
B.K.
GOEL
CHARTERED
& ASSOCTATES
ACCOUNTANTS
Phone:
401
58777. 4l
0 | ! 335
P-16,
N.D.S.E.
II I'r
Floor
NEW DELHI-110049
The
Boarci
of Eirectors
Sunflame
Enterprise
Private
Limited
Khasra
No,
7 2/4/7, Mundka
Industrial
Area
(North
Side)
Village
-
Ghevra
New Delhi
-
I1.004L
Report
on
special
purpose
financial
statements
1" This
report is
issued in
accordance with
the
terms of
our agreement.
2'
We have
audited
the accompanying
special
purpose
financial
statements
of Su;flame
Enterprises
Private
Limited
(the
"Company")
which
comprise the
balance
sheet
as at March
3L,2023,
and
the
statement
of
profit
and loss,
Statement
of Cash Flows
and
the statement
of changes
in
equity for
the
pei',od
January 12,
2023
to March
31, 2023 and
a summary
of
significant
accounting
policies
and
other explanatory
information,
which
we have
signed
under reference
to
this reperrt.
Management's
Responsibility
tor
the Financial
Statements
3. Management
is responsible
fer the
preparation
of these
special
purposc
finrn:i'lr
rtjhrnents
i1
accordance with
the Accounttng
Standards
specifierl rrnder
Section 133
of
the Co'np.anir:s
A.r:t, 20i
j
read
witlt Rule
7 of the
Companies
(Accounts)
Rul€s, 2AI4,tothe
extent
considered
relevurrt
by
;t
for
the
purpose
for
whrch
these special
purpose
financial
statements
have
been
prepared
(rhe
"accounting
principles
generally
accepted
in India").
The
responsibility
ineludes
the design,
implementation
and maintenance
of internal
control relevant
to the
preparation
of
special
purpose
financial
statements
that are free
from material
misstaternent,
whether
due
to fraud
or
error.
Auditor's
Responsibility
4.
Our responsibility
is to
express an
opinion
on these speeial
purpose
flnancial
statements
based on
our
audit" We
conducted
our
audit in accordance
with
the
Standards
on Auditing
specified
under
Section
143(10)
of the
Companies
Act,2013
("the
Act")
and
other
applicable
authoritative
pronouncements
issued
by the Institute
of
Chartered Accountants
of India.
Those
Standards
require
that we
comply
with
ethical requirements
a rd
plan
and
perform
the
audit
to obtain
reasonable
assurance
about
whether
the financial
statements
are free
from
rnaterial
misstate;,nent.
5' An
audit involves
perfornrii'rg
procedures
to obtain audit
evidence
about
the
amounts
and
disclosures
in
the special
purpose
finai:cial
statements. The
procedures
selected
depend
on
the auditors'
judgment,
including
the assessrnent
of the risks
of material misstaternent
of the finane
ial
statements,
whether
due
to fraud
or error.
In making
those risk
assessments,
the auditors
consider
internal
eontrol relevanttothe
entity's
preparation
and fair
presentation
of
the financial
statements
in
order
to design
audit
procedures
that
are appropriate
in the
circumstances,
but not for
the
purpose
of
'i
,r;fl
i.
ii
,{
h

B"K"
GOEL
& ASSOCIATES
phone:
40rs8777,410n33s
CHARTERED
ACCOUNTANTS
P-I6,
N.D.S.E,
II I.tFIooT
NEW DELHI-t7OO49
expressing
an
opinion on the
effectiveness
of the entity's internal
control.
Anr audit
also includes
evaluating
the
appropriateness
of accounting
policies
used
and the
reasonableness
of accounting
estimates made
by Management,
as well
as evaluating
the
overall
presentation
of
the financial
statements.
6. We
believe that
the audit
evidence we have
obtained is
sufficient and
appropriate
to
provide
a basis
for
our
audit opinion.
Opinion
7
"
Based
on
our audit, we report
that:
a. We
have obtained
all
the
information
and explanations
which,
to the
best of
our knowledge
and
belief, were
necessary
for the
purposes
of
our audit;
b" The Balance
Sheet,
Statement
of
Profit
and Loss,
Statement
of
Changes in Equity
and Statement
of Cash
Flows dealt with
by this report
are in
agreement with
the
books
of account;
c. ln
our opinion
and to the best
of our information
and
according
to the
explanations
given
to us,
the
specialpurpose
financialstatements,
togetherwith
the notes
thereon
and
attached
thereto,
fairly
present,
in
all material
respects, in
conformity
with
the accounting
principles
generally
accepted
in India:
(i)
in
the
case of the Balance
Sheet,
the state of
affairs of the
Company
as at March
3I,2023;
(ii)
inthecaseof
theStatementof
Profitand Loss,the
profitforthe
periodJanuary
12,2}23to
March
31,2023;
(iii)
in
the case
of Statement
of Changes in Equity,
of the
change in
equity for
the
period
January
12,
2A23
b March
3I,
2A23;
and
(iv)
in
the case of
the Statennent
of eash Flows,
of the eash flows
forthe
period
ended March
31,2023"
Other Matter
8. The
special
purpose
financial
statements
dealt with
by this report,
have
been
prepared
for
the
express
purpose
to
enable the
Group auditor's
(PWe)
to
express
opinion
on eonsolidated
finaneial
statements
of
V-Guard
group
for the
year
ended Mlarch
31,2A23
pursuant
to
the agreement
between
the Company
and B.K. Goel
&
Associates.
Restriction
sn
Use
9. Our obligations
in respect
of this report
are entirely
separate from,
and
our responsibility
and liability
is in no way
changed
by, any
other role we rnay
have
(or
may
have
had)
as auditors
of the
Company
l^

Phone:
40158777,
410l 1335
P-16,
N.D.S.E.
II I't Floor
NEW DELHI-110049
or
otherwise. Nothing in
this report,
nor
anything said or
done in the
course
of or in connection
with
the
services
that are the subject
of this report,
will extend
any
duty of
care we may have
in
our
capacity
as auditors of any financial
statements of
the Company.
10. This
report is
addressed
to the Board
of
Directors
of the Company
and
has been
prepared
for
and
only for
the
purposes
set out in
paragraph
8 above.
This report
should
not be
othenryise
used
or
shown
to or
otherwise distributed
to any
other
party
or used for
any other
purpose
except with
our
prior
consent
in writing. B.K
Goel
&
Associates
neither
accepts
nor assumes
any
duty, responsibility
or liability
to any other
party
or for
any other
purpose.
For
B.K
Goel & Associates
Firm Registration
No:
016642N
Accountants
B.K.
GOEL
& ASSOGIATES
CIIARTERED
ACCOUNTA}ITS
Place:
Gurugram
Date:15.05.2023
B.K
Goel
(Proprietor)
Membership
No:
082081
U>)N
19a
*to&l
(t|wtl-
FA
aQtg

Sunflame
Enterprises Private
Limited
Special
Purpose Financial
Statement as at March
31, 2023
(Amount
in t lakhs, unless
otherwise
stated)
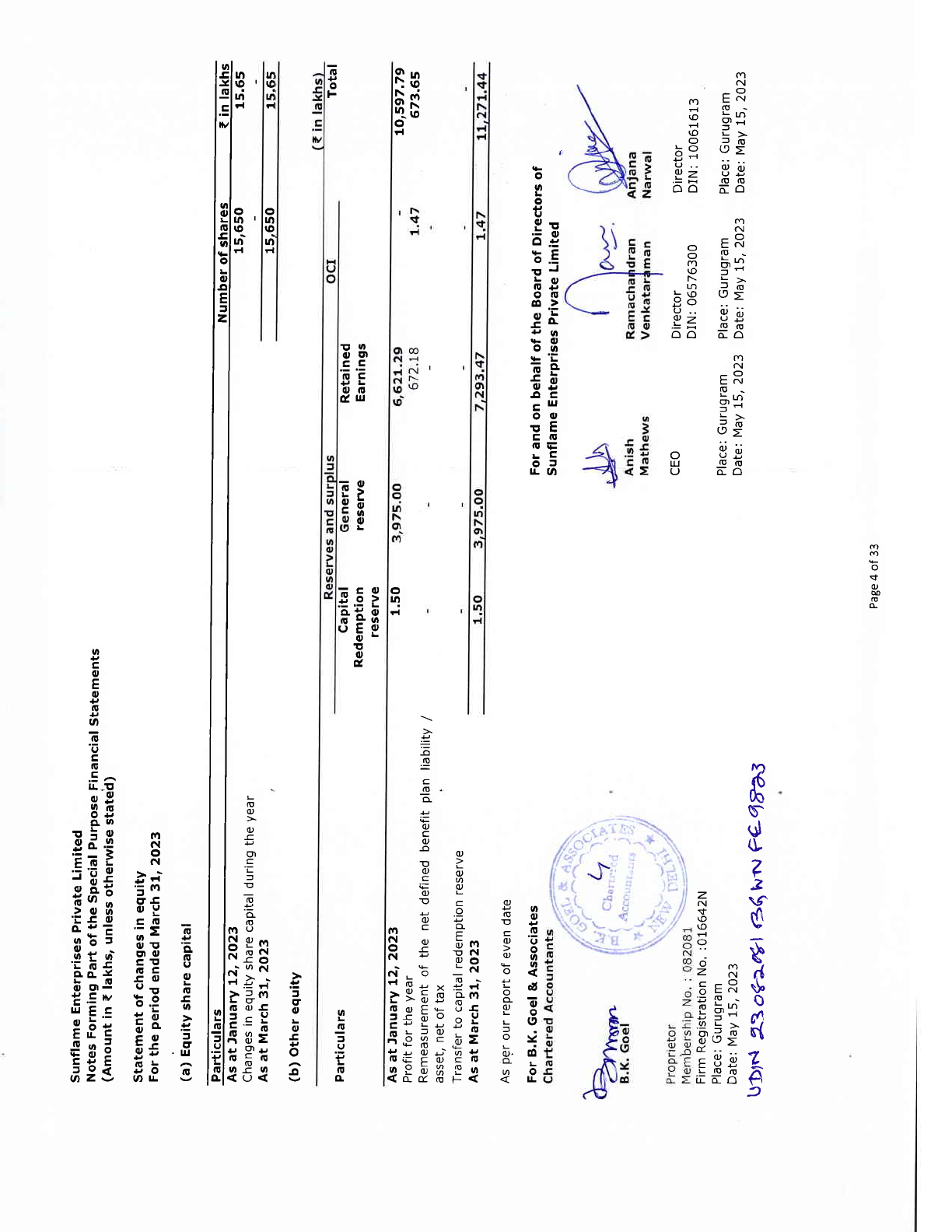
Particulars
Notes
As at
March 31. 2()23
Opening
as at
January
12,2023
Assets
Non-current
assets
Property,
plant
and
equipment
Right-of-use assets
Investment
ProperW
Other
intangible assets
Financial assets
Investments
Loans
Deferred tax assets
(net)
Other
non-current assets
Total non-current assets
Current
assets
Inventories
Financial
assets
Trade
receivables
Cash
and cash equivalents
Other bank
balances
Current tax
asseG
(net)
Other
current assets
Total current assets
Total Assets
Equity and
liabilities
Equity
Equity share
capital
Other equity
Total Equity
Liabilities
Non-current
laabilitaes
Financial
liabilities
Lease liabilities
Provisions
Other
non-current liabilities
Total non-cu
rrent
liabilities
Current
liabilitaes
Financial
liabilities
Lease liabilities
Trade
payables
Total
outstanding
dues of micro enterprises
and small enterprises
Total outstanding dues of credatoG other
than micro enterprises
and
small enterDrises
Other
current liabilities
Current
tax liabilities
(net)
Provisions
Total current
liabilities
Total liabilities
5
9
10
11
11
LZ
13
t4
4,209.94
220.52
150.00
2.44
0.45
400.00
34.97
15.36
4,247.4a
'
150.00
o.45
400.00
33.7r
15.38
6
7
31
B
ao
L7
18
5,()33.72
4,a5(J.39
3,642.84
3,358.85
634.83
2,688.33
39.40
184.59
3,274.L3
4,297.97
138.98
474.65
L27.99
124.72
10,544.44
15,542.56
15.65
tL277.44
tl,2a7.o9
720.24
18.36
168.69
307.29
LOt.70
3,334.2t
489.69
55.47
7.tr
3,988.18
4.295.47
Board of Directors
of
Place:
Gurugram
Place:
Gurugram
Date:
May 15,2023
Date: May L5,2023
8.772-3A
13.622-77
1( Aq
10.597, t9
1o,613.44
20.42
1 69.1 6
149.94
16
19
20
22
L,626.22
L,t44.76
4.37
2,819.3s
3.OO9-33
Membershio
No. :
082081
Firm Registration No. :016642N
Place:
Gurugram
Date:
May L5,2023
Narwal
Darector
DIN:10061613
Place:
Gurugram
Date: May
L5,2023
Total equity and liabilities
The accompanying
notes
are an integral
part
of the special
purpose
financial statements.
As
per
our
report of
even date
For B.K. Goel &
Associates
Chartered
Accountants
For and
o
Sunflame
Anish
Mathews
cEo
#':E'S
K-,{
8(
c)
{;-r#.
UD,sr
-S
UeIo*)
N)v{N
ee
4€23
Page
1 of 33

