Detail Form Template on page 347
■ Search, Top Form Template on page 349
■ Title, Form Template on page 349
■ Four Column, Merged, Form Template for Base, Edit, or New Mode on page 350
Basic Form Template
The Form/1-Column/Basic template uses the dCCAppletFormBasic.swt file.
Figure 78 includes an example of this template.
Figure 78. Example of the Form/1-Column/Basic Applet Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer Form Templates
340
One Column Form Template
The DotCom Applet Form 1-Column template uses the dCCAppletForm1Col.swt file. It can do the
following:
■ Display labels to the left of fields.
■ Display buttons at the bottom of the form.
Figure 79 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 80 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletForm1Col.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCForm1Col.swt
dCCButtons_Form.swt
Figure 79. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet Form 1-Column Template
Figure 80. Example of the Form/1-Column Applet Template

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 341
Table 115 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 115. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletForm1Col.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 110 Control
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
157 through 158 Control
1000 FormSection
1001 FormSection
1002 FormSection
1003 FormSection
1004 FormSection
1005 FormSection
1006 FormSection
1300 through 1305 Required or Label
1306 through 1311 Required or Label
1312 through 1317 Required or Label
1318 through 1323 Required or Label
1324 through 1329 Required or Label
1330 through 1335 Required or Label
1336 through 1341 Required or Label
1500 Required or Legend

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer Form Templates
342
Two Column Form Template
The DotCom Applet Form 2-Column template uses the dCCAppletForm2Col.swt file. It can do the
following:
■ Display labels to the left of fields.
■ Display two columns of label and field pairs followed by one wide column that spans these pairs.
Figure 81 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletForm2Col.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCFormButtonsTop.swt
dCCButtons_Form.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCFormButtonsTopRight.swt
dCCForm2Col.swt
Table 116 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 81. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet Form 2-Column Template
Table 116. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletForm2Col.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
91 through 92 Inside Applet Help Text

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 343
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 110 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 152 Control
157 through 158 Control
160 through 164 Control
1001 FormSection
1002 FormSection
1003 FormSection
1004 FormSection
1030 FormSection
1035 FormSection
1100 through 1104 Required or Label
1105 through 1109 Required or Label
1110 through 1114 Required or Label
1115 through 1119 Required or Label
1130 through 1134 Label or Field
1135 through 1139 Label or Field
1500 Required or Legend
Table 116. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletForm2Col.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer Form Templates
344
Four Column Form Template
The DotCom Applet Form 4-Column template uses the dCCAppletForm4Col.swt file. It can do the
following:
■ Define a large number of control placeholders that can span one column, two columns, or all four
columns.
■ Map fields for up to four columns.
■ Display labels above field values.
■ Display validation errors at the top of the form.
■ Use ID 91 to add text that spans all four columns.
Figure 82 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
2001 FormSection
2002 FormSection
2003 FormSection
2004 FormSection
2100 through 2104 Required or Label
2105 through 2109 Required or Label
2110 through 2114 Required or Label
2115 through 2119 Required or Label
Figure 82. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet Form 4-Column Template
Table 116. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletForm2Col.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 345
Figure 83 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletForm4Col.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCFormButtonsTop.swt
dCCButtons_Form.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCFormButtonsTopRight.swt
CCForm4ColBody.swt
Table 117 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 83. Example of the Form/4 Column Applet Template
Table 117. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletForm4Col.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Control
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer Form Templates
346
109 through 110 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
150 through 152 Control
157 through 158 Control
160 through 164 Control
1001 through 1009 FormSection
1020 FormSection
1296 through 1300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1301 through 1310 Required or Label
1311 through 1315 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1316 through 1330 Required or Label
1331 through 1335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1336 through 1340 Required or Label or 4-Column Wide Field
1360 through 1374 Required or Label
1500 Required or Legend
1801 through 1810 Required or Label
1816 through 1830 Required or Label
1860 through 1874 Required or Label
2001 through 2009 FormSection
2296 through 2300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2301 through 2310 Required or Label
Table 117. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletForm4Col.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 347
Item Detail Form Template
The DotCom Applet Form Item Detail template uses the dCCAppletFormItemDetail.swt file. It uses
ID 1301 to map the product title and ID 1300 to map the product image.
Figure 84 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
2316 through 2330 Required or Label
2331 through 2335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2360 through 2374 Required or Label
2801 through 2810 Required or Label
2811 through 2815 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2816 through 2830 Required or Label
2860 through 2874 Required or Label
Figure 84. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet Form Item Detail Template
Table 117. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletForm4Col.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer Form Templates
348
Figure 85 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletFormItemDetail.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCFormItemDetail.swt
Table 118 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 85. Example of the Form/Item Detail 1 Applet Template
Table 118. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletFormItemDetail.swt File
ID Placeholder
132 through 133 Control
141 Control
142 Control

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 349
Search, Top Form Template
The DotCom Applet Form Search Top template uses the dCCAppletSearchTop.swt file. It creates a
drop-down list that the user can use to do a dot-com search.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletSearchTop.swt
CCTitle.swt
dCCFormSearch.swt
Table 119 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Title, Form Template
The DotCom Applet Form Title template uses the dCCAppletFormTitle.swt file. It displays a simple
applet that includes a free-form title. It gets the title from the Title property of the applet.
157 through 158 Control
159 Control
160 Control
1102 through 1107 Label or Field
1112 through 1133 Label or Field
1300 Large Image (120X120)
1301 Item Name
Table 119. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletSearchTop.swt File
ID Placeholder
91 Inside Applet Help Text
1101 through 1130 Label or Field
1500 Required or Legend
Table 118. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletFormItemDetail.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer Form Templates
350
Figure 86 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 87 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletFormTitle.swt
You cannot map items for this template.
Four Column, Merged, Form Template for Base, Edit, or
New Mode
The Dotcom Form 4-Col Merged (Base/Edit/New) template uses the
dCCAppletForm4ColMerged_B_E_N.swt file. It supports a specialized applet that does not include an
applet tab. It can do the following:
■ Display the applet title in the button bar. This configuration allows Siebel CRM to stack these
applets without any intervening white space. You can use it to create a summary view.
■ Define a large number of control placeholders that span one column, two columns, or four
columns.
■ Map fields for up to four columns.
■ Display labels above field values.
■ Display validation errors at the top of the form.
■ Use ID 91 to add text that spans all four columns.
■ Use the predefined applet styles.
Figure 86. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet Form Title Template
Figure 87. Example of the Form/Title Only Applet Template

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer Form Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 351
Figure 88 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletForm4ColMerged_B_E_N.swt
dCCFormButtonsTopWithTitle.swt
dCCButtons_Form.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCForm4ColBody.swt
Table 120 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 88. Generic Layout of the DotCom Form 4-Col Merged (Base/Edit/New) Template
Table 120. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletForm4ColMerged_B_E_N.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Inside Applet Help Text
91 Inside Applet Help Text
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 110 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
132 Edit

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
352
Customer List Templates
This topic describes customer list templates. It includes the following topics:
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
157 through 158 Control
1001 through 1009 FormSection
1020 FormSection
1296 through 1300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1301 through 1310 Required or Label
1311 through 1315 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1316 through 1330 Required or Label
1331 through 1335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
1336 through 1340 Required or Label or 4-Column Wide Field
1360 through 1374 Required or Label
1801 through 1810 Required or Label
1816 through 1830 Required or Label
1860 through 1874 Required or Label
2001 through 2009 FormSection
2296 through 2300 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2301 through 2310 Required or Label
2316 through 2330 Required or Label
2331 through 2335 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2360 through 2374 Required or Label
2801 through 2810 Required or Label
2811 through 2815 Required or Label or 2-Column Wide Field
2816 through 2830 Required or Label
2860 through 2874 Required or Label
Table 120. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletForm4ColMerged_B_E_N.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 353
■ Brief, Bullet, List Template on page 353
■ Brief, Bullet, Border, List Template on page 355
■ Brief, Bullet, Shade, List Template on page 357
■ Brief, Image Bullet, List Template on page 358
■ Brief, Image Bullet Two, List Template on page 360
■ Brief, Image Bullet, Border, List Template on page 362
■ Brief, Image Bullet, Shade, List Template on page 365
■ Categorized List Template With Tabs on page 363
■ Categorized List Template With No Tabs on page 364
■ Categorized Bullet, List Template on page 366
■ Categorized Bullet, List Template With Tabs on page 368
■ Categorized Table of Contents, List Template on page 369
■ Detailed, Image Bullet, List Template on page 370
■ Detailed, Image Bullet, List Template With Record Navigation on page 372
■ Detailed, Image Bullet, List Template With Record Navigation Two on page 374
■ Go To View, List Template on page 376
■ Horizontal List Template on page 377
■ List Template With Tabs on page 379
■ Light List Template on page 381
■ Search Results, List Template on page 383
■ Subcategory List Template on page 385
■ Subcategory, One Per Row, List Template on page 385
■ Subcategory, Four Per Column, List Template on page 386
■ Subcategory, Six Per Column, List Template on page 387
■ Subcategory, Indented, List Template on page 388
■ Merged List Template for Base or Edit List Mode on page 389
■ Links List Template on page 390
Brief, Bullet, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Brief Bullet template uses the dCCAppletListBriefBullet.swt file. It displays a
bulleted list of records that include a record title and a brief description.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
354
Figure 89 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 90 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListBriefBullet.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
dCCTitle_Portal.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCListTitleNoRule.swt
dCCListBodyBullet.swt
Figure 89. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Brief Bullet Template
Figure 90. Example of the List Brief/Bullet Applet Template

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 355
Table 121 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Brief, Bullet, Border, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Brief Bullet/Border template uses the dCCAppletListBriefBulletBorder.swt
file. It displays a bulleted list of records that include a record title and a brief description.
Table 121. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListBriefBullet.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Title or DrillDown or New
90 Title
106 Find
107 Search
109 through 111 Control
131 New
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
157 Label
184 DrillDown Title
203 MinimizeApplet
204 MaximizeApplet
207 MoveAppletUp
208 MoveAppletDown
211 ShowApplet
212 HideApplet
501 Field
502 through 511 Field
555 Label
1100 Outside Applet Help Text

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
356
Figure 91 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 92 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListBriefBulletBorder.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCListTitleNoRule.swt
dCCListBodyBullet.swt
Table 122 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 91. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Brief Bullet/Border Template
Figure 92. Example of the List Brief/Bullet/Border Applet Template
Table 122. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListBriefBulletBorder.swt File
ID Placeholder
90 Title or DrillDown or New
106 Find
107 Search
109 through 111 Control
131 New
134 Reset

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 357
Brief, Bullet, Shade, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Brief Bullet / Shade template uses the dCCAppletListBriefBulletShaded.swt
file. It displays a bulleted list of records that include a record title and a brief description.
Figure 93 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 94 includes an example of this template. It uses the dCCAppletListBriefBulletShade.swt file.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListBriefBulletShaded.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
135 Cancel
136 Save
184 DrillDown Title
501 Field
502 through 511 Field
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
Figure 93. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Brief Bullet/Shade Template
Figure 94. Example of the List Brief/Bullet/Shaded Applet Template
Table 122. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListBriefBulletBorder.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
358
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCListTitleNoRule.swt
dCCListBodyBullet.swt
Table 123 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Brief, Image Bullet, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet template uses the dCCAppletListBriefImgBullet.swt file. It
displays a bulleted list of records that include a record title, image, and a brief description.
Figure 95 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Table 123. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListBriefBulletShaded.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Title or DrillDown or New
90 Title
106 Find
107 Search
109 through 111 Control
131 New
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
184 DrillDown Title
501 Field
502 through 511 Field
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
Figure 95. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet Template

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 359
Figure 96 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListBriefImgBullet.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
dCCTitle_Portal.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCListTitleNoRule.swt
dCCListBodyImgBullet.swt
Table 124 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 96. Example of the List Brief/Image Bullet Applet Template
Table 124. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListBriefImgBullet.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Anchor or Title
2 Title or DrillDown or New
90 Title
106 Find
107 Search
109 through 111 Control

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
360
Brief, Image Bullet Two, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet 2 template uses the dCCAppletListBriefImgBullet2.swt file.
It displays a bulleted list of records that include a record title, image, and a brief description.
Figure 97 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
131 New
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
157 Label
184 DrillDown Title
203 MinimizeApplet
204 MaximizeApplet
207 MoveAppletUp
208 MoveAppletDown
211 ShowApplet
212 HideApplet
501 Small Image (30x30)
502 Title
503 Description
504 through 513 Other Text
520 through 529 Other
555 Label
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
Figure 97. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet 2 Template
Table 124. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListBriefImgBullet.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 361
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListBriefImgBullet2.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
dCCTitle_Mapped.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCListBodyImgBullet2.swt
Table 125 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 125. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListBriefImgBullet2.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Anchor or Title
2 Small Image (30x30)
90 Title or DrillDown Title or Label
157 Label
184 DrillDown Title
203 MinimizeApplet
204 MaximizeApplet
207 MoveAppletUp
208 MoveAppletDown
211 ShowApplet
212 HideApplet
501 Small Image (30x30)
502 Title
503 Description
504 through 513 Other Text
520 through 529 Other
555 Label
1100 Outside Applet Help Text

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
362
Brief, Image Bullet, Border, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet / Border template uses the
dCCAppletListBriefImgBulletBorder.swt file. It displays a bulleted list of records that include a record
title, image, and a brief description.
Figure 98 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 99 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListBriefImgBulletBorder.swt
dCCListTitleNoRule.swt
dCCListBodyImgBullet.swt
Table 126 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 98. Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet/Border Template
o
Figure 99. Example of the List Brief/Image Bullet/Border Applet Template
Table 126. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListBriefImgBulletBorder.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Anchor or Title
90 Title or DrillDown or New

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 363
Categorized List Template With Tabs
The DotCom Applet List Categorized Tabbed template uses the dCCAppletListCategorizedTab.swt file.
It displays top-level bulleted items in a hierarchical list.
Figure 100 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListCategorizedTab.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
106 Find
107 Search
109 through 111 Control
131 New
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
184 DrillDown Title
501 Small Image (30x30)
502 Title
503 Description
504 through 513 Other Text
520 through 529 Other
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
Figure 100.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Categorized Tabbed Template
Table 126. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListBriefImgBulletBorder.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
364
CCTitle.swt
dCCButtons_List.swt
Table 127 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Categorized List Template With No Tabs
The DotCom Applet List Categorized (No Tab) template uses the dCCAppletListCategorizedNoTab.swt
file. It displays top-level items in a hierarchical list.
Figure 101 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Table 127. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListCategorizedTab.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
131 New
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 141 Control
501 Image
502 Field
1500 Required or Legend
Figure 101.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Categorized (No Tab) Template

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 365
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListCategorizedNoTab.swt
Table 128 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Brief, Image Bullet, Shade, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet / Shade template uses the
dCCAppletListBriefImgBulletShaded.swt file. It displays a bulleted list of records that include a record
title, image, and a brief description.
Figure 102 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 103 includes an example of this template. The List Brief/Image Bullet/Shaded template uses
the dCCAppletListBriefImgBulletShade.swt file.
Table 128. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListCategorizedNoTab.swt File
ID Placeholder
90 Title
501 Image
502 Field
Figure 102.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet/Shade Template
Figure 103.Example of the List Brief/Image Bullet/Shaded Applet Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
366
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListBriefImgBulletShaded.swt
dCCListTitleNoRule.swt
dCCListBodyImgBullet.swt
Table 129 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Categorized Bullet, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Categorized Bullet template uses the dCCAppletListCategorizedBullet.swt
file. It displays top-level bulleted items in a hierarchical list.
Table 129. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListBriefImgBulletShaded.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Anchor or Title
90 Title or DrillDown or New
106 Find
107 Search
109 through 111 Control
131 New
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
184 DrillDown Title
501 Small Image (30x30)
502 Title
503 Description
504 through 513 Other Text
520 through 529 Other
1100 Outside Applet Help Text

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 367
Figure 104 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 105 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListCategorizedBullet.swt
dCCListCategorized.swt
Table 130 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 104.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Categorized Bullet Template
Figure 105.Example of the List/Categorized/Bulleted Applet Template
Table 130. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListCategorizedBullet.swt File
ID Placeholder
132 Field
502 Field