Sunflame
Enterprises Private
Limited
Speciaf Purpose
Financial
Statementfor the
period
January L2,2023
to March
3L,2023
(Amount
in t lakhs, unless otherwise
stated)
(<
an lakhs)
For
the
period
Particufars
Notes
tanuary
!2,20.22
to March 3L,2'J23
Revenue
Revenue from ooerations
Other income
Total income
Expenses
Cost of
materials consumed
Purchases of
Finished Products
Changes
in Inventories
Employee benefits expense
Finance costs
Depreciation
and amortization
expense
Other expenses
Total
expenses
Profit/(loss) before exceptional items and
tax
Exceptional
ltems
Profit before tax
Current
tax expense
Income tax adjustment
related
to
prior years
Net deferred
tax benefit
Income tax expense
Profit after tax
Other comprehensive
income
A. Items that
will not be reclassified
to
profit
or loss
Re-measurement
losses on defined
benefit
plans
Tax imDact on above
B. Items that
wall be reclassified
to
profit
or loss
Total other comprehensive
gain
for
the
year,
net of
tax
Total comprehensive
income
for the
year
Earnings
per
equity share:
Basic and diluted
The accompanying
notes are an Integral
part
of the financial statements.
As
per
our
report of even date
For B.K. Goel
& Associates
Chartered
Accountants
Propraetor
Membershio
No. : 082081
Firm Reoistration
No. :016642N
23
24
25a
26
25b
27
2A
29
30
ry-
5,690.10
46.)'l
s,736.31
1,340.85
2,600.35
(4s2.9e)
243.24
4.63
93.a7
973.89
31
4.443-44
892.47
'392.47
222.O5
(t.761
220'29
672.r8
1.95
{o.49)
1.47
4,295"07
Narwal
Director
DIN:10061613
Place:
Gurugram
Date: May
75,2023
1.47
Place: Gurugram
Date: May 15,2023
ub|sr
z1oh.o&l
b6,w*Fa
qhs
,67
Q*;9
andran
raman
Director
DIN: 06576300
Place:
Gurugram Place: Gurugram
Date:
May 75,2023 Date: May
75,2023
Ramac
Page
2 of 33

Sunflame Enterprises Private
Limated
Speciaf Purpose
Financial
Statement
for the
period
tanuary 12, 2023
to March 31, 2023
(Amount
in t lakhs, unless
otherwise stated)
Particulars
For
the
period
January 12,2(J23
to March 31,2(J23
Cash
flow from operating
activities
Profat
before tax
Adjustment to reconcile
profat
before
tax to net cash flows
Depreciation and amortization expense
Finance
cost
Finance income
Operating
profit
before working
capital
changes
Movements
in working
capital?
Trade
payables
In ventory
Current tax liabilities
(net)
Deferred tax assets
(net)
Provisions
Current tax assets
(net)
Trade receivables
Other non current
liabilities
Other current liabilities
Other current assets
Other non current
assets
Cash
generated
from
operations
Direct taxes
paad
(nel
of
refunds)
Net cash
generated
from
operating activities
(A)
Cash flows from investing actavaties
Net sales/(Purchases) of
property, plant
and equipment,
including CWIP
Investments in bank deposits
(net)
Interest received
Net
cash
generated
from/(used
in) anvesting activities
(B)
Cash flows from financing activities
Lease Payments
made during
the
year
Other interest costs
Net
cash
used in fanancing activities
(C)
Net decrease an cash and cash equivalents
(A+B+C)
Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of
the
year
Cash
and
cash equivalents at
the end of the
year
The accompanying noteJare an integral
part
of the special
purpose
financial
statements.
492.47
93.47
4.63
(38.67)
952.30
7,707
.99
(428.71)
55.47
(r.26)
(2.26)
82.60
939.06
(0.47)
(6es.07)
(ss.87)
0.02
2F49.8O
(220.291
2.329-51
(2e.t2)
(
1,813.68)
38.68
(1,804.12)
(2e.3e)
(0.1
5)
(29-S4l
495.85
138.98
634.43
For B.K. Goel & Associates
Chartered Accountants
\-
A}rfi\.nm/-
B.K. Goel
Proprietor
Membership
No. :
082081
Firm Registration No. :01664iN
.,-
-
Place: Gurugram
Date: May 15,2023
UDrs
*ogA.o&f
rD6,X
tv
For and on
behalf of the Eoard
of Directors of
Sunflame Enterprises
Private Limated
lA
4
dran
man
CEO Director
Director
DIN: 06576300
DIN:10061613
Place:
Gurugram Place:
Gurugram
Place: Gurugram
Date:
May t5,2023 Date:
May 15,2023 Date:
May 15,2023
Ramacha
FO
48a3
Page
3 of 33
cn
N
_o
FN
;;
L6
6
:>
o
lo
xo
(,>
U
--
nr ;:
9z
6.Y
UU
LU
m
C\l
-o
o
trc{
m
=d
N
=>-
tr)J6
bP
cr:
u
..
oJ ;i
g)7
Ui:
.=F
o
G
oo
6:o
rr)
N
-o
IN
l
=>
.=o
u/>
i4;
UOG
u a:o
$u
il$
I
o
o
o
u
u
EJ
etr
o.:
EJ
hg
oo
t0
.:
;A
Pvl
sC,
O('
s'i
E9
5g
llc
-uJ
oo
sE
trlu
t!
i=
LL
OJ
trUl
o
st
o
@
@
c
o
4
=
-o
.o
l1,l
t6
0o
s
,ul
(L
7
3
K\t
g$
5T
;
-B
ziiirl
F ER $
*q;
o
-b
5'i
A
a;F'(
tsn z
r-#E
F
2
c
o-
=
a
a
-oo
xL
zg
c)L
!:g.n
E E
€g
m-o
q!
c.r F-
q'l
'O
R
E
iil
d
3
ri.b
jx
b
i
*fr.-Ej
! d
lxbp *oo
3
='
t!otrs
UE I X
:5F9eg
:6
:
=fi
-
G
f
ripB;&E
3
X
t#E6EE
g'T
{,ieHEt &
E
t
u
o
Elo
ogl
oc
oo
d,u
o
I
tu
o
o
EEi
.s"s$
o-
It
o
d
IE
L
o
It
L
3
l
L
o
o.
.:
a
c'
o
L
o
o
.Ct
l;lll
lq--
ll
tl
Pll
fI
E"ll
[g
| |
q
E*:
H
IIF
lgiEgnll,F,
gigEiilfligi

Sunflame
Enterprises Private Limited
Notes Forming
Part ofthe Financaal
Statements
(Amount
in { lakhs, unless otherwise
stated)
CIN No.
: U74899DL1984PTCO18992
2.2
2.1
CORPORATE
INFORMATION
Sunflame
Enterprises Private
Limited
(hereinafter
referred
to
as
'SEPL'
or 'the
Company')
is
a
private
limited
company
domicifed
in India with its registered
office
at
Khasra
No.
72/4/7, Mundka Industrial
Area
(North
Side)
Village
-
chevra, New
Delhi- 110041.
The
Company was incorporated on August 27, 7984.
The Company
is engaged in manufacturing
and selling
kitchen
appliances in India.
Company's
product portfolio
includes a wide
range of kitchen
appliances such as
gas
stoves,
cooktops,
chimneys,
induction cookers, electric cookers, and more. The
Company's manufacturing
facility is located
at IMT,
Fa rida
bad.
SIGNIFICANT
ACCOUNTING
POLICIES
This note
provides
a list of the significant accounting
policies
adopted in the
preparation
of these Indian Accounting
Standards
(Ind
AS) financial statements. These
policies
have
been consistently applied
to all the
years
except where
newly issued
accounting standard is initially adopted.
Basis of
preparation
of financial statements
The
financial statements
of the Company
have
been
prepared
in
accordance with Indian Accounting
Standards
(Ind
AS)
notified under Companies
(Indian
Accounting
Standards) Rules, 2015
(as
amended from time
to time) and
presentation
requirements of Division II of Schedule III to the
Companies
Act, 2013.
The
financial statements have
been
prepared
on a historical cost basis, except
certain financial assets
and liabilities that are
measured at fair value.
The
financial
statements are
presented
in
Indian Rupees
('t').
These Values
are
also
rounded
to nearest lakhs upto
two
decimal
places ({00,000),
except
when
otherwise
indicated.
Summary
of sagnificant accountang
policies
a)
Current versus non-current classificataon
The Company
presents
assets
and
liabilities in
the Balance Sheet based
on current
/
non-current
classification. An asser ts
treated
as current when it is:
.
Expected to be realized or intended to be sold
or consumed
in
normal operating
cycle
.
Held
primarily
for the
purpose
of trading
.
Expected to
be realized within
twelve months after the reporting
period,
or
.
Cash
or cash equivalent unless restricted from
being exchanged or used
to settle a liability for
at
least
twelve months after
the reporting
period.
All other
assets are
classified as
non-current.
A liability
is
current when:
.
It
is
expected
to be seEtled in normal
operating cycle
.
It is held
primarily
For the
purpose
of trading
.
It is due to be settled within twelve months
after the
reporting
period,
or
.
There is no unconditional right to defer the
settlement of the liability For
at least twelve months after the reporting
period.
All other
liabilities are classified as non-current.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are classified as non-current
assets and liabilities.
The operating cycle is the time between the acquisition
of assets for
processing
and their realization in
cash and cash
equivalents.
The Company has identified
twelve months as its operating
cycle.
b) Foreign
currencaes
The
Company's
financial statements are
presented
in
Indian Rupees
('{')
which is
also the Company's lunctional
currency.
Transactions and balances
Transactions in Foreign currencies are initially recorded
by the Company
at their respective functional
currency spot rates at
the date the transaction
first
qualifies
for recoqnition. However, for
practical
reasons,
the Company uses an average rate ifthe
average
approximates the actual rate
at the date of the transaction.
Page
5 of 33

Sunflame
Enterprises
Private
Lim:ted
Notes Forming
Part ofthe Financial
Statements
(Amount
in t lakhs, unless otherwise stated)
CIN No. : U74899DL1984PTCO18992
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies
are translated
at the tunctional currency
spot rates of
exchange
at
the
reporting
date. Exchange differences arising
on settlement or translation
of monetary items
are
recognised
in
the Statement
of Profit
and
Loss.
Non-monetary
items
that are
measured in
terms of historical cost in
a
foreign
currency are
translated using the
exchange
rates at the dates of the initial
transactions.
Non-monetary
items measured
at
fair value
in a foreign
currency are translated
using the exchange rates at the date when
the
fair value is
determined. The
gain
or loss arising
on translation oF non-
monetary
items
measured at fair value is treated in line with
the recognition ot
the
gain
or loss on the
change in fair value of
the item
(i.e.,
translation differences on items whose fair value
gain
or loss is recognised in
OCI or Statement
of
Profit
and
Loss
are also recognised in OCI or
Statement
of Profit and
Loss, respectively).
c) Fair
value measurement
Fair
value is the
price
that would
be
received
to sell an asset or
paid
to transfer a liability in an
orderly transaction between
market
participants
at the measurement date. The
fair
value
measurement is
based on the
presumption
that the transaction
to sell the
asset or
transfer the
liability
takes
place
either:
.
In the
principal
market For asset or liability, or
.
In
the absence of a
principal
market, in then most
advantageous market for
the asset or liability.
The
principal
or the most advantageous market must
be
accessible
by the Company.
The
fair
value
of an asset or liability is measured
using the assumptions
that market
participants
would use when
pricing
the
asset
or
liability,
assuming that market
participants
act
in
their economic best interest,
A fair
value measurement
of a
non-financial
asset takes into account
a market
participant's
ability to
generate
economic
benefits
by using the asset in its highest and
best use or by selling it to another
market
participant
that would
use the asset in
its
highest and best use.
The Company uses
valuation
techniques that are appropriate
in the circumstances
and for which sufficient data
are available
to measure
fair value, maximising
the use of relevant observable inputs
and minimizing
the use of unobservable inputs.
All assets and liabilities
for which fair value
is measured or disclosed
in the financial
statements are categorized within
the
Fair
value hierarchy, described as follows, based on
the lowest level input that is
significant to the fair value measurement
as a
whole:
.
Level 1
-
Quoted
(unadjusted)
market
prices
in
active markets for identical
assets or liabilities
.
Level
2
-
Valuation
techniques
for which
the lowest level input
that is significant
to the
fair value
measurement is directly
or
indirectly
obseruable
.
Level 3
-
Valuation techniques for which the lowest level
inout that is
siqnificant to the fair value measurement is
unobservable.
For assets
and liabilities that are recognised in
the
financial
statements
on a
recurring
basis, the
Company determines whether
transfers
have
occurred between levels in the hierarchy
by
re-assessing
categorization
(based
on the lowest level input
that
is
significant
to fair value
measurement as a whole) at the end
of each reporting
period.
d)
Revenue
Revenue
from contract wath
customers
-
Revenue
from contracts
with
customers is recognised when
control ofthe
goods
are transferred to the customer
at an amount
that
reflects the consideration to
which
the Company
expects to be entitled in
exchange for those
goods
or services. The
Company
has
generally
concluded that it is
the
principal
in its revenue arrangements
because it typically
controls the
goods
or
services
before transferring them to the customer.
(i)
Sale
of
products
Revenue
from
sale of
products
is recognised at
the
point
in
time
when
control
of the asset is transferred to
the customer,
generally
on delivery of the
products
to customer's
premises.
Company deals
primarily
with Super-distributors
(General
trade),
Canteen
stor€s, Police canteens, Modern retails, Institutional
buyers & E-commerce
platforms.
The normal credit
term
is
7 to
60 days
upon
delivery
of
goods.
The Company
considers whether there are other
promises
in the contract that
are separate
performance
obligations
to
which
a
portion
of the transaction
price
needs
to be allocated if any. In
determining
the transaction
price
for the sale of
goods,
the
Company considers
the
effects of
variable
consideration,
the existence of
significant financing components, non-cash
consideration,
and consideration
payable
to the customer
(if
any).
Page
6 of l3
w

Sunflame
Enterprises Private Limited
Notes Forming
Part
ofthe Financial Statements
(Amount
in { lakhs, unless otherwise
stated)
CIN No, ? U74899DL1984PTCO1a992
Variable consideration
If
the
consideration in
a contract
includes
a variable
amount, the Company
estimates the amount
of consideration
to
which
it
will be entitled in exchange for transferring
the
goods
to
the customer.
The variable
consideration is
estimated at contract
inception and constrained
until
it is
highly
probable
that a significant revenue reversal
in the
amount of cumulative revenue
recognised
will
not occur when
the associated uncertainty with
the variable
consideration is
subsequently resolved. The
contracts for the sale of
goods provide
customers with a right
of return, cash
discounts and volume
rebates/trade incentives,
The rights of return, cash discounts and volume
rebates/ trade incentives
give
rise
to
variable
consideration.
Volume
rebates
The
Company
provides
retrospective volume
rebates
/
trade
incentives
to
customers once the
quantity
of
products purchased
during
the
period
exceeds a threshold
specified in the
contract. Rebates are
offset against amounts
payable
by the customer.
The Company estimates the variable
consideration for
the
expected
future rebates
/
trade incentives
based on its experience
of the expected
value,
The Company then
applies the requirements
on constraining estimates
of variable consideration,
Trade receivables
A
receivable represents
the Company's right
to
an amount
of consideration
that is unconditional
(i.e,,
only the
passage
oftime
is required before
payment
of the consideration is due).
contract liabilitaes
A contract liability
is
the obligation to transfer
goods
or services
to a customer for which
the Company has received
consideration
(or
an
amount of consideration is due) from
the customer. If
a customer
pays
consideration before
the Company
transfers
goods
or services to the
customer, a contract liability is
recognised when
the
payment
is made
or the
payment
is
due
(whichever is
earlier). Contract liabilities are recognised
as revenue when
the Company
performs
under the contract,
(ii)
Assets and liabilities arising from rights
of return
Raght of return assets
Riqht of
return
asset represents the
Company's right to recover
the
goods
expected
to be returned by customers.
The asset is
measured at the
former
carrying amount of
the
inventory,
less any
expected costs to recover
the
goods,
including
any
potential
decreases in
the
value
of the
returned
goods.
The
Company updates
the
measurement
of
the asset recorded tor
any
revisions to its expected level of returns,
as well as any
additional decreases in
the
value
of the returned
products.
Interest income
For all
debt instruments measured
either at
amortised cost or at fair value
through other comprehensive
income, interest
income is recorded usinq the effective interest
rate
(EIR).
EIR is
the rate
that exactly discounts
the estimated future
cash
payments
or receipts over the expected life
oF the financial instrument
or a
shorter
period,
where appropriate,
to the
gross
carrying
amount
of the
financial
asset or to
the amortised cost of
a
financial
liability. When
calculating the effective
interest
rate, the Company estimates
the expected cash flows by
considering all the contractual
terms of the financial
instrument
(for
example,
prepayment,
extension,
call and similar options)
but does not consider
the expected credit
losses. Interest income is
included
in finance income
in the Statement
of Profit and Loss.
Dividends
Revenue is recognised when
the Company's right
to
receive
the
payment
is
established, which is
generally
when shareholders
approve
the dividend.
e) Taxes
current income tax
Current
income
tax assets and liabilities
are
measured
at the
amount expected to be recovered from
or
paid
to the taxation
authorities.
The tax rates and
tax
laws
used to compute
the amount are
those that are enacted or
substantively
enacted, at
the
reporting date.
Current
income tax relating
to
items recognised
outside
the Statement
of
Profit
and Loss is recognised
outside the Statement
of
Profit and Loss
(either
in
other comprehensive income
or equity). Current
tax items are recognised in
correlation
to the
underlying transactions either in OCI or directly
in equity.
Management
periodically
evaluates
positions
taken in the tax returns with
respect
to
situations
in which applicable
tax
regulations are subject to interpretation
and considers whether
it is
probable
that a taxation authority will
accept an uncertain
tax treatment.
The
Company shall reFlect
the effect of uncertainty for
each uncertain
tax treatment by using either most
likely
method
or expected value
method, depending
on
which
method
predicts
better resolution
of the
treatment.
Page 7 of 33

Sunfl ame
Enterprises Private Limited
Notes Forming
Part of
the
Financial
Statements
(Amount
an { lakhs,
unless
otherwise stated)
CIN No.
I U7 4899DLL9a4PTCO18992
Deferred tax
Deferred
tax is
provided
on temporary differences between the tax bases
of assets and liabilities
and their carrying amounts
for financial
reporting
purposes
at the
reporting date.
Deferred
tax
liabilities are
recognised for
all taxable temporary differences,
except:
.
When
the deferred
tax liability
arises
From the initial recognition of
goodwill
or an asset or liability in
a transaction that is not
a business
combination and, at the
time
of
the transaction, affects neither
the
accounting
prorit
nor taxable
profit
or
loss,
.
In respect of taxable temporary differences associated with investments
in subsidiaries,
associates and interests in
joint
ventures,
when
the timing ofthe
reversal
ofthe temporary differences
can be controlled and it is
probable
that the temporary
differences
will not reverse in the Foreseeable future.
Deferred tax assets are recognised for all deductible temporary
differences, the carry forward
of unused tax credits and any
unused
tax losses. Deferred
tax
assets
are recognised to the extent
that
it is
probable
that
taxable
profit
will be available
against
which the deductible temporary differences,
and the carry forward of unused
tax credits and unused
tax losses can be
utilised,
except:
.
When
the deferred tax
asset
relating
to the deductible temporary difference
arises from the initial recognition
of an asset or
liability
in a transaction that is not a business
combination and, at the time of
the transaction, affects neither
the accounting
profit
nor taxable
profit
or loss.
.
In respect of deductible temporary differences associated with investments
in subsidiaries,
associates and interests in
joint
ventures, deferred tax assets are recognised only to the
extent that it is
probable
that
the temporary differences will reverse
in the
foreseeable future and
taxable
profit
will be available against which
the temporary differences
can be utilised.
The carrying
amount of deferred
tax assets
is
reviewed at each reporting date
and
reduced
to
the
extent
that
it is no
longer
probable
that sufficient taxable
profit
will
be available to allow all or
part
ofthe deferred tax asset to be
utilised. Unrecognised
deferred
tax assets are re-assessed
at each reporting date and are recognised
to the extent
that
it has
become
probable
that
future
taxable
orofits
will allow the deferred
tax asset to be recovered.
Deferred tax
relating
to
items recognised
outside
profit
or
loss
is
recognised outside
profit
or loss
(either
in other
comprehensive
income or in equity). Deferred
tax items are recognised in
correlation to the underlying
transaction either in
OCI or
directly in equity.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured
at
the tax rates
that are expected to apply in
the
year
when the asset is
realized
or the liability is
settled, based on tax rates
(and
tax laws)
that
have
been enacted or substantively
enacted at the
reporting
date.
Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities
are offset
if
a legally enforceable right
exists to set off current
tax assets
against current
tax liabilities and the
deferred taxes relate to the same
taxable entity and the same taxation
authority.
Goods
and services taxes
paid
on acquisation
of
assets
or on Incurrtng expenses
Expenses
and assets are recognised net of
the amount of
goods
and seruices
taxes
paid,
except:
.
When the tax
incurred on a
purchase
of assets or services is not recoverable from
the taxation authority, in which
case, the
tax
paid
is recognised as
part
of the
cost of acquisition of the asset or as
part
of the expense item, as applicable.
.
When receivables and
payables
are stated with
the
amount
of tax included.
The
net amount of tax recoverable from,
or'payable to, the taxation
authority
is included
as
part
of receivables
or
payables
in
the
Balance Sheet.
f) Property,
plant
and
equipment
Property,
plant
and equipment are stated
at
cost, net
of accumulated depreciation
and accumulated impairment
losses, if any.
Capital
work-in-progress is
stated at cost, net of accumulated impairment
loss, it any. The
cost comprises of
purchase price,
taxes,
duties,
freight
and other incidental expenses
directly attributable and related
to acquisition and installation
of the
concerned
assets and are further adjusted by the amount
of tax credit availed wherever applicable.
When significant
parts
of
plant
and equipment are required
to be
replaced
at intervals,
the Company depreciates them separately
based on their
respective useful
lives.
Likewise, when a major inspection
is
performed,
its cost is recognised in
the carrying amount
of the
plant
and
equipment as a replacement if
the recognition criteria
are satisfied. All other repair and maintenance
costs are
recognised
in Statement of Profit and Loss as incurred.
An
item oF
property, plant
and equipment and any
significant
part
initially recognised is
derecognised upon disposal
or
when
no future
economic benefits are
expected from its use or
disposal.
Any
gain
or loss arising on
derecognition of the asset
(calculated
as the dirference between
the
net
disposal
proceeds
and the carrying amount of the asset) is included
in the
income statement
when
the asset is derecoqnised,
\-
Page
8 of 33

Sunflame
Enterprases Private Limated
Notes Forming
Part ofthe Financial Statements
(Amount
in t
lakhs,
unless
otherwise
stated)
CIN No.
: U74899DLl9a4PTCO1a992
Capital
work-in-progress includes
cost of
property,
plant
and equipment
under installation
/
under
development as at the
Balance
Sheet date.
The residual
values,
useful lives and methods of depreciation of
property,
plant
and equipment
are reviewed at each financial
year
end
and adjusted
prospectively,
if appropriate.
Depreciation on
property, plant
and equipment is calculated on a written
down value basis
using the rates arrived at
based on
the useful
lives
estimated by the management. The Company identifies
and determines cost
of each component
/
part
of
the
asset separately,
if the component
/
part
has
a cost
which is
significant to
the total cost of the
asset
having
useful life that is
materially different trom that of the remaining
asset,
These
components are depreciated
over their useful lives;
the
remaining
asset
is depreciated over
the life
of
the
principal
asset.
The Company
has used
the
following
useful lives to
provide
depreciation
on
its
property, plant
and
equipment:
Asset Cateoorv Useful
life
estimated bv the manaoement
(in
vears)
Factory
land NA
Factory
Building
30
Plant &
Machinery
15
Electrical Installations 15
Furniture
& Fixtures 10
Lab
Equipment 10
Motor
Vehicles 8
Office
Equipment
5
ComDuter
Hardware
3
g)
Investment
properties
Property
that is held for long term rental
yields
or
for
capital appreciation
or
for
both, and that is not
occupied by the
Company,
is classified as investment
property.
Investment
property
is measured initially
at its cost, including related
transaction cost and
where
applicable, borrowing costs. Subsequent
to
initial
recognition, investment
properties
are stated
at
cost less
accumulated deprecaation
and accumulated
impairment
loss, if any,
Subsequent expenditure is capitalised
to asset's
carrying
amount only when it is
probable
that
future
economic benefits associated
with the expenditure will
flow to the
Company
and the cost of the item can be measured reliably. All
other repair and maintenance
cost are expensed when
incu rred.
Investment
properties
are de-recognised
either when they have been
disposed off or when they
are
permanently
withdrawn
from
use and no future economic benefit is
expected
from
their disposal. The
difference between the net disposal
proceeds
and
the carrying amount of the asset is recognised in
Statement of Profit and Loss in
the
period
of de-recognition.
h) Intangible
assets
Intangible assets acquired separately are measured on initial recognition
at cost. Following initial recognition,
intangible assets
are carried
at cost less any
accumulated amortisation and accumulated impairment
losses. Internally
generated
intangibles,
excluding
capitalised development costs, are not capitalised
and the
related
expenditure is reflected
in the Statement
of
Profit
and
Loss in the
Deriod
in which
the exDenditure
is
incurred.
Cost comprises
the
purchase
price
and any attributable cost ot bringing
the asset to its working
condition
For
its intended use.
The useful
lives
of
intangible
asseG are assessed as either finite
or indefinite. Intangible assets with
finite lives are
amortised
over their
useful economic
lives and assessed for impairment whenever
there
is
an indication that
the
intangible
asset may be
impaired.
The amortization
period
and
the
amortization method for
an intangible
asset
with
a finlte useful
life
is reviewed
at
least
at the end of each
reporting
period.
Changes
in
the expected useful life or the
expected
pattern
of consumption of future
economic benefits embodied in
the asset
is
accounted for by changing the amortization
period
or method, as appropriate
and are treated as changes in
accounting
estimates.
The amortization
expense on intangible assets with finite lives
is recognised in the
Statement of Profit and Loss.
Intangible
assets with indefinite
useful lives are not amortised, but are
tested for impairment annually, either individually
or at
the
cash-generating unit level. The assessment
oF
indeFinite
liFe is reviewed annually
to determine whether the indefinite
liFe
continues
to be supportable. If not,
the change in useful life from indefinite
to finite is made on a
prospective
basis.
An intangible asset
is de-recognised
upon disposal
(i.e.,
at
the
date
the
recipient
obtains control)
or
when
no future economic
benefits
are expected from
its use or disposal. Gains or losses
arising
from
disposal of the intangible
assets are measured as
the
difference
between
the
net
disposal
proceeds
and
the carrying amount ofthe asset and are recognised
in the Statement
of
Profit and
Loss
when
the assets
are
disoosed.
Software
is amortized over
an estimated useful life of 3 vears.
Page
9 of 33