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
368
Categorized Bullet, List Template With Tabs
The DotCom Applet List Categorized Bullet / Tabbed template uses the
dCCAppletListCategorizedBulletTab.swt file. It displays top-level bulleted items in a hierarchical list.
Figure 106 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 107 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListCategorizedBulletTab.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCTitle.swt
dCCButtons_List.swt
dCCListCategorized.swt
Table 131 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 106.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Categorized Bullet/Tabbed Template
Figure 107.Example of the List/Categorized/Bulleted/Tabbed Applet Template
Table 131. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListCategorizedBulletTab.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 369
Categorized Table of Contents, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Categorized TOC template uses the dCCAppletListCategorizedTOC.swt file.
It can do the following:
■ Display a table of contents from top-level categories.
■ Use ID 90 to map the TOC title.
■ Use ID 501 to map an image or bullet.
■ Use ID 502 to map the item name.
Figure 108 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListCategorizedTOC.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
131 New
132 Field
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 141 Control
502 Field
1500 Required or Legend
Figure 108.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Categorized TOC Template
Table 131. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListCategorizedBulletTab.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
370
Table 132 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Detailed, Image Bullet, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Detailed ImgBullet template uses the dCCAppletListDetailedImgBullet.swt
file. It displays detailed product descriptions in a list. It displays a product image, title description,
and buttons for each record.
Figure 109 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Table 132. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListCategorizedTOC.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Anchor
90 TOC Title
501 Image
502 Field
Figure 109.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Detailed ImgBullet Template

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 371
Figure 110 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListDetailedImgBullet.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCTitle_Mapped.swt
CCLayoutButtons.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCListBodyImgBulletDetailed.swt
Figure 110.Example of the List Detailed/Image Bullet Applet Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
372
Table 133 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Detailed, Image Bullet, List Template With Record
Navigation
The DotCom Applet List Detailed ImgBullet RecNav template uses the
dCCAppletListDetailedImgBulletRecNav.swt file. It displays detailed product descriptions in a list. It
displays a product image, title description, and buttons for each record.
Table 133. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListDetailedImgBullet.swt File
Id Placeholder
2 Small Image (30x30)
90 Title: DrillDown title or Label
142 through 143 Control
145 through 146 Control
157 Control
158 Control
184 DrillDown Title
203 MinimizeApplet
204 MaximizeApplet
207 MoveAppletUp
208 MoveAppletDown
211 ShowApplet
212 HideApplet
501 Small Image (30x30)
502 through 503 Item Name
504 through 505 Label or Field
510 through 512 Label or Field
555 Label

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 373
Figure 111 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 112 includes an example of this template.
Figure 111.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Detailed ImgBullet RecNav Template
Figure 112.Example of the List Detailed/Image Bullet/Record Navigation Applet Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
374
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListDetailedImgBulletRecNav.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCTitle_RecNav.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCListBodyImgBulletDetailed.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
Table 134 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Detailed, Image Bullet, List Template With Record
Navigation Two
The DotCom Applet List Detailed ImgBullet RecNav2 template uses the
dCCAppletListDetailedImgBulletRecNav2.swt file. It displays a detailed description for each product
in a list. It includes a product image, title, and buttons for each record.
Table 134. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListDetailedImgBulletRecNav.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Small Image (30x30)
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
142 through 143 Control
145 through 146 Control
157 through 158 Control
501 Small Image (30x30)
502 through 503 Item Name
504 through 505 Label or Field
510 through 512 Label or Field
1100 Outside Applet Help Text

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 375
Figure 113 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 114 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListDetailedImgBulletRecNav2.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCTitle_RecNav.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCListBodyImgBulletDetailed2.swt
Figure 113.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Detailed ImgBullet RecNav2 Template
Figure 114.Example of the List Detailed/Image Bullet/Record Navigation 2 Applet Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
376
Table 135 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Go To View, List Template
Figure 115 includes an example of this template.
Table 135. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListDetailedImgBulletRecNav2.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Small Image (30x30)
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
142 through 143 Control
145 Control
501 Small Image (30x30)
502 through 503 Item Name
504 through 505 Label or Field
506 through 508 Control
510 through 511 Label or Field
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
Figure 115.Example of the Go To View List Template

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 377
Horizontal List Template
The DotCom Applet List Horizontal template uses the dCCAppletListHorizontal.swt file. It can do the
following:
■ Display a list of records horizontally.
■ Create a layout that allows the user to compare items.
■ Include a product image, title, and a brief description.
■ Support record navigation.
Figure 116 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 117 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListHorizontal.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCListButtonsTop.swt
Figure 116.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Horizontal Template
Figure 117.Example of the List/Horizontal Applet Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
378
dCCButtons_List.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
dCCListBodyHorizontal.swt
Table 136 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 136. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListHorizontal.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Control
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 141 Control
142 through 143 Control
145 Control
150 through 151 Control
160 through 164 Control
161 through 164 Control
501 Small Image (30x30)
502 Item Name
503 through 505 Field
510 through 512 Label or Field

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 379
List Template With Tabs
The DotCom Applet List Tabbed template uses the dCCAppletListTabbed.swt file. It can map up to
twenty fields. For more information about how to configure this mapping, see “Configuring How Siebel
CRM Uses the Columns Displayed Feature” on page 243.
Figure 118 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 119 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListTabbed.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
dCCListButtonsTop.swt
dCCButtons_List.swt
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
1500 Required or Legend
Figure 118.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Tabbed Template
Figure 119.Example of the List Tabbed Applet Template
Table 136. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListHorizontal.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
380
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
dCCListHeader.swt
dCCListBodyNoRowHilite.swt
Table 137 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 137. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListTabbed.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Control
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
132 through 133 Control
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 141 Control
142 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Save
147 Pick Control
150 through 151 Control
160 through 164 Control
161 through 164 Control

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 381
Light List Template
The DotCom Applet List Light template uses the dCCAppletListLight.swt file. It can do the following:
■ Display a specialized list that includes a totals row at the bottom of the list. You must use Siebel
Tools to configure a column that creates a total.
■ Include a double line above the totals row.
■ Use ID 199 to map a totals row label.
■ Use one label for all row totals. This label must be generic so that it describes all rows.
Figure 120 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
Figure 121 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
501 through 520 Field
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
1500 Required or Legend
Figure 120.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Light Template
Figure 121.Example of the List/Light Applet Template
Table 137. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListTabbed.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
382
dCCAppletListLight.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
CCTitle.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCListButtonsTop.swt
dCCButtons_List.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
dCCListHeaderTotals.swt
dCCListBodyTotalsNoRowHilite.swt
Table 138 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 138. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListLight.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
125 Info-Button
126 Query Assistant
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 383
Search Results, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Search Results template uses the dCCAppletListSearchResults.swt file. It
displays search results in a list. This list does not support record selection. It does not highlight a
record selection.
Figure 122 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListSearchResults.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
CCTitle_Named.swt
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Save
147 Pick Control
150 through 151 Control
160 through 164 Control
199 Totals Label
501 through 520 Control
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
1500 Required or Legend
Figure 122.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Search Results Template
Table 138. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListLight.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
384
CCTitle.swt
dCCListButtonsTop.swt
dCCButtons_List.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
dCCListHeader.swt
dCCListBodySearchResults.swt
Table 139 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 139. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListSearchResults.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
125 Info-Button
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
144 Select
145 through 146 Control

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 385
Subcategory List Template
The DotCom Applet List Subcategory template uses the dCCAppletListSubCategory.swt file. It
displays subcategory links where a comma separates each link.
Figure 123 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListSubCategory.swt
Table 140 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Subcategory, One Per Row, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Subcategory 1 Per Row template uses the
dCCAppletListSubCategory_1PerRow.swt file. It displays one subcategory link in each row.
147 Pick
150 through 151 Control
160 through 164 Control
501 through 520 Control
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
1500 Required or Legend
Figure 123.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Subcategory Template
Table 140. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListSubCategory.swt File
ID Placeholder
502 Field
503 Field
Table 139. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListSearchResults.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
386
Figure 124 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListSubCategory_1PerRow.swt
Table 141 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Subcategory, Four Per Column, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Subcategory 4-Per-Column template uses the
dCCAppletListSubCategory_4PerColumn.swt file. It displays four subcategory links in each column.
Figure 125 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListSubCategory_4PerColumn.swt
Figure 124.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Subcategory 1 Per Row Template
Table 141. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListSubCategory_1PerRow.swt File
ID Placeholder
501 Image or Subcategory or Count
502 Subcategory
503 Count
Figure 125.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Subcategory 4-Per-Column Template

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 387
Table 142 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Subcategory, Six Per Column, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Subcategory 6-Per-Column template uses the
dCCAppletListSubCategory_6PerColumn.swt file. It displays six subcategory links in each column.
Figure 126 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListSubCategory_6PerColumn.swt
Table 143 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 142. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListSubCategory_4PerColumn.swt File
ID Placeholder
501 Image: Subcategory or Count
502 Subcategory
503 Count
Figure 126.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Subcategory 6-Per-Column Template
Table 143. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListSubCategory_6PerColumn.swt File
ID Placeholder
501 Image: Subcategory or Count
502 Subcategory
503 Count

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
388
Subcategory, Indented, List Template
The DotCom Applet List Subcategory Indented template uses the
dCCAppletListSubCategoryIndented.swt file. It displays subcategory links where a comma separates
each link. It indents links to indicate the hierarchical nature of the data.
Figure 127 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListSubCategoryIndented.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
dCCListTitleNoRule.swt
Table 144 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 127.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet List Subcategory Indented Template
Table 144. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListSubCategoryIndented.swt File
ID Placeholder
90 Title or DrillDown Title or New
106 Find
107 Search
109 through 111 Control
131 New
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
184 DrillDown Title
502 Field
503 Field
1100 Outside Applet Help Text

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer List Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 389
Merged List Template for Base or Edit List Mode
The DotCom List Merged (Base/EditList) template uses the dCCAppletListMerged_B_EL.swt file. It is
a specialized applet template that can stack applets one on top of the other without intervening white
space. You can use it on a report or summary page. It displays the applet title in the upper right
corner.
Figure 128 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletListMerged_B_EL.swt
dCCListButtonsTopWithTitle.swt
dCCButtons_List.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
dCCListHeader.swt
dCCListBodyNoRowHilite.swt
Table 145 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 128.Generic Layout of the DotCom List Merged (Base/Edit) Template
Table 145. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListMerged_B_EL.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer List Templates
390
Links List Template
The DotCom Applet Links template uses the dCCAppletLinks.swt file. It displays a list of links that
include an image and a description. You can use it to create a small table of contents.
Figure 129 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletLinks.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
123 Next
124 Last
125 Info-Button
131 New
132 through 133 Control
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Save
147 Pick Control
501 through 520 List Header
Figure 129.Generic Layout of the DotCom Applet Links Template
Table 145. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletListMerged_B_EL.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 391
Table 146 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Customer View Templates
This topic describes customer view templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Admin View Template on page 391
■ Basic View Template on page 393
■ Detail View Template on page 394
■ Detail View Two Template on page 395
■ Detail, Multiple Child, View Template on page 396
■ 25 50 25, View Template on page 398
■ 25 50 25, Home, View Template on page 399
■ 50 50, View Template on page 401
■ 66 33, View Template on page 402
■ 100 66 33 100, View Template on page 403
Each gray area in the view diagrams in this topic represents an area where you can place one or
more applets. Siebel CRM expands each applet horizontally to fit the column where you assign this
applet. The amount of data that it displays determines the amount of vertical space the applet uses.
Admin View Template
The DotCom View Admin template uses the dCCViewAdmin1.swt file. It displays each subview as a
tab across the top of the view. You can use it to configure an administrative view that must display
nonrelated views that are difficult to categorize.
Table 146. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletLinks.swt File
ID Placeholder
1097 Title
1098 Intro Text
1099 Thematic Image
1100 Text
1101 through 1130 Image or Link (Required) or Description or Text

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer View Templates
392
Figure 130 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCViewAdmin1.swt
dCCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
dCCSubViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 147 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 130.Generic Layout of the DotCom View Admin Template
Table 147. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCViewAdmin1.swt File
ID Placeholder
5 Child Applet With Pointer
6 Child Applet
7 through 9 Grandchild Applet
10 through 12 Grandchild Applet
13 through 15 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 393
Basic View Template
The DotCom View Basic template uses the dCCView_Basic.swt file. It displays applets that use the
full window width. It stacks these applets on top of each other.
Figure 131 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCView_Basic.swt
dCCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
dCCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 148 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 131.Generic Layout of the DotCom View Basic Template
Table 148. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCView_Basic.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet
102 through 111 Applet

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer View Templates
394
Detail View Template
The DotCom View Detail template uses the dCCViewDetail.swt file. It can do the following:
■ Display a parent applet.
■ Display noncontext views as tabs.
■ Display categorized subviews in a drop-down list.
■ Display a child applet.
■ Display multiple grandchild applets.
Figure 132 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCViewDetail.swt
dCCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
dCCViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCSubViewbar_Drop.swt
dCCHTMLFooter.swt
Figure 132.Generic Layout of the DotCom View Detail Template

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 395
Table 149 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Detail View Two Template
The DotCom View Detail2 template uses the dCCViewDetail2.swt file. It displays the same items that
the DotCom View Detail displays. For more information, see “Detail View Template” on page 394.
Figure 133 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCViewDetail2.swt
Table 149. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCViewDetail.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet
3 through 5 Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet
8 through 9 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet
Figure 133.Generic Layout of the DotCom View Detail 2 Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer View Templates
396
dCCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
dCCViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCSubViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 150 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Detail, Multiple Child, View Template
The DotCom View Detail MultiChild template uses the dCCViewDetailMultiChild.swt file. It displays
the same items that the DotCom View Detail displays. For more information, see “Detail View
Template” on page 394.
Table 150. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCViewDetail2.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child Applet
3 Child Applet
4 Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet
8 through 9 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 397
Figure 134 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCViewDetailMultiChild.swt
dCCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
dCCViewbar_Tabs.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
dCCSubViewbar_Drop.swt
dCCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 151 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 134.Generic Layout of the DotCom View Detail MultiChild Template
Table 151. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCViewDetailMultiChild.swt File
ID Placeholder
1 Parent Applet
2 Child
3 through 5 Child or Grandchild Applet
6 through 7 Grandchild Applet

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer View Templates
398
25 50 25, View Template
The DotCom View 25 50 25 template uses the dCCView_25_50_25.swt file. It includes the following
columns:
■ The first column uses 25 percent of the window width.
■ The second column uses 50 percent of the window width.
■ The third column uses 25 percent of the window width.
■ The top region uses the full window width.
Figure 135 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCView_25_50_25.swt
dCCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
8 through 9 Grandchild Applet
201 Mini-Applet
Figure 135.Generic Layout of the DotCom View 25 50 25 Template
Table 151. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCViewDetailMultiChild.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 399
CCThreadbar.swt
dCCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 152 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
25 50 25, Home, View Template
The DotCom View 25 50 25 Home template uses the dCCView_25_50_25_home.swt file. It includes
the following columns:
■ The first column uses 25 percent of the window width.
■ The second column uses 50 percent of the window width.
■ The third column uses 25 percent of the window width.
■ The top region uses the full window width.
Table 152. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCView_25_50_25.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet
102 through 111 Applet
202 through 211 Applet
302 through 311 Applet

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer View Templates
400
Figure 136 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCView_25_50_25_home.swt
dCCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
dCCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 153 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 136.Generic Layout of the DotCom View 25 50 25 Home Template
Table 153. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCView_25_50_25_home.swt File
ID Placeholder
102 through 111 Applet
202 through 211 Applet
302 through 311 Applet

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 401
50 50, View Template
The DotCom View 50 50 template uses the dCCView_50_50.swt file. It includes the following
columns:
■ The first column uses 50 percent of the window width.
■ The second column uses 50 percent of the window width.
Figure 137 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCView_50_50.swt
dCCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
dCCHTMLFooter.swt
Figure 137.Generic Layout of the DotCom View 50 50 Template

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer View Templates
402
Table 154 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
66 33, View Template
The DotCom View 66 33 template uses the dCCView_66_33.swt file. It includes the following
columns:
■ The first column uses 66 percent of the window width.
■ The second column uses 33 percent of the window width.
Figure 138 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCView_66_33.swt
Table 154. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCView_50_50.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet
102 through 111 Applet
202 through 211 Applet
302 through 311 Applet
Figure 138.Generic Layout of the DotCom View 66 33 Template

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer View Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 403
dCCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
dCCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 155 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
100 66 33 100, View Template
The DotCom View 100 66 33 100 template uses the dCCView_100_66_33_100.swt file. It includes
the following columns:
■ The first column uses 66 percent of the window width.
■ The second column uses 33 percent of the window width.
■ Applets in the top or bottom regions use the full window width.
Table 155. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCView_66_33.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet or Layout Controls
102 through 111 Applet
202 through 211 Applet
302 Applet
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer View Templates
404
Figure 139 includes the generic layout that this template uses.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCView_100_66_33_100.swt
dCCHTMLHeader.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
dCCHTMLFooter.swt
Table 156 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 139.Generic Layout of the DotCom View 100 66 33 100 Template
Table 156. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCView_100_66_33_100.swt File
ID Placeholder
101 Salutation Applet
102 through 106 Applet
201 Mini-Applet
202 through 206 Applet
302 through 306 Applet