Sunflame
Enterprises Private Limated
Notes Forming Part ofthe Financaal Statements
(Amount
in t lakhs, unless otherwase stated)
CIN No. : U74899DLL984PTCO18992
i)
Borrowing costs
Borrowing costs directly attributable to the acquisition, construction
or
production
of an asset that necessarily
takes a
substantial
period
of
time to
get
ready for its intended use
or sale are capitalised as
part
of the cost of the asset. All other
borrowing costs are expensed in the
period
in which they occur. Borrowing
costs consist of interest
and
other
costs that an
entity
incurs in connection with the borrowing of funds. Borrowing
cost also
includes
exchange differences
to the extent
regarded as an adjustment to the borrowinq costs.
j)
Leases
The Company assesses at contract inception whether a contract is,
or contains, a lease. That is, if
the contract conveys the
right to control the use of an identified asset for a
period
oF time in exchange for
consideration.
Company
as a
lessee
The
Company's
lease asset class
primarily
comprise
of lease for
land and buildings. The Company
assesses
whether
a contract
contains a lease, at
inception
of a contract.
A
contract
is,
or contains, a lease if
the contract conveys the right to control
the
use of an
identified asset for
a
period
of time in exchange for consideration. To assess whether
a contract conveys
the
right
to
control the
use oF
an
identified
asset, the Company assesses
whether:
(i)
the contract involves
the use of an identified
asset
(ii)
the Company has substantially all of the
economic
benefits from
use of the asset through
the
period
of the lease and
(iii)
the
Company has the right to direct the use oFthe asset.
The Company
applies a
single
recognition
and
measurement
approach for all leases. except for
short-term
leases
and leases
of
low-value assets. For these short-term and low-value leases,
the Company recognizes the lease
payments
as an operating
expense on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease. The
Company
recognises
lease liabilities to make
lease
payments
and
right-of-use
assets
representing
the right to use the underlying assets.
i)
Right-of-use assets
The Company
recognises right-of-use
assets at the commencement date of the lease
(i.e.,
the date the underlying
asset is
available
for use). Right-of-use assets are measured
at cost, less any accumulated depreciation and impairment
losses,
and
adjusted
for any remeasurement oF lease liabilities. The cost of right-of-use
assets includes the amount
oF lease liabilities
recognised,
initial direct
costs
incurred,
and lease
payments
made at or before
the commencement date
less any lease
incentives received. Right-of-use assets in
the
nature
of buildings are depreciated on a s[raight-line
basis over the shorter
of
the
lease term and the estimated useful lives ofthe underlying
asset. The right-or-use assets
comprising
ofland
is depreciated
based
on the lease term.
If ownership
ot
the
leased asset
transfers to the Company at the end of the lease
term or the cost
reflects
the exercise
of a
purchase
option, depreciation is calculated using the estimated useful
life oF the asset.
The
right-of-use assets
are also subject to impairment, Refer to the accounting
policies
in
section
(l)
Impairment
of
non-
financial assets.
ii) Lease
Iiabilities
At the commencement date of the lease, the Company recognises lease liabilities measured
at the
present
value
of lease
payments
to be made over
the lease term.
The
lease
payments
include fixed
payments
(including
in
substance fixed
payments)
less any lease incentives receivable, variable lease
payments
that depend on an index or a rate,
and amounts
expected
to be
paid
under residual value
guarantees.
The
lease
payments
also include the exercise
price
oF
a
purchase
option
reasonably certain to be exercised by the Company and
payments
of
penalties
for terminating the lease, if
the lease term
reflects the Company exercising the option to terminate. Variable lease
payments
that do
not
depend on an index or
a rate are
recognised
as expenses
(unless
they are
incurred
to
produce
inven-tories)
in the
period
in which
the event or condition
that
triggers the
payment
occurs.
In calculating the
present
value of lease
payments,
the
Company
uses its
incremental borrowing rate at
the lease
commencement
date
because the
interest rate implicit
in the lease is not readily determinable. After
the commencement
date,
the amount
ot lease liabilities is
increased to reflect the accretion of interest and reduced for
the lease
payments
made,
In
addition,
the carrying amount ot lease liabilities is remeasured
if there is a modification, a change in
the
lease
term, a change
in the lease
payments (e.9.,
changes to future
payments
resulting from
a change
in
an
index
or rate used to determine
such
lease
payments)
or a
change
in the
assessment of an option to
purchase
the underlyang asset.
The Company's lease liabilities are included in financial liabilities.
iii) Short-term
leases
and
leases
of
low-value
assets
The Company applies the short-term lease recognition exemption to its
short-term leases
(i.e.,
those leases that have
a lease
term of
12 months
or less
from
the commencement date and do not
contain a
purchase
option). It also applies
the lease of
low-value assets
recognition
exemption to leases that are considered to be low value. Lease
payments
on short-term
leases
and
leases of low-value assets are recognised
as expense on a straight-line basis over
the
lease
term.
14-
Page 10 of 33

Sunflame Enterprises Private Limited
Notes Forming Part
of the
Financial
Statements
(Amount
in t lakhs, unless otherwise stated)
CIN No. : U74899DL1984PTCO18992
k) Inventories
Inventories
are valued
at lower of cost or net realizable value.
Costs incurred
in bringing
each
product
to its
present
location
and condition are accounted for as follows:
.
Raw
materials,
packing
materials, consumables and
stores and
spares: Cost includes
cost of
purchase
and other costs
incurred in bringing
the
inventories
to their
present
location
and condition.
Cost is determined
on FIFO basis. The
materials
and other items held for use in the
production
of inventories
are not
written
down
below cost if the finished
products
in which
they will be
incorporated
are expected to
be
sold
at or above cost,
.
Finished
goods
and work in
progress:
Cost includes cost of
direct materials
and labour and a
proportion
of manufacturing
overheads based on
the
normal
operating capacity, but excludes
borrowing costs.
Cost is determined
on FIFO basis.
.
Traded
goods:
Cost includes cost of
purchase
and other costs incurred
in bringing
the inventories to
their
present
location
and condition. Cost is determined on FIFO basis.
Net realisable value is the
estimated selling
price
in
the ordinary
course of
business, less estimated
costs of completion
and
the estimated costs necessary to make
the sale,
I) Impairment of non-financial
assets
The Company assesses, at each
reporting
date, whether
there is an indication
that an asset may
be impaired, If
any indication
exists, or
when
annual
impairment
testing for an asset is
requiied, the
Company estimates
the asset's recoverable
amount. An
asset's recoverable amount is the higher
of an asset's or cashgenerating
unit's
(CGU)
fair value less cosLs
of disposal
and its
value
in
use.
Recoverable
amount is determined for
an
individual
asset,
unless the asset
does not
generate
cash inflows
that
are largely
independent
of those from other assets
or Company's assets. Where
the carrying
amount of an
asset or CGU
exceeds
its recoverable amount, the
asset
is
considered impaired
and is written
down to its recoverable
amount.
In assessing value in use, the estimated future
cash flows are
discounted to their
present
value using a
pre-tax
discount rate
that
reflects current market assessments
of the time value
of money and the risks
specific to the asset.
In determining
fair
value less costs of disposal, recent market
transactions are
taken
into
account. If no
such transactions can
be identified,
an
appropriate
valuation model
is used. These calculations
are corroborated
by valuation multiples,
quoted
share
prices
for
publicly
traded companies or other
available fair
value
indicators.
For assets excluding
goodwill,
an assessment is made
at each reporting
date to determine whether
there is an
indication that
previously
recognised impairment
losses no longer
exist or have decreased.
If such indication
exists, the
Company estimates
the asset's
or
CGU's
recoverable
amount. A
previously
recognised
impairment
loss is reversed only if
there has been
a change
in the assumptions used to determine
the asset's
recoverable
amount since the
last
impairment
loss
was
recognised.
The
reversal
is limited
so that the carrying amount of
the asset does not
exceed
its
recoverable
amount, nor exceed
the carrying
amount
that would have
been determined, net of depreciation,
had no impairment
loss been recognised
for the
asset in
prior
years.
Such reversal is recognised in
the Statement of Profit
and Loss unless
the
asset
is carried at
a
revalued
amount.
in
which case, the reversal is treated
as a
revaluation
increase.
m) Provisions
A
provision
is recognised when
the Company has
a
present
obligation
(legal
or constructive)
as a
result
of
past
event, it is
probable
that an outflow of resources
embodying economic benefits
will be required
to settle the obligation
and
a
reliable
eslimate
can be made of the
amount of the obligation.
The amount
recognized
as a
provision
is the best
estimate of the consideration
required
to settle the
present
obligation at
the
end
of the rep-orting
period,
taking into account the risks
and uncertainties
surrounding the obligation. When
a
provision
is
measured using the cash flows estimated
to s.ttle the
present
obligation, its c-arrying
amount is the
present
vilue
of those
cash flows
(when
the effect oFthe time value of money is
material).
If the effect of the time value of money is material,
provisions
are discounted using
a current
pretax
rate
that reflects, when
appropriate, the risks specific
to the
liability.
When discounting
is used, the increase in
the
provision
due to the
passage
of
time
is recognised
as a finance cost.
Contingent laabilaties
A contingent liability is a
possible
obligation
that arises from
past
events whose
existence
will
be confirmed
by the occurrence
or non-occu[rence of one or more
uncertain
future
events beyond
the control of the
Company or a
present
obligation
that is
not
recognised because it is not
probable
that an
outflow of resources will
be required to settle
the obligation. A
contingent
liability also arises in extremely rare
cases,
where
there is a liability
that cannot be recognised
because it
cannot be measured
reliably,
The
Company does not recognize
a
contingent
liability but discloses
its existence in
the
financial
statements
unless
the
probability
of outflow of resources is
remote. Provisions,
contingent
laabilities, contingent assets
and commitments
are
reviewed
at each Balance
Sheet date.
I
)'t:
Page 11
of 33

Sunflame
Enterprises Private Limited
Notes Forming
Part
ofthe
Fanancial
Statements
(Amount
in < lakhs, unless otherwase
stated)
CIN No. : U74899DLl984PTCO18992
n)
Employee benefits
Short term employee benefits
All
employee
benefits expected to
be settled
wholly within
twelve months
of rendering
the service are classified as
short-term
employee
benefits.
When
an employee has rendered
service to
the Company during an
accounting
period,
the Company
recognizes the undiscounted amount of
short-term employee benefits expected
to be
paid
in
exchange for that service as
an
expense unless another
Ind
AS requires or
permits
the inclusion of the benefits in
the cost of an asset.
Benefits such as
salaries,
wages
and
short-term
compensated absences and
bonus etc. are recognized in
Statement oF Profit
and
Loss
in the
period
in which the employee renders
the
related
service.
Defined
contribution
schemes
Contributions
to defined contribution
schemes such as
provident
fund,
employees'state insurance,
labour welfare fund
etc. are
charged as an expense based on
the
amount
of contribution required
to be made as and when
services are rendered by
the
employees.
The
Company has no obligation, other
than the contribution
payable
to the fund towards
such schemes. The
Company
recognizes
contribution
payable
as an expense, when
an employee renders
the
related
services, If
the contribution
payable
to scheme for service received before
the
Balance
Sheet date
exceeds the contribution
already
paid,
the deficit
payable
to the scheme is recognised as liability after
deducting the contribution
already
paid.
If the
contribution already
paid
exceeds the contribution due
for
services received before
the Balance Sheet date,
then excess recognised
as an asset to
the
extent that
the
prepayment
will
lead to, for example, a reduction in
future
payment
or a cash refund.
Defined benefit scheme
The
Company
operates a defined
benefit
gratuity plan
in India, which
requires
contributions to be made
to a separately
administered
fund maintained with
Life Insurance Corporation
of India. The cost of
providing
benefits under
the defined benefit
plan
is determined using the
projected
unit credit method.
Re-measurements, comprising of actuarial
gains
and losses,
the effect
of
the asset ceiling,
excluding amounts included
in net
interest on
the net
defined benefit liability and the return
on
plan
assets
(excluding
amounts included in net interest
on the net
defined
benefit liability),
are
recognised
immediately in
the
Balance
Sheet with a
corresponding debit or
credit to
retained
earnings through
OCI in
the
period
in which they occur. Re-measurements
are not reclassified
to
Statement of
Profit
and Loss
in subsequent
periods.
Past service costs are
recognised
in
Statement of
Profit
and Loss on the
earlier of:
.
The date of the
plan
amendment or curtailment,
or
.
The date that the Company recognises related restructuring
costs
Net interest is calculated by applying
the discount rate to the net
defined benefit liability
or asset. The Company recognises
the
following changes
in
the net defined benefit
obligation as an expense in
the Statement of Profit
and
Loss:
.
Seruice
costs comprising
current service costs,
past-service
costs,
gains
and losses on curtailments
and non-routine
settlements;
a nd
.
Net interest expense or income
Compensated
absences
Accumulated leave,
which
is expected
to be utilized within the next 12
months, is treated as
short-term employee benefit.
The
Company
measures
the expected cost of such absences
as the additional
amount that it expects to
pay
as a result of
the
unused
entitlement that has accumulated
at the reporting date.
The Company
treats accumulated leave
expected to be
carried forward beyond
twelve
months,
as long-term
employee benefit
for measurement
purposes.
Such
long-term compensated absences
are
provided
for based
on the actuarial valuation
using the
projected
unit
credit
method
at the
year-end,
Actuarial
gains
/
losses are immediately
taken to the
Statement of Profit
and
Loss and are not deferred. The
Company
presents
the leave as a current liability in
the
Balance
Sheet,
as the Company
believes
that it does not have an
unconditional right to defer
its settlement for 12 months
after the reporting date.
o)
Financial instruments
A financial
instrument is
any contract that
gives
rise
to a financial asset of
one entity and a financial liability
or equity
instrument of another entity.
Financial
assets
Initial
recognition and
measurement
Financial assets are classiFied, at initial
recognition, as
subsequently measured at amortised
cost, fair value
through other
comprehensive
income
(OCI),
and fair value
through
profit
or loss.
L
Page
12 of 33