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer Container Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 405
Customer Container Templates
This topic describes customer container templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Container Template With Frames on page 405
■ Container Template Without Frames on page 406
■ Container Template for Employee and Customer Applications on page 407
Siebel CRM comes predefined with HTML frames enabled and with a set of nonframed templates that
you can use in a customer application.
A Siebel employee application requires frames. You can remove frames only in a customer
application. You use the page container to remove these frames. For information about configuring
a customer application that does not use frames, see Siebel eSales Administration Guide.
Container Template With Frames
The DotCom Page Container (Framed) template uses the dCCPageContainer_Frames.swt file. It
defines the framed container page for a customer application. It defines the banner, screen bar, view
bar, and content frames.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCPageContainer_Frames.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
dCCFrameBanner_Hybrid.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
dCCFrameBanner.swt
dCCFrameViewbar.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
dCCFrameScreenbar_Hybrid.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
dCCScreenbar_Tabs_Hybrid.swt
402 through 406 Applet
502 through 506 Applet
602 through 606 Applet
Table 156. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCView_100_66_33_100.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Customer Container Templates
406
dCCScreenbar_Tabs.swt
CCFrameContent_Logic.swt
CCFrameContent_VSD.swt
CCFrameContent_VST.swt
CCFrameContent_VS.swt
CCFrameContent_VDT.swt
CCFrameContent_VD.swt
CCFrameContent_VT.swt
CCFrameContent_V.swt
Table 157 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Container Template Without Frames
The DotCom Page Container No Frames template uses the dCCPageContainer_NoFrames.swt file. It
defines the nonframed page container.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCPageContainer_NoFrames.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
CCThreadbar.swt
Table 158 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 157. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCPageContainer_Frames.swt File
ID Placeholder
11 through 19 Page Item
50 through 55 Page Item
Table 158. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCPageContainer_NoFrames.swt File
ID Placeholder
11 through 19 Page Item

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Customer Container Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 407
Container Template for Employee and Customer
Applications
The DotCom Page Container (Hybrid) template uses the dCCPageContainer_Hybrid.swt file. It defines
a hybrid frame container. This hybrid can include the functionality that Siebel CRM includes in a
customer application and in an employee application. The banner uses the customer application style
that does not include application menus. The view bar uses the employee application style that
supports the Search Center and the History bar.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCPageContainer_Hybrid.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
dCCFrameBanner_Hybrid.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
dCCFrameBanner.swt
CCFrameViewbar.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
dCCFrameScreenbar_Hybrid.swt
CCStylesChoice.swt
dCCScreenbar_Tabs_Hybrid.swt
dCCScreenbar_Tabs.swt
CCFrameContent_Logic.swt
CCFrameContent_VSD.swt
CCFrameContent_VST.swt
CCFrameContent_VS.swt
CCFrameContent_VDT.swt
CCFrameContent_VD.swt
CCFrameContent_VT.swt
CCFrameContent_V.swt

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Specialized Customer Templates
408
Table 159 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Specialized Customer Templates
This topic describes specialized customer templates. It includes the following topics:
■ Find Template on page 408
■ License, Base, One Column Template on page 409
■ Parametric Search, Head Template on page 410
■ Parametric Search, Tail Template on page 411
■ Real-Time Shopping Cart Template on page 412
■ Advanced Search Template on page 413
■ Advanced Search Template With Tabs on page 413
■ Basic Search Template on page 414
■ Totals Template on page 415
Find Template
The DotCom Applet Find template uses the dCCAppletSearchFind.swt file. It displays the fields that
the user can use in a search.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletSearchFind.swt
dCCFormSearch.swt
Table 159. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCPageContainer_Hybrid.swt File
ID Placeholder
11 through 19 Page Item
21 through 22 Page Item
23 History Label
33 through 34 Control
35 Favorites Label
36 through 38 Control
50 through 55 Page Item

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Specialized Customer Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 409
Table 160 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
License, Base, One Column Template
The DotCom Applet License Base 1 Column template uses the dCCAppletLicenseBase1Col.swt file. It
uses ID 2 to map the applet toggle control.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletLicenseBase1Col.swt
CCApplet_NamedSpacer.swt
dCCTitle_Named.swt
dCCTitle.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
Table 161 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 160. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletSearchFind.swt File
ID Placeholder
91 Inside Applet Help Text
132 Menu
133 New
141 through 142 Control
143 Control
1101 through 1130 Label or Field
Table 161. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletLicenseBase1Col.swt File
ID Placeholder
91 Inside Applet Help Text
132 through 133 Control
141 through 142 Control
157 through 158 Control
1200 through 1201 Label
1400 through 1401 Label

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Specialized Customer Templates
410
Parametric Search, Head Template
The DotCom Applet Parametric Search Head template uses the dCCAppletPSearchHead.swt file. It
displays the fields that the user can use to do a parametric search. A parametric search is a type of
search that includes multiple criteria. For example, finding an opportunity within one of three
territories, with a revenue of more than $35000, and with a lead quality of Very High.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletPSearchHead.swt
CCApplet_Spacer.swt
CCTitle.swt
dCCListButtonsTop.swt
dCCButtons_List.swt
CCRecordNav.swt
CCTogglebar_drop.swt
CCListButtonsTopRight.swt
CCListBodyInverted.swt
Table 162 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 162. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletPSearchHead.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Control
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 111 Control
121 First
122 Previous
123 Next
124 Last
131 New
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Specialized Customer Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 411
Parametric Search, Tail Template
The DotCom Applet Parametric Search Tail template uses the dCCAppletPSearchTail.swt file. It
displays the result list of a parametric search.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletPSearchTail.swt
CCListBodyNoRowHilite.swt
CCBottomApplet.swt
Table 163 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
139 through 141 Control
142 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Control
147 Pick Control
150 through 151 Control
160 through 164 Control
161 through 164 Control
499 Record Title Row
501 through 520 Control
1100 Outside Applet Help Text
1500 Required or Legend
Table 163. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletPSearchTail.swt File
ID Placeholder
142 through 143 Control
144 Selected Row
145 Control
146 Save
Table 162. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletPSearchHead.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Specialized Customer Templates
412
Real-Time Shopping Cart Template
The DotCom Applet Realtime Cart template uses the dCCAppletRealtimeCart.swt file. It displays the
real-time shopping cart applet.
Figure 140 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletRealtimeCart.swt
Table 164 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
147 Pick Control
501 through 540 Field
Figure 140.Example of the Real-Time Shopping Cart Template
Table 164. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletRealtimeCart.swt File
ID Placeholder
132 through 133 Control
133 Control
140 Icon or Mapped Title or Item Name or Quantity or Line Items Label or Line
Items Field: Total Price Label or Total Price Field
141 Control
500 Mapped Title
501 Item Name
502 Quantity
1222 Line Items Label
1223 Total Price Label
1322 Line Items Field
Table 163. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletPSearchTail.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Specialized Customer Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 413
Advanced Search Template
The DotCom Applet Search Advanced template uses the dCCAppletSearchAdvanced.swt file. It
displays the fields that the user can use to do an advanced search.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletSearchAdvanced.swt
dCCFormSearch.swt
Table 165 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Advanced Search Template With Tabs
The DotCom Applet Search Advanced Tabbed template uses the
dCCAppletSearchAdvancedTabbed.swt file. It displays the fields that the user can use to do an
advanced search. It includes tabs.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletSearchAdvancedTabbed.swt
1323 Total Price Field
2222 Label
2223 Label
2322 Field
2323 Field
Table 165. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletSearchAdvanced.swt File
ID Placeholder
91 Inside Applet Help Text
132 Menu
133 New
141 through 142 Control
143 Control
1101 through 1130 Label or Field
1199 Label
Table 164. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletRealtimeCart.swt File
ID Placeholder

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Specialized Customer Templates
414
CCTitle.swt
dCCFormSearch.swt
Table 166 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Basic Search Template
The DotCom Applet Search Basic template uses the dCCAppletSearchBasic.swt file. It displays the
fields that the user can use to do a basic search.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletSearchBasic.swt
dCCFormSearch.swt
Table 167 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Table 166. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletSearchAdvancedTabbed.swt File
ID Placeholder
91 Inside Applet Help Text
132 Menu
133 New
141 through 142 Control
143 Control
1101 through 1130 Label or Field
1199 Label
1500 Required or Legend
Table 167. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletSearchBasic.swt File
ID Placeholder
91 Inside Applet Help Text
132 Menu
133 New
141 through 142 Control
143 Control
1101 through 1130 Label or Field

Siebel Templates for Customer Applications ■ Specialized Customer Templates
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 415
Totals Template
The DotCom Applet Totals template uses the dCCAppletFormTotals.swt file. It is a specialized form
template that creates multiline form totals, and then displays these totals beneath a quote or order.
Figure 141 includes an example of this template.
This template uses the following structure:
dCCAppletFormTotals.swt
dCCFormTotals.swt
dCCButtons_Form.swt
Table 168 lists the items that Siebel CRM can map for this template. For more information, see “About
Mapping IDs to Placeholders” on page 220.
Figure 141.Example of the Form/Totals Applet Template
Table 168. Items Siebel CRM Can Map for the dCCAppletFormTotals.swt File
ID Placeholder
2 Back
106 Query
107 Go (ExecuteQuery)
108 Cancel (Query)
109 through 110 Control
131 New
132 Edit
133 Delete
134 Reset
135 Cancel
136 Save
139 through 143 Control
157 through 158 Control
1112 through 1117 Field or Label

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Siebel Templates for Customer Applications
■ Specialized Customer Templates
416

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 417
10Cascading Style Sheets
This chapter describes cascading style sheets. It includes the following topics:
■ Overview of Cascading Style Sheets on page 417
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets on page 417
Overview of Cascading Style Sheets
This chapter describes the class names of the cascading style sheets that Siebel CRM uses and the
interface elements that they control. You can find the settings for these cascading style sheet
settings in the following files:
■ main.css for employee applications
■ dCCmain.css for customer applications
The class names that these style sheets reference typically include level 1 attributes of the style
sheet. You typically modify the following items:
■ Font characteristics
■ Link characteristics
■ Background colors
Siebel CRM includes cascading style sheets in the following directory of a Siebel installation:
PUBLIC\
lang
\FILES
where:
■ lang is the language code, such as enu.
You can use an HTML editor to modify a cascading style sheet.
For more information about cascading style sheets, see Configuring Siebel Business Applications.
Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
This topic describes elements of cascading style sheets. It includes the following topics:
■ Applet Elements on page 419
■ Banner Elements on page 422
■ Calendar Elements on page 422
■ Control Elements on page 423
■ Customer Application Elements on page 425

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
418
■ Dashboard Elements on page 425
■ Dialog Box Elements on page 426
■ Divider Elements on page 426
■ ePortal Elements on page 426
■ External News Elements on page 429
■ Fonts and Link Color Elements on page 430
■ Form Elements on page 430
■ Login Page Elements on page 431
■ Navigation Elements on page 432
■ Page Header Elements on page 435
■ Rich Text Component Elements on page 436
■ Search Center Elements on page 436
■ SmartScript Player Elements on page 436
■ Status Message Elements on page 437
■ Text Elements on page 437

Cascading Style Sheets ■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 419
Applet Elements
This topic describes applet elements.
Applet Layout Style Elements
Table 169 describes the elements that define applet layout styles.
Applet Highlight Elements
Table 170 describes the elements that define how Siebel CRM highlights an applet that the user
chooses.
Table 169. Elements That Define Applet Layout Styles
Element Description
You can use one of the following
elements:
■ LayoutButtonOn
■ LayoutButtonOff
Defines the background color of layout buttons. You can
use these elements with a transparent GIF file to create
two button states.
You can use one of the following
elements:
■ LayoutView
■ LayoutStyleHide
■ LayoutStyleMax
■ LayoutStyleMin
Defines the color and font characteristics of an applet
that Siebel CRM displays in layout mode.
Table 170. Elements That Define Applet Highlights
Element Description
Selected TD.AppletHIFormBorder Defines the border color of a form applet that Siebel CRM
sets if the user chooses this applet. If a tag uses the
Selected class, and if this tag encloses an applet, then
Siebel CRM highlights the applet border.
Selected TD.AppletHIListBorder Defines the border color of a list applet that Siebel CRM
sets if the user chooses this applet. If a tag uses the
Selected class, and if this tag encloses an applet, then
Siebel CRM highlights the applet border.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
420
Applet Style Elements
Table 171 describes the elements that define applet styles.
List Applet Elements
Table 172 describes the elements that define a list applet.
Table 171. Elements That Define Applet Substyles
Element Description
AppletBlank Defines the background color of the empty space that
Siebel CRM displays in the applet. Siebel CRM uses it to
make sure that the area to the right of the applet tab
displays white and not the background color of the form
or list.
AppletBorder Defines the applet border. This border is the rectangle
that surrounds the form or list, not including tabs or
button bars.
AppletButtons Defines the font and color of elements that Siebel CRM
displays on the button bar.
You can use the following elements:
■ AppletHIFormBorder
■ AppletHIListBorder
Defines the applet highlight color that Siebel CRM
displays if the user chooses this applet. For more
information, see “Applet Highlight Elements” on page 419.
AppletStyle# Defines a number of one through eight. The AppletStyle#
element is the root class for an applet. If you configure
Siebel CRM to switch this root applet style, then it uses
the substyles that are associated with this root style.
AppletBack Defines the background color of the form or list.
AppletTitle Defines the background color, text, and link
characteristics of the applet title. Siebel CRM typically
displays this title in a tab at the top of the applet.
Table 172. Elements That Define a Login Page
Element Description
Header Defines the font and alignment of field column headers.
You can use the following elements:
■ Header
■ listRowEven
■ listRowOdd
Defines the background color of even or odd rows. Siebel
CRM does not use this element in a release template.

Cascading Style Sheets ■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 421
Tree Applet Elements
Table 173 describes the elements that define the styles of a tree applet.
ListBorder Creates a border around a list. If the user chooses an
applet in high interactivity mode, then Siebel CRM uses
this border to highlight this applet.
listRowError Defines the background color of a row that creates an
error. Siebel CRM does not use this element in a release
template.
listRowOff Defines the background color of a dechosen row.
listRowOn Defines the background color of a chosen row in standard
interactivity mode.
You can use the following elements:
■ Row
■ RowCenter
■ RowRight
Defines the background color, text color, and alignment
of field values that Siebel CRM displays in a list row.
Table 173. Elements That Define Tree Applet Styles
Element Description
treeActive Defines the link characteristics for the chosen tree node.
treeBack Defines the background and border characteristics for a
tree applet.
treeInactive Defines the link characteristics for a nonchosen tree
node.
Table 172. Elements That Define a Login Page
Element Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
422
Banner Elements
Table 174 describes the elements that define the banner. Siebel CRM displays it in the topmost
element in the client. It contains global navigation elements and the Oracle logo.
Calendar Elements
This topic describes calendar elements.
Calendar Elements
Table 175 describes the elements that define calendar applets.
Table 174. Elements That Define Banner Elements
Element Description
banner Defines characteristics of the text, line, and background
of the banner area.
You can use the following elements:
■ bannerDiv
■ bannerDiv2
■ bannerDiv3
Defines the color of the bevel that Siebel CRM displays
above and below the banner elements.
Table 175. Elements That Define Calendar Applets
Element Description
calendarActivity Defines the characteristics for a single day activity that
Siebel CRM displays in the Daily, Weekly, or Monthly
calendar.
calendarActivityBack Defines the characteristics for the border that surrounds
a range of activities in the Daily or Weekly calendar.
calendarBorder Defines the external border for the Calendar applet.
calendarBorder2 Defines the border for the Home Page Calendar applet
that includes a different usability.
calendarDay Defines the external characteristics for the header of a
day in the Monthly calendar. This header is one level
above the CalendarDayBar element and the
CalendarDayBarDark element.
calendarDayBar Defines the characteristics for the header of a day in the
Monthly calendar. Siebel CRM uses this element if the day
is not the current view day for the Monthly calendar.

Cascading Style Sheets ■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 423
Service Calendar Elements
Table 176 describes the elements that define the Service Calendar applet.
Control Elements
The following file defines graphical user interface (GUI) controls:
<
SIEBEL_ROOT
>\PUBLIC\
lang
\files\jctrls.css
It includes the following controls:
■ clsJGCTextBox2D
■ clsJGCTextBox3D
■ clsJGCComboBox2D
■ clsJGCComboBox3D
calendarDayBarDark Defines the characteristics for the header of a day in the
Monthly calendar. If the day is the current view day for
the Monthly calendar, then Siebel CRM uses this element
to highlight this day.
calendarInterval Defines the characteristics for an interval for the
following:
■ An hour in the Daily calendar.
■ A day in the Weekly calendar.
■ A week in the Monthly calendar.
calendarMultiDayActivity Defines the characteristics for a multiday activity that
Siebel CRM displays in the Daily, Weekly, or Monthly
calendar.
Table 176. Elements That Define the Service Calendar
Element Description
calendarServiceActivityOff Defines an interval that does not contain an activity. It is
an empty cell.
calendarServiceActivityOn Defines an interval that contains an activity.
calendarServiceBorder Defines a new row in the Service Calendar.
ServiceCalRow Defines the external border for the Service Calendar.
Table 175. Elements That Define Calendar Applets
Element Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
424
■ clsJGCPickList2D
■ clsJGCPickList3D
■ clsJGCTextArea2D
■ clsJGCTextArea3D
■ clsJGCHyperList2D
■ clsJGCHyperList3D
■ clsJGCCheckBox2D
■ clsJGCCheckBox3D
■ clsJGCButton2D
■ clsJGCButton3D
■ clsJGCDropArrow2D
■ clsJGCDropArrow3D
■ clsJGCJTime
■ clsJGCJTimeReadOnly
■ clsJGCJTimeDisabled
■ clsJGCJDateFont
■ clsJGCMain
■ clsJLCMain
■ clsScreenBar
■ clsVisibilityPicker
■ clsDetailCategory
■ clsSubDetailView
■ clsAlphaTab
If you must modify the background color of a subview link, then you can add the following item to
the clsDetailCategory control:
NC-LINK-FRAME-BACKGROUND-COLOR

Cascading Style Sheets ■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 425
Customer Application Elements
Table 177 describes the elements that define customer application elements.
Dashboard Elements
Table 178 describes the elements that define the Dashboard.
Table 177. Elements That Define Customer Application Elements
Element Description
dCCAppletBorder1 Defines the border characteristics that Siebel CRM
displays in a customer applet.
dCCAppletRule1 Defines the size and color that Siebel CRM displays in a
customer applet.
dCCAppletShade1 Defines the background characteristics of a customer
applet that uses a shaded background.
dCCAppletTitle Defines the text, line, and background characteristics of
the applet title that Siebel CRM displays in a customer
applet.
You can use the following elements:
■ dCCItemLabel
■ dCCItemLabelLeft
Defines the text characteristics of product labels that
Siebel CRM displays in a form or list. If the user reads the
language that Siebel CRM displays from right-to-left,
then it reverses the alignments that these classes define.
dCCItemTitle Defines the text characteristics of a product title.
dCCItemValue Defines the text characteristics of each product field
value.
dCCItemValue150 Defines the text characteristics of each product field
value. It sets the field width to 150 pixels.
Table 178. Elements That Define the Dashboard
Element Description
dashbrdBack Defines the background color of the dashboard.
dashbrdBorder Defines the border color and size of the dashboard.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
426
Dialog Box Elements
Table 179 describes the elements that define a dialog box.
Divider Elements
Table 180 describes the elements that define the divider.
ePortal Elements
This topic describes ePortal elements.
Add Info Section Elements
Table 181 describes the elements that define the Add Info section.
Table 179. Elements That Define a Dialog Box
Element Description
You can define the following elements:
■ mvgBack
■ mvgBorder
Defines the background color and border of forms and
lists that Siebel CRM displays in a dialog box.
Table 180. Elements That Define the Divider
Element Description
divider Defines the border for the divider that Siebel CRM
displays between elements on the view bar frame.
Table 181. Elements That Define the Add Info Section
Element Description
AddInfoBullet Defines the style for the bullet in the Additional
information section of the Account/Company Briefing
object.
AddInfoDescr Defines the style of the description text for each link in
the Additional Info section of the Account/Company
Briefing object.

Cascading Style Sheets ■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 427
Company Header Elements
Table 182 describes the elements that define the company header.
Company Search Elements
Table 183 describes the elements that define the company search.
AddInfoHeader Defines the style for each section heading in the
Additional Info section of the Account/Company Briefing
object.
AddInfoWebSite Defines the style for each link in the Additional Info
section of the Account/Company Briefing object.
Table 182. Elements That Define the Company Header
Element Description
CompanyLink Defines the style for the URL of the company home page
that Siebel CRM displays in a company briefing.
CompanyName Defines the style for the company name that Siebel CRM
displays in a company briefing.
Table 183. Elements That Define the Company Search
Element Description
CnsHead Defines the style for the header in the CompanySearch
results screen.
CnsLink Defines the style for the Acct Topic Management link in
the D-U-N-S assignment (ATM) screen.
CnsRow Defines the style for each result line in the
CompanySearch results screen.
Table 181. Elements That Define the Add Info Section
Element Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
428
Profile Data Elements
Table 184 describes the elements that define profile data.
Search Page Elements
Table 185 describes the elements that define the Search Page.
Table 184. Elements That Define Profile Data
Element Description
ProfCopyright Defines the style that Siebel CRM uses for copyright text
in the DNB (Dunn & Bradstreet) profile in the Account/
Company Briefing object.
ProfData Defines the style for each data element in the DNB
profile.
ProfLabel Defines the style for each label in the DNB profile.
ProfSection Defines the style for each section header in the DNB
profile.
Table 185. Elements That Define the Search Page
Element Description
ExSearchField Defines the font and width of fields that Siebel CRM
displays in search pages, such as Web search, map
search, and yellow pages.
ExSearchLabel Defines the style for each row in the Web search, map
search, and yellow pages.
ExSearchTable Defines the style for table in the Web search, map
search, and yellow pages.

Cascading Style Sheets ■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 429
Subsidiary Elements
Table 186 describes the elements that define a subsidiary.
External News Elements
Table 187 describes the elements that define external controls that include news content.
Table 186. Elements That Define a Subsidiary
Element Description
SubsidCompanyName Defines the style for the parent company in the
Corporate Relations section of the Account/Company
Briefing object.
SubsidCompleteList Defines the style for the link that displays the entire
Corporate-Relations section of the Account/Company
Briefing object.
SubsidCopyright Defines the copyright text in the Corporate-Relations
section of the Account/Company Briefing object.
SubsidDisclaimer Defines the disclaimer text in the Corporate-Relations
section of the Account/Company Briefing object.
SubsidSubsidName Defines the style for the child company in the Corporate-
Relations section of the Account/Company Briefing
object.
Table 187. Elements That Define External News
Element Description
NewsBullet Defines the style for the bullets.
NewsColumnLogo Defines the style for the logo.
NewsCompanyName A Defines the style for the company name in the Headlines
section.
NewsHeadline Defines the style for each headline.
NewsPageControl Defines the style for navigation.
NewsSource Defines the style for the string that contains the news
source description.
NewsSummary Defines the style for each summary headline.
NewsTable Defines the style for the table in the Headlines section.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
430
Fonts and Link Color Elements
The following elements define font family and size and default link color:
■ Body
■ TD
■ Input
■ Select
■ Textarea
■ A
Form Elements
This topic describes form elements.
Single Column Form Elements
Table 188 describes the elements that define a single column (sc) form in a customer application
where Siebel CRM displays labels adjacent to fields.
NewsTimeStamp Defines the style for the time stamp in the Headlines
section.
NewsTotalStories Defines the style for the story count.
Table 188. Elements That Define Single Column Forms
Element Description
scField Defines the font characteristics of fields.
scLabel Defines the label font of a label and field pair.
scLabelRight Defines the label font of a label and field pair. If Siebel
CRM uses a language that the reader reads from:
■ Left to right. The class aligns the right side of the
labels. For example, English.
■ Right to left. The class aligns the left side of the
labels. For example, Mandarin.
Table 187. Elements That Define External News
Element Description
Cascading Style Sheets ■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 431
Multicolumn Editable Form Elements
Siebel CRM uses the multicolumn editable (mce) element in an employee application to conserve
space. It displays labels above fields. It displays the same field width for each field. The mce class
names only affect fields that display in standard interactivity mode. If Siebel CRM runs in high
interactivity mode, then the control determines the field size.
Table 189 describes the elements that define a multicolumn editable form.
Login Page Elements
This topic describes the elements that define the usability of the HTML login page that Siebel CRM
displays when the user logs in to the Siebel Web Server from a supported Web browser. They do not
affect the login page if the user logs in through some other context. For example, when starting up
the Mobile Web Client.
Table 190 describes the elements that define the Login Page.
Table 189. Elements That Define Multicolumn Editable Forms
Element Description
mceField Defines the font for a field. It sets the field width to one
of the following:
■ 190 pixels wide in an employee application.
■ 120 pixels wide in a customer application.
mceLabel Defines the label font of the label in a label and field pair.
mceReadOnly Defines the characteristics of disabled text.
mceWideFields Defines the font characteristics for a field that Siebel
CRM maps to a placeholder that spans two or four
columns. The following modes determine sizing:
■ If in standard interactivity mode, then Siebel CRM
sizes the field to fit the width.
■ If an employee application runs in high interactivity
mode, then the control determines the field width.
Table 190. Elements That Define a Login Page
Element Description
loginAppTitle Defines the font and color of the client title.
loginCopy Defines the color of the copyright text.
loginError Defines the color of the error message that Siebel CRM
displays if a login attempt creates an error.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
432
Navigation Elements
This topic describes elements that affect the style of objects that allow the user to navigate Siebel
CRM.
Site Map Elements
Table 191 describes the elements that define the Site Map.
loginField Defines the characteristics of login fields.
You can use the following elements:
■ loginBody
■ loginForm
■ loginText
Defines the text characteristics of the login page.
loginLabel Defines the label characteristics for login fields.
You can use the following elements:
■ loginBtm
■ loginMid
■ loginTop
Defines the background color of the regions in the HTML
login page.
Table 191. Elements That Define the Site Map
Element Description
fader Defines the background of the object that divides sections in the Site
Map.
screenName1 Defines the characteristics of the screen link that Siebel CRM displays
at the top of the Site Map.
screenName2 Defines the characteristics of the screen link that Siebel CRM displays
at the lower portion of the Site Map.
viewName Defines the characteristics of the view link.
Table 190. Elements That Define a Login Page
Element Description

Cascading Style Sheets ■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 433
Table of Contents Elements
Table 192 describes the elements that define the table of contents.
Menu Bar Elements
Table 193 describes the elements that define menu bars.
Navigation Tab Elements
Elements that define navigation tabs in the main.css file determine how Siebel CRM displays the
following items:
■ First-level screen tabs
■ Second-level menu drop-down lists in an applet
■ Third-level detail tabs
You can use the jctrls.jss file to modify how Siebel CRM displays controls. For more information, see
“Control Elements” on page 423.
Table 192. Elements That Define the Table of Contents
Element Description
TOCRule Defines the size and color of the horizontal rule that
Siebel CRM displays adjacent to the title in the table of
contents categorized applet.
TOCTitle Defines the title text that Siebel CRM displays on a page
that uses the categorized applet for the table of contents.
Table 193. Elements That Define Menu Bars
Element Description
globalMenu Defines how Siebel CRM displays page item links that
reference a page container. Siebel CRM typically displays
these links in the banner of a customer application.
Siebel CRM hard-codes the background color of the
menu bar in the jmenubar.js file.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
434
Table 194 describes the elements that define navigation tabs.
Table 194. Elements That Define Navigation Tabs
Element Description
You can define the following elements:
■ tier1Back
■ tier1Rule
■ tier1On
■ tier1Off
Defines the background and link colors for screen tabs.
You can define the following elements:
■ tier2Back
■ tier2Rule
■ tier2On
■ tier2Off
Defines the background and link colors for elements that
Siebel CRM displays in the view bar frame, including the
following items:
■ Second-level drop-down list
■ History drop-down list
■ Dashboard icon
■ Favorites drop-down list
■ Search Center icon
You can define the following elements:
■ tier3Back
■ tier3Rule
■ tier3On
■ tier3Off
Defines the background and link colors for detail tabs.
You can define the following elements:
■ tier4Back
■ tier4Rule
■ tier4On
■ tier4Off
Defines the background and link colors for subview tabs.

Cascading Style Sheets ■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 435
Threadbar Elements
Table 195 describes the elements that define the threadbar.
Minibutton Elements
Table 196 describes the elements that define minibuttons. They define record navigation and other
buttons in applets.
Page Header Elements
Table 197 describes the elements that define page headers.
Table 195. Elements That Define the Threadbar
Element Description
threadbar Defines links in the threadbar that Siebel CRM displays at
the top of a view.
threadbarDiv Defines the separators that Siebel CRM uses between
links.
Table 196. Elements That Define Minibuttons
Element Description
You can use the following elements:
■ minibutton
■ minibuttonOn
■ minibuttonOff
Defines the text, link, and background characteristics for
On and Off states. For more information, see the
documentation in the CCHtmlType.swf file that is located
in the following directory:
SIEBEL_ROOT
\WEBTMPL
Table 197. Elements That Define Navigation Page Headers
Element Description
PageHeader Defines the page title text that Siebel CRM displays on
some customer home pages.
PageRule Defines the size of the horizontal rule that Siebel CRM
displays adjacent to the page header text.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
436
Rich Text Component Elements
Table 198 describes the elements that define a container that uses Rich Text Component (RTC).
Search Center Elements
Table 199 describes the elements that define the Search Center.
SmartScript Player Elements
Table 200 describes the elements that define SmartScript Player applets.
Table 198. Elements That Rich Text Components
Element Description
You can use one of the following
elements:
■ rtcEmbedded
■ rtcPopup
■ rtcReadOnly
■ rtcTextarea
Defines the dimensions and font characteristics for a
container that uses RTC.
Table 199. Elements That Define Search Center
Element Description
SrchCntrTitle Defines the font characteristics of the applet title in the
Search Center. It is slightly larger than a typical applet
title.
Table 200. Elements That Define SmartScript Player
Element Description
smartDialog Defines the font and background characteristics of a
SmartScript form.

Cascading Style Sheets ■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 437
Status Message Elements
Table 201 describes the elements that define status messages. The Communications toolbar can
display lengthy status messages.
Text Elements
Table 202 describes the elements that define various text elements.
Table 201. Elements That Define Status Messages
Element Description
#MsgLayer Defines a region that the Document Object Model can
access. The toolbar can access this element to insert a
text message.
Message Defines the text and background characteristics of the
message.
Table 202. Elements That Define Text Style
Element Description
You can use the following elements:
■ CmdTxt
■ CmdTxtNormal
Defines text characteristics of the outside applet text.
error Defines text characteristics of the error text that Siebel
CRM displays in an error message at the top of a form or
list.
Required Defines the color of required text.
Welcome Defines the text characteristics of the greeting text that
Siebel CRM displays in a salutation applet.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Cascading Style Sheets
■ Elements of Cascading Style Sheets
438

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 439
11Operators and Expressions
This chapter describes operators and expressions. It includes the following topics:
■ Operators on page 439
■ Expressions on page 447
Operators
This topic describes operators. It includes the following topics:
■ Operator Precedence on page 439
■ Comparison Operators on page 440
■ Logical Operators on page 441
■ Arithmetic Operators on page 441
■ LIKE and NOT LIKE Operators on page 441
■ NULL Operator on page 443
■ Using the EXISTS Operators with Multivalue Groups on page 445
Operator Precedence
Precedence is the order that Siebel CRM uses to evaluate the operators that a single expression
contains. It evaluates higher precedence operators before it evaluates lower precedence operators.
It evaluates operators that are equal in precedence from left to right.
You can use parentheses to modify the order of precedence that Siebel CRM uses to evaluate an
expression. It evaluates the expression in the parentheses first, and then evaluates parts of the
expression that reside outside of the parentheses.
Table 203 describes the levels of precedence. A lower level indicate higher precedence. For example,
level 1 possess the highest precedence.
Table 203. Operator Precedence
Level Operator
1 ()
2 - (negation)
3 ^ (exponentiation)

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Operators
440
Comparison Operators
Table 204 describes each comparison operator.
4 The following operators possess this level:
■ * (multiplication)
■ / (division)
5 The following operators possess this level:
■ + (addition)
■ - (subtraction)
■ NOT logical operator
6 AND logical operator.
7 OR logical operator.
8 Comparison operators. The following operators possess this level:
= (equal to)
<> (not equal to)
> (greater than)
< (less than)
>= (greater than or equal to)
<= (less than or equal to)
Table 204. Comparison Operators
Operator Description Example
= Equality test. [Last Name] = "Smith"
<> Inequality test. [Role] <> "End-User"
> Greater than. [Revenue] > 5000
< Less than. [Probability] < .7
>= Greater than or equal to. [Revenue] >= 5000
<= Less than or equal to. [Probability] <= .7
Table 203. Operator Precedence
Level Operator

Operators and Expressions ■ Operators
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 441
Logical Operators
Table 205 describes logical operators.
Arithmetic Operators
Table 206 describes arithmetic operators.
LIKE and NOT LIKE Operators
The LIKE operator matches a portion of one character value to another value. Siebel CRM uses the
following format for a LIKE operator in a character string comparison that uses pattern matching:
char1
LIKE
char2
where:
■ char1 is the value that Siebel CRM compares to the pattern.
■ char2 is the pattern where Siebel CRM compares char1.
To exclude a pattern, you can use the NOT logical operator with the LIKE operator. It uses the
following format:
Table 205. Logical Operators
Operator Returns TRUE Returns FALSE
NOT If Siebel CRM evaluates the condition to
FALSE.
If Siebel CRM evaluates the condition to
TRUE.
AND If Siebel CRM evaluates all component
conditions to TRUE.
If Siebel CRM evaluates any component
condition to FALSE.
OR If Siebel CRM evaluates any component
condition to TRUE.
If Siebel CRM evaluates all component
conditions to FALSE.
Table 206. Arithmetic Operators
Operator Purpose Example
+ Add [Record Number] + 1
- Subtract [Record Number] - 1
- Negate [Revenue] < -100
* Multiply [Subtotal] * 0.0625
/ Divide [Total Items] / [Total Orders]
^ Exponent [Grid Height] ^ 2

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Operators
442
char1
NOT LIKE
char2
or
NOT (
char1
LIKE
char2
)
Each character is case-sensitive.
The NOT operator requires parentheses.
The Search Engine Table property of a view or applet must reference the same table that the index
references. For example, if the search index references the S_EVT_ACT table, then the view and the
applet must reference the Action business component.