sunflame Enterprises
Private Limated
Notes Forming
Part
of the
Financial
Statements
(Amount
in {
lakhs, unless otherwise stated)
CIN No. : U74899DL1984PTCO18992
The classification of
financial
assets at initial recognition depends
on the
financial
asset's contractual
cash flow characteristics
and the Company's business
model for managing
them. With the
exception of trade receivables
that do not contain
a
significant
Financing component or for which
the Company has applied the
practical
expedient, the Company initially
measures
a
financial asset at its fair value
plus,
in the case of
a
financial
asset not at fair value
through
proFit
or loss, transaction
costs.
Trade receivables that do not contain a significant financing component
or for which the
Company has applied the
practical
exoedient
are measured at
the transaction
Drice
determined under Ind AS 115.
In
order
for
a financial asset to be classified and measured
at amortised cost or fair value
through OCI, it needs
to
give
rise
to
cash flows that are'solely
payments
of
principal
and interest
(SPPI)'on
the
principal
amount outstanding.
This assessment is
referred to as the SPPI test and is
performed
at an instrument level. Financial
assets with cash flows
that are not
SPPI are
classified
and measured at tair value throuqh
profit
or loss,
irrespective of the business model,
The Company's
business model for
managing
financial
assets refers to how it
manages its financial assets in
orderto
generate
cash
flows.The business model determines whether
cash flows
will
result from
collectinq contractual cash flows,
sellino the
financial assets, or both.
Financial
assets classified and measured at
amortised cost are held within a
business model with the objective
to hold financial
assets
in order to collect contractual
cash flows
while
financial assets classified
and
measured
at fair value
throuoh OCI are
held within a business model with the objective of both holding
to collect contractual
cash
flows
and selling.
Purchases or sales of financial assets that require delivery
of assets within a time frame
established by regulation
or
convention
in
the
market
place (regular
way
trades) are recognised
on the trade date, i.e.,
the date that the
Company
commits
to
ourchase
or sell the asset.
Subsequent
measurement
For
purposes
of subsequent measurement financial
assets are classified in following
categories:
1. Financial assets at amortised cost
(debt
instruments)
2.
Financial assets at fair value
through other comprehensive income
(FVTOCI)
with recycling
of cumulative
gains
and losses
(debt
instruments)
3. Financial assets
designated
at
fair value
through OCI with no recycling
of cumulative
gains
and
losses upon de-recognition
(equity
instruments)
4. Financial assets at fair value throuoh
Drofit
or loss
Financial
assets at amortased
cost
(debt
instruments)
A financial asset is measured at amortised cost if both
the following conditions are met:
.
The asset
is held within
a business
model whose
objective is to hold assets for
collecting contractual cash Flows,
and
.
Contractual terms
of
the asset
give
rise
on specified dates to cash flows
that are solely
payments
of
principal
and interest
(SPPI)
on the
principal
amount
outstanding.
This
category
is most relevant
to the Company,
After initial
measurement, such financial
assets are subsequently
measured at
amortised
cost using the effective interest rate
(EIR)
method, Amortised cost is calculated
by taking into account
any discount
or
premium
on
acquisition and fees or costs that are an integral
part
of EIR, The EIR amortization is included
in finance income
in Statement of ProFit and Loss. The losses arising From impairment
are recognised in the
statement ot
profit
and
loss. This
category
generally
applies to loans, deposits, trade and other receivables.
Financial assets at fair value through other
comprehensive income
(FVTOCI)
_
A'financial
asset'is classified as
at the
FVTOCI
if both of the following criteria
are
met:
a)
The objective of the business model is
achieved both by collecting contractual cash flows and
selling the financial
assets,
and
b)
The asset's contractual cash flows represent
SPPI.
Debt instrument
included within
the FWOCI category are measured initially
as
well
as at each reporting
date at fair value. For
debt
instruments, at fair value
through OCI, interest income, foreign exchange revaluation
and
impairment
losses or reversals
are recoqnised
in
the
profit
or loss and computed in
the same
manner
as for financial assets measured
at amortised
cost.
The
remaining
fair value changes are recognised
in OCI. Upon de-recognition, the
cumulative fair value changes
recognised in OCI
is reclassified from the equity to
profit
or loss.
Financial
assets at FVTPL
Financial assets at fair value
through
proFit
or loss are carried in the Balance
Sheet at
fair value
with net changes
in fair value
recognised in the Statement of Profit and Loss.
w/t
I
Page 13 of 33

sunflame Enterprises
Private Limited
Notes Forming Part of the Financial Statements
(Amount
in
< lakhs, unless otherwise
stated)
CIN No. : U74899DL1984PTCO18992
This category includes derivative instruments. Investments
in other entity
and listed equity investments
which the Company
had
not irrevocably elected to classify at fair value
through OCI. Dividends
on listed equity investments
are recognised in
the
Statement
of
Profit
and Loss when the right of
payment
has been established.
De-recognitaon
A financial
asset
(or,
where
applicable, a
part
of a financial
asset or
part
of a
group
of similar
financial
assets) is
primarily
de-
recognised
(i.e,
removed from
the Company's Balance
Sheet)
when:
.
The
rights
to
receive
cash flows from the asset have
expired, or
.
The Company
has
transferred
its rights
to
receive
cash
flows
from
the asset or has
assumed an obligation
to
pay
the
received cash flows in full without material delay
to a third
party
under
a
'passthrough'
arrangement:
and either
(a)
the
Company
has
transferred substantially all the risks
and
rewards
oF the asset,
or
(b)
the Company has neither
transFerred nor
retained substantially all the risks and rewards of
the asset, but has transterred
control of the asset.
When the Company has transferred its rights
to
receive
cash flows from
an asset or has entered
into a
pass-through
arrangement,
it
evaluates if and to what extent it has retained
the risks and rewards
of ownership. When
it has neither
transferred
nor
retained substantially all of the risks
and rewards oF the
asset, nor transferred
control oF the asset,
the
Company
continues
to recognise the transferred asset to
the extent of the Company's
continuing involvement.
In that case,
the Company
also recognises
an associated liability. The
transferred asset and the associated liability
are measured
on a basis
that
reflects the rights and
obligations that the Company has retained.
Continuing
involvement
that takes the
form
of a
guarantee
over
the transferred asset is measured
at the lower of
the original
carryinq
amount otthe asset
and the
maximum
amount ofconsideration
that the Company could
be required to repay.
Impairment
of financial
assets
In accordance
with Ind AS 109,
the Company applies the
expected credit losses
(ECL)
model for
measurement and recognition
of
imDairment loss.
The Company tollows "simpliFied
approach"
For
recognition of impairment
loss allowance on Trade receivables.
The
application
of simplified
approach
does
not require
the Company to track changes
in credit risk. Rather, it recognises
impairment
loss
allowance
based on liFetime ECL5
at each reportinq date, right from its
initial recognition.
For
recognition of impairment
loss on other flnancial
assets and risk exposure, the
Company determines whether
there has
been
a significant increase in
the credit
risk
since initial recognition. If
credit
risk
has not increased
significantly, 12-month
ECL
is used to
provide
for impairment loss. However, if
credit risk has increased
significantly, lifetime ECL is
used. If, in subsequent
period,
credit
quality
of
the
instrument improves
such that there is no longer
a signiticant increase in
credit risk since initial
recognltion, then the Company reverts
to
recognizing impairment
loss allowance
based on 12- months ECL.
Lifetime
ECL are
the expected credit losses resulting
from all
possible
default
events over the expected
life of a financial
instrument.
The 12-month ECL is
a
portion
of the liFetime ECL which
results from default
events that are
Dossible
within
12
months
after the reporting
date.
ECL is the difference between all contractuaI
cash
flows
that are due to
the Company
in
accordance with
the contract and
all
the cash
flows
that the entity expects to receive
(i.e.,
all cash shortfalls), discounted
at the original EIR. When
estimating
the
cash
flows, an entity is required
to consider:
.
All contractual terms
oF the
financial
instrument
(including prepayment,
extension, call
and similar options)
over the
expected
life oF the financial instrument. However,
in rare cases when
the expected life of the financial instrument
cannot be
estimated
reliably,
then the entity is required
to
use
the
remaining
contractual
term of the
financial
instrument
.
Cash
flows from the
sale of collateral held or other credit
enhancements that are integral
to the contractual terms.
As a
practical
expedient,
the Company uses a
provision
matrix
to determine impairment loss
allowance on the
portfolio
of its
trade receivables
(other
than
canteen receivables).
The
provision
matrix is
based on its historically
obserued default rates
over
the expected life of the trade receivables and is
adjusted
for
forward-looking estimates.
At every reporting
date,
the
historically observed default rates
are updated and changes in the forward
looking estimates are
analysed. On that
basis, the
Company estimates the following
provision
matrix
at the
reporting
date:
a
Page
14 of 33
1^

Sunflame
Enterprises Private Limited
Notes Forming
Part of
the
Financial
Statements
(Amount
in < lakhs, unless otherwise stated)
CIN No.
: U74899DL1984PTCO18992
Particulars
0 to
90 days
91 to
180 days
181 to
365 days
Above
1
years
Above 2
years
Default Rate
2.0Oo/o
5.00o/o
25.0Oo/o
7O.O0o/o
100.00o/o
ECL impairment loss allowance
(or
reversal) recognized
during the
period
is recognized
as income,/ expense
in the Statement
of Profit and Loss. This amount is reflected under
the
head 'other
exDenses' in
the Statement of Profit and Loss. For
financial
assets
measured
as at amortised cost, contractual revenue receivables
and lease receivables
ECL is
oresented
as
an
allowance,
i.e., as an integral
part
of
the measurement
of those assets in
the Balance
Sheet.
The allowance
reduces the net
carrying amount, Until the asset meets write-off
criteria, the Company does not reduce
impairment allowance from
the
gross
carrying amount.
Financial
liabilities:
fnitaal
recognation and measurement
Financial liabilities are
classified at
initial recognition
as financial liabilitaes
at
fair
value through
profit
or loss, loans and
borrowings,
payables/
or as derivatives designated
as hedging
instruments
in
an effective hedge, as appropriate.
All financial
liabilities
are recognised initially at fair value
and,
in
the case of loans and
borrowings and
payables,
net of directly
attributable
transaction
costs, The Put Option on the Non-
Controlling Interest
("NCI")
ofsubsidiary
is
initially measured
at the
present value
of the amount
payable
on exercise
oF the option.
The Company's financial liabilities include trade and other
payables,
loans and borrowings.
Subsequent
measurement
The measurement of financial liabilities deDends
on their classification, as described
below:
Loans and borrowings
After initial
recognition,
interest-bearing loans and
borrowings are subsequently measured
at amortised
cost using the EIR
method. Gains and losses
are recognised in Statement of Profit and
Loss
when
the liabilities are
de-recognised as well
as
through
the EIR amortisation
process.
Amortised cost is
calculated by taking
into
account any discount or
premium
on acquisition and fees
or costs that are
an
integral
part
oF
the
EIR, The EIR
amortization
is
included as finance
costs
in
the Statement of Profit and Loss.
De-recognition
A financial liability is de-recognised
when the obligation under the liability is
discharged or cancelled or
expires. When an
existing
financial liability is
replaced by another from the same lender
on substantially different
terms, or the terms of
an
existing liability are substantially modified,
such an exchange or modification is
treated as the de-recognition
of the original
liability and the
recognition
of a new liability. The difference in
the
respective
carrying amounts is recognised
in
the Statement
of ProFit and Loss.
Reclassificataon of fanancial assets
The Company determines classification
of
financial
assets and liabilities on initial recognition.
After initial recognition,
no
reclassification
is made
for financial assets which are
equaty
instruments
and financial
liabilities.
For financial
assets which
are
debt instruments,
a
reclassification is
made only if there is.a
change
in
the business model for managing
those
assets.
Changes
to the business model
are expected to be inFrequent. The Company's
senior management determines
change in
the
business model as a result of external or internal
changes which are significant
to the Company's operations.
Such changes
are
evident to external
parties.
A
change
in
the business model occurs when the
Company either begins
or ceases to
perform
an activity that is significant to its operations. If
the Company reclassifies financial
assets, it applies the reclassification
prospectively
from
the
reclassification
date which is the first day
of the
immediately
next reporting
period
following
the change
in
business model. The
Company does not restate any
previously
recognised
gains,
losses
(including
impairment
gains
or
losses) or interest.
The following table
shows
various
reclassification and how they are
accounted
for:
Original Classification RevisedClassifacation
Ammortised Cost FVTPL
Accounting
Treatment
Fair
value
is measured at reclassification
date. Difference
between
previous
amortized cost and fair value is recognised
in
Statement of
Profit
and
Loss.
l.r
'-:
.
.,
li:
\, ;.
"";. ',.
'r\
,-.'-'-.,
-1
"i:;,.-;l
1.:.t;'v"
,.it:t_.
---,,.-t
-:.
. .1"\
..
.,
r\
ii\
,:l
".:
!
<,
:l
.'l
,..
I
i','
"i
.'
'
/,-/
Page
15 of 33

Sunflame
Enterprises Private Limited
Notes Forming
Part
of the
Financaal
Statements
(Amount
in
-
lakhs, unless otherwise stated)
CIN No. : U74899DL1984PTCO14992
Ammortised Cost
Ammortised Cost FVTOCI
FVTOCI Ammortised
Cost
Fair value
at reclassification
date becomes its new
gross
carrying
amount.
EIR
is calculated based
on the
new
gross
carrying amount,
Fair value is
measured at reclassification
date. Difference between
previous
amortised
cost and fair value is recognised
in OCI. No
change
in
EIR due
to
reclassification.
Fair value at reclassification
date
becomes
its new
amortised
cost
carrying amount.
However, cumulative
gain
or loss in OCI is adjusted
against fair value.
Consequently, the asset is measured
as if it had
always
been measured at amortised
cost,
Fair value
at reclassification date
becomes its new carrying
amount.
No other adjustment
is required.
Assets
continue to be measured
at
fair value.
Cumulative
gain
or loss
previously
recognized in
OCI
is reclassified
to
Statement of Profit and
Loss at the reclassification
date.
FVTPL
FVTOCI
FVTOCI
FVTPL
Offsetting
of financial instru ments
Financials assets and Rnancial liabilities are otfset and
the
net amount
is reported in the Balance
Sheet if there is a
currently
enforceable
legal right
to offset the
recognised
amounts and there is
an
intention
to settle on a net
basis, i,e. to realize
the
assets
and settle the liabilities simultaneouslv,
p)
Cash
and cash equivalents
Cash
and cash equivalents in the Balance
Sheet comprise cash at banks and on hand
and short-term deposits with
an original
maturity of three months or less, that are readily
convertible to a known amount of
cash and
which
are subject to insignificant
risk of changes
in value.
q)
Earnings Per Share
Basic
earnings
per
share
are calculated
by dividing the net
profit
or loss for
the
year
attributable to equity
shareholders by
the
weighted average number of equity shares outstanding during
the
year,
For calculating diluted earnings
per
share, the net
profit
or loss for the
year
attributable
to equity shareholders
and the
weighted
average
number
of shares outstanding during the
year
are adjusted for the eFfects of
all dilutive
potential
equity
shares,
r)
Cash
flow
statement
,
Cash flows are
reported
using the indirect method, whereby
profit/(loss)
before tax is adjusted for
the erfects of transactions
of a non-cash nature and any deferrals or
accruals of
past
or
future
cash receipts or
payments.
The cash flows from
operating,
investing and
financing
activities of the Company are segregated
based on the available inFormation,
2.3 Changes
in accounting
policies
and disclosures
New and amended standards
The Company applied for
the
first-time
certain standards and amendments, which
are effective for annual
periods
beginning
on or after
I April 2022. The
Company has not early adopted
any other standard or amendment
that has been issued
but is
not
vet
effective:
Page
16 of 33