Operators and Expressions ■ Operators
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 443
Wildcard Characters You Can Use with the LIKE Operator
Table 207 describes wildcard characters that you can use with the LIKE operator.
NULL Operator
The NULL operator in an SQL statement represents a value that is not known or is not applicable.
Siebel CRM evaluates an expression that includes a NULL operator differently than it evaluates other
operators. NULL is not a value. A comparison function does not operate correctly if a NULL operator
exists in the comparison. For instance, if NULL = NULL is not TRUE. Note the following:
■ SQL and Siebel CRM provide special functions and grammar that support NULL, including the IS
NULL operator and the IfNull function. A comparison, string concatenation, and Boolean
operation include special behavior that handles a NULL operator.
Table 207. Wildcard Characters You Can Use with the LIKE Operator
Character Description
* Replace zero or more characters.
For example:
[Last Name] LIKE "Sm*"
This example returns all records whose last name starts with Sm. For example, Smith,
Smythe, Smart, and so on.
For example:
[Last Name] LIKE "*om*"
This example returns all records whose Last Name field includes om. For example,
Thomas, Thompson, Tomlin, and so on.
Using the * (asterisk) wildcard to find all entries in a field might cause a performance
problem. If it does, then you can use IS NOT NULL instead. For more information, see
“NULL Operator” on page 443.
? Replace one character.
For example:
[First Name] NOT LIKE "Da?"
This example returns all records whose first name is three characters long and does
not start with the letters Da. For example, it returns records that include Ted, Tom,
and Sam. It does not return records that start with Dax or Dan.
For example:
NOT ([First Name] LIKE "?o?")
This example returns all records whose first name is three characters long and does
not include o as the middle character. For example, it returns Ted and Sam. It does
not return Tom or Bob.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Operators
444
■ You can set the type for a NULL operator similar to how you set the type for a value. An operand
or result can be a NULL string, NULL number, NULL Boolean, and so on.
■ If one side of a comparison is:
■ NULL. The comparison returns a NULL of type Boolean.
■ Is not NULL. The comparison returns TRUE or FALSE. For example, 1>2 is FALSE, and
1<NULL is NULL.
■ If one side of an arithmetic operation is NULL, then the operation returns NULL of the appropriate
type, except for a string concatenation. NULL adds no characters during a string concatenation
operation. For example:
■ 1 + 2 is 3
■ 1 + NULL is NULL (of type Integer)
■ "Fred" + ", Smith" is "Fred, Smith"
■ "Fred" + NULL is "Fred"
IS NULL Operator
The IS NULL operator is a unary operator. A unary operation is an operation that includes only one
operand. If you use the IS NULL operator, and if the operand for this operator evaluates to:
■ TRUE. IS NULL evaluates to NULL.
■ FALSE. IS NULL evaluates to not NULL.
You cannot use the = (equal) operator to determine if a value is NULL because a NULL operand does
not contain a value.
IfNull Function
The IfNull function contains two arguments and returns the value of the first or second argument
depending on if the first argument is NULL. IfNull (a,b) returns one of the following values:
■ a if a is not NULL
■ b if a is NULL
Siebel CRM sets the return type of the IfNull function to the type of the first argument that it
contains, even if this first argument is NULL. Siebel CRM converts the second argument to the type
of the first argument before it returns the value of the IfNull function.
Flag Fields and NULL
A flag field is a type of field that Siebel CRM can evaluate to a Boolean value, such as True or False,
or Y or N. You can use a flag field to turn functionality on or off. A flag field is typically but not always
a calculated field.

Operators and Expressions ■ Operators
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 445
If you configure Siebel CRM to query a flag field, then you must use caution. The <> (not equal to)
and NOT IN comparison operators cannot evaluate a field that contains a null value. Siebel CRM sets
the default value of a flag field to null, so a workflow condition of <>'Y' does not work. To avoid this
situation, you can do one of the following:
■ Use IS NOT NULL as a comparison operator.
■ Use IN ('N',NULL).
■ Predefault the business component field to 'N'.
Using the EXISTS Operators with Multivalue Groups
This topic describes how to use the EXISTS operator with multivalue groups.
Using the [NOT] EXISTS Operator with Multivalue Groups
To reference a multivalue group field, you can specify the [NOT] EXISTS operator in a query by
example or in the Search Specification property of an object. Siebel CRM uses a multivalue group
field to display the child records of a parent record in the parent record applet. For example, assume
the following:
■ Opportunities are a separate entity.
■ Contacts are a separate entity.
■ The Opportunity business object references the Opportunity and Contact business components.
■ A many-to-many relationship exists between opportunities and contacts:
■ One or more contacts can modify an opportunity.
■ A contact can modify one and only one opportunity.
■ A form applet displays and manages opportunity information and displays any contact
information that is specific to the opportunity. This applet includes the following fields that
reference the Opportunity business component:
■ Opportunity Name
■ Contact First Name
■ Contact Last Name
This form applet displays the opportunity name in a predefined text box control. Siebel CRM
defines the contact first name as a multivalue group field and the last name as a multivalue group
field instead of as predefined edit controls. If you use query by example on a multivalue field
(MVF), then you must include only multivalue fields that Siebel CRM displays in the originating
business component.
Assume you set the search specification for the opportunity name to the following value:
Wine Festival
In this example, the Opportunity business component returns all opportunities that contain a name
of Wine Festival.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Operators
446
Assume you set the search specification for the contact last name to the following value:
Smith
In this example, the Opportunity business component returns all opportunities that include a contact
with a last name of Smith. This situation occurs because you defined the search specification on the
Opportunity business component and not on the Contact business component.
Examples of Using EXISTS and NOT EXISTS
A query by example that resides in the last name field in the client must use the following format:
EXISTS(Smith)
A predefined query where the Opportunity is the business component must use the following format:
Opportunity.Search = "EXISTS ([Last Name] = ""Smith"")"
A search specification that resides in the Search Specification property of the business component
or applet must use the following format:
EXISTS ([Last Name] = 'Smith')
The following example chooses records according to multiple child and grandchild criteria. It defines
a more complex query and demonstrates that a query can use all the business components involved
in the view without specifying the business component that contains the field:
EXISTS ([ChildField1] = 'X' AND [ChildField2] = 'Y')
EXISTS ([GrandchildField1] = 'A' AND [GrandchildField2] = 'B')
You can add NOT in front of EXISTS to query for everything other than the value that you include
after EXISTS.
Using the EXISTS Operator with a Primary
If a multivalue field includes a primary ID field, and if the Use Primary Join property of the Multi Value
Link that this multivalue field references contains a check mark, and if the search specification:
■ Includes EXISTS. The query results include every record in the multivalue group that matches
the search specification.
■ Does not include EXISTS. The query results include every primary record in the multivalue
group that matches the search specification.
If you do not specify a primary ID field for the multivalue group, or if the Use Primary Join property
does not contain a check mark, then the query must include EXISTS.
If you specify a query that does not use EXISTS, then the object manager automatically inserts
EXISTS as part of the search specification. If the field value for a child record is empty, then the
object manager uses the EXISTS clause to get the parent record. It does not get any parent record
that does not include a child. You can use the following code to query for parent records that do not
include a child:
NOT EXISTS(*)

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 447
To query a multivalue group, Siebel CRM specifies a value for a multivalue group or multivalue field
for the primary value, by default. For example, if you use the following value to query the Account
Team, and if the multivalue group supports a primary, then Siebel CRM returns all records that
contain VSILVER as the primary position on the team:
VSILVER
If a view includes sales team visibility, then you must not use query by example to constrain the
account team. Instead, you can use a view that includes the All visibility filter. For example, assume
you log in as SADMIN, navigate to the My Accounts view, and then query the Account Team with a
login name, such as VSILVER. In this situation, Siebel CRM does not return all accounts where
SADMIN is on the team and VSILVER is the primary.
Expressions
This topic describes expressions you can use in a calculated field. It includes the following topics:
■ Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression on page 448
■ Using the Division Functions on page 458
■ Using the IIf Function on page 460
■ Using Julian Functions on page 460
■ Using the Timestamp Function on page 461
■ Using Functions in the Predefault and Postdefault Properties on page 462
■ Using Expressions In the Calculated Field and Field Validation Properties on page 466
■ Using the Invoke Service Method in a Calculated Field on page 468
■ Using Calculated Fields with Chart Coordinates on page 469
■ How Siebel CRM Handles Data Types During a Calculation on page 470
■ Guidelines for Configuring Calculated Fields on page 471
A calculated expression is a type of expression that includes a calculated field and a validation
expression.
You can use the following functions to set a predefault or postdefault value in a business component.
Siebel VB or COM objects do not support these functions:
■ AccountId
■ ContactLogin
■ JobTitle
■ OrganizationId
You cannot use a custom function in a calculated expression.
You can only use numbers between negative 2147483647 and 2147483648 in a field validation
expression.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
448
For more information, see Siebel VB Language Reference.
Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Table 208 describes the functions that you can use in a calculated expression. The Result column
describes the type of result the function returns. The Query column indicates if Siebel CRM can use
the function in a query.
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description
AccountId String Yes Returns the account ID of the current user.
ContactLoginId String Yes Returns the contact ID of the current user.
If you configure Siebel CRM to not use the contact
login method for a Web application, then this
function cannot get any value and it returns an
empty string. It is recommended that you use a
contact login and an external security authentication
service. For example, LDAP.
Count ("mvlink") Integer No Returns the number of rows in the multivalue group
that the mvlink defines, where mvlink identifies the
name of a multivalue link.
Currency String Yes Returns the currency code for the current position.
For example, USD.
DivisionId Integer Yes Returns the division ID of the current user.
To limit visibility to employees who reside in the
same division as the person who is currently logged
in, you can add the following code to the Search
Specification property of the applet:
[Division Id] = DivisionId()

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 449
DivisionName String Yes Returns the division name of a user who is an
employee. You can use this function to do the
following:
■ Limit visibility to employees who reside in the
same division as the person who is currently
logged in.
■ Display the division name of the user who is
logging the service request.
You can create a new calculated field so that Siebel
CRM displays the division name in the calculated
field. It displays the division name of the user who is
logged in when this user creates a service request.
If you use the configuration that the “Using the
Division Functions” on page 458 topic describes, then
Siebel CRM predefaults the Reported By Division
joined field to this division name, and this field never
receives another value after Siebel CRM creates this
service request.
EXISTS String Yes For example:
IIf(EXISTS([Participant-Employee Login] =
LoginName()), "Y", "N")
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
450
GetProfileAttr
("Attribute")
String Yes Returns the value that Siebel CRM stores in the
profile attribute if this attribute is defined. You can
use this function in personalization to do the
following:
■ Get attribute values in a user profile.
■ Send information from a script to the client.
You can set a personalization attribute for a session
that is equal to the value of the shared global
attribute, and then reference the personalization
attribute in a calculated field.
GetProfileAttr returns NULL for an undefined
attribute or for an attribute that is not configured.
For example:
GetProfileAttr("Attribute") = ""
If the attribute does not exist, or if it exists and if the
value is different than "", then this code returns
FALSE.
For example:
GetProfileAttr("Attribute") IS NULL
If the attribute does not exist, then this code returns
TRUE.
IfNull (expr1, expr2) Type of
expr1
Yes Returns one of the following values:
■ If expr1 is not NULL, then this function returns
the value of expr1.
■ If expr1 is NULL, then this function returns the
value of expr2.
IIf (testExpr, expr1,
expr2)
Type of
expr1
No Returns one of the following values:
■ If testExpr is TRUE, then this function returns
the value of expr1.
■ If testExpr is not TRUE, then this function
returns the value of expr2.
If the expression references a DTYPE_NUMBER field,
then the data type of expr1 determines the data type
of the value that this function returns.
For more information, see “Using the IIf Function” on
page 460.
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 451
InvokeServiceMethod
("ServiceName",
"MethodName",
"InputProp1=val1,
InputProp2=val2, ...",
"OutputProp")
String No For more information, see “Using the Invoke Service
Method in a Calculated Field” on page 468.
JobTitle Integer Yes Returns the Job Title of the employe who is currently
logged in. It is similar to the PositionId and
DivisionId methods.
JulianDay Integer Yes Equal to the Oracle Julian Day for all dates in the
20th and 21st centuries.
JulianMonth Integer Yes Equal to:
JulianYear()* 12 + currentMonth
where:
■ January = 1.
JulianQtr Integer Yes Equal to:
JulianYear() * 4 + currentQuarter
where:
■ currentQuarter = (currentMonth - 1) / 3 + 1
rounded down to the next integer.
JulianWeek Integer Yes Equal to the following, rounded down to the next
integer:
JulianDay()/ 7
JulianYear Integer Yes Equal to the current year plus 4713.
Language String Yes Returns the language code for the language that the
client currently uses. For example, ENU.
One of the following items sets this language:
■ Language parameter in the CFG file
■ /L parameter when starting Siebel CRM.
This setting is not the OM - Resource Language Code
server parameter that the Administration - Server
Configuration screen contains.
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
452
Left (text, integer) String Yes Returns the leftmost n characters in the text string
or field. For example, the following code returns
Adam:
Left ("Adams", 4)
Len String Yes Returns the length of a string or string variable. You
can specify the number of characters between
parentheses.
Locale String Yes Returns the locale code that is associated with the
Application Object Manager (AOM). A locale is a set
of rules that determine how Siebel CRM displays data
to the user or receives data from the user.
Siebel CRM stores locale codes in the LOCALE_CODE
column of the S_LOCALE table. For more
information, see Siebel Global Deployment Guide.
LocalCurrency String Yes Returns the currency code for the client computer.
For example, JPY.
LoginId String Yes Returns the login ID. For example, 0-3241.
LoginName String Yes Returns the login name. For example, BSTEVENS.
Lookup (type, value) String No Returns the value of the ORDER_BY column of a row
in the S_LST_OF_VAL list of values where:
■ The TYPE column matches the type argument.
■ The VALUE column matches the value argument.
You can use this function to avoid creating joins in a
business component.
LookupExpr (type,
value_expr)
String No Returns the value of the ORDER_BY column of the
first row in the S_LST_OF_VAL list of values that the
expression evaluates to TRUE.
To do this, it searches rows in this list of values
where the TYPE column matches the type argument.
It evaluates the contents of the VALUE column as an
expression.
This function does an in-memory linear parse
evaluate search. You must make sure that the LOV
type contains less than 30 rows.
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description
Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 453
LookupName (type,
lang_ind_code)
String Yes Returns the language-independent code that resides
in the NAME column of the S_LST_OF_VAL list of
values where:
■ The TYPE column matches the type argument.
■ The NAME column matches the lang_ind_code
argument.
■ The LANG_ID column matches the language
code of the language that is currently active.
This function gets the untranslated value from this
list of values.
LookupTranslation([field
name])
String No Returns the value of the field in the language that
the client displays.
LookupValue (type,
lang_ind_code)
String No Returns the display value that the VAL column
contains in a row in the S_LST_OF_VAL list of values
where:
■ The TYPE column matches the type argument.
■ The NAME column matches the lang_ind_code
argument.
■ The LANG_ID column matches the language
code of the currently active language.
This method finds the display value for the
lang_ind_code. If it does not find this value, then it
returns the value that lang_ind_code contains.
This function gets the translation of the untranslated
value from this list of values.
Max ([mvfield]) Integer No Returns the maximum value from a field in child
records. You must define the child record that this
function examines as a multivalue field that a
multivalue group contains. This multivalue group is
associated with the business component that
contains the field that this method evaluates.
For example:
Max ([Number of Employees])
This code gets the maximum number of employees
for all locations.
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
454
Min ([mvfield]) Integer No Returns the minimum value from a field in child
records.
You must define the child record that Siebel CRM
examines as a multivalue field that is part of a
multivalue group. The multivalue group is associated
with the business component of the field that Siebel
CRM evaluates.
For example:
Min ([Number of Employees])
This code returns the minimum number of
employees that exist for all locations.
OrganizationId Integer Yes Returns the organization ID of the user who is
currently logged in. It returns this value if Siebel
CRM does not define an organization for the user. For
example, if the user uses a customer application,
then it returns the ID of the Default Organization.
OrganizationName String Yes Returns the organization name of a user who is an
employee.
ParentBCName String Yes Returns the name of the parent business component
of an active link. For example, Opportunity.
ParentFieldValue
(field_name)
String Yes Returns the value of the field_name field that resides
in the parent business component. It returns the
result as a string. If Siebel CRM updates the parent
row, then it does not modify this result. You must
use Link Specification = TRUE to export the parent
business component field.
If a parent business component does not exist, or if
Siebel CRM does not instantiate it, such as in a
script, then this function returns the following error:
No active link
PositionId String Yes Returns the position ID of the user who is currently
logged in as an employee. For example, 0-4432.
PositionName String Yes Returns the position name of the user who is
currently logged in as an employee.
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 455
Preference ("category",
"pref_name")
String Yes Returns the value for a category and preference
name. For example, the Price List field in the Service
Agreement business component contains the
following predefault value:
Expr: "Preference (""Quote"",
""PriceList"")"
This example returns the price list that Siebel CRM
uses for a quote that the Price List Sales
Methodology view of the User Preferences screen
specifies. This view resides in the client.
Right (text, integer) String Yes Returns the rightmost n characters in the text string
or field. For example, the following code returns
dams.
Right ("Adams", 4)
RowIdToRowIdNum
([Id])
String Yes Converts an alphanumeric row ID to a unique,
numeric row ID in the Service Request business
component.
Sum ([mvfield]) Integer No Sums the values from a field in child records into a
field in a parent record. You must define this child
record as a multivalue field that is part of a
multivalue group. This multivalue group is
associated with the business component that
contains the field in the parent record.
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
456
SystemPreference
("Preference")
String Yes Returns the value of a system preference. For
example:
SystemPreference("Training: Employee
Calendar")
This code returns TRUE for an employee.
You can use this function to set a predefault or
postdefault value. For example, the following code
sets a predefault value:
Expr: 'SystemPreference("Default Time
Zone")'
You can set these values in the following ways:
■ In the client. Use the System Preferences view
of the Administration - Application screen.
■ In Siebel Tools. Click the Screens menu,
System Administration, and then click System
Preferences.
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 457
ToChar ([field_name],
'format')
String No Returns a string that represents a number or date in
a format that the optional format argument
specifies. For example:
ToChar([Start Date], '
MM
/
DD
/
YYYY
')
This code returns the starting date of a record as a
string that uses the following format:
MM
/
DD
/
YYYY
The following examples describe the difference
between using # and 0 for a number that does or
does not include decimal places. The # symbol only
returns decimal places if they exist. The 0 symbol
adds decimal places if the number contains fewer
decimals than the format argument specifies:
■ ToChar (10, '##.##') returns 10
■ ToChar (10, '##.00') returns 10.00
■ ToChar (10.2345, '##.00') returns 10.23
■ ToChar (10.2345, '##.##') returns 10.23
If you do not specify the format argument, then the
ToChar function returns a string that it formats
according to the current locale. For example, if the
current locale is ESN, then ToChar formats the string
according to the ESN locale.
Timestamp Date
Time
or
UTC
Date
Time
Yes For more information, see “Using the Timestamp
Function” on page 461.
Today Date Yes Returns the date for today. For example, 1/26/2012.
The Today function and the Timestamp function
functions might return different results. For more
information, see “Using the Timestamp Function” on
page 461.
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
458
Using the Division Functions
This topic includes examples that use the division functions.
Using the Division Name Function to Display the Division Name
This example describes how to create a calculated field that displays the division name of the user
who is currently logged in. If this user creates a service request, then Siebel CRM displays this field.
UtcConvert
("utc_date_time",
"time_zone")
Date
Time
Yes This function converts UTC time to local time in the
time zone that the time_zone argument specifies.
For example:
UtcConvert("12/14/2012 5:07:05 PM",
"Eastern Standard Time")
This code returns the following value:
12/14/2012 12:07:05 PM
UtcOffset
("utc_date_time",
"time_zone")
Integer Yes Returns the UTC offset in minutes for a date and
time in the time zone that the time_zone argument
specifies. It returns one of the following values:
■ Positive value. Indicates the number of
minutes ahead of UTC.
■ Negative value. Indicates the number of
minutes behind UTC.
For example:
UtcOffset("3/30/2012 14:00:00", "Pacific
Standard Time")
This code returns the following value because 3/30/
2012 14:00:00 occurs 7 hours behind UTC:
-420
For example:
UtcOffset("3/30/2012 14:00:00", "India
Standard Time")
This code returns the following value because the
time occurs 5.5 hours ahead of UTC:
330
Table 208. Functions You Can Use in a Calculated Expression
Function Result Query Description

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 459
To use the DivisionName function to display the division name
1
In Siebel Tools, in the Object Explorer, click Business Component.
2 In the Business Components list, locate the Service Request business component.
3 In the Object Explorer, expand the Business Component tree, and then click Field.
4 In the Fields list, create a new field using values from the following table.
5 In the Fields list, create another new field using values from the following table.
6 Display the field you created in Step 5 in the relevant applets.
Searching or Sorting According to the Division
You can use the DivisionId function and DivisionName function in a search specification, sort
specification, or calculated value. For example, assume Siebel CRM must display only the employees
who reside in the same division as the person who is currently logged in. To configure this
requirement, you can add the following DivisionId function to the Search Specification property of
an applet:
"DivisionId() = [Division Id]"
These functions are not available in a script. To get the division ID or division name in a script, you
must use the GetFieldValue business component method. For example, you can use the following
code in a Siebel eScript script to get the division ID:
var oEmpl = TheApplication().GetBusObject("Employee");
Property Value
Calculated TRUE
Calculated Value DivisionName()
Name Division (Calc)
Parent Name Service Request
Type DTYPE_TEXT
Property Value
Column ATTRIB_03
Join S_SRV_REQ_X
Name Reported By Division
Pre Default Value Field: 'Division Name'
Read Only TRUE

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
460
var bcEmp = oEmpl.GetBusComp("Employee");
bcEmp.ActivateField("Division Id");
bcEmp.ActivateField("Login Id");
bcEmp.SetSearchSpec("Login Id", TheApplication().LoginId());
bcEmp.ExecuteQuery(ForwardOnly);
bcEmp.FirstRecord;
var divId = bcEmp.GetFieldValue("Division Id");
Using the IIf Function
This topic describes using the IIf Function with string concatenation. The following example assigns
an expression to the Calculated Value property:
[Field]
Name = "Full Name"
TextLen = 102 // Last Name + First Name + 2
Calculated = "TRUE"
CalculatedValue = "[Last Name] + "," + [First Name]"
Double quotation marks must enclose the "," string constant because double quotation marks
enclose the entire value. If the Last Name field contains NULL, and if the First Name contains Bob,
then the Full Name field contains the following value:
, Bob
Consider the following example:
CalculatedValue = "[Last Name] + IIf ([Last Name] IS NULL,
"", ",") + [First Name]"
If the Last Name field contains NULL, and if the First Name field contains Bob, then the result
contains the following value:
Bob
The CalculatedValue expression must reside on one line.
Using Julian Functions
The Julian functions must include the Today function or a field name as an argument. For example:
JulianMonth([Created]) (of a field) or JulianMonth(Today()) (of the current date).
The following example includes the JulianMonth function in a predefined query to get the
opportunities that Siebel CRM closed during the previous month:
'Opportunity'.Search = "JulianMonth([Close Date]) = JulianMonth(Today()) - 1"
The following example returns all service requests that include a commit time that occurs two days
in the future:
'Service Request'.Search = "JulianDay([Commit Time]) = JulianDay(Today()) + 2"

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 461
The following example sets a variable to the integer value of the current month:
currentMonth = JulianMonth(Today()) - JulianYear(Today()) * 12
Using the Timestamp Function
The Timestamp function returns the date and time for today. For example:
01/02/2012 11:15:22
You can use this function in a query. For example:
Created >= Timestamp() - 0.1
This code returns records that Siebel CRM created in the last one-tenth of a day.
Any expression that uses the TimeStamp function uses the date and time from the user computer
even if the Siebel Server computer uses a different time zone.
The Today function and the Timestamp function might return different results. The TimeStamp
function does UTC (universal time code) conversion. The Today function does not do UTC conversion.
Configuring Siebel CRM to Do Calculations with the Timestamp
Function
Use the Timestamp function for fields of type DTYPE_DATETIME and DTYPE_UTCDATETIME. If you
configure Siebel CRM to do a calculation that involves seconds, then it is recommended that you use
at least five significant figures for accuracy.
You can configure Siebel CRM to do calculations with a date and time field in a calculated field. If the
user enters a number in a date and time field, then:
■ Integers and hours represent days.
■ Fractions represent minutes and seconds.
For example, to add one minute to the current date and time, you can use the following expression,
where one day contains 1440 minutes:
Timestamp() + 1/1440
In this example, Siebel CRM adds the product delivery interval, in seconds, to the current date and
time:
Timestamp() + [Product Delivery Interval]/86400
You must set the Type property of the calculated field to DTYPE_DATETIME or DTYPE_UTCDATETIME.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
462
Using Functions in the Predefault and Postdefault
Properties
The Pre Default Value property of a field assigns a value to this field for a new record. If Siebel CRM
displays this field, and if it is not set to Read Only, then the user can modify this field. For example,
the Currency Code field contains the following predefault value:
System: Currency
Siebel CRM sets the currency code for a new contact to the default system currency.
If you set the predefault value for a date and time field, then you must not use quotes to enclose
the value. For example, assume you use the following predefault value for a DTYPE_UTCDATETIME
field:
"07/31/2007 23:59:59"
This configuration results in an error message that is similar to the following:
The value "'07/31/2007 23:59:59'" cannot be converted to a date time value.(SBL-DAT-
00359)
The Post Default Value property of a field assigns a value to a field before Siebel CRM writes the
record to the database. For example, the Personal Contact field contains a postdefault value of N. If
the user does not designate a new contact as personal, then Siebel CRM assumes that it is not a
personal contact.
If the Type property of a field contains any of the following values, then this field is a date and time
field:
■ DTYPE_DATE
■ DTYPE_DATETIME
■ DTYPE_TIME
■ DTYPE_UTCDATETIME