Sunflame Enterprises
Private
Lamated
Notes Forming Paft of the Financial
Statements
(Amount
an t
lakhs,
unless otherrrise stated)
CIN No. : u74899DL1984PTCo18992
2.4
Standards notified but not
yet
effective
The Ministry of corporate Affairs has notified
companies
(Indian
Accounting
Standard) Amendment Rules
2022 dated March
23,2022 to amend the following Ind AS which
are effective from April
Ot,2023.
Ind
AS 1 - Presentation
of Financaal
Statements
-
This amendment
requires the
entities to disclose
their material
accounting
policies
rather
than their significant
accounting
policies,
The
effective date for adoption
of this amendment
is
annual
periods
beginning
on or after April L, 2023. The
Company has
evaluated the amendment
and the impact
of the
amendment
is
insignificant in the financial
statements.
Ind AS 8
-
Accounting Polici6,
Changes an Accounting
Estimates
and
Errors
- This
amendment has introduced
a
definition of'accounting estimates'
and included amendments
to
Ind
AS 8 to help
entities distinguish
changes in accounting
policies
from
chanqes in accounting
estimates. The effective date for
adoption of this amendment
is annual
periods
beginning
on or after April 1. 2023. The Company has
evaluated the amendment
and there is no impact
on its financial
statements.
Ind AS
12
- lncome Taxes - This
amendment has narrowed
the scope of the initial recognition
exemption
so that it does not
apply to
transactions
that
give
rise to
equal and offsetting temporary
differences. The
effective date for
adoption of this
amendment
is
annual
periods
beginning on
or after Apill l,2023. The
Company has evaluated
the amendment
and there is no
impact on its financial
statement.
Page 17 of
33

It
a0
o!r
d(o
jd
dlo
(Yl
9*
noi'
iiN
d
NO
or;'
N
6;
N
c
(,
CI
u
F
bE
!lt
*;
EE
oo
(JI
lr
-
N!-
.N
N
nN
o
ON
.N
O
o
@n
.N
N.
nN
@
oo
-n
N.
N$
o
E!
I.9
0,
5E
E
ct
o
o
Jx
N.
J
o
IU
z
o
$
SN
oo
$
OO
N@
@N
@
N
O
o
N
a2
':.E
o6
u
.ii
o
c
H
d8
(,L
L=
au
9X
'E
ii
L
d-
+!
Qt
LC
T':
AE
o
E
>g|
+.1
tt
6'=
L6
c
,o
.q
-
g
@!
!O
fo
oo
o<
c-
OO
!o
a!
<U
d
IE
o
o
t!
o
g
c
.9
=
.9-
'-d
o-
o.=
'E-
o!
CC
oo
2?
!!
!!
N
t!
t!
c
o
o
t!
o
I
!
o
.E
o
o
>t
llc
o
E
J
o.
F
d
ul
o.
o
d
o.
rl
I
a,
E
o
E
It
6
'6
c^
EE
r!E
gfi
o0,
clo
r
5'i
!a h
.E
E;
=Ho
drXq
i
6'3
.:9E
o.9-
oh
ui
o:t
6?x
L
tg.:9
3a
c
o
ci?
!
c;
fi'i c
e5I
Et!:
-9oi
!qr:
E.liE
a9a
rrzJ

Sunflame
Enterprises
Private Limited
Notes Forming
Palt of the Special
Purpose
Financial Statements
(Amount
in INR lakhs,
unless otherwise stated)
4 INVESTMENT
PROPERW
Particulars
As
at
March
31,
2023
Opening
balance as on January
t2,2023
Addition on account
of acquisition
-
Flat at Jasola
Closing
balance as on
March 31,2()23
5
OTHER
INTANGIBLE ASSETS
1so.oo
(t
in lakhs'l
Particulars
March
31
As at
2023
Opening
balance
as on
January
L2,2023
Addition
on account acouisition
Additions
during the
period
Disposals during
the
period
Adi"ctment< drrrinn thp nari^d /if:nv\
-
31.51
Accumulated
Amortization
(t
in lakhs'l
Opening
balance as on January
12,2023
JI.fI
Addition on
account acquisition
Charge for the
period
Net block
28.15
0.88
Disoosals
Closing
balance as on March 31, 2023
29.03
(t
in lakhs'l
As at Januarv
11, 2023
3.36
As at March
31, 2023
2,4a
INVESTMENTS
As at
March
31, 2023
7 LOANS
(NON-
CURRENT)
Particulars
As at
March
31, 2O23
Opening
balance as on January
12,2023
Addition on account
of acouisition
Closing
balance
as on March
31,
2O23
Opening
balance
as on
January
12,2023
Addition on account
of
acquisition
-
M/s Universal
Build
well
Pvt. Ltd.
-
M/s International
Land Developers Pvt Ltd.
- M/s ALM Infotech City
Pvt
Ltd.
Cfosing balance
as on March 3L,2{J23
8 OTHER
NON-CURRENTASSETS
0.45
o.45
50.00
304.64
4
400,oo
(t
in lakhsl
Particulars
As at
2023March 31
15.36
Security
deposits
(unsecured,
considered
good)
Total other
non-cu|.rent assets
INVENTORIES
[Valued
at lower of cost or
net realisable value]
March
31, 2023
Raw materials
Finished
goods
closing balance
as on March 31, 2023
Notes:
(a)
The above includes
goods
in
transit as
908.1 0
2,734.74
3,642.84
includes
goods
in
transit as under
.
111.09
1 11.O9
u/
Page 19
of 33
Finished
goods
Total

Sunflame
Enterprises
Private Limited
Notes Forming
Part ofthe Special
Purpose Fanancial
Statements
(Amount
in INR lakhs,
unless otherwise stated)
10
TRADE RECEIVAELES
As
at
March
31, 2023
3,393.16
(34.31)
3,358.85
(t
in lakhs)
Secured, considered
good
Unsecured, considered
good
Trade receivables
which
have significant
increase in
credit
risk
Trade receivables
- credit impaired
Less: Impairment
allowance
(allowance
for
bad & doubtful debts)
Unsecured, considered
good
based on expected credit loss
provisioning
Trade receivables
whlch have significant increase in credit risk
Trade receivables
- credit imDaired
Closing balance
as on
March
3'-,2023
Trade receivable
ageing schedule
Particulars
Current
but
Outstanding for following
periods
from the date of booking
not
due
the invoice
Total
as at
March
31, 2023
Less than 6 months
6 months
-1
year
More than
1-2
years
2-3
years 3
years
i) Undisputed
trade
receivables
-
considered
good
ii) Undisputed trade
receivables
-
which
have significant increase
in
credit
risk
iii) Undisputed
trade receivables
-
credit impaired
iv) Disputed trade
receivables
-
considered
good
v) Disputed trade
receivables
-
which
have significant increase
in
-
3,076.33 207.96
108.25 0.62
3,393.16
credit
risk
vi) Disputed trade
receivables
-
.rFdif im^AirFd
Total
-
3,076.33 207.96 108.25
0.62
-
3,393-16
11 CASH AND CASH
EQUIVALENTS
AND OTHER BANK
BALANCES
tin
Particulars
As
at
March 31, 2023
Cash
and cash
equivalents
(a)
Cash on hand
(b)
Balances with banks:
On current
accounts
Closing
balance as on
March
31.2023
Other
bank balances
0.88
633.95
634.83
(t
in lakhs)
Particulars
March 31
As
at
2023
Deposits with original
maturity for more
than 3
months but
less than
12 months
Total
12 CURRENT TAX
ASSETS
(NET)
2,688.33
2.684.33
(<
in
lakhs)
Particulars As
at
March
31,
2023
Income tax
refundable
Closing
balance as on
March
31,2023
39.40
39.40
13 OTHER
CURRENT
ASSETS
Particulars As
at
March
31, 2023
Balance
with
government
authorities
Advance to suppliers/Employees
Prepaid expenses
Cfosing
balance'as
on March 3I,2()23
724.52
36.38
23.69
Page 20 of
33
.
184.59

Sunflame Enterprises
Private
Limited
Notes Forming Part of the Special Purpose Financial
Statements
(Amount
in INR lakhs,
unless
otheruise stated)
14 EQUITY SHARE CAPITAL
particulars
As at March
31, 2023
Number of
t
in lakhs
(a)
Authorised share capital:
Equity shares
of face
value
{ 100
(b)
Issued, subscribed and fully
paid-up
share capital:
Equity shares of
{ 100
100,000
15,650
100.00
15.65
(a)
Reconciliation of the number of shares and amount outstanding
at the beginning and at
the end of the reporting
period:
Number
of
Amount
Equity shares
opening as at lanuary
L2,2023
Changes
during the
period
Outstanding at as March 3L,2()23
(c)
Details
of shareholders
holding more
than 5olo shares in the Company:
15,650
15.65
15650
Name
of
As
at March
Number
ot
o/o
ot
holding
in that
shares held
class of shares
V-Guard Industries Limited
&
its nominees
r-5,650
lOOo/o
15.6sO aOOo/o
(d)
Details of shares
held
by
promoters:
No. of shares at the
Change No. of shares
at the
Promoter Name beginning of the
year
during
the
end of the
year
year
Equity shares of
{ 100 each fully
paid
Promoters
V-Guard Industries
Limited
& its nominees
(e)
Shares held by
holding
/
ultimate holding company
and
/
or theirsubsidiaries
/
associates:
1 5,650
1 5,650
As at March
31.2023
Number of
t in lakhs
V-Guard Industries Limited
(along
with its nominees),
the holding company 15,650
shares of
face value of ? 100 each
15
OTHER EQUITY
15
650
15.65
tin
Particulars
As
at
March
31,
2023
Capital Redemption reserve
Balance at
the
beginning of the
year
Transfer to reserue
Transfer from reserve
Balance at th6
end of
the
year
General
reserve
Balance at the beginning of the
year
Transfer to reserve
Balance at the end of the
year
Retained earnings
Balance at the beginning of the
year
Profit/(loss) made during the
year
Tranfer
to
Capital
redemption
reserye
Ealance at the end
of
the
year
Other Comprehensive
Income
Balance at the beginning of the
year
Additions during the
year
Balance at
the
end of the
year
Total
a
I.)U
1.50
3,975.00
3,975.OO
6,62t.24
672.r4
7,293.46
1.47
t.47
Page 21
of 33
L[,27I.44

Sunflame Enterprises
Private
Limited
Notes Forming Part of
the Special Purpose Financial
Statements
(Amount
in
INR lakhs,
unless
otheruise stated)
16
Lease
liability
(t
in lakhs)
Particulars
(+)
Addition of
lease
liability
(+)
Finance cost
on lease liability
(-)
Lease
Payments made during the
year
Balance
as at the end of
the
year
As at
March
31. 2O23
Bafance as at January
l2r 2|J23
246.47
4.47
Maturity analysis
of lease
liabilities
is tabulated below :-
Particulars
As
at
March 31, 2023
Year 1
135.00
(29.40)
--------------
z[s4-
135.00
(48.06)
22t.94
10 1.70
L20.24
(t
in lakhsl
Year 7
Less: unearned
interest
Classification
Current
Lease Liability
Non-Current Lease
Liability
17 NON.CURRENT
PROVISIONS
Particulars
As at
t4.48
March 31, 2023
Provision for Gratuity
3.88
Provision for Leave
Encashment
Closing
balance as on
March 31, 2023
18
OTHER
NON-CURRENT
LIABILITIES
(t
in
lakhs)
Particulars
As
at
2023March 3
122.57
168.69
f { in lakhs)
19
Security deposits
Retention
money
Closing balance
as on March 31, 2023
TRADE PAYABLES
Particulars
As at
2023
[carried
at
a) Total outstanding
dues of micro enterprises and
small enterprises
b)
Total outstanding
dues
of creditors other than
micro
enterprises and small enterprises
Total
Trade
payables
ageing schedule
March 3
3,334.27
3.334.2r
-
Total outstanding
dues of micro enterprises enterprises
- Total outstanding
dues of creditors other
than
micro
enterprises and
small
enterDrises
-
Disputed dues
of micro enterprises and small enterprises
-
Disputed
dues of creditors other than micro enterprises and
small
3,32L.23 5.29
7.69
3,334.2L
334.2L
xThe
information required to be disclosed underthe Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
Development Act, 2006
has been determined
to the extent such
parties
can
be identified on the basis of information available with the Company. There
are no overdue amounts
payable
to
parties
on account of the
principal
amounts and/or
interest.
Micro, Smal!
and Medium Enterprises
The Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises has issued an office memorandum
dated 28 August 2008
which recommends
that the Micro and
Small
Enterprises should
mention
in their correspondence with its customers, the Entrepreneurs
Memorandum Number
as allocated
after
filing
of the Memorandum
in
accordance
with the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprise Development Act, 2006
('the
Act').
Accordingly, the disclosure
in respect
of the
amounts
payable
to such enterprises as at March
3L, 2023 has been
made in the financial
statements based on
information received
and available with
the Company.
Further in view
of the Management, no interest
is
payable
in
accordance with the
provisions
of the Act.
The Company
has not received
any claim
for interest from
any supplier as at the balance sheet date.

Sunflame
Enterprises Private
Limited
Notes
Forming Part
of
the Special Purpose Financial
Statements
(Amount
in INR lakhs, unless otherwise stated)
(t
in lakhs)
Particulars
As at
a)
The
principal
amount
and
the
interest
due thereon
(to
be shown separately) remaining unpaid
to
any supplier
as at the end of each accounting
year;
b)
The amount of interest
paid
by the buyer under MSMED Act, 2006
along with the amounts of the
payment
made
to the
supplier beyond
the
appointed
day during each accounting
year;
c)
The amount of
interest due
and
payable
for the
period
of delay in making
payment
(which
has
been
paid
but beyond the appointed day during the
year)
but without adding the interest
specified
underthe MSMED Act, 2006);
d)
The amount of interest accrued and remaining unpaid at the end
of
accounting
year;
and
e)
The amount of further interest due and
payable
even in
the succeeding
year,
until such date
when
the
interest dues as above are
actually
paid
to the small enterprise, for the
purpose
of
disallowance as a deductible exoenditure under section 23.
20 OTHER CURRENT
LIABILITIES
(t
in
lakhs)
Particulars
As
at
March
31, 2O23
(a)
Statutory
liabilities*
(b)
Contract
Liabilities
(c)
Staff reimbursements
(e)
Expenses
payable
Total
*
Represents contributions to
Provident fund,
employee state insurance, 8onus, withholding
taxes & GST etc.
21
CURRENTTAX
LIABILITIES
(NET)
132.85
138.53
20.39
797
fa in lakhsl
Particulars
As
at
March 31, 2023
Provision for taxation
Total
55.47
55.47
22 CURRENT
PROVISIONS
Particulars
As at
March
31, 2023
Provision for
leave
encashment
Provision for Gratuity
Total
7.Ll
h
Pate 23
of 33

Sunflame Enterprises Private
Limited
Notes
Forming Part of the Special
Purpose Financial
Statements
(Amount
in INR lakhs, unless
otherwise
stated)
23
REVENUE FROM OPERATIONS
Particulars
For
the
period
January L2,2f)23
to
March 31,2023
Revenue from contracts wath
customers
Sale
of
products
Total
revenue from
contracts with
customers
24
OTHER INCOME
5,690.10
5.59().10
Particulars
For
the
period
January
L2,2023
to March
31,2023
Finance
income*
Exchange differences
(net)
Others
Total
*
Finance income comprises
of following:
Interest income from bank
on deposits
Interest income on
tax
free
bonds
Total
25a
COST OF
MATERIALS
CONSUMED
38.67
7.46
0.08
46.2L
38.68
3a.5A
Partaculars
For
the
period
Januarv L2.2()23
to March 31.2023
Inventory
at the beginning of
the
period
Add: Purchases
Less: Inventory
at the end of the
period
Total
25b
(INCREASE)
/
DECREASE
IN INVENTORIES
OF FINTSHED
GOODS
973.57
1,335.38
908.10
1,34()_85
Particulars
For
the
period
January L2,2023
to March
3L,2tJ23
Inventories at the end
of the
period
Finished
goods
Total
(A)
Inventories at the beginning
of the
period
Finished
goods
Total
(B)
Net
(Increase)/decrease
in inventories
Finished
goods
Total
26 Purchase of Finished
products
3,O29.54
2,5-t6.55
(4s2.9e)
(452.99)
Pa rticulars
For
the
period
January 12,2023
to
March
31,2023
Finished
goods
Total
2,600.35
Lt
r,
it
I!
-
j;
.'/
Page
24 of 33
2.5()()-3s

Sunflame
Enterprises Private Limited
27
EMPLOYEE
BENEFITS EXPENSES
Particulars
For
the
period
January a2,2lJ23
to
March
31-,2()23
Salaries
& Wages
Contribution
to
provident
and other funds
Gratuity
expense
Staff
welfare expenses
Total
28
FINANCE
COSTS
27L.91
5.83
1.53
3.97
243-24
Particulars
For the
period
January
'-2,2()23
to March
3'-,2023
Interest on lease
liability
Other
interest expense
Total
29 DEPRECIATION AND AMORTISATION EXPENSES
4.47
0.16
Particulars
For the
period
L2,2023
to March
3L,2023
66.65
0.88
26.34
93.47
30
Depreciation of
property, plant
and
equipment
Amortisation
of intangible
assets
Depreciation of
right-of-use
assets
Tota!
OTHER
EXPENSES
Particulars
For the
period
Januarv t2.2()23
to March 3t.2fJ23
Power and
fuel
Rent
-Building
-Plant
and
machinery
-Vehicle
-Others
Rates and
taxes
Travelling
and conveyance
Freight
& forwarding charges
Advertisement and business
promotion
expenses
CSR
expenditure
(refer
below)
Legal and
professional
fees*
Provision
for doubtful debts
Diminution in
value
of inventory
After sales services
Commission
expense
Insurance
expenses
lob work charges
Printing and
stationery
Tp<finn cYnen<a<
Security
charges
Write off of
fixed
assets
Donation
paid
Miscellaneous expenses
Total
4.56
0.36
9.23
7.42
0.89
2.99
2.7L
65.05
242.44
168.24
19.38
55.33
(
1s.69)
18.81
305.00
22.77
4.O9
44.O5
2.24
3.16
6.!7
4.10
o.29
6.30
Particulars
For
the
period
January
L2,2023 to March
31.,2o23
ImDairment allowance
Page 25
of 33
L,l_

Sunflame Enterprises Private Limited
3O(a) EXPENDITURE ON CORPORATE
SOCIAL RESPONSIBIIJTY
Particulars
For the
period
January 12,2o23
to March
31-,20.23
(a)
Gross amount
required
to be spent by
the company during the
period
(b)
Amount of expenditure incurred
(c)
Shortfall at the end of
the
year*
(d)
Shortfall at the end of last
year,
spent during the
year
(d)
Total of
previous year
shortfall
(e)
Reason for shortfall
(f)
Details
of
related
party
transactions, e.9.,
contribution to a trust
controlled by the company
in
relation
to
CSR expenditure
as
per
relevant Accounting
Standard
(g)
Where a
provision
is made with respectto
a
liability
incurred
by entering into
a contractual
obligation, the movements in
the
provision
during
the
year
shall be shown
separately
*
Shortfall amount has been transferred
to the scheduled
bank account within
30 days fi'om the
end of the financial
year.
19.38
19.38
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil
Nil
ffi
\h
Page 26
of 33

Sunflame Enterprises Pravate Limited
Notes Formang Part of the
Special Purpose Financial
Statements
(Amount
in t lakhs, unless
otherwise stated)
31
INCOME TAXES
The major components
oF income tax expense for
the
period
ended
March
3t,2023 are:
(a)
Statement of
profit
and
loss
(t
in lakhs'l
Particulars
For the
period
Januarv L2,2()23
to March 3'.,2023
Current income tax:
Current income tax charge
Income tax adjustment related to
earlier
years
Deferred tax:
Relating to origination and reversal
of temporary differences
fncome
tax
expense
reported in the
statement of
profit
or loss
(b)
OCI Section
787.a3
(6.74)
(
1.91)
779.14
(t
in lakhsl
Particulars
For the
peraod
January L2,2|J23
to March 3'.,2(J23
Income tax related
to
items recognised
in OCI during
the
year
on re-measurement
(losses)
/
gains
on defined benefit
plans
(c)
Reconciliation of tax expense
and the accounting
profit
multiplied
by
tax
rate:
1.89
(a
in lakhs'l
Particulars
For the
period
Januarv
12,2fJ23 to March 31.2023
Accounting
profit
before income
tax
At statutory income tax rate of 25.1680/o
(March
31, 2O27:25.7680/o)
Permanent differences
-Interest
Income on Tax free Bonds
-Donation
exDense
-Interest expense under
section
234C
of the Income Tax Act,
1961
-Others
-ImDairment
allowance on Loans
(d)
Reconciliation of deferred tax
asset/(liability)
(net)
7,,728,L4
434.94
(23.18)
19.58
0.55
19.27
324.O2
779.La
(t
in lakhs)
Particulars
For the
period
,anuarv
!2,2()23 to March
3L,2(J23
Tax effect of items constituting
deferred tax liability
On difference between book balance
and tax base of
property,
plant
and equipment
Provision For Gratuity
Provision
for Leave
Encashment
Bonus Payable Disallowed
Uls 43 B
Total deferred tax
asset
(A)
10.02
0.98
5.43
18.54
Deferred
payment
liabilities
Total deferredtax liability
(B)
Deferred
tax
asset recognised
(net) (C
=
(A-B))
Reflected in the Balance
Sheet as follows:
34.97
(t
in lakhs'l
Particulars
As at March
31,2(J23
Deferred
tax
assets
Deferred tax liabilities
Deferred tax assets, net
34.97
34.97
The
company offsets tax assets and liabilities if and
only if it has
a
legally
enforceable right
to set off
current tax assets and
current tax
liabilities and the deferred
tax assets and deferred tax liabilities
relate to income
taxes levied bv
the same tax authoritv.
In assessing the realisability
of deferred tax assets, management
considers whether
it is
probable,
that some
portion,
or all, of the deferred
tax assets will not be realised. The ultimate realisation
of deferred
tax assets is dependent
upon
the
generation
of future
taxable income
during the
periods
in which
the temporary differences
become deductible. Management
considers
the
projected
future taxable income
and tax
planning
strategies in making this
assessment. Based on the level
of historical taxable
income and
projections
for future
taxable incomes
over
the
periods
in which
the deferred tax assets are
deductible, management
believes that it is
pt:obable
that the Company will be
able to realise
the benefits of those deductible
differences in future.

Sunflame
Enterprises Private Limited
Notes Forming
Part of the
Special
Purpose
Financial
Statements
(Amount
in t lakhs, unless otherwise
stated)
32 COMMITMENTS
AND
CONTTNGENCIES
a) Capital
commatments
(Net
of advances)
Particulars
As
at March 3L,2(J23
Estimated amount of contracts remaining to be
executed on capital account and
not orovrded
tor
b)
contingentliabilities
In
the
ordinary course of business, the
Company
faces
claims and assertions
by
various
parties.
The
Company assesses
such
claims and
assertions and
monitors
the legal environment on an ongoing
basis
with
the assistance
of external legal
counsel, wherever
necessary.
The
Company
records a liability for any
claims
where
a
potential
loss is
probable
and capable of
being estimated
and discloses
such
matters
in its
financial statements, if material. For
potential
losses that are considered
possible,
but not
probable,
the Company
provides
disclosure in
the
financial statements but does
not record
a liability in its accounts
unless the loss becomes
probable.
The following
is
a
description
of claims and assertions where
a
potential
loss is
possible,
but not
probable.
The
Company
believes that none
of
the
contingencies described below would have a material
adverse effect on the
Company's financial
condition, results
of operations
or casn
flows,
Particulars
As at March
3L,2(J23
Potential bonus
liability
Total
Notes:
t7.34
7,7-34
*Due
to an amendment
in
the Payment of Bonus Act with retrospective
effect from
O1.O4.2O74,
the company has
estimated a
potential
fiability
of < 17.34 lakhs. As
petitions
are currently
pending
for
adjudication before High
Courts challenging
the
retrospective
effect of
the
amendment,
the company has recognized this liability
as a contingent liability
and has not
accounted for it as a
provision
in its frnancial
statements.
33 LEASES
(i)
The Company's
lease
asset consist of leases for land and buildings.
The Company
also has certain leases with
lease terms
of 12 months
or
less.
The Company applies the short
term
lease recognition
exemptions tor
these leases.
(ii)
The
carrying value of right of use
assets recognised and the movements
thereof during
the
period
ended March
3L,2023:
Particulars
Right of
use assets
(Leasehold
Buildinos'l
Addition
Accretion
of interest
Payments
Closing
Balance at
March
31,2023
246.A7
4.47
(2e.40)
221.94
(iii)
Amounts recognised in Statement of Profit
and
Loss
during the
period:
(?
in lakhs)
January 12, 2023
to March
31, 2023
Depreciation
charge of right-of-use
assets
26.34
Particulars
Finance cost accrued during the
year
Total
For
the
period
4.47
30.41
(iv)
The
Company
does not face
a significant
liquidity
risk with regard
to
its lease
liabilities
as the current assets
are sufficient to meet
the
obligations
related to
lease
liabilities as and when they fall
due.
Page 28
of 33