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 463
Table 209 describes the format that Siebel CRM uses in a function that references a predefault or
postdefault field.
Table 209. Format That Siebel CRM Uses in Functions That Reference Predefault or Postdefault Fields
Function
Result
Type
Description
Expr: 'Timestamp()' Date
Time
or
UTC Date
Time
Returns the date and time. This expression is equivalent
to the Timestamp function that returns the current date
and time. It returns the same value as System:
Timestamp. For example:
Expr: 'Timestamp()' + 0.041667
This code returns the current date and time plus one
hour.
For more information, see “Using the Timestamp
Function” on page 461.
Expr: 'Today()' Date Returns the day. This expression is equivalent to the
Today function. It returns the current date. It returns the
same value as System: Today. For example:
Expr: 'Today() - 1'
This code returns the date for yesterday.
You can use the Today function only with a DTYPE_DATE
field. If you use it with a DTYPE_DATETIME or
DTYPE_UTCDATETIME field, then Siebel appends the
following value to the current date:
12:00:00 AM
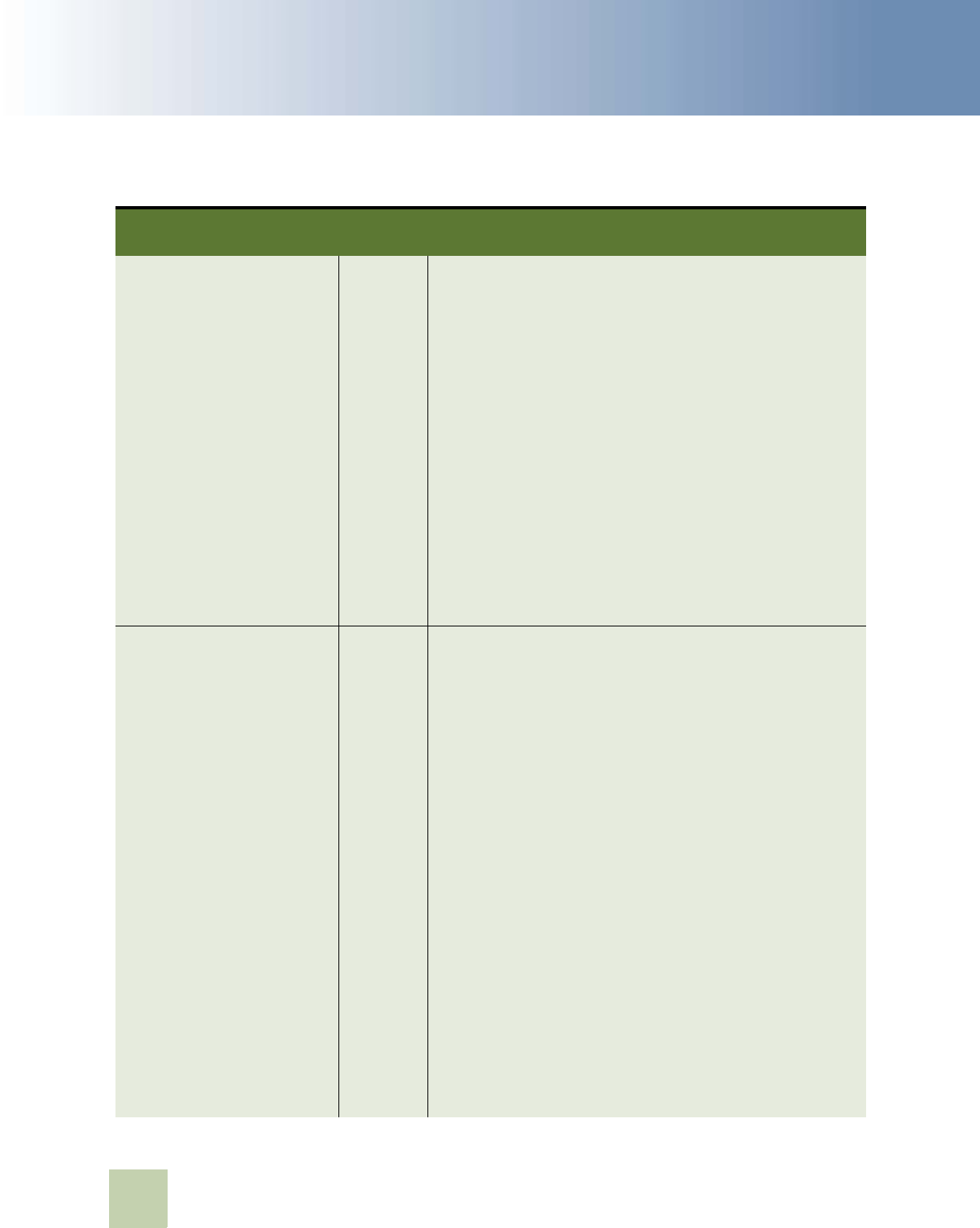
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
464
Field: 'FieldName' String Returns a value that the FieldName field of the current
business component contains.
If FieldName is a joined field, then Field: 'FieldName'
does not work in the Predefault Value property.
You must make sure the field that Siebel CRM defaults
and the referenced field are the same field type. For
example:
■ If the defaulted field is a DTYPE_DATE field, and if
the referenced field is a DTYPE_DATETIME field or a
DTYPE_UTCDATETIME field, then Siebel CRM does
not include time in the defaulted field.
■ If the defaulted field is a DTYPE_DATETIME field or a
DTYPE_UTCDATETIME field, and if the referenced
field is a DTYPE_DATE field, then Siebel CRM
appends the following string to the defaulted field:
12:00:00 AM
Parent: 'BusComp.Field',
'BusComp.Field'
String Returns the value that a field in the parent business
component contains.
To default a value, the Link Specification property of the
field in the parent business component must be set to
TRUE.
You can include multiple BusComp.Field arguments
where a comma separates each argument. Siebel CRM
examines these arguments from first to last until it finds
a value. For example:
Parent: 'ServiceRequest.Account',
'Account.Name'
You must include a space after each comma that
separates a field. If the business component name
includes an apostrophe, then you must enclose the name
with double quotation marks. For example:
Parent: "FINS AG Agent's Contracts.Status Of
Contract"
You can use a System call to terminate a chain of parent
calls. For example:
Parent: 'Opportunity.Currency Code',
'Account.Currency Code', System: Currency
Table 209. Format That Siebel CRM Uses in Functions That Reference Predefault or Postdefault Fields
Function
Result
Type
Description
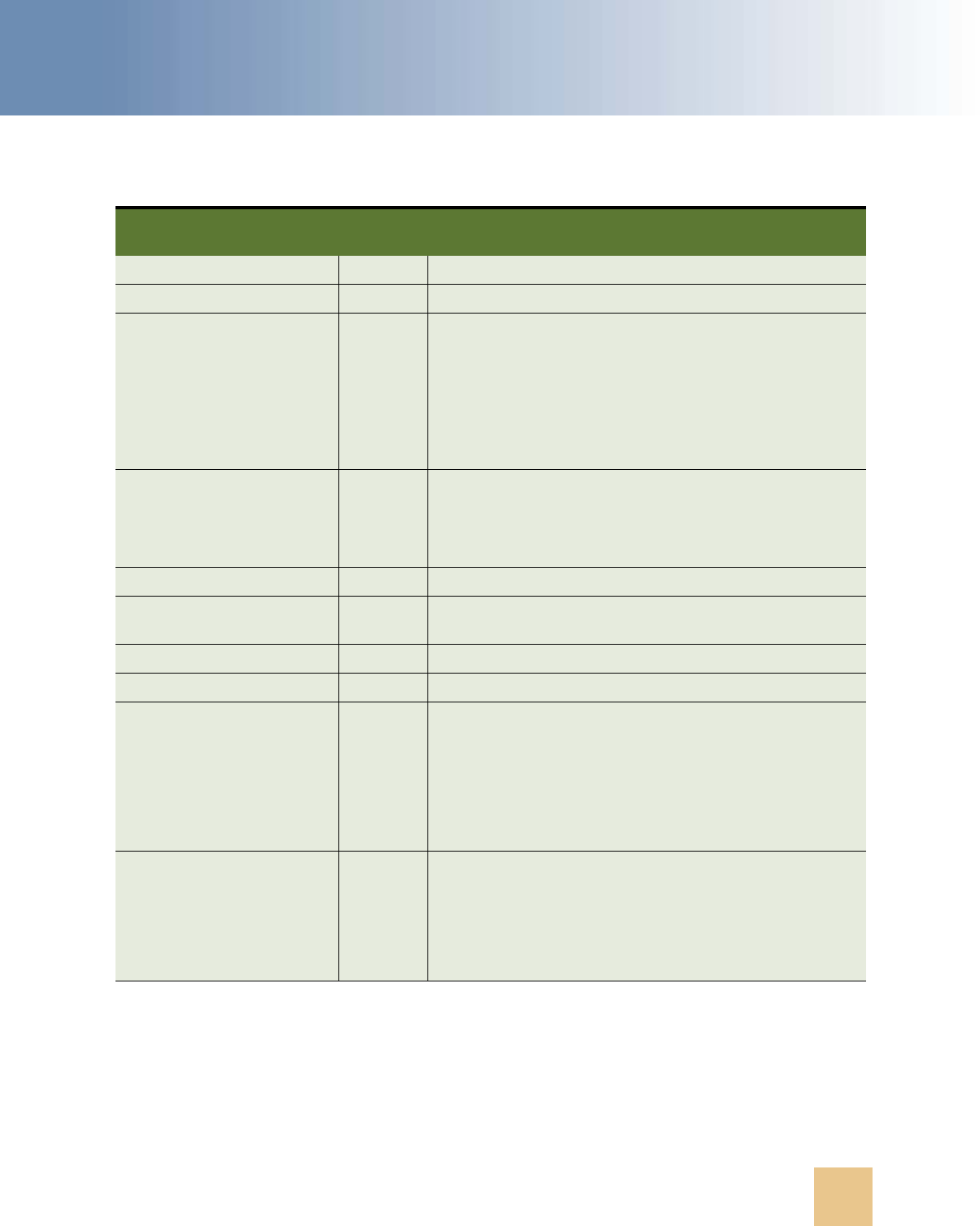
Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 465
System: Creator String Returns the login name. For example, BSTEVENS.
System: CreatorId String Returns the login ID. For example, 0-3241.
System: Currency String Returns the currency for this position. For example,
USD. The Currency field in the Divisions or Organizations
view of the Group Administration screen sets this
currency.
If the division uses a currency that is different than the
currency that the organization uses, then Siebel CRM
uses the division currency.
System: LocalCurrency String Returns the currency that the client computer uses. For
example, JPY.
This function is not available for a client that runs in
standard interactivity mode.
System: OrganizationId String Returns the organization ID. For example, 1-24E1.
System: OrganizationName String Returns the organization name. For example, Siebel
Service.
System: Position String Returns the position name. For example, VP of Sales.
System: PositionId String Returns the position ID. For example, 0-4432.
System: Timestamp Date
Time or
UTC Date
Time
Returns the date and time for today. For example:
04/02/12 11:15:22
If you use the System: Timestamp function as the
predefault value for a field, then the data type for this
field must be DTYPE_DATETIME or
DTYPE_UTCDATETIME.
System: Today Date Returns the date for today. For example:
04/26/12
If you use the System: Today function as the predefault
value for a field, then the data type for this field must be
DTYPE_DATE.
Table 209. Format That Siebel CRM Uses in Functions That Reference Predefault or Postdefault Fields
Function
Result
Type
Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
466
Using Expressions In the Calculated Field and Field
Validation Properties
The Calculated Value property of a field specifies an expression that Siebel CRM uses to calculate the
value of a field. The Validation property restricts the values for a single value field. Siebel CRM
evaluates the Validation property only if the user modifies the value in this field in the client. It
evaluates the Validation property of the business component fields that the current applet
references. If these fields are part of other business components, then Siebel CRM also validates
these fields.
Note the following:
■ The entire expression for the calculated value or validation must reside on one line.
■ The Calculated Value property and the Validation property can contain no more than 255
characters.
■ To reference a field value, you must use [Field Name].
■ You cannot use the Validation property to make the field required if this property references
another field value.
■ Siebel CRM cannot validate a multivalue field.
Elements You Can Use in Calculated Fields and Query By Example
Table 210 describes the elements that you can use in the Calculated Value property, Validation
property, or in a query by example expression.
Table 210. Elements You Can Use in Calculated Fields and Query By Example
Element Description
Calculated value or
validation statement
You can use the following statements:
■ condition
■ expression
Condition You can use the following conditions:
■ comparison
■ AND
■ NOT
■ OR

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 467
Comparison You can use the following comparisons:
■ = (equal to)
■ < (less than)
■ > (greater than)
■ <= (less than or equal to)
■ >= (greater than or equal to)
■ ~ (tilde. Case-insensitive string comparison in the Calculated
Value property.)
■ NOT (not equal to)
■ [~] LIKE (Case-insensitive string comparison)
Expression You can use the following expressions:
■ constant
■ identifier
■ function
Table 210. Elements You Can Use in Calculated Fields and Query By Example
Element Description

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
468
Searching with Query By Example
You can configure Siebel CRM to use query by example (QBE) through list columns or controls as a
predefined query or in the Search Specification property. The format is slightly different in the client
but in all situations the format is simple BNF (Backus-Naur Format).
Using the Invoke Service Method in a Calculated Field
The InvokeServiceMethod method calls a business service from a calculated field and returns
OutputProp. If you configure Siebel CRM to call this method, then it is recommended that you use
the following guidelines:
Constant You can use the following constants for the Calculated Value
property, the Validation property, and query by example:
■ number.
■ string. You must enclose this string in double quotes.
■ date. You must enclose this date in double quotes and you must
use a forward slash (/) for the separator:
"
MM
/
DD
/
YYYY
"
■ time. You must enclose this time in double quotes and you must
use a colon (:) for the separator:
"
HH
:
MM
:
SS
"
■ date and time. You must enclose this date and time in double
quotes and you must use a space to separate the date from the
time:
"
MM
/
DD
/
YYYY
HH
:
MM
:
SS
"
To reference a date and time format in a control or list column, you
must use the format that the Control Panel specifies.
You can use the following constants only for the Calculated Value
property, the Validation property, but not query by example:
■ integer.
■ currency.
■ Boolean.
■ phone number. You must enclose this phone number in double
quotes.
Identifier [field name]
Table 210. Elements You Can Use in Calculated Fields and Query By Example
Element Description

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 469
■ This method requires an input argument in the third field. If you do not specify this argument,
then the calculated field does not provide a return value and a parsing error results. If the
business service method does not require an input argument, then you must provide an
argument as a placeholder. For example, if MyMethod does not use an input argument, then you
can use code that is similar to the following:
InvokeServiceMethod("MyService","MyMethod",
"a=a","MyReturn")
■ If you configure Siebel CRM to send a field value instead of a string literal as an input argument,
then you must enclose the field name in brackets. The following example uses input arguments
that specify the value in the Name and Location fields:
InvokeServiceMethod("MyService","MyMethod",
"prop1=eval([Name]),prop2=eval([Location])","MyReturn")
Siebel CRM evaluates the following code before it calls the business service:
eval(
expression
)
■ The name of the return property in the calculated field, such as MyReturn in these examples,
must match the name of a property in the output property set of the business service. If Siebel
CRM cannot call the method due to this incorrect format, then it does not create an error and the
calculated field is empty.
You must not display a calculation expression that calls a business service in a list applet. Doing so
might result in poor performance because Siebel CRM repeatedly instantiates the business service
each time it displays the field in the list.
Using Calculated Fields with Chart Coordinates
This example uses calculated fields with chart coordinates. Assume you must set the following
coordinates:
■ 0-200
■ 200-999
■ 1000-4999
■ 5000-24999
■ 25000+
To use calculated fields with chart coordinates
1
Create a calculated field that contains the one relevant value of the five coordinate values.
For example, if the record contains a value of 500, then the calculated field value is 200-999.
2 To view the coordinates in the chart in the order you require, create a list of values that contains
the following values:
■ 0-200

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
470
■ 200-999
■ 1000-4999
■ 5000-24999
■ 25000+
How Siebel CRM Handles Data Types During a
Calculation
The Type property of a field specifies the data type. A multivalue field gets the data type from the
source field. Siebel CRM can convert some types to another type during a calculation. Some
operations might create different results with different types. For example, "10" + "10" creates
"1010", while 10 + 10 creates 20.
An item that occurs first in a calculation possesses a higher precedent. For example, "10" + 10
creates the following result. Siebel CRM converts the argument that is to the right of the operator to
a string:
"1010"
For example, 10 + "10" creates the following result. Siebel CRM converts the argument that is to the
right of the operator to a number:
20
The Type property of a field can contain one of the following values. The user cannot query a
DTYPE_NOTE field:
■ DTYPE_BOOL
■ DTYPE_CURRENCY
■ DTYPE_DATE
■ DTYPE_DATETIME
■ DTYPE_ID
■ DTYPE_INTEGER
■ DTYPE_NOTE
■ DTYPE_NUMBER
■ DTYPE_PHONE
■ DTYPE_TEXT
■ DTYPE_TIME
■ DTYPE_UTCDATETIME

Operators and Expressions ■ Expressions
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 471
How Data Type Affects Order of Precedence
If the Calculated Value property references more than one field value, and if these fields use different
data types, then the order of the data types can affect the calculation. For example, the Quote Item
business component includes the Line Total calculated field. This field uses the following calculated
value:
[Item Price] * [Quantity]
where:
■ The data type of the Item Price field is DTYPE_INTEGER.
■ The data type of the Quantity field and the Line Total field is DTYPE_CURRENCY.
In this example, if Item Price is 2.25, and if Quantity is 5, then Siebel CRM sets the Line Total to
11.25.
Assume you modify the calculated value of the Line Total field to the following:
[Quantity] * [Item Price]
In this example, if Item Price is 2.25, and if Quantity is 5, then Siebel CRM sets the Line Total to
11.00.
Guidelines for Configuring Calculated Fields
If you configure a calculated field, then use the following guidelines:
■ You must not use a calculated field to do an update. A calculated field does not support an update
for even a simple expression, such as [Field]). The exception is that a specialized business
component can override SqlSetFieldValue. For important caution information, see “Using
Specialized Classes” on page 28.
■ If the calculated value of a calculated field is not a DTYPE_TEXT value, then you must explicitly
specify the field type.
■ You must not configure Siebel CRM to store a calculated field in a column.
■ You must not create validation criteria on a calculated field. Siebel CRM ignores this criteria.
■ Siebel CRM supports a query on a calculated field. The work that Siebel CRM performs if it does
a query on a calculated field depends on the functions that it uses in the calculation. If Siebel
CRM:
■ Can use the function directly in the WHERE clause in the SQL statement, then it uses the
function.
■ Cannot use the function directly in the WHERE clause, then Siebel CRM must examine each
record in the business component to identify the records that it displays to the user. This
configuration impacts performance. The IIf function and Lookup function are examples of
functions that Siebel CRM cannot use in the WHERE clause.
■ You must not configure Siebel CRM to sort calculated fields.

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Operators and Expressions
■ Expressions
472
■ You can configure Oracle’s Siebel CRM so that a calculated field references the results of another
calculated field in the same business component.
■ To place a link in a calculated field, you can use the following HTML tag:
<a href= …></a>

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 473
Index
Symbols
* (asterisk), using in pattern matching 443
? (question), using in pattern matching 443
A
Admin NoUpdate user property 134
applet classes
about 21
CSSFrame and CSSSWEFrame 21
CSSFrameBase and CSSSWEFrameBase 22
CSSFrameList and CSSSWEFrameList 23
CSSFrameListBase and
CSSSWEFrameListBase 23
CSSFrameListDocGen and
CSSSWEFrameListDocGen 23
CSSFrameListFile and
CSSSWEFrameListFile 23
CSSFrameListWeb and
CSSSWEFrameListWeb 24
CSSFrameSalutation and
CSSSWEFrameSalutation 24
CSSSWEFrameContactOrgChart 24
CSSSWEFrameFINApplication and
CSSSWEFrameListFINApplication 25
CSSSWEFrameUserRegistration 25
applet layout
grid form 222
non-grid form 222
applet select, cascading style sheets 419
applet style, cascading style sheets 420
applet templates
Advanced Search 278
Applet Calendar Daily (Portal) 257
Applet Chart 263
Applet Dashboard 321
Applet Email Response - Inbound 322, 324
Applet Find 279
Applet Form 1-Col (Base/Edit/New) 227
Applet Form 4 Column (Base) 231
Applet Form 4 Column (Edit/New) 234
Applet Form 4-Col (No Record Nav) 236
Applet Form Grid Layout 239
Applet Items Displayed 320
Applet List (Base/Edit List) 241
Applet List Edit (Edit/New/Query) 227
Applet List Inverted 243
Applet List Message 245
Applet List Portal 248
Applet List Portal (Graphical) 250
Applet List Search Results 285
Applet List Totals (Base/Edit List) 253
Applet Salutation 326
Applet Salutation (Graphical) 326
Applet Screen Links 327
Applet Send Mail 329
Applet Tree 2 287
Applet Tree Marketing 289
Applet Wizard 333
DotCom Applet Find 408
DotCom Applet Form 1-Column 340
DotCom Applet Form 2-Column 342
DotCom Applet Form 4-Column 344
DotCom Applet Form Item Detail 347
DotCom Applet Form Search Top 349
DotCom Applet Form Title 349
DotCom Applet License Base 1 Column 409
DotCom Applet Links 390
DotCom Applet List Brief Bullet 353
DotCom Applet List Brief Bullet / Shade 357
DotCom Applet List Brief Bullet/Border 355
DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet 358
DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet /
Border 362
DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet /
Shade 365
DotCom Applet List Brief ImgBullet 2 360
DotCom Applet List Categorized (No
Tab) 364
DotCom Applet List Categorized Bullet 366
DotCom Applet List Categorized Bullet /
Tabbed 368
DotCom Applet List Categorized Tabbed 363
DotCom Applet List Categorized TOC
template 369
DotCom Applet List Detailed ImgBullet 370
DotCom Applet List Detailed ImgBullet
RecNav 372
DotCom Applet List Detailed ImgBullet
RecNav2 template 374
DotCom Applet List Horizontal 377
DotCom Applet List Light 381
DotCom Applet List Search Results 383
DotCom Applet List Subcategory 385
DotCom Applet List Subcategory 1 Per

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Index
■ B
474
Row 385
DotCom Applet List Subcategory 4-Per-
Column 386
DotCom Applet List Subcategory 6-Per-
Column 387
DotCom Applet List Subcategory
Indented 388
DotCom Applet List Tabbed 379
DotCom Applet Parametric Search Head 410
DotCom Applet Parametric Search Tail 411
DotCom Applet Realtime Cart 412
DotCom Applet Search Advanced 413
DotCom Applet Search Advanced
Tabbed 413
DotCom Applet Search Basic 414
DotCom Applet Totals 415
Dotcom Form 4-Col Merged (Base/Edit/
New) 350
DotCom List Merged (Base/EditList) 389
DotCom Page Container (Framed) 405
DotCom Page Container (Hybrid) 407
DotCom Page Container No Frames 406
eActivityGanttChart Applet 266
eCalendar Daily Applet 255
eCalendar Monthly Applet 260
eCalendar Weekly Applet 259
eGantt Chart Applet 265
eGanttChart Applet (Portal) 266
Error Page 334
Form/Totals 415
guidelines for using 219
Page Container 268
Popup Form Grid Layout 272
Popup List 273
Popup Query 276
Save Search 280
Search Applet 277
Search Preference 281
Search Results 283
Service Calendar Applet 262
Site Map 331
Smart Script Player Applet (Player Only) 335
Smart Script Player Applet (Tree Only) 336
Spell Checker Popup Applet 275
applets
Drilldown Visibility user property 82
HighInteractivityEnabled user property 76
page container templates 267
simple search applet, UI element
described 338
specialized applet templates 319, 408
view template descriptions 292
visual reference 221, 339
WebGotoPlayerErrorPage user property 85
Application Name user property 168
application-level menus, defined 220
Aspect user properties
Aspect (CSSBCBase) 168, 169
Aspect (CSSSWEFrameBase and
CSSSWEFrameListBase) 169
Assignment Object user property 120
AssocFieldName [Field Name] user
property 98
Associate: Completion Timeout (Client) user
property 114
Associate: Sleep Time Between Attempts
user property 114
Association user property 97
asterisk (*) character, using in pattern
matching 443
AutoPopulateResponsibility user
property 118
B
Backus-Naur Format (BNF), query by
example syntax 468
banner definitions, cascading style
sheets 422
banner, UI element, described 338
BAPIAdapterService user property 86
BatchSize user property 87
BNF (Backus-Naur Format), query by
example syntax 468
branding area, UI element defined 220
business component classes 28
See also generalized business component
classes, specialized business
component classes
business components
Aspect (CSSBCBase) user properties 168,
169
Aspect (CSSSWEFrameBase and
CSSSWEFrameListBase) user
properties 169
Associate: Completion Timeout (Client) user
property 114
Associate: Sleep Time Between Attempts user
property 114
CloseOutFlag user property 119
Copy Contact user property 113
Credit Card user properties 167
Credit Check user property 166
Credit Check Workflow user property 166
Day Number: Arrival Date Field user
property 166
DB2 Optimization Level user property 172
FileMustExist user property 170

Index ■ C
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 475
Forecast Rollup user property 115
Named Method n user property 148
On Condition Set Field Value user
property 140
OnAddAssocUpdateParent: buscompname
user property 152
Required user property 90
Response Type Call Back user property 158
Response Type More Info user property 158
Response Type Unsubscribe user
property 158
Revenue Aggregation Field n user
property 112
Revision Condition n user property 171
Sequence Use Max user property 135
Sort Search Optimization user property 121
State Model user property 120
ViewMode Sort user property 125
business services
BatchSize user property 87
C
Calc Actual OnWriteRecord user
property 135
Calculated Value property
about and syntax 466
text limitation 466
calculation expressions
chart coordinates, setting 469
Julian functions, about using 460
calendar templates
eCalendar Daily Applet 255
eCalendar Monthly Applet 260
eCalendar Weekly Applet 259
calendars
service calendar definitions, cascading style
sheets 423
ChargeBusinessService user property 111
chart coordinates, setting 469
ClearGridBeginEndDate method, about 40
ClientBusinessService user property 70
CloseOutFlag user property 119
comparison operators
about and table of 440
CompleteActivity method, about 40
content area, UI element described 338
context filter, UI element described 221
control banner, UI element described 221
controls
date and time formats in 468
Page user property 88
View user property 88
Copy Contact user property 113
CreateFile method, about and argument 45
Credit Card field, note, turning off
encryption 91
Credit Card user properties 167
Credit Card Expired Month 167
Credit Card Expired Year 167
Credit Card Number 167
Credit Card Type 167
Credit Check user property 166
Credit Check Workflow user property 166
CSSBCActivity
about 36
CSSBCActivity methods 40
CSSBCActivity methods
ClearGridBeginEndDate 40
CompleteActivity 40
IsPrimaryMVG 41
SetEmployeeLD 41
SetGridBeginEndDate 42
CSSBCActivityPlan 42
CSSBCBase
about 30
Aspect user properties 168, 169
EvalBoolExpr method, about and
argument 32
EvalExpr method, about and argument 32
IsActive method, about and argument 32
RefreshBusComp method, about and
invoking 32
RefreshRecord method, about and
invoking 33
Revise method, about and argument 33
Sequence method, about and argument 34
SetAspect method, about and argument 34
CSSBCContactSIS 43
CSSBCFile
about 44
CSSBCFile methods
CreateFile 45
DeleteFile 46
GetFile 46
PutfFile 47
UpdateSrcFromLink 47
CSSBCFundReq 55
CSSBCOppty 56
CSSBCOrderMgmtQuoteItem 56
CSSBCServiceRequest 58
CSSBCTaskTransient 59
CSSBCTaskTransientBase 60
CSSBCUser 60
CSSBusComp
30
CSSFrame
about 21
CSSFrameBase

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Index
■ D
476
about 22
CSSFrameList 23
CSSFrameListBase 23
CSSFrameListDocgen 23
CSSFrameListFile 23
CSSFrameListWeb 24
CSSFrameSalutation 24
CSSSWEFrame
about 21
CSSSWEFrameBase
about 22
CSSSWEFrameContactOrgChart 24
CSSSWEFrameFINApplication 25
CSSSWEFrameList 23
CSSSWEFrameListBase
about 23
CSSSWEFrameListDocGen 23
CSSSWEFrameListFile 23
CSSSWEFrameListFINApplication 25
CSSSWEFrameListWeb 24
CSSSWEFrameSalutation 24
CSSSWEFrameUserRegistration 25
Currency Field n user property 145
customer application definitions, cascading
style sheets 425
customer applications, template guide
page containers 405
specialized applets 408
UI elements, overview (table) 338
D
dashboard definitions, cascading style
sheets 425
Day Number: Arrival Date Field user
property 166
DB2 Optimization Level user property 172
Default Bookmark View user property 170
DefaultAppletFocus user property 100
DeleteFile method, about and argument 46
detail applet UI element described 221
Detail tab UI element described 221
Disable Automatic Trailing Wildcard Field
List user property 125
DisableNewRecord user property 75
DisableSearch field user property 89
DisableSort
list column user property 99
Drilldown Visibility user property 82
Dynamic Hierarchy user properties
Dynamic Hierarchy Parent Field Id 131
DynHierarchy Hierarchy Id Field 130
DynHierarchy Visibility Organization Id
Field 131
DynHierarchy Visibility Position Id Field 131
E
employee applications, template guide
frames, about mapping controls IDs by
region 225
page container template 268
page container templates 267
specialized applet templates 319
view template descriptions 292
Enable Dispatch Board user property 170
Encrypted user property 92
encryption, turning on and off 91
ePortal definitions, cascading style
sheets 426
error messages, displaying error messages
within form 189
EvalBoolExpr method, about and
argument 32
EvalExpr method, about and argument 32
EXISTS, using in a query with a primary ID
field 446
expressions, precedence of operators 439
F
favorites, UI element described 221
field Validation, about and syntax 466
fields
data types of 470
DisableSearch user property 89
Encrypted user property 92
SubCompUpdate user property 94
syntax for predefault 462
file attachments
See CSSBCFile
file replication
See CSSBCFile
FileMustExist user property 170
FINS Query Mode Disabled Method n user
property 75
first-level navigation UI element,
described 221
fonts, cascading style sheets 430
Forecast Rollup user property 115
frames
mapping controls IDs by region, about and
example 225
G
Gantt chart templates
eActivityGanttChart Applet 266
eGantt Chart Applet 265
eGanttChart Applet (Portal) 266

Index ■ H
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 477
generalized business component classes
CSSBCBase 30
CSSBusComp 30
list of 28
GetFile method, about and argument 46
Global menu definitions, cascading style
sheets 433
global navigation hyperlinks, UI element
described 338
GotoPage method 88
GotoView method 88
grid form applet layout 222
H
header, UI element described 338
HighInteractivityEnabled applet user
property 76
hyperlinks, global navigation hyperlinks,
user interface elements 338
I
IfNull function, about 444
integration component fields
AssocFieldName [Field Name] user
property 98
AutoPopulateResponsibility user
property 118
NoUpdate user property 98
integration components
Association user property 97
MVG user property 97
NoDelete user property 98
IS NULL operator, using 444
IsActive method, about and argument 32
IsPrimaryInMVG method, about and
argument 41
J
Julian functions, about using 460
L
layout styles, cascading style sheets 419
LIKE operator, using and syntax 442
list columns
date and time formats in 468
DisableSort user property 99
list definitions, cascading style sheets 420
Login Page definitions, cascading style
sheets 431
M
Maintain Master Account user property 110
Master Account Field user property 110
message layer, cascading style sheets 437
mini-button definitions, cascading style
sheets 435
multicolumn editable (mce) form mode,
cascading style sheets 431
multivalue groups (MVGs)
primary field, searching with 446
MVG format definitions, cascading style
sheets 426
MVG user property 97
N
Named Method n
business component user property 148
navigation tabs, cascading style sheets 433
No Clear Field n user property 139
NoDelete user property 98
non-grid form applet layout 222
Non-SalesRep View Mode SearchSpec user
property 129
NOT LIKE, using and syntax 442
NoUpdate user property 98
NULL operator
about using 443
IS NULL operator, using 444
O
On Condition Set Field Value user
property 140
OnAddAssocUpdateParent: buscompname
user property 152
opportunities
See CSSBCOppty
OverrideViewCache user property 70
P
page containers
DotCom Page Container (Framed)
template 405
DotCom Page Container (Hybrid)
template 407
DotCom Page Container No Frames
template 406
Page control user property 88
page header definitions, cascading style
sheets 435
pattern matching
LIKE and NOT LIKE, using and syntax 442
special characters, using and examples 443
PDQDisabledView user property 70
Position Join Fields user property 162
precedence of operators in expressions 439

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Index
■ Q
478
predefined query form, about date and time
formats 468
primary applet, UI element described 221
primary tabs UI element, described 221
Product pick map, must be last 56
Protect Seed Data user property 120
PutFile method, about and arguments 47
Q
Query By Example search syntax 468
QueryAssistantNumQueries business
component user property 126
question (?) character, using in pattern
matching 443
R
Recipient Communications user
properties 156
record navigation, UI element
described 221
Recursive Link user property 153
RefreshBusComp method, about and
invoking 32
RefreshRecord method, about and
invoking 33
Required user property 90
Response Type Call Back user property 158
Response Type More Info user property 158
Response Type Unsubscribe user
property 158
responsibility, about
AutoPopulateResponsibility user
property 118
Revenue Aggregation Field n user
property 112
Revise method, about and argument 33
Revision Condition n business component
user property 171
Revision Copy Field n user property 117
rich text component classes, cascading style
sheets 436
RSA encryptor service, using 91
S
screenbar, UI interface described 338
Search Center definitions, cascading style
sheets 436
Search Engine Table property, about using
for pattern matching 442
Search Specification, about date and time
formats 468
search syntax
multivalue groups with primary field,
searching 446
Query By Example 468
search, applet used to perform search 338
second-level navigation, UI element
described 221
Sequence method, about and argument 34
Sequence Use Max user property 135
service calendar definitions, cascading style
sheets 423
service requests
CSSBCServiceRequest 58
Set Primary Sales Rep As Owner user
property 147
SetAspect method, about and argument 34
SetEmployeeID method, about and
argument 41
SetGridBeginEndDate method, about 42
Show Required n user property 77
Siebel Web Engine, HTML tags
See swe tags 177
single-column (sc) form mode, cascading
style sheets 430
site branding, about 338
Site Map 331
site map definitions, cascading style
sheets 432
SmartScript definitions, cascading style
sheets 436
Sort Field Map n user property 129
Sort Search Optimization user property 121
specialized applet templates
Advanced Search 278
Applet Dashboard 321
Applet Email Response - Inbound 322, 324
Applet Find 279
Applet Items Displayed 320
Applet Salutation 326
Applet Salutation (Graphical) 326
Applet Screen Links 327
Applet Send Mail 329
DotCom Applet Find 408
DotCom Applet License Base 1 Column 409
DotCom Applet Parametric Search Head 410
DotCom Applet Parametric Search Tail 411
DotCom Applet Realtime Cart 412
DotCom Applet Search Advanced 413
DotCom Applet Search Advanced
Tabbed 413
DotCom Applet Search Basic 414
DotCom Applet Totals 415
eActivityGanttChart Applet 266
eGantt Chart Applet 265
eGanttChart Applet (Portal) 266
Save Search 280

Index ■ T
Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2 479
Search Applet 277
Search Preference 281
Search Results 283
Site Map 331
Spell Checker Popup Applet 275
specialized business component classes
CSSBCActivity 36
CSSBCActivityPlan 42
CSSBCContactSIS 43
CSSBCFile 44
CSSBCFundReq 55
CSSBCOppty 56
CSSBCOrderMgmtQuoteItem 56
CSSBCServiceRequest 58
CSSBCTaskTransient 59
CSSBCTaskTransientBase 60
CSSBCUser 60
specialized view templates
Search Results View 286
View Dashboard 331
View SME Segment Detail 332
State Model user property 120
SubCompUpdate field user property 94
swe tags
about 177
swe:child-applet 180
swe:current-view 209
swe:error 189
swe:for-each 180
swe:for-each-child 180
swe:for-each-view 212
swe:nav-control 187
swe:scripts 190
swe:select-row 182
swe:stepseparator 200
swe:subviewbar 198
swe:this 195
swe:threadbar 200
swe:threadlink 200
swe:togglebar 203
swe:togglelink 203
swe:togglename 203
swe:toolbar 205
swe:toolbaritem 205
swe:view 209
swe:viewbar 209
swe:viewlink 209
swe:viewname 209
swe:xsl-stylesheet 216
swe:child-applet tag, described 180
swe:current-view tag, described 209
swe:error tag, described 189
swe:for-each tag, described 180
swe:for-each-child tag, described 180
swe:for-each-view tag, described 212
swe:nav-control tag, described 187
swe:scripts tag, described 190
swe:select-row tag, described 182
swe:stepseparator tag, described 200
swe:subviewbar tag, described 198
swe:this tag, described 195
swe:threadbar tag, described 200
swe:threadlink tag, described 200
swe:togglebar tag, described 203
swe:togglelink tag, described 203
swe:togglename tag, described 203
swe:toolbar tag, described 205
swe:toolbaritem tag, described 205
swe:view tag, described 209
swe:viewbar tag, described 209
swe:viewlink tag, described 209
swe:viewname tag, described 209
swe:xsl-stylesheet tag, described 216
T
table of contents definitions, cascading style
sheets 433
templates
See customer applications, template guide;
employee applications, template
guide
text messages, displaying 338
third-level navigation UI element,
described 221
threadbar, UI element described 338
tree style, cascading style sheets 421
U
UI elements
customer applications, table of 338
Update Status To Synchronized user
property 111
UpdateSrcFromLink method, about and
argument 47
Use Literals For Merge user property 137
user properties
about and list of types 63
setting numbered instances of 65
V
Validate Parent Account user property 109
Validation property, text limitation 466
View control user property 88
View Mode Sort user property 125
view templates
DotCom View 100 66 33 100 403
DotCom View 25 50 25 398

Siebel Developer’s Reference Version 8.1/8.2
Index
■ W
480
DotCom View 25 50 25 Home 399
DotCom View 50 50 401
DotCom View 66 33 402
DotCom View Basic 393
DotCom View Detail 394
DotCom View Detail MultiChild 396
DotCom View Detail2 395
employee applications, visual reference and
list of 292
guidelines for using 293
Search Results View 286
View 1 Over 2 Over 1 293
View 25 - 50 – 25 295
View 25 – 75 296
View 25 – 75 Framed 297
View 25 75 Framed 2 298
View 50 – 50 299
View 66 – 33 300
View Admin 1 302
View Admin 1 (Grandchild Indented) 303
View Basic 304
View Catalog Admin 305
View Dashboard 331
View Detail 306
View Detail (Grandchild Indented) 308
View Detail 2 309
View Detail 2 (Grandfather Indent) 311
View Detail 3 312
View Detail 3 (Grandchild Indented) 314
View Detail 3 Multi Child 315
View Detail Multi-Child 316
View Parent List With Tabs 317
View SME Segment Detail 332
View Tree 289
View Tree 2 291
viewbar, UI interface element
described 338
W
WebGotoPlayerErrorPage user property 85
WriteRecord method
saving forecasts 52