Sunfl ame
Enterprises
Private Limited
Notes Forming
Part of the Special Purpose Financial
Statements
(Amount
in < lakhs, unless otherwise
stated)
34 EMPLOYEE BENEFTT PLANS
A. Defined Contributions Plans
The Company makes Provident Fund
contributions to defined contribution
plan
for all
qualifying
employees.
Under the
Scheme, the
Company
is required
to contribute a specified
percentage
of the
payroll
costs
to
fund
the benefits. The
Company recognized
? 5.82 lakhs
for Provident Fund
contributions in the
Statement of
Profit
and Loss. The
contributions
payable
to these
plans
by the company
are at rates
specified in the rules of the schemes.
B. Defined Benefit Plans
a) Contribution to Gratuity Funds
- Employee's Gratuity Fund
The Company has
a defined benefit
gratuity plan,
which is regulated
as
per
the
provisions
of Payment
of Gratuity ACr, 7972.
The liability
for
the same
is
recognized on the basis of actuarial valuation,
b) L€ve Encashment/
Compensated Absence
The
company
has a
long
term employee beneifit
plan
related
to leave
encashment for its employees.
Under this
plan,
they are entitled
to
encashment of earned leaves subject
to certain limits and other
conditions sp{ified for
the same. The liabilities
towards leave
encashment
have
been
Drovided on the basis of actuarial valuation.
These
plans
typically expose the company
to actuarial risks such as: Investment
risk, Interest rate
risk, Longevity
risk and Salary risk.
Investment risk: The
probability
or likelihood
of occurrence of losses relative
to the expected return
on any
particular
investment.
Interest Rate risk:
The defined benefit obligation
clculated uses a discount rate
based on the
prevailing
market
yields
of Government
of
India securities as at the Balance
Sheet date for the estimated
term of the obligations. If
bond
yields
fall, the
defined benefit
obligation will
tend
to increase.
Longevity risk: The
present
value of
the defined benefit
plan
liability
is calculated by reference
to the best
estimate of the mortality
of
plan participants
both during
and after their employment. An increase
in the life
expectancy of the
plan participants
will increase
the
plan's
liability.
Salary Escalation Risk: The
estimate of future salary increases
considered, takes into
account the inflation,
seniority,
promotion,
increments and other relevant factors.
Higher than expected increases
in salary will increase
the defined
benefit obligation.
The components of the
gratuity plan
benefit obligations are
shown below:
t in lakhs
Particulare
Bafance as at January t2, 2023
Current
service
cost
Interest cost
Benefits
paid
Re-measurements due to:
Actuarial loss arising from change in demographic
assumptions
Actuarial loss arising from change in financial
assumptions
Actuarial loss arising
on account of experience changes
Balance as at
the end of the
year
45.67
1.50
0.60
(2.34)
0.01
3L,2|J23
Balance
as at at January
L2t 2023
Employer contributions
Expected return on
plan
assets
Benefits
Daid
Previous
payment
received from LIC
Re-measurements due to:
Actual
return
on
plan
assets less Interest on
plan
assets
Balance as at
the
end of the
year
4r.82
0.58
(2.34)
(0.46)
o.70
t in
lakhs
March
31, 2023
Present value of defined
benefit obligations as at end of
the
year
Fair
value
of
plan
assets as at the end of the
year
Liability recognised in the Balance Sheet
as at the end of the
year
Classification
Current
Non-current
il
{:l
44.17
40.
3.47
3.47
Sunfl ame
Enterprises Private Limited
Notes
Forming Part of the Special Purpose Financial
Statements
(Amount
in
-
lakhs, unless
otherwise stated)
The
major categories of
plan
assets of the
fair value
of the total
plan
assets are as
follows:
Particulars
investments
Insurer manaoed funds
({
in lakhs)
Pa rticu la
rs
For
the
period
January L2,2023
to March 31,2023
Service
cost
Interest
cost
Expected return on
plan
assets
1.50
0.60
(0.s7)
Particulars
Current
service cost
Net
interest expense
Re-measurements
the
p€riod
due
to:
Changes in
financial
assumptions
Changes
in demographic assumptions
Experience
adjustments
Return on
plan
assets
(excluding
amounts included in net interest
expense)
0.01
(L.27)
(0.70)
Amount
recognised
in Other Comprehensive
Income
Discount
rate
Future salary
increase
Mortality rate
(%
of IALM 12-14)
Attrition
/
Withdrawal rates, based
on completed
years
of service:
(per
annum)
Upto 30
years
From 31 to 44
years
Above 44
years
The estimates of future salary increases, considered
in actuarial valuation,
take account of inflation,
seniority,
promotion
relevant
factors such as supply and demand factors in
the employment market.
Particulars
March 31.2023
Discount rate
Salary Gcalation rate
(
1.e6)
7 .O4Vo
10.00%
100.00%
15.00%
35.00%
50.o090
and other
t in
lakhs
Effect
on DBO due to 0.5Yo increase
Effect
on DBO due to 0.5olo
decrease
(
1.3e)
(0.44)
(0.4s)
(
1.38)
The
sensitivity analysis above have been determined
based on a method that
extrapolates the impact
on defined benefit
obligation as a
result
of reasonable changes in key assumptions
occurring at the
end
of
the
reporting
period
Maturity
profile
of Defined Benefit Obligation:
0 to
1 Year
1 to
2 Year
2 to
3 Year
3 to
4 Year
4 to 5
Year
5 to 6
Year
6
Year onwards
Total
qpected
payments
44.L7
35 SEGMENT
REPORTING
The segment
reportinq
of the Company
has
been
prepared
in
accordance with Ind AS-108,
"Operating
Segment". Based on the
"management
approach" as defined in Ind-AS 108 -
Operating Segments,
the Chief Operatinq Decision
Maker evaluates the
Company's
performance
and allocates'resources based
on an analysis of various
performance
indicators
by business segments
and segment
information is
presented
accordingly.
Accordingly,
the management has identified
only one segment i.e. Consumer
durables.
For the
period
ended March 2023, no individual customer
accounted for 10
percent
or more of the
Company's revenue.
16.20
12.05
5.55
3.58
2.O2
7.22
3.55
l^-
Page 30 of 33
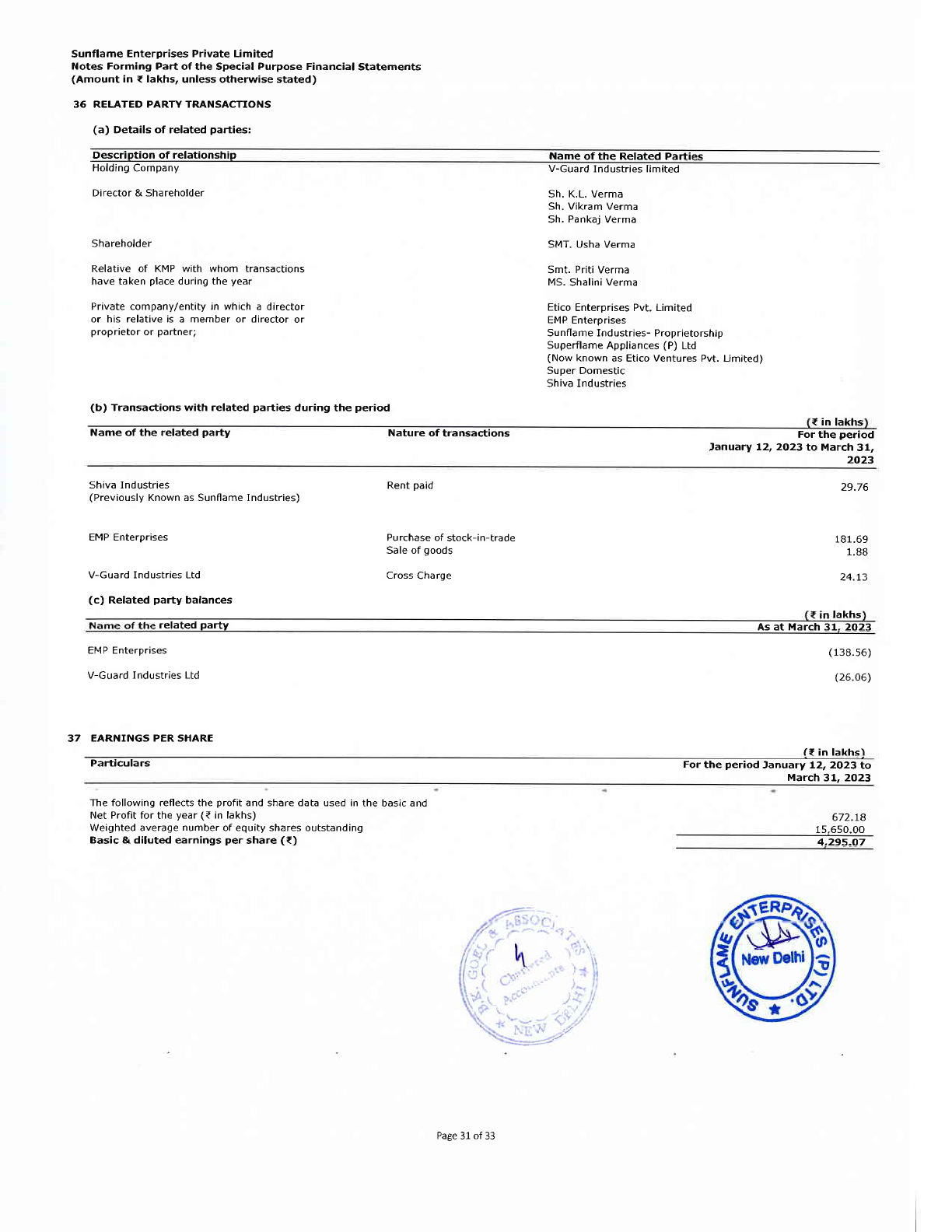
Sunflame
Enterprises Private Limited
Notes Forming Part
of the Special
Purpose
Financial
Statements
(Amount
in
{
lakhs,
unless otherwise stated)
36 RELATED PARW TRANSACTIONS
(a)
Details of related
parties:
Description of relationship
Name
of the Related Parties
Holding Company
Director & Shareholder
Shareholder
Relative of KMP with whom transactions
have
taken
place
during the
year
Private company/entity in which a director
or his relative is a member or director
or
proprietor
or
partner;
V-Guard
Industries Iimited
Sh. K.L. Verma
Sh. Vikram Verma
Sh.
Pankaj
Verma
SMT. Usha Verma
Smt.
Priti
Verma
MS.
Shalini
Verma
Etico
Enterprises Pvt. Limited
EMP Enterprises
Sunflame Industries- Proprietorship
Superflame Appliances
(P)
Ltd
(Now
known
as Etico Ventures Pvt. Limited)
Super Domestic
Shiva Industries
(b)
Transactions with related
parties
during
the
period
t in
lakhs
Name of the related
party
Nature of
transactions
For the
period
tanuary L2, 2023
to March
31,
2023
Shiva Industries
(Previously
Known as Sunflame Industries)
EMP Enterprises
V-Guard Industries Ltd
(c)
Related
party
balances
Rent
paid
Purchase of
stock-in-trade
Sale of
goods
Cross
Charge
29.76
181.69
1.88
24.t3
related
party
lakhs
As at March 3L.2|J23
FMP Fntarnricp<
V-Guard Industries Ltd
37
EARNINGS PERSHARE
(
138.
s6)
(26.06)
(t
in lakhs l
Particulars
For
the
period
January L2,2023
to
March
31, 2023
The following reflects the
profit
and share data used in
the basic and
Net
Profit
for the
year (?
in lakhs)
Weighted average
number
of equity shares outstanding
Basic & diluted earnings
per
share
(t)
:./
672.rA
15.650.00
4.295-O7
Page
31
of
33

Sunflame
Enterprises Private Limited
Notes Forming
Part of the
Special
Purpose
Financial Statements
(Amount
in
-
lakhs, unless otheruise
stated)
below,
is
a comparison by class of
the carrying amounts and fair value of
the Company's financial instruments:
3r,2023
Fair value
Financial
assets
Financial assets
at amortised
cost
Cash and cash equivalents
Trade receivables
Other bank
balances
LOa n
Investments
Total
Financial liabilities
Financial
liabilities
at amortised
cost
Lease liability
Trade
payables
Total
Note:
634.83
3,358.85
2,688.33
.
400.o0
0.45
634.83
3,358.85
2,688.33
400.o0
o-45
7,|J82.46
7.082.46
227.94
22L.94
27
34
556.1s
The management
assessed
that fair value of
cash
and
cash equivalents, trade receivables,
other bank
balances, Bank deposits with
original maturity
of more
than
12 months,
investments, loan,
other non-current financial assets, and
trade
payables
approximate
their carrying
amounts largely
due to the short-term
maturities
of these instruments.
The
fair value of loans and lease liabilities is
estimated by discounting future
cash flows using rates
currently available
for debt on
similar terms, credit
risk and
remaining
maturities. The same would
be sensitive to a reasonably
possible
change in
the
forecasted
cash
flows or the discount rate. There
are no unobseruable
inpuLs that impact
fair value.
39 CAPITAL
MANAGEMENT
For the
purpose
of
the Company's capital management,
capital
includes
issued equity
capital and other
equity reserues
attributable to the
equity holders
of the
Company.
The
primary
objective of
the Company's capital management is
to
maximise
the shareholder
value.
The Company
manages its
capital so as to safeguard its ability to continue
as a
going
concern
and to optimise returns
to shareholders.
The capital structure
of
the
Company
is
based
on manaqement's
judgement
of its strategic
and day-to-day needs with
a focus on total
equaty so as
to
maintain investor,
creditors
and market
confidence.
The Company monitors
Capital using Gearing ratio, which
is net debt divided
by total capital
plus
net debt.
Particulars
Debt
Less: Cash and
cash equivalents
and other bank balances
tan
221.94
634.84
Net debt
(A)
Equity share capital
Other equity
Total capital
Capital
and
Net Debt
(B)
Gearing
Ratio
(A/B)
(4L2.eo)
15.65
71,277.42
rr,2a7.o7
40 OTHER STATUTORY
INFORMATION
(i)
The Company
does not have
any
Benami
property,
where
any
proceeding
has
been initiated
or
pending
against
the Company for holding
any Benami
property
under
the Benami
Transactions
(Prohibition)
Act, 1988 and rules
made thereunder.
(ii)
The Company
does not have
any charges or satisfaction which is
yet
to be registered
with ROC beyond
the statutory
period.
(iii)
The Company
has not traded
or
invested in
Cryptocurrency or Virtual
Currency during
the
period
ended March
31, 2023.
(iv)
The Company
has not
advanced or loaned or invested funds
to any other
persons
or entities, including foreign
entities
(Intermediaries)
with
the understanding
that the
Intermediary shall:
(a)
directly
or indirectly lend or invest in other
persons
or entities identified in
any manner whatsoever
by or on behalf
of the Company
(Ultimate
Beneficiaries)
or,
(b)
provide
any
guarantee,
security or the
like to
or
on behalf of the Ultimate Beneficiaries.
(v)
The Company
has not received
any
fund from
any
persons
or entities, including
foreign
entities
(Funding
Party)
with the understanding
(whether
recorded
in
writing or otheMise) that the Company shall:
(a)
directly or
indirectly
lend or
invest
in other
persons
or entities
identified
in
any manner whatsoever
by or on
behalf of the Funding Party
(Ultimate
Beneficiaries) or,
(b) provide
any
guarantee,
security or the like on behalf of
the Ultimate Beneficiafles.
(vi)
The Company
does not have any
such transaction which is not recorded
in the books
of accounts that has
been surrendered or disclosed
as income
during the
year
in the
tax assessments under
the
Income
Tax Act, 1961
(such
as, search or
suryey or any other relevant
provisions
of the Income
Tax Act,
1961). The
Company
does
not have
any
previously
unrecorded
income.
(vii)
The Company
does not have any transactions with
companies struck
off under section 248
of the Companies Act,
2013 or section
560 of Companies Acr,
(viii)
The Company
has not
been declared as a Wilful Defaulter
by any bank or financial institution
or
Government or any Government
authoritv.
14
Page 32 of 33

41 APPROVAL OF SPECIAL PURPOSE
FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
The
special
purpose
financial
statements were approved
by the Board of Directors
on
May
15, 2023
42
Previous
year's
figures have
been regrouped
/
reclassified, wherever
necessary,
to conform
to the current
year's
classification.
As
per
our
report of even date
For B.lC Goel & Associates
Chartered
Accountants
For
and on behalf
of the Board of Directors
of
Ramacharldran
Proprietor
'i
Membership
No. :
082081
Firm Reqistration
No. :O16542N
Place:
Gurugram
Date: May
15,2023
uDtlr
Etofui
g
I34W
N
e
Q-
at*zZ
CEO
Director
DIN:065763O0
Place:
Gurugram
Place: Gurugram
Date: May 15,2023
Date: May 75,2023
Narual
Director
DIN:10061613
Place:
Gurugram
Date:
May 15,2023
Page 33 of 33
